France
France (French: [fʁɑ̃s] (![]()
![]()
French Republic République française (French) | |
|---|---|
 Emblem
| |
.svg.png)  Location of metropolitan France (dark green) (Note the overseas department of French Guiana highlighted on the extreme lefthand side of the globe image.)– in Europe (green & dark grey) | |
.svg.png)
| |
| Capital and largest city | Paris 48°51′N 2°21′E |
| Official language and national language | French[upper-roman 1] |
| Nationality (2018) |
|
| Religion (2019[2]) |
|
| Demonym(s) | French |
| Government | Unitary semi-presidential constitutional republic |
| Emmanuel Macron | |
| Jean Castex | |
• President of the Senate | Gérard Larcher |
• President of the National Assembly | Richard Ferrand |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| Senate | |
| National Assembly | |
| Establishment | |
| 25 December 496 | |
| August 843 | |
| 22 September 1792 | |
| 1 January 1958 | |
| 4 October 1958 | |
| Area | |
• Total | 640,679 km2 (247,368 sq mi) |
| 551,695 km2 (213,011 sq mi) | |
• Metropolitan France (Cadastre) | 543,940.9 km2 (210,016.8 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• June 2020 estimate | |
• Density | 104/km2 (270/sq mi) (106th) |
• Metropolitan France, estimate as of June 2020 | |
• Density | 116/km2 (300.4/sq mi) (89th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2019 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| GDP (nominal) | 2019 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| Gini (2018) | low |
| HDI (2018) | very high · 26th |
| Currency |
|
| Time zone | UTC+1 (Central European Time) |
| UTC+2 (Central European Summer Time[upper-roman 9]) | |
| Note: various other time zones are observed in overseas France.[upper-roman 10] Although France is in Western European Time/UTC (Z) zone, since 25 February 1940, upon WW2 German occupation, Central European Time/UTC+1 was enforced as standard time, with a +0:50:39 offset (and +1:50:39 during DST) from Paris LMT (UTC+0:09:21). | |
| Date format | dd/mm/yyyy (AD) |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +33[upper-roman 11] |
| ISO 3166 code | FR |
| Internet TLD | .fr[upper-roman 12] |
Source gives area of metropolitan France as 551,500 km2 (212,900 sq mi) and lists overseas regions separately, whose areas sum to 89,179 km2 (34,432 sq mi). Adding these give the total shown here for the entire French Republic. The CIA reports the total as 643,801 km2 (248,573 sq mi). | |
During the Iron Age, what is now metropolitan France was inhabited by the Gauls, a collection of Celtic tribes. The area was annexed by Rome in 51 BC, developing a distinct Gallo-Roman culture that laid the foundation of the French language. The Germanic Franks arrived in 476 and formed the Kingdom of Francia, which became the heartland of the Carolingian Empire. The Treaty of Verdun of 843 partitioned the empire, with West Francia becoming the Kingdom of France in 987. In the High Middle Ages, King Philip Augustus achieved remarkable success in the expansion of his realm, defeating his rivals and doubling its size. By the end of his reign, France had emerged as the most powerful state in Europe.[11] In the mid-14th century, French monarchs were embroiled in a series of dynastic conflicts with their English counterparts, which lasted over 100 years. Emerging victorious from said conflicts, disputes with Spain and the Holy Roman Empire soon followed during the Renaissance but were ultimately less successful. However, French culture flourished and a global colonial empire was established, which by the 20th century would become the second largest in the world.[12] The second half of the 16th century was dominated by religious civil wars between Catholics and Protestants (Huguenots), which severly weakened the country. But France once again emerged as Europe's dominant cultural, political, and military power in the 17th century under Louis XIV following the Thirty Years' War.[13] Endless conflicts, notably colonial struggles with Great Britain and intervention in the American War of Independence, left the state on the brink of economic collapse by the end of the 18th century. The French Revolution in 1789 overthrew the absolute monarchy that characterized the Ancien Régime and established one of modern history's earliest republics, drafting the Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen which expresses the nation's ideals to this day.
Following the revolution, France reached its political and military zenith in the early 19th century under Napoleon Bonaparte, subjugating much of continental Europe and establishing the First French Empire. The French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars shaped the course of European and world history. After the collapse of the empire and a relative decline, France endured a tumultuous succession of governments culminating in the establishment of the French Third Republic in 1870 in the midst of the Franco-Prussian War. France was one of the prominent participants of World War I, from which it emerged victorious, and was one of the Allied powers in World War II, but came under occupation by the Axis in 1940. Following liberation in 1944, a Fourth Republic was established and later dissolved in the course of the Algerian War. The Fifth Republic, led by Charles de Gaulle, was formed in 1958 and remains to this day. Algeria and nearly all other French colonies became independent in the 1960s, with most retaining close economic and military connections with France.
France retains its centuries-long status as a global centre of art, science, and philosophy. It hosts the world's fifth-largest number of UNESCO World Heritage Sites and is the leading tourist destination, receiving over 89 million foreign visitors in 2018.[14] France is a developed country with the world's seventh-largest economy by nominal GDP, and the tenth-largest by PPP. In terms of aggregate household wealth, it ranks fourth in the world.[15] France performs well in international rankings of education, health care, life expectancy, and human development.[16][17] It remains a great power in global affairs,[18] being one of the five permanent members of the United Nations Security Council and an official nuclear-weapon state. France is a founding and leading member of the European Union and the Eurozone,[19] and a member of the Group of 7, North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), the World Trade Organization (WTO), and La Francophonie.
Etymology and pronunciation
Originally applied to the whole Frankish Empire, the name France comes from the Latin Francia, or "realm of the Franks".[20] Modern France is still named today Francia in Italian and Spanish, while Frankreich in German, Frankrijk in Dutch and Frankrike in Swedish all mean "Land/realm of the Franks".
There are various theories as to the origin of the name Frank. Following the precedents of Edward Gibbon and Jacob Grimm,[21] the name of the Franks has been linked with the word frank (free) in English.[22] It has been suggested that the meaning of "free" was adopted because, after the conquest of Gaul, only Franks were free of taxation.[23] Another theory is that it is derived from the Proto-Germanic word *frankon, which translates as javelin or lance as the throwing axe of the Franks was known as a francisca.[24] However, it has been determined that these weapons were named because of their use by the Franks, not the other way around.[25]
In English, 'France' is pronounced /fræns/ FRANSS in American English and /frɑːns/ FRAHNSS or /fræns/ FRANSS in British English. The pronunciation with /ɑː/ is mostly confined to accents with the trap-bath split such as Received Pronunciation, though it can be also heard in some other dialects such as Cardiff English, in which /frɑːns/ is in free variation with /fræns/.[26][27]
History
Prehistory (before the 6th century BC)

The oldest traces of human life in what is now France date from approximately 1.8 million years ago.[28] Over the ensuing millennia, Humans were confronted by a harsh and variable climate, marked by several glacial eras.
Early hominids led a nomadic hunter-gatherer life.[28] France has a large number of decorated caves from the upper Palaeolithic era, including one of the most famous and best preserved, Lascaux[28] (approximately 18,000 BC). At the end of the last glacial period (10,000 BC), the climate became milder;[28] from approximately 7,000 BC, this part of Western Europe entered the Neolithic era and its inhabitants became sedentary.
After strong demographic and agricultural development between the 4th and 3rd millennia, metallurgy appeared at the end of the 3rd millennium, initially working gold, copper and bronze, and later iron.[29] France has numerous megalithic sites from the Neolithic period, including the exceptionally dense Carnac stones site (approximately 3,300 BC).
Antiquity (6th century BC–5th century AD)

In 600 BC, Ionian Greeks from Phocaea founded the colony of Massalia (present-day Marseille), on the shores of the Mediterranean Sea. This makes it France's oldest city.[30][31] At the same time, some Gallic Celtic tribes penetrated parts of eastern and northern France, gradually spreading through the rest of the country between the 5th and 3rd century BC.[32]
.jpg)
The concept of Gaul emerged during this period, corresponding to the territories of Celtic settlement ranging between the Rhine, the Atlantic Ocean, the Pyrenees and the Mediterranean. The borders of modern France roughly correspond to ancient Gaul, which was inhabited by Celtic Gauls. Gaul was then a prosperous country, of which the southernmost part was heavily subject to Greek and Roman cultural and economic influences.
Around 390 BC, the Gallic chieftain Brennus and his troops made their way to Italy through the Alps, defeated the Romans in the Battle of the Allia, and besieged and ransomed Rome.[33] The Gallic invasion left Rome weakened, and the Gauls continued to harass the region until 345 BC when they entered into a formal peace treaty with Rome.[34] But the Romans and the Gauls would remain adversaries for the next centuries, and the Gauls would continue to be a threat in Italy.[35]
Around 125 BC, the south of Gaul was conquered by the Romans, who called this region Provincia Nostra ("Our Province"), which over time evolved into the name Provence in French.[36] Julius Caesar conquered the remainder of Gaul and overcame a revolt carried out by the Gallic chieftain Vercingetorix in 52 BC.[37] According to Plutarch and the writings of scholar Brendan Woods, the Gallic Wars resulted in 800 conquered cities, 300 subdued tribes, one million men sold into slavery, and another three million dead in battle.
Gaul was divided by Augustus into Roman provinces.[38] Many cities were founded during the Gallo-Roman period, including Lugdunum (present-day Lyon), which is considered the capital of the Gauls.[38] These cities were built in traditional Roman style, with a forum, a theatre, a circus, an amphitheatre and thermal baths. The Gauls mixed with Roman settlers and eventually adopted Roman culture and Roman speech (Latin, from which the French language evolved). The Roman polytheism merged with the Gallic paganism into the same syncretism.
From the 250s to the 280s AD, Roman Gaul suffered a serious crisis with its fortified borders being attacked on several occasions by barbarians.[39] Nevertheless, the situation improved in the first half of the 4th century, which was a period of revival and prosperity for Roman Gaul.[40] In 312, Emperor Constantin I converted to Christianity. Subsequently, Christians, who had been persecuted until then, increased rapidly across the entire Roman Empire.[41] But, from the beginning of the 5th century, the Barbarian Invasions resumed.[42] Teutonic tribes invaded the region from present-day Germany, the Visigoths settling in the southwest, the Burgundians along the Rhine River Valley, and the Franks (from whom the French take their name) in the north.[43]
Early Middle Ages (5th–10th century)
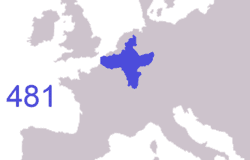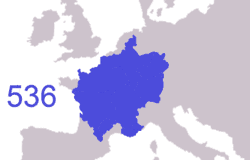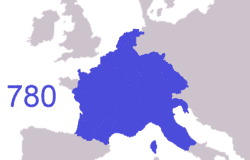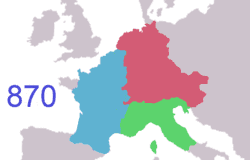
At the end of the Antiquity period, ancient Gaul was divided into several Germanic kingdoms and a remaining Gallo-Roman territory, known as the Kingdom of Syagrius. Simultaneously, Celtic Britons, fleeing the Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, settled the western part of Armorica. As a result, the Armorican peninsula was renamed Brittany, Celtic culture was revived and independent petty kingdoms arose in this region.
The first leader to make himself king of all the Franks was Clovis I, who began his reign in 481, routing the last forces of the Roman governors of the province in 486. Clovis claimed that he would be baptized a Christian in the event of his victory against the Visigoths, which was said to have guaranteed the battle. Clovis regained the southwest from the Visigoths, was baptized in 508, and made himself master of what is now western Germany.
Clovis I was the first Germanic conqueror after the fall of the Roman Empire to convert to Catholic Christianity, rather than Arianism; thus France was given the title "Eldest daughter of the Church" (French: La fille aînée de l'Église) by the papacy,[44] and French kings would be called "the Most Christian Kings of France" (Rex Christianissimus).

The Franks embraced the Christian Gallo-Roman culture and ancient Gaul was eventually renamed Francia ("Land of the Franks"). The Germanic Franks adopted Romanic languages, except in northern Gaul where Roman settlements were less dense and where Germanic languages emerged. Clovis made Paris his capital and established the Merovingian dynasty, but his kingdom would not survive his death. The Franks treated land purely as a private possession and divided it among their heirs, so four kingdoms emerged from Clovis's: Paris, Orléans, Soissons, and Rheims. The last Merovingian kings lost power to their mayors of the palace (head of household). One mayor of the palace, Charles Martel, defeated an Islamic invasion of Gaul at the Battle of Tours (732) and earned respect and power within the Frankish kingdoms. His son, Pepin the Short, seized the crown of Francia from the weakened Merovingians and founded the Carolingian dynasty. Pepin's son, Charlemagne, reunited the Frankish kingdoms and built a vast empire across Western and Central Europe.
Proclaimed Holy Roman Emperor by Pope Leo III and thus establishing in earnest the French Government's longtime historical association with the Catholic Church,[45] Charlemagne tried to revive the Western Roman Empire and its cultural grandeur. Charlemagne's son, Louis I (Emperor 814–840), kept the empire united; however, this Carolingian Empire would not survive his death. In 843, under the Treaty of Verdun, the empire was divided between Louis' three sons, with East Francia going to Louis the German, Middle Francia to Lothair I, and West Francia to Charles the Bald. West Francia approximated the area occupied by, and was the precursor to, modern France.[46]
During the 9th and 10th centuries, continually threatened by Viking invasions, France became a very decentralized state: the nobility's titles and lands became hereditary, and the authority of the king became more religious than secular and thus was less effective and constantly challenged by powerful noblemen. Thus was established feudalism in France. Over time, some of the king's vassals would grow so powerful that they often posed a threat to the king. For example, after the Battle of Hastings in 1066, William the Conqueror added "King of England" to his titles, becoming both the vassal to (as Duke of Normandy) and the equal of (as king of England) the king of France, creating recurring tensions.
High and Late Middle Ages (10th–15th century)


The Carolingian dynasty ruled France until 987, when Hugh Capet, Duke of France and Count of Paris, was crowned King of the Franks.[47] His descendants—the Capetians, the House of Valois, and the House of Bourbon—progressively unified the country through wars and dynastic inheritance into the Kingdom of France, which was fully declared in 1190 by Philip II of France (Philippe Auguste). Later kings would expand their directly possessed domaine royal to cover over half of modern continental France by the 15th century, including most of the north, centre and west of France. During this process, the royal authority became more and more assertive, centered on a hierarchically conceived society distinguishing nobility, clergy, and commoners.
The French nobility played a prominent role in most Crusades to restore Christian access to the Holy Land. French knights made up the bulk of the steady flow of reinforcements throughout the two-hundred-year span of the Crusades, in such a fashion that the Arabs uniformly referred to the crusaders as Franj caring little whether they really came from France.[48] The French Crusaders also imported the French language into the Levant, making French the base of the lingua franca (litt. "Frankish language") of the Crusader states.[48] French knights also made up the majority in both the Hospital and the Temple orders. The latter, in particular, held numerous properties throughout France and by the 13th century were the principal bankers for the French crown, until Philip IV annihilated the order in 1307. The Albigensian Crusade was launched in 1209 to eliminate the heretical Cathars in the southwestern area of modern-day France. In the end, the Cathars were exterminated and the autonomous County of Toulouse was annexed into the crown lands of France.[49]
From the 11th century, the House of Plantagenet, the rulers of the County of Anjou, succeeded in establishing its dominion over the surrounding provinces of Maine and Touraine, then progressively built an "empire" that spanned from England to the Pyrenees and covering half of modern France. Tensions between the kingdom of France and the Plantagenet empire would last a hundred years, until Philip II of France conquered, between 1202 and 1214 most of the continental possessions of the empire, leaving England and Aquitaine to the Plantagenets. Following the Battle of Bouvines, the Angevin court retreated to England, but persistent Capetian–Plantagenet rivalry would pave the way for another conflict, the Hundred Years' War.
Charles IV the Fair died without an heir in 1328.[50] Under the rules of the Salic law the crown of France could not pass to a woman nor could the line of kingship pass through the female line.[50] Accordingly, the crown passed to Philip of Valois, a cousin of Charles, rather than through the female line to Charles' nephew, Edward of Plantagenet, who would soon become Edward III of England. During the reign of Philip of Valois, the French monarchy reached the height of its medieval power.[50] Philip's seat on the throne was contested by Edward III of England in 1337, on the eve of the first wave of the Black Death,[51] and England and France went to war in what would become known as the Hundred Years' War.[52] The exact boundaries changed greatly with time, but French landholdings of the English Kings remained extensive for decades. With charismatic leaders, such as Joan of Arc and La Hire, strong French counterattacks won back most English continental territories. Like the rest of Europe, France was struck by the Black Death; half of the 17 million population of France died.[53][54]
Early modern period (15th century–1789)
- Main articles: French Renaissance (c. 1400–c. 1650), Early modern France (1500–1789), French Wars of Religion (1562–1598) and Ancien Régime (c. 1400–1792)

The French Renaissance saw a spectacular cultural development and the first standardisation of the French language, which would become the official language of France and the language of Europe's aristocracy. It also saw a long set of wars, known as the Italian Wars, between France and the House of Habsburg. French explorers, such as Jacques Cartier or Samuel de Champlain, claimed lands in the Americas for France, paving the way for the expansion of the First French colonial empire. The rise of Protestantism in Europe led France to a civil war known as the French Wars of Religion, where, in the most notorious incident, thousands of Huguenots were murdered in the St. Bartholomew's Day massacre of 1572.[55] The Wars of Religion were ended by Henry IV's Edict of Nantes, which granted some freedom of religion to the Huguenots. Spanish troops, the terror of Western Europe,[56] assisted the Catholic side during the Wars of Religion in 1589–1594, and invaded northern France in 1597; after some skirmishing in the 1620s and 1630s, Spain and France returned to all-out war between 1635 and 1659. The war cost France 300,000 casualties.[57]
Under Louis XIII, the energetic Cardinal Richelieu promoted the centralisation of the state and reinforced the royal power by disarming domestic power holders in the 1620s. He systematically destroyed castles of defiant lords and denounced the use of private violence (dueling, carrying weapons, and maintaining private army). By the end of the 1620s, Richelieu established "the royal monopoly of force" as the doctrine.[58] During Louis XIV's minority and the regency of Queen Anne and Cardinal Mazarin, a period of trouble known as the Fronde occurred in France. This rebellion was driven by the great feudal lords and sovereign courts as a reaction to the rise of royal absolute power in France.

The monarchy reached its peak during the 17th century and the reign of Louis XIV. By turning powerful feudal lords into courtiers at the Palace of Versailles, Louis XIV's personal power became unchallenged. Remembered for his numerous wars, he made France the leading European power. France became the most populous country in Europe and had tremendous influence over European politics, economy, and culture. French became the most-used language in diplomacy, science, literature and international affairs, and remained so until the 20th century.[59] France obtained many overseas possessions in the Americas, Africa and Asia. Louis XIV also revoked the Edict of Nantes, forcing thousands of Huguenots into exile.
Under Louis XV, Louis XIV's great-grandson, France lost New France and most of its Indian possessions after its defeat in the Seven Years' War (1756–63). Its European territory kept growing, however, with notable acquisitions such as Lorraine (1766) and Corsica (1770). An unpopular king, Louis XV's weak rule, his ill-advised financial, political and military decisions – as well as the debauchery of his court– discredited the monarchy, which arguably paved the way for the French Revolution 15 years after his death.[60][61]
Louis XVI, Louis XV's grandson, actively supported the Americans, who were seeking their independence from Great Britain (realised in the Treaty of Paris (1783)). The financial crisis aggravated by France's involvement in the American Revolutionary War was one of many contributing factors to the French Revolution. Much of the Enlightenment occurred in French intellectual circles, and major scientific breakthroughs and inventions, such as the discovery of oxygen (1778) and the first hot air balloon carrying passengers (1783), were achieved by French scientists. French explorers, such as Bougainville and Lapérouse, took part in the voyages of scientific exploration through maritime expeditions around the globe. The Enlightenment philosophy, in which reason is advocated as the primary source for legitimacy and authority, undermined the power of and support for the monarchy and helped pave the way for the French Revolution.
Revolutionary France (1789–1799)

Facing financial troubles, King Louis XVI summoned the Estates-General (gathering the three Estates of the realm) in May 1789 to propose solutions to his government. As it came to an impasse, the representatives of the Third Estate formed into a National Assembly, signalling the outbreak of the French Revolution. Fearing that the king would suppress the newly created National Assembly, insurgents stormed the Bastille on 14 July 1789, a date which would become France's National Day.
In early August 1789, the National Constituent Assembly abolished the privileges of the nobility such as personal serfdom and exclusive hunting rights. Through the Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen (27 August 1789) France established fundamental rights for men. The Declaration affirms "the natural and imprescriptible rights of man" to "liberty, property, security and resistance to oppression". Freedom of speech and press were declared, and arbitrary arrests outlawed. It called for the destruction of aristocratic privileges and proclaimed freedom and equal rights for all men, as well as access to public office based on talent rather than birth.
In November 1789, the Assembly decided to nationalize and sell all property of the Roman Catholic Church which had been the largest landowner in the country. In July 1790, a Civil Constitution of the Clergy reorganized the French Catholic Church, cancelling the authority of the Church to levy taxes, et cetera. This fueled much discontent in parts of France, which would contribute to the civil war breaking out some years later. While King Louis XVI still enjoyed popularity among the population, his disastrous flight to Varennes (June 1791) seemed to justify rumors he had tied his hopes of political salvation to the prospects of foreign invasion. His credibility was so deeply undermined that the abolition of the monarchy and establishment of a republic became an increasing possibility.
In August 1791, the Emperor of Austria and the King of Prussia in the Declaration of Pillnitz threatened revolutionary France to intervene by force of arms to restore the French absolute monarchy. In September 1791, the National Constituent Assembly forced King Louis XVI to accept the French Constitution of 1791, thus turning the French absolute monarchy into a constitutional monarchy. In the newly established Legislative Assembly (October 1791), enmity developed and deepened between a group, later called the 'Girondins', who favored war with Austria and Prussia, and a group later called 'Montagnards' or 'Jacobins', who opposed such a war. A majority in the Assembly in 1792 however saw a war with Austria and Prussia as a chance to boost the popularity of the revolutionary government, and thought that France would win a war against those gathered monarchies. On 20 April 1792, therefore, they declared war on Austria.[upper-roman 14]
On 10 August 1792, an angry crowd threatened the palace of King Louis XVI, who took refuge in the Legislative Assembly.[62][63] A Prussian army invaded France later in August 1792. In early September, Parisians, infuriated by the Prussian army capturing Verdun and counter-revolutionary uprisings in the west of France, murdered between 1,000 and 1,500 prisoners by raiding the Parisian prisons. The Assembly and the Paris city council seemed unable to stop that bloodshed.[62][64] The National Convention, chosen in the first elections under male universal suffrage,[62] on 20 September 1792 succeeded the Legislative Assembly and on 21 September abolished the monarchy by proclaiming the French First Republic. Ex-King Louis XVI was convicted of treason and guillotined in January 1793. France had declared war on Great Britain and the Dutch Republic in November 1792 and did the same on Spain in March 1793; in the spring of 1793, Austria and Prussia invaded France; in March, France created a "sister republic" in the "Republic of Mainz".
Also in March 1793, the civil war of the Vendée against Paris started, evoked by both the Civil Constitution of the Clergy of 1790 and the nationwide army conscription early 1793; elsewhere in France rebellion was brewing too. A factionalist feud in the National Convention, smoldering ever since October 1791, came to a climax with the group of the 'Girondins' on 2 June 1793 being forced to resign and leave the convention. The counter-revolution, begun in March 1793 in the Vendée, by July had spread to Brittany, Normandy, Bordeaux, Marseilles, Toulon, and Lyon. Paris' Convention government between October and December 1793 with brutal measures managed to subdue most internal uprisings, at the cost of tens of thousands of lives. Some historians consider the civil war to have lasted until 1796 with a toll of possibly 450,000 lives.[65][66] By the end of 1793 the allies had been driven from France. France in February 1794 abolished slavery in its American colonies, but would reintroduce it later.
Political disagreements and enmity in the National Convention between October 1793 and July 1794 reached unprecedented levels, leading to dozens of Convention members being sentenced to death and guillotined. Meanwhile, France's external wars in 1794 were going prosperous, for example in Belgium. In 1795, the government seemed to return to indifference towards the desires and needs of the lower classes concerning freedom of (Catholic) religion and fair distribution of food. Until 1799, politicians, apart from inventing a new parliamentary system (the 'Directory'), busied themselves with dissuading the people from Catholicism and from royalism.
Napoleon and 19th century (1799–1914)

Napoleon Bonaparte seized control of the Republic in 1799 becoming First Consul and later Emperor of the French Empire (1804–1814; 1815). As a continuation of the wars sparked by the European monarchies against the French Republic, changing sets of European Coalitions declared wars on Napoleon's Empire. His armies conquered most of continental Europe with swift victories such as the battles of Jena-Auerstadt or Austerlitz. Members of the Bonaparte family were appointed as monarchs in some of the newly established kingdoms.[68] These victories led to the worldwide expansion of French revolutionary ideals and reforms, such as the Metric system, the Napoleonic Code and the Declaration of the Rights of Man. In June 1812, Napoleon attacked Russia, reaching Moscow. Thereafter his army disintegrated through supply problems, disease, Russian attacks, and finally winter. After the catastrophic Russian campaign, and the ensuing uprising of European monarchies against his rule, Napoleon was defeated and the Bourbon monarchy restored. About a million Frenchmen died during the Napoleonic Wars.[68] After his brief return from exile, Napoleon was finally defeated in 1815 at the Battle of Waterloo, the monarchy was re-established (1815–1830), with new constitutional limitations.
The discredited Bourbon dynasty was overthrown by the July Revolution of 1830, which established the constitutional July Monarchy. In that year, French troops conquered Algeria, establishing the first colonial presence in Africa since Napoleon's abortive invasion of Egypt in 1798. In 1848 general unrest led to the February Revolution and the end of the July Monarchy. The abolition of slavery and introduction of male universal suffrage, which were briefly enacted during the French Revolution, were re-enacted in 1848. In 1852, the president of the French Republic, Louis-Napoléon Bonaparte, Napoleon I's nephew, was proclaimed emperor of the second Empire, as Napoleon III. He multiplied French interventions abroad, especially in Crimea, in Mexico and Italy which resulted in the annexation of the duchy of Savoy and the county of Nice, then part of the Kingdom of Sardinia. Napoleon III was unseated following defeat in the Franco-Prussian War of 1870 and his regime was replaced by the Third Republic. By 1875, the French conquest of Algeria was complete and approximately 825,000 Algerians were killed as a result.[69]
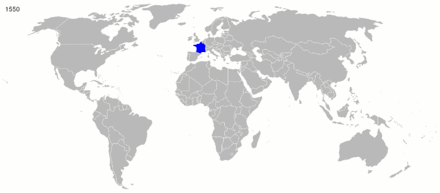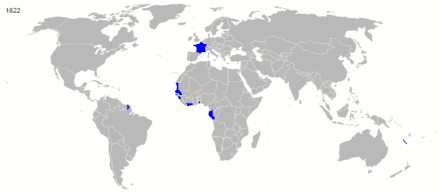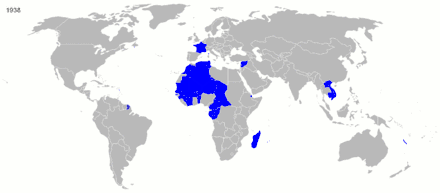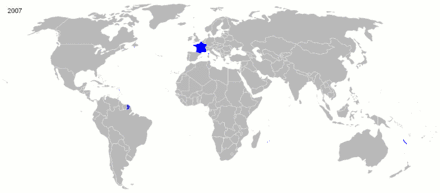
France had colonial possessions, in various forms, since the beginning of the 17th century, but in the 19th and 20th centuries, its global overseas colonial empire extended greatly and became the second largest in the world behind the British Empire. Including metropolitan France, the total area of land under French sovereignty almost reached 13 million square kilometers in the 1920s and 1930s, 8.6% of the world's land. Known as the Belle Époque, the turn of the century was a period characterized by optimism, regional peace, economic prosperity and technological, scientific and cultural innovations. In 1905, state secularism was officially established.
Contemporary period (1914–present)

France was a member of the Triple Entente when World War I broke out. A small part of Northern France was occupied, but France and its allies emerged victorious against the Central Powers at a tremendous human and material cost. World War I left 1.4 million French soldiers dead, 4% of its population.[70] Between 27 and 30% of soldiers conscripted from 1912 to 1915 were killed.[71] The interbellum years were marked by intense international tensions and a variety of social reforms introduced by the Popular Front government (annual leave, eight-hour workdays, women in government).
In 1940, France was invaded and occupied by Nazi Germany and Italy. Metropolitan France was divided into a German occupation zone in the north, an Italian occupation zone in the south-east and Vichy France, a newly established authoritarian regime collaborating with Germany, in the south, while Free France, the government-in-exile led by Charles de Gaulle, was set up in London.[72] From 1942 to 1944, about 160,000 French citizens, including around 75,000 Jews,[73][74][75] were deported to death camps and concentration camps in Germany and occupied Poland.[76] In September 1943, Corsica was the first French metropolitan territory to liberate itself from the Axis. On 6 June 1944, the Allies invaded Normandy and in August they invaded Provence. Over the following year the Allies and the French Resistance emerged victorious over the Axis powers and French sovereignty was restored with the establishment of the Provisional Government of the French Republic (GPRF). This interim government, established by de Gaulle, aimed to continue to wage war against Germany and to purge collaborators from office. It also made several important reforms (suffrage extended to women, creation of a social security system).

The GPRF laid the groundwork for a new constitutional order that resulted in the Fourth Republic, which saw spectacular economic growth (les Trente Glorieuses). France was one of the founding members of NATO (1949). France attempted to regain control of French Indochina but was defeated by the Viet Minh in 1954 at the climactic Battle of Dien Bien Phu. Only months later, France faced another anti-colonialist conflict in Algeria. The systematic torture and repression, as well as the extrajudicial killings that were perpetrated to keep control of Algeria, then considered as an integral part of France and home to over one million European settlers,[77][78] wracked the country and nearly led to a coup and civil war.[79]
In 1958, the weak and unstable Fourth Republic gave way to the Fifth Republic, which included a strengthened Presidency.[80] In the latter role, Charles de Gaulle managed to keep the country together while taking steps to end the Algerian War. The war was concluded with the Évian Accords in 1962 that led to Algerian independence. The Algerian independence came at a high price; the large toll on the Algerian population. It resulted in half million to a million deaths and over 2 million internally displaced Algerians.[81][82][83] A vestige of the colonial empire are the French overseas departments and territories.

In the context of the Cold War, de Gaulle pursued a policy of "national independence" towards the Western and Eastern blocs. To this end, he withdrew from NATO's military integrated command (while remaining in the NATO alliance itself), launched a nuclear development programme, and made France the fourth nuclear power. He restored cordial Franco-German relations to create a European counterweight between the American and Soviet spheres of influence. However, he opposed any development of a supranational Europe, favouring a Europe of sovereign nations. In the wake of the series of worldwide protests of 1968, the revolt of May 1968 had an enormous social impact. In France, it is considered to be the watershed moment when a conservative moral ideal (religion, patriotism, respect for authority) shifted towards a more liberal moral ideal (secularism, individualism, sexual revolution). Although the revolt was a political failure (as the Gaullist party emerged even stronger than before) it announced a split between the French people and de Gaulle who resigned shortly after.
In the post-Gaullist era, France remained one of the most developed economies in the world, but faced several economic crises that resulted in high unemployment rates and increasing public debt. In the late 20th and early 21st centuries France has been at the forefront of the development of a supranational European Union, notably by signing the Maastricht Treaty (which created the European Union) in 1992, establishing the Eurozone in 1999, and signing the Lisbon Treaty in 2007.[84] France has also gradually but fully reintegrated into NATO and has since participated in most NATO sponsored wars.[85]

Since the 19th century France has received many immigrants. These have been mostly male foreign workers from European Catholic countries who generally returned home when not employed.[86] During the 1970s France faced economic crisis and allowed new immigrants (mostly from the Maghreb)[86] to permanently settle in France with their families and to acquire French citizenship. It resulted in hundreds of thousands of Muslims (especially in the larger cities) living in subsidized public housing and suffering from very high unemployment rates.[87] Simultaneously France renounced the assimilation of immigrants, where they were expected to adhere to French traditional values and cultural norms. They were encouraged to retain their distinctive cultures and traditions and required merely to integrate.[88]
Since the 1995 Paris Métro and RER bombings, France has been sporadically targeted by Islamist organisations, notably the Charlie Hebdo attack in January 2015 which provoked the largest public rallies in French history, gathering 4.4 million people,[89][90] the November 2015 Paris attacks which resulted in 130 deaths, the deadliest attack on French soil since World War II,[91][92] and the deadliest in the European Union since the Madrid train bombings in 2004[93] and the 2016 Nice truck attack, which caused 87 deaths during Bastille Day celebrations. Opération Chammal, France's military efforts to contain ISIS, killed over 1,000 ISIS troops between 2014 and 2015.[94][95]
Geography
Location and borders
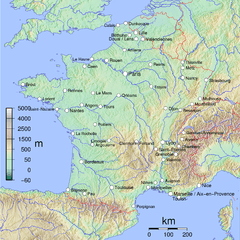

The vast majority of France's territory and population is situated in Western Europe and is called Metropolitan France, to distinguish it from the country's various overseas polities. It is bordered by the Northern Sea in the north, the English Channel in the northwest, the Atlantic Ocean in the west and the Mediterranean sea in the southeast. Its land borders consist of Belgium and Luxembourg in the northeast, Germany and Switzerland in the east, Italy and Monaco in the southeast, and Andorra and Spain in the south and southwest. With the exception of the northeast, most of France's land borders are roughly delineated by natural boundaries and geographic features: to the south and southeast, the Pyrenees and the Alps and the Jura, respectively, and to the east, the Rhine river. Due to its shape, France is often referred to as l'Hexagone ("The Hexagon"). Metropolitan France includes various coastal islands, of which the largest is Corsica. Metropolitan France is situated mostly between latitudes 41° and 51° N, and longitudes 6° W and 10° E, on the western edge of Europe, and thus lies within the northern temperate zone. Its continental part covers about 1000 km from north to south and from east to west.
France has several overseas regions across the world, which are organized as follows:
- In South America: French Guiana.
- In the Atlantic Ocean: Saint Pierre and Miquelon and, in the Antilles: Guadeloupe, Martinique, Saint Martin and Saint Barthélemy.
- In the Pacific Ocean: French Polynesia, the special collectivity of New Caledonia, Wallis and Futuna and Clipperton Island.
- In the Indian Ocean: Réunion island, Mayotte, Kerguelen Islands, Crozet Islands, St. Paul and Amsterdam islands, and the Scattered Islands in the Indian Ocean
- In the Antarctic: Adélie Land.
France has land borders with Brazil and Suriname via French Guiana and with the Kingdom of the Netherlands through the French portion of Saint Martin.
Metropolitan France covers 551,500 square kilometres (212,935 sq mi),[96] the largest among European Union members.[19] France's total land area, with its overseas departments and territories (excluding Adélie Land), is 643,801 km2 (248,573 sq mi), 0.45% of the total land area on Earth. France possesses a wide variety of landscapes, from coastal plains in the north and west to mountain ranges of the Alps in the southeast, the Massif Central in the south central and Pyrenees in the southwest.
Due to its numerous overseas departments and territories scattered across the planet, France possesses the second-largest Exclusive economic zone (EEZ) in the world, covering 11,035,000 km2 (4,260,000 mi2), just behind the EEZ of the United States, which covers 11,351,000 km2 (4,383,000 mi2), but ahead of the EEZ of Australia, which covers 8,148,250 km2 (4,111,312 mi2). Its EEZ covers approximately 8% of the total surface of all the EEZs of the world.
Geology, topography and hydrography
Metropolitan France has a wide variety of topographical sets and natural landscapes. Large parts of the current territory of France were raised during several tectonic episodes like the Hercynian uplift in the Paleozoic Era, during which the Armorican Massif, the Massif Central, the Morvan, the Vosges and Ardennes ranges and the island of Corsica were formed. These massifs delineate several sedimentary basins such as the Aquitaine basin in the southwest and the Paris basin in the north, the latter including several areas of particularly fertile ground such as the silt beds of Beauce and Brie. Various routes of natural passage, such as the Rhône valley, allow easy communications. The Alpine, Pyrenean and Jura mountains are much younger and have less eroded forms. At 4,810.45 metres (15,782 ft)[97] above sea level, Mont Blanc, located in the Alps on the French and Italian border, is the highest point in Western Europe. Although 60% of municipalities are classified as having seismic risks, these risks remain moderate.

The coastlines offer contrasting landscapes: mountain ranges along the French Riviera, coastal cliffs such as the Côte d'Albâtre, and wide sandy plains in the Languedoc. Corsica lies off the Mediterranean coast. France has an extensive river system consisting of the four major rivers Seine, the Loire, the Garonne, the Rhône and their tributaries, whose combined catchment includes over 62% of the metropolitan territory. The Rhône divides the Massif Central from the Alps and flows into the Mediterranean Sea at the Camargue. The Garonne meets the Dordogne just after Bordeaux, forming the Gironde estuary, the largest estuary in Western Europe which after approximately 100 kilometres (62 mi) empties into the Atlantic Ocean.[98] Other water courses drain towards the Meuse and Rhine along the north-eastern borders. France has 11 million square kilometres (4.2×106 sq mi) of marine waters within three oceans under its jurisdiction, of which 97% are overseas.
Climate
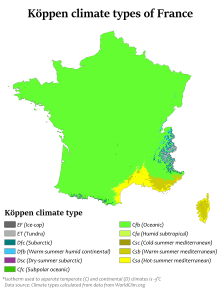
The French metropolitan territory is relatively large, so the climate is not uniform, giving rise to the following climate nuances:
• The hot-summer mediterranean climate (Csa) is found along the Gulf of Lion. Summers are hot and dry, while winters are mild and wet. Cities affected by this climate: Arles, Avignon, Fréjus, Hyères, Marseille, Menton, Montpellier, Nice, Perpignan, Toulon.
• The warm-summer mediterranean climate (Csb) is found in the northern part of Brittany. Summers are warm and dry, while winters are cool and wet. Cities affected by this climate: Belle-Île-en-Mer, Saint-Brieuc.
• The humid subtropical climate (Cfa) is found in the Garonne and Rhône's inland plains. Summers are hot and wet, while winters are cool and damp. Cities affected by this climate: Albi, Carcassonne, Lyon, Orange, Toulouse, Valence.
• The oceanic climate (Cfb) is found around the coasts of the Bay of Biscay, and a little bit inland. Summers are pleasantly warm and wet, while winters are cool and damp. Cities affected by this climate: Amiens, Biarritz, Bordeaux, Brest, Cherbourg-en-Cotentin, Dunkirk, Lille, Nantes, Orléans, Paris, Reims, Tours.
• The degraded oceanic climate (degraded-Cfb) is found in the interior plains and in the intra-alpine valleys, far from the ocean (or sea). Summers are hot and wet, while winters are cold and gloomy. Cities affected by this climate: Annecy, Besançon, Bourges, Chambéry, Clermont-Ferrand, Colmar, Dijon, Grenoble, Langres, Metz, Mulhouse, Nancy, Strasbourg.
• The subalpine oceanic climate (Cfc) is found at the foot of all the mountainous regions of France. Summers are short, cool and wet, while winters are moderately cold and damp. No major cities are affected by this climate.
• The warm-summer mediterranean continental climate (Dsb) is found in all the mountainous regions of southern France between 700 and 1400 meters a.s.l. Summers are pleasantly warm and dry, while winters are very cold and snowy. City affected by this climate: Barcelonnette.
• The cool-summer mediterranean continental climate (Dsc) is found in all the mountainous regions of southern France between 1400 and 2100 meters a.s.l. Summers are cool, short and dry, while winters are very cold and snowy. Place affected by this climate: Isola 2000.
• The warm-summer humid continental climate (Dfb) is found in all the mountainous regions of the Northern half of France between 500 and 1000 meters a.s.l. Summers are pleasantly warm and wet, while winters are very cold and snowy. Cities affected by this climate: Chamonix, Mouthe. In January 1985, in Mouthe, the temperature has dropped under -41°C.
• The subalpine climate (Dfc) is found in all the mountainous regions of the northern half of France between 1000 and 2000 meters a.s.l. Summers are cool, short and wet, while winters are very cold and snowy. Places affected by this climate: Cauterets Courchevel, Alpe d'Huez, Les 2 Alpes, Peyragudes, Val-Thorens.
• The alpine tundra climate (ET) is found in all the mountainous regions of France, generally above 2000 or 2500 meters a.s.l. Summers are chilly and wet, while winters are extremely cold, long and snowy. Mountains affected by this climate: Aiguilles-Rouges, Aravis, the top of Crêt de la neige (rare, altitude 1718 m) and the top of Grand-Ballon (rare, altitude 1423 m).
• The ice cap climate (EF) is found in all the mountainous regions of France that have a glacier. Summers are cold and wet, while winters are extremely cold, long and snowy. Mountains affected by this climate: Aiguille du midi, Barre des Écrins, Belledonne, Grand-Casse, Mont Blanc (4810 m), Pic du Midi de Bigorre.
• In the overseas regions, there are three broad types of climate:
- A tropical climate (Am) in most overseas regions including eastern French Guiana: high constant temperature throughout the year with a dry and a wet season.
- An equatorial climate (Af) in western French Guiana: high constant temperature with even precipitation throughout the year.
- A subpolar oceanic climate (Cfc), characterized by mild, wet summers and cool, but generally not cold, damp winters. Cities or places affected by this climate: Port-aux-Français, Saint-Pierre-et-Miquelon.
- An ice cap climate (EF): extremely cold year-round in Adélie Land.
France was one of the first countries to create an environment ministry, in 1971.[99] Although it is one of the most industrialized countries in the world, France is ranked only 19th by carbon dioxide emissions, behind less populous nations such as Canada or Australia. This is due to the country's heavy investment in nuclear power following the 1973 oil crisis,[100] which now accounts for 75 percent of its electricity production[101] and results in less pollution.[102][103] According to the 2018 Environmental Performance Index conducted by Yale and Columbia, France was the second-most environmentally-conscious country in the world (after Switzerland), compared to tenth place in 2016 and 27th in 2014.[104][105]
Like all European Union state members, France agreed to cut carbon emissions by at least 20% of 1990 levels by the year 2020,[106] compared to the United States plan to reduce emissions by 4% of 1990 levels.[107] As of 2009, French carbon dioxide emissions per capita were lower than that of China's.[108] The country was set to impose a carbon tax in 2009 at 17 euros per tonne of carbon emitted,[109] which would have raised 4 billion euros of revenue annually.[110] However, the plan was abandoned due to fears of burdening French businesses.[111]
.jpg)
Forests account for 31 percent of France's land area—the fourth-highest proportion in Europe—representing an increase of 7 percent since 1990.[112][113][114] French forests are some of the most diverse in Europe, comprising more than 140 species of trees.[115] There are nine national parks[116] and 46 natural parks in France,[117] with the government planning to convert 20% of its Exclusive economic zone into a Marine protected area by 2020.[118] A regional nature park[119] (French: parc naturel régional or PNR) is a public establishment in France between local authorities and the national government covering an inhabited rural area of outstanding beauty, to protect the scenery and heritage as well as setting up sustainable economic development in the area.[120] A PNR sets goals and guidelines for managed human habitation, sustainable economic development and protection of the natural environment based on each park's unique landscape and heritage. The parks foster ecological research programs and public education in the natural sciences.[121] As of 2019 there are 54 PNRs in France.[122]
Administrative divisions
The French Republic is divided into 18 regions (located in Europe and overseas), five overseas collectivities, one overseas territory, one special collectivity – New Caledonia and one uninhabited island directly under the authority of the Minister of Overseas France – Clipperton.
Regions
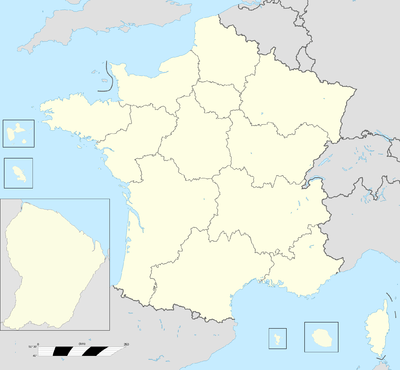
Since 2016 France is mainly divided into 18 administrative regions: 13 regions in metropolitan France (including the territorial collectivity of Corsica),[123] and five located overseas.[96] The regions are further subdivided into 101 departments,[124] which are numbered mainly alphabetically. This number is used in postal codes and was formerly used on vehicle number plates. Among the 101 departments of France, five (French Guiana, Guadeloupe, Martinique, Mayotte, and Réunion) are in overseas regions (ROMs) that are also simultaneously overseas departments (DOMs), enjoy exactly the same status as metropolitan departments and are an integral part of the European Union.
The 101 departments are subdivided into 335 arrondissements, which are, in turn, subdivided into 2,054 cantons.[125] These cantons are then divided into 36,658 communes, which are municipalities with an elected municipal council.[125] Three communes—Paris, Lyon and Marseille—are subdivided into 45 municipal arrondissements.
The regions, departments and communes are all known as territorial collectivities, meaning they possess local assemblies as well as an executive. Arrondissements and cantons are merely administrative divisions. However, this was not always the case. Until 1940, the arrondissements were territorial collectivities with an elected assembly, but these were suspended by the Vichy regime and definitely abolished by the Fourth Republic in 1946.
Overseas territories and collectivities
In addition to the 18 regions and 101 departments, the French Republic has five overseas collectivities (French Polynesia, Saint Barthélemy, Saint Martin, Saint Pierre and Miquelon, and Wallis and Futuna), one sui generis collectivity (New Caledonia), one overseas territory (French Southern and Antarctic Lands), and one island possession in the Pacific Ocean (Clipperton Island).
Overseas collectivities and territories form part of the French Republic, but do not form part of the European Union or its fiscal area (with the exception of St. Bartelemy, which seceded from Guadeloupe in 2007). The Pacific Collectivities (COMs) of French Polynesia, Wallis and Futuna, and New Caledonia continue to use the CFP franc[126] whose value is strictly linked to that of the euro. In contrast, the five overseas regions used the French franc and now use the euro.[127]
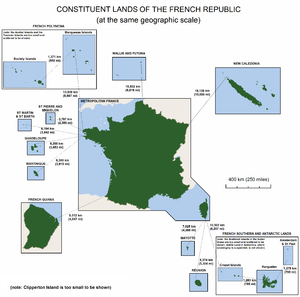
| Name | Constitutional status | Capital |
|---|---|---|
| State private property under the direct authority of the French government | Uninhabited | |
| Designated as an overseas land (pays d'outre-mer or POM), the status is the same as an overseas collectivity. | Papeete | |
| Overseas territory (territoire d'outre-mer or TOM) | Port-aux-Français | |
| Sui generis collectivity | Nouméa | |
| Overseas collectivity (collectivité d'outre-mer or COM) | Gustavia | |
| Overseas collectivity (collectivité d'outre-mer or COM) | Marigot | |
| Overseas collectivity (collectivité d'outre-mer or COM). Still referred to as a collectivité territoriale. | Saint-Pierre | |
| Overseas collectivity (collectivité d'outre-mer or COM). Still referred to as a territoire. | Mata-Utu |
Politics
Government
 |
 |
| Emmanuel Macron President |
Jean Castex Prime Minister |
The French Republic is a unitary semi-presidential representative democratic republic with strong democratic traditions.[128] The Constitution of the Fifth Republic was approved by referendum on 28 September 1958.[129] It greatly strengthened the authority of the executive in relation to parliament. The executive branch itself has two leaders: the President of the Republic, currently Emmanuel Macron, who is head of state and is elected directly by universal adult suffrage for a 5-year term (formerly 7 years),[130] and the Government, led by the president-appointed Prime Minister.

The French Parliament is a bicameral legislature comprising a National Assembly (Assemblée nationale) and a Senate.[131] The National Assembly deputies represent local constituencies and are directly elected for 5-year terms.[132] The Assembly has the power to dismiss the government, and thus the majority in the Assembly determines the choice of government. Senators are chosen by an electoral college for 6-year terms (originally 9-year terms), and one half of the seats are submitted to election every 3 years.[133]
The Senate's legislative powers are limited; in the event of disagreement between the two chambers, the National Assembly has the final say.[134] The Government has a strong influence in shaping the agenda of Parliament.
Until World War II, Radicals were a strong political force in France, embodied by the Republican, Radical and Radical-Socialist Party which was the most important party of the Third Republic. Since World War II, they were marginalized while French politics became characterized by two politically opposed groupings: one left-wing, centred on the French Section of the Workers' International and its successor the Socialist Party (since 1969); and the other right-wing, centred on the Gaullist Party, whose name changed over time to the Rally of the French People (1947), the Union of Democrats for the Republic (1958), the Rally for the Republic (1976), the Union for a Popular Movement (2007) and The Republicans (since 2015). In the 2017 presidential and legislative elections, radical centrist party En Marche! became the dominant force, overtaking both Socialists and Republicans.
As of 2017, voter turnout was 75 percent during recent elections, higher than the OECD average of 68 percent.[135]
Law
France uses a civil legal system, wherein law arises primarily from written statutes;[96] judges are not to make law, but merely to interpret it (though the amount of judicial interpretation in certain areas makes it equivalent to case law in a common law system). Basic principles of the rule of law were laid in the Napoleonic Code (which was, in turn, largely based on the royal law codified under Louis XIV). In agreement with the principles of the Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen, law should only prohibit actions detrimental to society. As Guy Canivet, first president of the Court of Cassation, wrote about the management of prisons: Freedom is the rule, and its restriction is the exception; any restriction of Freedom must be provided for by Law and must follow the principles of necessity and proportionality. That is, Law should lay out prohibitions only if they are needed, and if the inconveniences caused by this restriction do not exceed the inconveniences that the prohibition is supposed to remedy.

French law is divided into two principal areas: private law and public law. Private law includes, in particular, civil law and criminal law. Public law includes, in particular, administrative law and constitutional law. However, in practical terms, French law comprises three principal areas of law: civil law, criminal law, and administrative law. Criminal laws can only address the future and not the past (criminal ex post facto laws are prohibited).[136] While administrative law is often a subcategory of civil law in many countries, it is completely separated in France and each body of law is headed by a specific supreme court: ordinary courts (which handle criminal and civil litigation) are headed by the Court of Cassation and administrative courts are headed by the Council of State.
To be applicable, every law must be officially published in the Journal officiel de la République française.
France does not recognise religious law as a motivation for the enactment of prohibitions; it has long abolished blasphemy laws and sodomy laws (the latter in 1791). However, "offences against public decency" (contraires aux bonnes mœurs) or disturbing public order (trouble à l'ordre public) have been used to repress public expressions of homosexuality or street prostitution. Since 1999, civil unions for homosexual couples are permitted, and since 2013, same-sex marriage and LGBT adoption are legal.[137] Laws prohibiting discriminatory speech in the press are as old as 1881. Some consider hate speech laws in France to be too broad or severe, undermining freedom of speech.[138] France has laws against racism and antisemitism,[139] while the 1990 Gayssot Act prohibits Holocaust denial.
Freedom of religion is constitutionally guaranteed by the 1789 Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen. The 1905 French law on the Separation of the Churches and the State is the basis for laïcité (state secularism): the state does not formally recognize any religion, except in Alsace-Moselle. Nonetheless, it does recognize religious associations. The Parliament has listed many religious movements as dangerous cults since 1995, and has banned wearing conspicuous religious symbols in schools since 2004. In 2010, it banned the wearing of face-covering Islamic veils in public; human rights groups such as Amnesty International and Human Rights Watch described the law as discriminatory towards Muslims.[140][141] However, it is supported by most of the population.[142]
Foreign relations

France is a founding member of the United Nations and serves as one of the permanent members of the UN Security Council with veto rights.[143] In 2015, France was described as being "the best networked state in the world", because it is a country that "is member of more multi-lateral organisations than any other country".[144]
France is a member of the G8, World Trade Organization (WTO),[145] the Secretariat of the Pacific Community (SPC)[146] and the Indian Ocean Commission (COI).[147] It is an associate member of the Association of Caribbean States (ACS)[148] and a leading member of the International Francophone Organisation (OIF) of 84 fully or partly French-speaking countries.[149]
As a significant hub for international relations, France hosts the second largest assembly of diplomatic missions in the world and the headquarters of international organisations including the OECD, UNESCO, Interpol, the International Bureau of Weights and Measures, and la Francophonie.[150]
Postwar French foreign policy has been largely shaped by membership of the European Union, of which it was a founding member. Since the 1960s, France has developed close ties with reunified Germany to become the most influential driving force of the EU.[151] In the 1960s, France sought to exclude the British from the European unification process,[152] seeking to build its own standing in continental Europe. However, since 1904, France has maintained an "Entente cordiale" with the United Kingdom, and there has been a strengthening of links between the countries, especially militarily.

France is a member of the North Atlantic Treaty Organisation (NATO), but under President de Gaulle, it excluded itself from the joint military command to protest the Special Relationship between the United States and Britain and to preserve the independence of French foreign and security policies. However, as a result of Nicolas Sarkozy's pro-American politics (much criticised in France by the leftists and by a part of the right), France re-joined the NATO joint military command on 4 April 2009.[153][154][155]
In the early 1990s, the country drew considerable criticism from other nations for its underground nuclear tests in French Polynesia.[156] France vigorously opposed the 2003 invasion of Iraq,[157][158] straining bilateral relations with the United States[159][160] and the United Kingdom.
France retains strong political and economic influence in its former African colonies (Françafrique)[161] and has supplied economic aid and troops for peacekeeping missions in Ivory Coast and Chad.[162] Recently, after the unilateral declaration of independence of Northern Mali by the Tuareg MNLA and the subsequent regional Northern Mali conflict with several Islamist groups including Ansar Dine and MOJWA, France and other African states intervened to help the Malian Army to retake control.
In 2017, France was the fourth-largest donor (in absolute terms) of development aid in the world, behind the United States, Germany, and the United Kingdom.[163] This represents 0.43% of its GNP, the 12th highest among the OECD.[164] The organisation managing the French help is the French Development Agency, which finances primarily humanitarian projects in sub-Saharan Africa.[165] The main goals of this support are "developing infrastructure, access to health care and education, the implementation of appropriate economic policies and the consolidation of the rule of law and democracy".[165]
Military

The French Armed Forces (Forces armées françaises) are the military and paramilitary forces of France, under the President of the Republic as supreme commander. They consist of the French Army (Armée de Terre), French Navy (Marine Nationale, formerly called Armée de Mer), the French Air Force (Armée de l'Air), the French Strategic Nuclear Force (Force Nucléaire Stratégique, nicknamed Force de Frappe or "Strike Force") and the Military Police called National Gendarmerie (Gendarmerie nationale), which also fulfils civil police duties in the rural areas of France. Together they are among the largest armed forces in the world and the largest in the EU.
While the Gendarmerie is an integral part of the French armed forces (gendarmes are career soldiers), and therefore under the purview of the Ministry of the Armed Forces, it is operationally attached to the Ministry of the Interior as far as its civil police duties are concerned.
When acting as general purpose police force, the Gendarmerie encompasses the counter terrorist units of the Parachute Intervention Squadron of the National Gendarmerie (Escadron Parachutiste d'Intervention de la Gendarmerie Nationale), the National Gendarmerie Intervention Group (Groupe d'Intervention de la Gendarmerie Nationale), the Search Sections of the National Gendarmerie (Sections de Recherche de la Gendarmerie Nationale), responsible for criminal enquiries, and the Mobile Brigades of the National Gendarmerie (Brigades mobiles de la Gendarmerie Nationale, or in short Gendarmerie mobile) which have the task to maintain public order.
The following special units are also part of the Gendarmerie: the Republican Guard (Garde républicaine) which protects public buildings hosting major French institutions, the Maritime Gendarmerie (Gendarmerie maritime) serving as Coast Guard, the Provost Service (Prévôté), acting as the Military Police branch of the Gendarmerie.
As far as the French intelligence units are concerned, the Directorate-General for External Security (Direction générale de la sécurité extérieure) is considered to be a component of the Armed Forces under the authority of the Ministry of Defense. The other, the Central Directorate for Interior Intelligence (Direction centrale du renseignement intérieur) is a division of the National Police Force (Direction générale de la Police Nationale), and therefore reports directly to the Ministry of the Interior. There has been no national conscription since 1997.[166]
France has a special military corps, the French Foreign Legion, founded in 1830, which consists of foreign nationals from over 140 countries who are willing to serve in the French Armed Forces and become French citizens after the end of their service period. The only other countries having similar units are Spain (the Spanish Foreign Legion, called Tercio, was founded in 1920) and Luxembourg (foreigners can serve in the National Army provided they speak Luxembourgish).
France is a permanent member of the Security Council of the UN, and a recognised nuclear state since 1960. France has signed and ratified the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty (CTBT)[167] and acceded to the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty. France's annual military expenditure in 2018 was US$63.8 billion, or 2.3% of its GDP, making it the fifth biggest military spender in the world after the United States, China, Saudi Arabia, and India.[168]
French nuclear deterrence, (formerly known as "Force de Frappe"), relies on complete independence. The current French nuclear force consists of four Triomphant class submarines equipped with submarine-launched ballistic missiles. In addition to the submarine fleet, it is estimated that France has about 60 ASMP medium-range air-to-ground missiles with nuclear warheads,[169] of which around 50 are deployed by the Air Force using the Mirage 2000N long-range nuclear strike aircraft, while around 10 are deployed by the French Navy's Super Étendard Modernisé (SEM) attack aircraft, which operate from the nuclear-powered aircraft carrier Charles de Gaulle. The new Rafale F3 aircraft will gradually replace all Mirage 2000N and SEM in the nuclear strike role with the improved ASMP-A missile with a nuclear warhead.
France has major military industries with one of the largest aerospace industries in the world.[170][171] Its industries have produced such equipment as the Rafale fighter, the Charles de Gaulle aircraft carrier, the Exocet missile and the Leclerc tank among others. Despite withdrawing from the Eurofighter project, France is actively investing in European joint projects such as the Eurocopter Tiger, multipurpose frigates, the UCAV demonstrator nEUROn and the Airbus A400M. France is a major arms seller,[172][173] with most of its arsenal's designs available for the export market with the notable exception of nuclear-powered devices.
The Bastille Day military parade held in Paris each 14 July for France's national day, called Bastille Day in English-speaking countries (referred to in France as Fête nationale), is the oldest and largest regular military parade in Europe. Other smaller parades are organised across the country.
Government finance
The Government of France has run a budget deficit each year since the early 1970s. As of 2016, French government debt levels reached 2.2 trillion euros, the equivalent of 96.4% of French GDP.[174] In late 2012, credit rating agencies warned that growing French Government debt levels risked France's AAA credit rating, raising the possibility of a future downgrade and subsequent higher borrowing costs for the French authorities.[175]
Economy
A member of the Group of Seven (formerly Group of Eight) leading industrialized countries, as of 2018, it is ranked as the world's tenth largest and the EU's second largest economy by purchasing power parity.[176] France joined 11 other EU members to launch the euro in 1999, with euro coins and banknotes completely replacing the French franc (₣) in 2002.[177]
France has a mixed economy that combines extensive private enterprise[178][179] with substantial state enterprise and government intervention. The government retains considerable influence over key segments of infrastructure sectors, with majority ownership of railway, electricity, aircraft, nuclear power and telecommunications.[96] It has been relaxing its control over these sectors since the early 1990s.[96] The government is slowly corporatising the state sector and selling off holdings in France Télécom, Air France, as well as in the insurance, banking, and defense industries.[96] France has an important aerospace industry led by the European consortium Airbus, and has its own national spaceport, the Centre Spatial Guyanais.
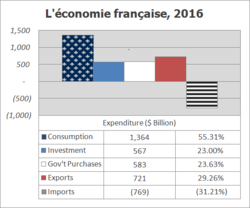
As of 2009, the World Trade Organization (WTO) reported France was the world's sixth largest exporter and the fourth largest importer of manufactured goods.[180] As of 2016, the World Factbook ranked France seventh largest exporter.[181] In 2008, France was the third largest recipient of foreign direct investment among OECD countries at $118 billion, ranking behind Luxembourg (where foreign direct investment was essentially monetary transfers to banks located there) and the United States ($316 billion), but above the United Kingdom ($96.9 billion), Germany ($25 billion), or Japan ($24 billion). In the same year, French companies invested $220 billion outside France, ranking France as the second largest outward direct investor in the OECD, behind the United States ($311 billion), and ahead of the UK ($111 billion), Japan ($128 billion) and Germany ($157 billion).[182][183]
Financial services, banking and the insurance sector are an important part of the economy. Three largest financial institutions cooperatively owned by their customers are located in France.[184] The Paris stock exchange (French: La Bourse de Paris) is an old institution, created by Louis XV in 1724.[185] In 2000, the stock exchanges of Paris, Amsterdam and Brussels merged into Euronext.[186] In 2007, Euronext merged with the New York stock exchange to form NYSE Euronext, the world's largest stock exchange.[186] Euronext Paris, the French branch of the NYSE Euronext group is Europe's 2nd largest stock exchange market, behind the London Stock Exchange.
France is a member of the Eurozone (around 330 million consumers) which is part of the European Single Market (more than 500 million consumers). Several domestic commercial policies are determined by agreements among European Union (EU) members and by EU legislation. France introduced the common European currency, the Euro in 2002.[187][188]
French companies have maintained key positions in the insurance and banking industries: AXA is the world's largest insurance company. The leading French banks are BNP Paribas and the Crédit Agricole, ranking as the world's first and sixth largest banks in 2010[189] (by assets), while the Société Générale group was ranked the world's eighth largest in 2009.
Agriculture

France has historically been a large producer of agricultural products.[190] Extensive tracts of fertile land, the application of modern technology, and EU subsidies have combined to make France the leading agricultural producer and exporter in Europe[191] (representing 20% of the EU's agricultural production)[192] and the world's third biggest exporter of agricultural products.[193]
Wheat, poultry, dairy, beef, and pork, as well as internationally recognized processed foods are the primary French agricultural exports. Rosé wines are primarily consumed within the country, but Champagne and Bordeaux wines are major exports, being known worldwide. EU agriculture subsidies to France have decreased in recent years but still amounted to $8 billion in 2007.[194] That same year, France sold 33.4 billion euros of transformed agricultural products.[195] France produces rum via sugar cane-based distilleries almost all of which are located in overseas territories such as Martinique, Guadeloupe and La Réunion. Agriculture is an important sector of France's economy: 3.8% of the active population is employed in agriculture, whereas the total agri-food industry made up 4.2% of French GDP in 2005.[192]
Tourism

.jpg)
With 83 million foreign tourists in 2012,[196] France is ranked as the first tourist destination in the world, ahead of the United States (67 million) and China (58 million). This 83 million figure excludes people staying less than 24 hours, such as North Europeans crossing France on their way to Spain or Italy. It is third in income from tourism due to shorter duration of visits.[197] The most popular tourist sites include (annual visitors): Eiffel Tower (6.2 million), Château de Versailles (2.8 million), Muséum national d'Histoire naturelle (2 million), Pont du Gard (1.5 million), Arc de Triomphe (1.2 million), Mont Saint-Michel (1 million), Sainte-Chapelle (683,000), Château du Haut-Kœnigsbourg (549,000), Puy de Dôme (500,000), Musée Picasso (441,000), and Carcassonne (362,000).[198]
Paris
France, especially Paris, has some of the world's largest and most renowned museums, including the Louvre, which is the most visited art museum in the world (5.7 million), the Musée d'Orsay (2.1 million), mostly devoted to Impressionism, and Centre Georges Pompidou (1.2 million), dedicated to contemporary art. Disneyland Paris is Europe's most popular theme park, with 15 million combined visitors to the resort's Disneyland Park and Walt Disney Studios Park in 2009.[199]
French Riviera
With more than 10 millions tourists a year, the French Riviera (French: Côte d'Azur), in Southeast France, is the second leading tourist destination in the country, after the Paris region.[200] It benefits from 300 days of sunshine per year, 115 kilometres (71 mi) of coastline and beaches, 18 golf courses, 14 ski resorts and 3,000 restaurants.[201]:31 Each year the Côte d'Azur hosts 50% of the world's superyacht fleet.[201]:66
Châteaux
With 6 millions tourists a year, the castles of the Loire Valley (French: châteaux) and the Loire Valley itself are the third leading tourist destination in France;[202][203] this World Heritage site is noteworthy for its architectural heritage, in its historic towns but in particular its castles, such as the Châteaux d'Amboise, de Chambord, d'Ussé, de Villandry, Chenonceau and Montsoreau. The Château de Chantilly, Versailles and Vaux-le-Vicomte, all three located near Paris, are also visitor attractions.
UNESCO World Heritage Sites and protected areas
France has 37 sites inscribed in UNESCO's World Heritage List and features cities of high cultural interest, beaches and seaside resorts, ski resorts, and rural regions that many enjoy for their beauty and tranquillity (green tourism). Small and picturesque French villages are promoted through the association Les Plus Beaux Villages de France (literally "The Most Beautiful Villages of France"). The "Remarkable Gardens" label is a list of the over 200 gardens classified by the French Ministry of Culture. This label is intended to protect and promote remarkable gardens and parks. France attracts many religious pilgrims on their way to St. James, or to Lourdes, a town in the Hautes-Pyrénées that hosts several million visitors a year.
Energy

Électricité de France (EDF), the main electricity generation and distribution company in France, is also one of the world's largest producers of electricity. In 2003, it produced 22% of the European Union's electricity, primarily from nuclear power. France is the smallest emitter of carbon dioxide among the G8, due to its heavy investment in nuclear power.[204] As of 2016, 72% of the electricity produced by France is generated by 58 nuclear power plants.[205][206] In this context, renewable energies are having difficulty taking off. France also uses hydroelectric dams to produce electricity, such as the Eguzon dam, Étang de Soulcem and Lac de Vouglans.
Transport

The railway network of France, which as of 2008 stretches 29,473 kilometres (18,314 mi)[207] is the second most extensive in Western Europe after that of Germany.[208] It is operated by the SNCF, and high-speed trains include the Thalys, the Eurostar and TGV, which travels at 320 km/h (199 mph) in commercial use.[209] The Eurostar, along with the Eurotunnel Shuttle, connects with the United Kingdom through the Channel Tunnel. Rail connections exist to all other neighboring countries in Europe, except Andorra. Intra-urban connections are also well developed with both underground services (Paris, Lyon, Lille, Marseille, Toulouse, Rennes) and tramway services (Nantes, Strasbourg, Bordeaux, Grenoble, Montpellier...) complementing bus services.
There are approximately 1,027,183 kilometres (638,262 mi) of serviceable roadway in France, ranking it the most extensive network of the European continent.[210] The Paris region is enveloped with the most dense network of roads and highways that connect it with virtually all parts of the country. French roads also handle substantial international traffic, connecting with cities in neighboring Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, Switzerland, Italy, Spain, Andorra and Monaco. There is no annual registration fee or road tax; however, usage of the mostly privately owned motorways is through tolls except in the vicinity of large communes. The new car market is dominated by domestic brands such as Renault (27% of cars sold in France in 2003), Peugeot (20.1%) and Citroën (13.5%).[211] Over 70% of new cars sold in 2004 had diesel engines, far more than contained petrol or LPG engines.[212] France possesses the Millau Viaduct, the world's tallest bridge,[213] and has built many important bridges such as the Pont de Normandie.

There are 464 airports in France.[96] Charles de Gaulle Airport, located in the vicinity of Paris, is the largest and busiest airport in the country, handling the vast majority of popular and commercial traffic and connecting Paris with virtually all major cities across the world. Air France is the national carrier airline, although numerous private airline companies provide domestic and international travel services. There are ten major ports in France, the largest of which is in Marseille,[214] which also is the largest bordering the Mediterranean Sea.[215][216] 12,261 kilometres (7,619 mi) of waterways traverse France including the Canal du Midi, which connects the Mediterranean Sea to the Atlantic Ocean through the Garonne river.[96]
Science and technology

Since the Middle Ages, France has been a major contributor to scientific and technological achievement. Around the beginning of the 11th century, Pope Sylvester II, born Gerbert d'Aurillac, reintroduced the abacus and armillary sphere, and introduced Arabic numerals and clocks to Northern and Western Europe.[218] The University of Paris, founded in the mid-12th century, is still one of the most important universities in the Western world.[219] In the 17th century, mathematician René Descartes defined a method for the acquisition of scientific knowledge, while Blaise Pascal became famous for his work on probability and fluid mechanics. They were both key figures of the Scientific Revolution, which blossomed in Europe during this period. The Academy of Sciences was founded by Louis XIV to encourage and protect the spirit of French scientific research. It was at the forefront of scientific developments in Europe in the 17th and 18th centuries. It is one of the earliest academies of sciences.
The Age of Enlightenment was marked by the work of biologist Buffon and chemist Lavoisier, who discovered the role of oxygen in combustion, while Diderot and D'Alembert published the Encyclopédie, which aimed to give access to "useful knowledge" to the people, a knowledge that they can apply to their everyday life.[220] With the Industrial Revolution, the 19th century saw spectacular scientific developments in France with scientists such as Augustin Fresnel, founder of modern optics, Sadi Carnot who laid the foundations of thermodynamics, and Louis Pasteur, a pioneer of microbiology. Other eminent French scientists of the 19th century have their names inscribed on the Eiffel Tower.
Famous French scientists of the 20th century include the mathematician and physicist Henri Poincaré, physicists Henri Becquerel, Pierre and Marie Curie, who remained famous for their work on radioactivity, the physicist Paul Langevin and virologist Luc Montagnier, co-discoverer of HIV AIDS. Hand transplantation was developed on 23 September 1998 in Lyon by a team assembled from different countries around the world including Jean-Michel Dubernard who, shortly thereafter, performed the first successful double hand transplant.[221] Telesurgery was developed by Jacques Marescaux and his team on 7 September 2001 across the Atlantic Ocean (New-York-Strasbourg, Lindbergh Operation).[222] A face transplant was first done on 27 November 2005[223][224] by Dr. Bernard Devauchelle.

France was the fourth country to achieve nuclear capability[225] and has the third largest nuclear weapons arsenal in the world.[226] It is also a leader in civilian nuclear technology.[227][228][229] France was the third nation, after the former USSR and the United States, to launch its own space satellite and remains the biggest contributor to the European Space Agency (ESA).[230][231][232] The European Airbus, formed from the French group Aérospatiale along with DaimlerChrysler Aerospace AG (DASA) and Construcciones Aeronáuticas SA (CASA), designs and develops civil and military aircraft as well as communications systems, missiles, space rockets, helicopters, satellites, and related systems. France also hosts major international research instruments such as the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility or the Institut Laue–Langevin and remains a major member of CERN. It also owns Minatec, Europe's leading nanotechnology research center.
The SNCF, the French national railroad company, has developed the TGV, a high speed train which holds a series of world speed records. The TGV has been the fastest wheeled train in commercial use since reaching a speed of 574.8 km/h (357.2 mph) on 3 April 2007.[233] Western Europe is now serviced by a network of TGV lines.
As of 2018, 69 French people have been awarded a Nobel Prize[234] and 12 have received the Fields Medal.[235]
Demographics
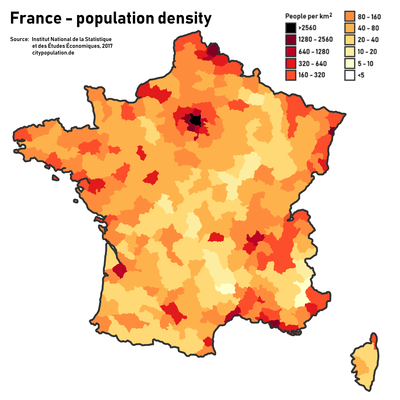
With an estimated 2020 population of 67.08 million people,[236] France is the 20th most populous country in the world, the third-most populous in Europe (after Russia and Germany), and the second most populous in the European Union (after Germany).
France is an outlier among developed countries in general, and European countries in particular, in having a relatively high rate of natural population growth: by birth rates alone, it was responsible for almost all natural population growth in the European Union in 2006.[237] Between 2006 and 2016, France saw the second highest overall increase in population in the EU, and was one of only four EU countries where natural births accounted for most population growth.[238] This was the highest rate since the end of the baby boom in 1973, and coincides with the rise of the total fertility rate from a nadir of 1.7 in 1994 to 2.0 in 2010.
As of January 2017 the fertility rate declined slightly to 1.93 children per woman, below the replacement rate of 2.1, and considerably below the high of 4.41 in 1800.[239][240][241][242] France's fertility rate and crude birth rate nonetheless remain among the highest in the EU. However, like many developed nations, France's population is aging; the average age is 42.6 years, while close to a fifth of French people are 65 or over.[243] Average life expectancy at birth is 82.2 years, the ninth highest in the world.
From 2006 to 2011 population growth averaged 0.6 percent per year;[244] since 2011, annual growth has been between 0.4 and 0.5 percent annually.[245] Immigrants are major contributors to this trend; in 2010, 27 percent of newborns in metropolitan France had at least one foreign-born parent and 24 percent had at least one parent born outside of Europe (excluding French overseas territories).[246]
Ethnic groups
Most French people are of Celtic (Gauls) origin, with an admixture of Italic (Romans) and Germanic (Franks) groups.[247] Different regions reflect this diverse heritage, with notable Breton elements in western France, Aquitanian in the southwest, Scandinavian in the northwest, Alemannic in the northeast and Ligurian in the southeast.
Large-scale immigration over the last century and a half has led to a more multicultural society. In 2004, the Institut Montaigne estimated that within Metropolitan France, 51 million people were White (85% of the population), 6 million were Northwest African (10%), 2 million were Black (3.3%), and 1 million were Asian (1.7%).[248][249]
Since the French Revolution, and as codified in the 1958 French Constitution, it is illegal for the French state to collect data on ethnicity and ancestry. In 2008, the TeO ("Trajectories and origins") poll conducted jointly by INED and the French National Institute of Statistics[250][251] estimated that 5 million people were of Italian ancestry (the largest immigrant community), followed by 3 million to 6 million[252][253][254] of Northwest African ancestry, 2.5 million of Sub-Saharan African origin, 500,000 ethnic Armenian, and 200,000 people of Turkish ancestry.[255] There are also sizable minorities of other European ethnic groups, namely Spanish, Portuguese, Polish, and Greek.[252][256][257]
France has a significant Gypsy (Gitan) population, numbering between 20,000 and 400,000.[258] Many foreign Romani people are expelled back to Bulgaria and Romania frequently.[259]
It is currently estimated that 40% of the French population is descended at least partially from the different waves of immigration the country has received since the early 20th century;[260] between 1921 and 1935 alone, about 1.1 million net immigrants came to France.[261] The next largest wave came in the 1960s, when around 1.6 million pieds noirs returned to France following the independence of its Northwest African possessions, Algeria and Morocco.[262][263] They were joined by numerous former colonial subjects from North and West Africa, as well as numerous European immigrants from Spain and Portugal.
France remains a major destination for immigrants, accepting about 200,000 legal immigrants annually.[264] In 2005, it was Western Europe's leading recipient of asylum seekers, with an estimated 50,000 applications (albeit 15% decrease from 2004).[265] In 2010, France received about 48,100 asylum applications—placing it among the top five asylum recipients in the world[266] and in subsequent years it saw the number of applications increase, ultimately doubling to 100,412 in 2017.[267] The European Union allows free movement between the member states, although France established controls to curb Eastern European migration, and immigration remains a contentious political issue.
In 2008, the INSEE (National Institute of Statistics and Economic Studies) estimated that the total number of foreign-born immigrants was around 5 million (8% of the population), while their French-born descendants numbered 6.5 million, or 11% of the population. Thus, nearly a fifth of the country's population were either first or second-generation immigrants, of which more than 5 million were of European origin and 4 million of Maghrebi ancestry.[268][269][270] In 2008, France granted citizenship to 137,000 persons, mostly from Morocco, Algeria and Turkey.[271]
In 2014, the INSEE published a study which reported doubling of the number of Spanish immigrants, Portuguese and Italians in France between 2009 and 2012. According to the French Institute, this increase resulting from the financial crisis that hit several European countries in that period, has pushed up the number of Europeans installed in France.[272] Statistics on Spanish immigrants in France show a growth of 107 percent between 2009 and 2012, i.e. in this period went from 5300 to 11,000 people.[272] Of the total of 229,000 foreigners who were in France in 2012, nearly 8% were Portuguese, 5% British, 5% Spanish, 4% Italians, 4% Germans, 3% Romanians, and 3% Belgians.[272]
Major cities
France is a highly urbanized country, with its largest cities (in terms of metropolitan area population in 2016[273]) being Paris (12,568,755 inh.), Lyon (2,310,850), Marseille (1,756,296), Toulouse (1,345,343), Bordeaux (1,232,550), Lille (1,187,824), Nice (1,006,402), Nantes (961,521), Strasbourg (785,839) and Rennes (727,357). (Note: There are significant differences between the metropolitan population figures just cited and those in the following table, which indicates the population of the communes). Rural flight was a perennial political issue throughout most of the 20th century.
Language
According to Article 2 of the Constitution, the official language of France is French,[274] a Romance language derived from Latin. Since 1635, the Académie française has been France's official authority on the French language, although its recommendations carry no legal weight. There are also regional languages spoken in France, such as Occitan, Breton, Catalan, Flemish (Dutch dialect), Alsatian (German dialect), Basque, and Corsican. Italian was the official language of Corsica until 9 May 1859.[275]
The Government of France does not regulate the choice of language in publications by individuals but the use of French is required by law in commercial and workplace communications. In addition to mandating the use of French in the territory of the Republic, the French government tries to promote French in the European Union and globally through institutions such as the Organisation internationale de la Francophonie. The perceived threat from anglicisation has prompted efforts to safeguard the position of the French language in France. Besides French, there exist 77 vernacular minority languages of France, eight spoken in French metropolitan territory and 69 in the French overseas territories.
From the 17th to the mid-20th century, French served as the pre-eminent international language of diplomacy and international affairs as well as a lingua franca among the educated classes of Europe.[276] The dominant position of French language in international affairs was overtaken by English, since the emergence of the United States as a major power.[59][277][278]
For most of the time in which French served as an international lingua franca, it was not the native language of most Frenchmen: a report in 1794 conducted by Henri Grégoire found that of the country's 25 million people, only three million spoke French natively; the rest spoke one of the country's many regional languages, such as Alsatian, Breton or Occitan.[279] Through the expansion of public education, in which French was the sole language of instruction, as well as other factors such as increased urbanisation and the rise of mass communication, French gradually came to be adopted by virtually the entire population, a process not completed until the 20th century.
As a result of France's extensive colonial ambitions between the 17th and 20th centuries, French was introduced to the Americas, Africa, Polynesia, South-East Asia, as well as the Caribbean. French is the second most studied foreign language in the world after English,[280] and is a lingua franca in some regions, notably in Africa. The legacy of French as a living language outside Europe is mixed: it is nearly extinct in some former French colonies (The Levant, South and Southeast Asia), while creoles and pidgins based on French have emerged in the French departments in the West Indies and the South Pacific (French Polynesia). On the other hand, many former French colonies have adopted French as an official language, and the total number of French speakers is increasing, especially in Africa.
It is estimated that between 300 million[281] and 500 million[282] people worldwide can speak French, either as a mother tongue or a second language.
According to the 2007 Adult Education survey, part of a project by the European Union and carried in France by the INSEE and based on a sample of 15,350 persons, French was the native language of 87.2% of the total population, or roughly 55.81 million people, followed by Arabic (3.6%, 2.3 million), Portuguese (1.5%, 960,000), Spanish (1.2%, 770,000) and Italian (1.0%, 640,000). Native speakers of other languages made up the remaining 5.2% of the population.[283]
Religion

France is a secular country in which freedom of religion is a constitutional right. French religious policy is based on the concept of laïcité, a strict separation of church and state under which public life is kept completely secular.
According to a survey held in 2016 by Institut Montaigne and Institut français d'opinion publique (IFOP), 51.1% of the total population of France was Christian, 39.6% had no religion (atheism or agnosticism), 5.6% were Muslims, 2.5% were followers of other faiths, and the remaining 0.4% were undecided about their faith.[284] Estimates of the number of Muslims in France vary widely. In 2003, the French Ministry of the Interior estimated the total number of people of Muslim background to be between 5 and 6 million (8–10%).[285][286] The current Jewish community in France is the largest in Europe and the third-largest in the world after Israel and the United States, ranging between 480,000 and 600,000, about 0.8% of the population as of 2016.[284]
Catholicism has been the predominant religion in France for more than a millennium, though it is not as actively practised today as it was. Among the 47,000 religious buildings in France, 94% are Roman Catholic.[287] During the French Revolution, activists conducted a brutal campaign of de-Christianisation, ending the Catholic Church as the state religion. In some cases clergy and churches were attacked, with iconoclasm stripping the churches of statues and ornaments. After alternating between royal and secular republican governments during the 19th century, in 1905 France passed the 1905 law on the Separation of the Churches and the State, which established the principle of laïcité.[288]
To this day, the government is prohibited from recognizing any specific right to a religious community (except for legacy statutes like those of military chaplains and the local law in Alsace-Moselle). It recognizes religious organisations according to formal legal criteria that do not address religious doctrine. Conversely, religious organisations are expected to refrain from intervening in policy-making.[289] Certain groups, such as Scientology, Children of God, the Unification Church, and the Order of the Solar Temple are considered cults ("sectes" in French), and therefore do not have the same status as recognized religions in France.[290] Secte is considered a pejorative term in France.[291]
Health

The French health care system is one of universal health care largely financed by government national health insurance. In its 2000 assessment of world health care systems, the World Health Organization found that France provided the "close to best overall health care" in the world.[293] The French healthcare system was ranked first worldwide by the World Health Organization in 1997.[294][295] In 2011, France spent 11.6% of GDP on health care, or US$4,086 per capita,[296] a figure much higher than the average spent by countries in Europe but less than in the United States. Approximately 77% of health expenditures are covered by government funded agencies.[297]
Care is generally free for people affected by chronic diseases (affections de longues durées) such as cancer, AIDS or cystic fibrosis. Average life expectancy at birth is 78 years for men and 85 years for women, one of the highest of the European Union and the World.[298][299] There are 3.22 physicians for every 1000 inhabitants in France,[300] and average health care spending per capita was US$4,719 in 2008.[301] As of 2007, approximately 140,000 inhabitants (0.4%) of France are living with HIV/AIDS.[96]
Even if the French have the reputation of being one of the thinnest people in developed countries,[302][303][304][305][306] France—like other rich countries—faces an increasing and recent epidemic of obesity, due mostly to the replacement in French eating habits of traditional healthy French cuisine by junk food.[307][302][303][308] The French obesity rate is still far below that of the United States—currently equal to American rate in the 1970s—and is still the lowest of Europe.[303][305][308] Authorities now regard obesity as one of the main public health issues and fight it fiercely.[309] Nevertheless, rates of childhood obesity are slowing in France, while continuing to grow in other countries.[310]
Education

In 1802, Napoleon created the lycée, the second and final stage of secondary education that prepares students for higher education studies or a profession.[311] Nevertheless, Jules Ferry is considered the father of the French modern school, leading reforms in the late 19th century that established free, secular, and compulsory education (currently mandatory until the age of 16)[312][313]
French education is centralized and divided into three stages: Primary, secondary, and higher education. The Programme for International Student Assessment, coordinated by the OECD, ranked France's education as about the OECD average in 2015.[314] Primary and secondary education are predominantly public, run by the Ministry of National Education. While training and remuneration of teachers and the curriculum are the responsibility of the state centrally, the management of primary and secondary schools is overseen by local authorities. Primary education comprises two phases, nursery school (école maternelle) and elementary school (école élémentaire). Nursery school aims to stimulate the minds of very young children and promote their socialization and development of a basic grasp of language and number. Around the age of six, children transfer to elementary school, whose primary objectives are learning about writing, arithmetic and citizenship. Secondary education also consists of two phases. The first is delivered through colleges (collège) and leads to the national certificate (Diplôme national du brevet). The second is offered in high schools (lycée) and finishes in national exams leading to a baccalaureate (baccalauréat, available in professional, technical or general flavors) or certificate of professional competence (certificat d'aptitude professionelle).
Higher education is divided between public universities and the prestigious and selective Grandes écoles, such as Sciences Po Paris for Political studies, HEC Paris for Economics, Polytechnique, the École des hautes études en sciences sociales for Social studies and the École nationale supérieure des mines de Paris that produce high-profile engineers, or the École nationale d'administration for careers in the Grands Corps of the state. The Grandes écoles have been criticized for alleged elitism, producing many if not most of France's high-ranking civil servants, CEOs, and politicians.[315]
Culture

France has been a center of Western cultural development for centuries. Many French artists have been among the most renowned of their time, and France is still recognized in the world for its rich cultural tradition.
The successive political regimes have always promoted artistic creation, and the creation of the Ministry of Culture in 1959 helped preserve the cultural heritage of the country and make it available to the public. The Ministry of Culture has been very active since its creation, granting subsidies to artists, promoting French culture in the world, supporting festivals and cultural events, protecting historical monuments. The French government also succeeded in maintaining a cultural exception to defend audiovisual products made in the country.
France receives the highest number of tourists per year, largely thanks to the numerous cultural establishments and historical buildings implanted all over the territory. It counts 1,200 museums welcoming more than 50 million people annually.[316] The most important cultural sites are run by the government, for instance through the public agency Centre des monuments nationaux, which is responsible for approximately 85 national historical monuments.
The 43,180 buildings protected as historical monuments include mainly residences (many castles) and religious buildings (cathedrals, basilicas, churches), but also statues, memorials and gardens. The UNESCO inscribed 45 sites in France on the World Heritage List.[317]
Art
The origins of French art were very much influenced by Flemish art and by Italian art at the time of the Renaissance. Jean Fouquet, the most famous medieval French painter, is said to have been the first to travel to Italy and experience the Early Renaissance at first hand. The Renaissance painting School of Fontainebleau was directly inspired by Italian painters such as Primaticcio and Rosso Fiorentino, who both worked in France. Two of the most famous French artists of the time of Baroque era, Nicolas Poussin and Claude Lorrain, lived in Italy.

The 17th century was the period when French painting became prominent and individualised itself through classicism. Louis XIV's prime minister Jean-Baptiste Colbert founded in 1648 the Royal Academy of Painting and Sculpture to protect these artists, and in 1666 he created the still-active French Academy in Rome to have direct relations with Italian artists.
French artists developed the rococo style in the 18th century, as a more intimate imitation of old baroque style, the works of the court-endorsed artists Antoine Watteau, François Boucher and Jean-Honoré Fragonard being the most representative in the country. The French Revolution brought great changes, as Napoleon favoured artists of neoclassic style such as Jacques-Louis David and the highly influential Académie des Beaux-Arts defined the style known as Academism. At this time France had become a centre of artistic creation, the first half of the 19th century being dominated by two successive movements, at first Romanticism with Théodore Géricault and Eugène Delacroix, and Realism with Camille Corot, Gustave Courbet and Jean-François Millet, a style that eventually evolved into Naturalism.

In the second part of the 19th century, France's influence over painting became even more important, with the development of new styles of painting such as Impressionism and Symbolism. The most famous impressionist painters of the period were Camille Pissarro, Édouard Manet, Edgar Degas, Claude Monet and Auguste Renoir.[318] The second generation of impressionist-style painters, Paul Cézanne, Paul Gauguin, Toulouse-Lautrec and Georges Seurat, were also at the avant-garde of artistic evolutions,[319] as well as the fauvist artists Henri Matisse, André Derain and Maurice de Vlaminck.[320][321]
At the beginning of the 20th century, Cubism was developed by Georges Braque and the Spanish painter Pablo Picasso, living in Paris. Other foreign artists also settled and worked in or near Paris, such as Vincent van Gogh, Marc Chagall, Amedeo Modigliani and Wassily Kandinsky.
Many museums in France are entirely or partly devoted to sculptures and painting works. A huge collection of old masterpieces created before or during the 18th century are displayed in the state-owned Musée du Louvre, such as Mona Lisa, also known as La Joconde. While the Louvre Palace has been for a long time a museum, the Musée d'Orsay was inaugurated in 1986 in the old railway station Gare d'Orsay, in a major reorganisation of national art collections, to gather French paintings from the second part of the 19th century (mainly Impressionism and Fauvism movements).[322][323]
Modern works are presented in the Musée National d'Art Moderne, which moved in 1976 to the Centre Georges Pompidou. These three state-owned museums welcome close to 17 million people a year.[324] Other national museums hosting paintings include the Grand Palais (1.3 million visitors in 2008), but there are also many museums owned by cities, the most visited being the Musée d'Art Moderne de la Ville de Paris (0.8 million entries in 2008), which hosts contemporary works.[324] Outside Paris, all the large cities have a Museum of Fine Arts with a section dedicated to European and French painting. Some of the finest collections are in Lyon, Lille, Rouen, Dijon, Rennes and Grenoble.
Architecture

During the Middle Ages, many fortified castles were built by feudal nobles to mark their powers. Some French castles that survived are Chinon, Château d'Angers, the massive Château de Vincennes and the so-called Cathar castles. During this era, France had been using Romanesque architecture like most of Western Europe. Some of the greatest examples of Romanesque churches in France are the Saint Sernin Basilica in Toulouse, the largest romanesque church in Europe,[325] and the remains of the Cluniac Abbey.
The Gothic architecture, originally named Opus Francigenum meaning "French work",[326] was born in Île-de-France and was the first French style of architecture to be copied in all Europe.[327] Northern France is the home of some of the most important Gothic cathedrals and basilicas, the first of these being the Saint Denis Basilica (used as the royal necropolis); other important French Gothic cathedrals are Notre-Dame de Chartres and Notre-Dame d'Amiens. The kings were crowned in another important Gothic church: Notre-Dame de Reims.[328] Aside from churches, Gothic Architecture had been used for many religious palaces, the most important one being the Palais des Papes in Avignon.

The final victory in the Hundred Years' War marked an important stage in the evolution of French architecture. It was the time of the French Renaissance and several artists from Italy were invited to the French court; many residential palaces were built in the Loire Valley, from 1450 with as a first reference the Château de Montsoreau.[329] Such residential castles were the Château de Chambord, the Château de Chenonceau, or the Château d'Amboise.
Following the renaissance and the end of the Middle Ages, Baroque architecture replaced the traditional Gothic style. However, in France, baroque architecture found a greater success in the secular domain than in a religious one.[330] In the secular domain, the Palace of Versailles has many baroque features. Jules Hardouin Mansart, who designed the extensions to Versailles, was one of the most influential French architect of the baroque era; he is famous for his dome at Les Invalides.[331] Some of the most impressive provincial baroque architecture is found in places that were not yet French such as the Place Stanislas in Nancy. On the military architectural side, Vauban designed some of the most efficient fortresses in Europe and became an influential military architect; as a result, imitations of his works can be found all over Europe, the Americas, Russia and Turkey.[332][333]

After the Revolution, the Republicans favoured Neoclassicism although it was introduced in France prior to the revolution with such buildings as the Parisian Pantheon or the Capitole de Toulouse. Built during the first French Empire, the Arc de Triomphe and Sainte Marie-Madeleine represent the best example of Empire style architecture.[334]
Under Napoleon III, a new wave of urbanism and architecture was given birth; extravagant buildings such as the neo-baroque Palais Garnier were built. The urban planning of the time was very organised and rigorous; for example, Haussmann's renovation of Paris. The architecture associated to this era is named Second Empire in English, the term being taken from the Second French Empire. At this time there was a strong Gothic resurgence across Europe and in France; the associated architect was Eugène Viollet-le-Duc. In the late 19th century, Gustave Eiffel designed many bridges, such as Garabit viaduct, and remains one of the most influential bridge designers of his time, although he is best remembered for the iconic Eiffel Tower.
In the 20th century, French-Swiss architect Le Corbusier designed several buildings in France. More recently, French architects have combined both modern and old architectural styles. The Louvre Pyramid is an example of modern architecture added to an older building. The most difficult buildings to integrate within French cities are skyscrapers, as they are visible from afar. For instance, in Paris, since 1977, new buildings had to be under 37 meters (121 feet).[335] France's largest financial district is La Defense, where a significant number of skyscrapers are located.[336] Other massive buildings that are a challenge to integrate into their environment are large bridges; an example of the way this has been done is the Millau Viaduct. Some famous modern French architects include Jean Nouvel, Dominique Perrault, Christian de Portzamparc or Paul Andreu.
Literature
The earliest French literature dates from the Middle Ages, when what is now known as modern France did not have a single, uniform language. There were several languages and dialects, and writers used their own spelling and grammar. Some authors of French medieval texts are unknown, such as Tristan and Iseult and Lancelot-Grail. Other authors are known, for example Chrétien de Troyes and Duke William IX of Aquitaine, who wrote in Occitan.
Much medieval French poetry and literature were inspired by the legends of the Matter of France, such as The Song of Roland and the various chansons de geste. The Roman de Renart, written in 1175 by Perrout de Saint Cloude, tells the story of the medieval character Reynard ('the Fox') and is another example of early French writing. An important 16th-century writer was François Rabelais, whose novel Gargantua and Pantagruel has remained famous and appreciated until now. Michel de Montaigne was the other major figure of the French literature during that century. His most famous work, Essais, created the literary genre of the essay.[337] French poetry during that century was embodied by Pierre de Ronsard and Joachim du Bellay. Both writers founded the La Pléiade literary movement.
During the 17th century, Madame de La Fayette published anonymously La Princesse de Clèves, a novel that is considered to be one of the very first psychological novels of all times.[338] Jean de La Fontaine is one of the most famous fabulists of that time, as he wrote hundreds of fables, some being far more famous than others, such as The Ant and the Grasshopper. Generations of French pupils had to learn his fables, that were seen as helping teaching wisdom and common sense to the young people. Some of his verses have entered the popular language to become proverbs, such as "À l'œuvre, on connaît l'artisan."[A workman is known by his chips].[339]

Jean Racine, whose incredible mastery of the alexandrine and of the French language has been praised for centuries, created plays such as Phèdre or Britannicus. He is, along with Pierre Corneille (Le Cid) and Molière, considered as one of the three great dramatists of France's golden age. Molière, who is deemed to be one of the greatest masters of comedy of the Western literature,[341] wrote dozens of plays, including Le Misanthrope, L'Avare, Le Malade imaginaire, as well as Le Bourgeois Gentilhomme. His plays have been so popular around the world that French language is sometimes dubbed as "the language of Molière" (la langue de Molière),[342] just like English is considered as "the language of Shakespeare".
French literature and poetry flourished even more in the 18th and 19th centuries. Denis Diderot's best-known works are Jacques the Fatalist and Rameau's Nephew. He is however best known for being the main redactor of the Encyclopédie, whose aim was to sum up all the knowledge of his century (in fields such as arts, sciences, languages, and philosophy) and to present them to the people, to fight ignorance and obscurantism. During that same century, Charles Perrault was a prolific writer of famous children's fairy tales including Puss in Boots, Cinderella, Sleeping Beauty and Bluebeard. At the start of the 19th century, symbolist poetry was an important movement in French literature, with poets such as Charles Baudelaire, Paul Verlaine and Stéphane Mallarmé.[343]
The 19th century saw the writings of many renowned French authors. Victor Hugo is sometimes seen as "the greatest French writer of all times"[344] for excelling in all literary genres. The preface of his play Cromwell is considered to be the manifesto of the Romantic movement. Les Contemplations and La Légende des siècles are considered as "poetic masterpieces",[345] Hugo's verse having been compared to that of Shakespeare, Dante and Homer.[345] His novel Les Misérables is widely seen as one of the greatest novel ever written[346] and The Hunchback of Notre Dame has remained immensely popular.
Other major authors of that century include Alexandre Dumas (The Three Musketeers and The Count of Monte-Cristo), Jules Verne (Twenty Thousand Leagues Under the Sea), Émile Zola (Les Rougon-Macquart), Honoré de Balzac (La Comédie humaine), Guy de Maupassant, Théophile Gautier and Stendhal (The Red and the Black, The Charterhouse of Parma), whose works are among the most well known in France and the world. The Prix Goncourt is a French literary prize first awarded in 1903.[347] Important writers of the 20th century include Marcel Proust, Louis-Ferdinand Céline, Albert Camus, and Jean-Paul Sartre. Antoine de Saint Exupéry wrote Little Prince, which has remained popular for decades with children and adults around the world.[348] As of 2014, French authors had more Literature Nobel Prizes than those of any other nation.[349] The first Nobel Prize in Literature was a French author, while France's latest Nobel prize in literature is Patrick Modiano, who was awarded the prize in 2014.[349] Jean-Paul Sartre was also the first nominee in the committee's history to refuse the prize in 1964.[349]
Philosophy
Medieval philosophy was dominated by Scholasticism until the emergence of Humanism in the Renaissance. Modern philosophy began in France in the 17th century with the philosophy of René Descartes, Blaise Pascal, and Nicolas Malebranche. Descartes revitalised Western philosophy, which had been declined after the Greek and Roman eras.[350] His Meditations on First Philosophy changed the primary object of philosophical thought and raised some of the most fundamental problems for foreigners such as Spinoza, Leibniz, Hume, Berkeley, and Kant.

French philosophers produced some of the most important political works of the Age of Enlightenment. In The Spirit of the Laws, Baron de Montesquieu theorised the principle of separation of powers, which has been implemented in all liberal democracies since it was first applied in the United States. Voltaire came to embody the Enlightenment with his defence of civil liberties, such as the right to a free trial and freedom of religion.
19th-century French thought was targeted at responding to the social malaise following the French Revolution. Rationalist philosophers such as Victor Cousin and Auguste Comte, who called for a new social doctrine, were opposed by reactionary thinkers such as Joseph de Maistre, Louis de Bonald and Félicité Robert de Lamennais, who blamed the rationalist rejection of traditional order. De Maistre is considered, together with the Englishman Edmund Burke, one of the founders of European conservatism, while Comte is regarded as the founder of positivism, which Émile Durkheim reformulated as a basis for social research.
In the 20th century, partly as a reaction to the perceived excesses of positivism, French spiritualism thrived with thinkers such as Henri Bergson and it influenced American pragmatism and Whitehead's version of process philosophy. Meanwhile, French epistemology became a prominent school of thought with Jules Henri Poincaré, Gaston Bachelard, Jean Cavaillès and Jules Vuillemin. Influenced by German phenomenology and existentialism, the philosophy of Jean-Paul Sartre gained a strong influence after World War II, and late-20th-century-France became the cradle of postmodern philosophy with Jean-François Lyotard, Jean Baudrillard, Jacques Derrida and Michel Foucault.
Music
France has a long and varied musical history. It experienced a golden age in the 17th century thanks to Louis XIV, who employed a number of talented musicians and composers in the royal court. The most renowned composers of this period include Marc-Antoine Charpentier, François Couperin, Michel-Richard Delalande, Jean-Baptiste Lully and Marin Marais, all of them composers at the court. After the death of the "Roi Soleil", French musical creation lost dynamism, but in the next century the music of Jean-Philippe Rameau reached some prestige, and today he is still one of the most renowned French composers. Rameau became the dominant composer of French opera and the leading French composer for the harpsichord.[351]
French composers played an important role during the music of the 19th and early 20th century, which is considered to be the Romantic music era. Romantic music emphasised a surrender to nature, a fascination with the past and the supernatural, the exploration of unusual, strange and surprising sounds, and a focus on national identity. This period was also a golden age for operas. French composers from the Romantic era included: Hector Berlioz (best known for his Symphonie fantastique), Georges Bizet (best known for Carmen, which has become one of the most popular and frequently performed operas), Gabriel Fauré (best known for his Pavane, Requiem, and nocturnes), Charles Gounod (best known for his Ave Maria and his opera Faust), Jacques Offenbach (best known for his 100 operettas of the 1850s–1870s and his uncompleted opera The Tales of Hoffmann), Édouard Lalo (best known for his Symphonie espagnole for violin and orchestra and his Cello Concerto in D minor), Jules Massenet (best known for his operas, of which he wrote more than thirty, the most frequently staged are Manon (1884) and Werther (1892)) and Camille Saint-Saëns (he has many frequently-performed works, including The Carnival of the Animals, Danse macabre, Samson and Delilah (Opera), Introduction and Rondo Capriccioso and his Symphony No. 3).
Later came precursors of modern classical music. Érik Satie was a key member of the early-20th-century Parisian avant-garde, best known for his Gymnopédies. Francis Poulenc's best known works are his piano suite Trois mouvements perpétuels (1919), the ballet Les biches (1923), the Concert champêtre (1928) for harpsichord and orchestra, the opera Dialogues des Carmélites (1957), and the Gloria (1959) for soprano, choir and orchestra. Maurice Ravel and Claude Debussy are the most prominent figures associated with Impressionist music. Debussy was among the most influential composers of the late 19th and early 20th centuries, and his use of non-traditional scales and chromaticism influenced many composers who followed.[352] Debussy's music is noted for its sensory content and frequent usage of atonality. The two composers invented new musical forms[353][354][355][356] and new sounds. Ravel's piano compositions, such as Jeux d'eau, Miroirs, Le tombeau de Couperin and Gaspard de la nuit, demand considerable virtuosity. His mastery of orchestration is evident in the Rapsodie espagnole, Daphnis et Chloé, his arrangement of Modest Mussorgsky's Pictures at an Exhibition and his orchestral work Boléro (1928). More recently, the middle of the 20th century, Maurice Ohana, Pierre Schaeffer and Pierre Boulez contributed to the evolutions of contemporary classical music.[357]

French music then followed the rapid emergence of pop and rock music at the middle of the 20th century. Although English-speaking creations achieved popularity in the country, French pop music, known as chanson française, has also remained very popular. Among the most important French artists of the century are Édith Piaf, Georges Brassens, Léo Ferré, Charles Aznavour and Serge Gainsbourg.[358] Although there are very few rock bands in France compared to English-speaking countries,[359] bands such as Noir Désir, Mano Negra, Niagara, Les Rita Mitsouko and more recently Superbus, Phoenix and Gojira,[360] or Shaka Ponk, have reached worldwide popularity.
Other French artists with international careers have been popular in several countries, most notably female singers Dalida, Mireille Mathieu, Mylène Farmer,[360] Alizée and Nolwenn Leroy,[361] electronic music pioneers Jean-Michel Jarre, Laurent Garnier and Bob Sinclar, later Martin Solveig and David Guetta. In the 1990s and 2000s (decade), electronic duos Daft Punk, Justice and Air also reached worldwide popularity and contributed to the reputation of modern electronic music in the world.[360][362][363]
Among current musical events and institutions in France, many are dedicated to classical music and operas. The most prestigious institutions are the state-owned Paris National Opera (with its two sites Palais Garnier and Opéra Bastille), the Opéra National de Lyon, the Théâtre du Châtelet in Paris, the Théâtre du Capitole in Toulouse and the Grand Théâtre de Bordeaux. As for music festivals, there are several events organised, the most popular being Eurockéennes (a word play which sounds in French as "European"), Solidays and Rock en Seine. The Fête de la Musique, imitated by many foreign cities, was first launched by the French Government in 1982.[364][365] Major music halls and venues in France include Le Zénith sites present in many cities and other places in Paris (Paris Olympia, Théâtre Mogador, Élysée Montmartre).
Cinema


France has historical and strong links with cinema, with two Frenchmen, Auguste and Louis Lumière (known as the Lumière Brothers) credited with creating cinema in 1895.[370] The world's first female filmmaker, Alice Guy-Blaché, was also from France.[371] Several important cinematic movements, including the late 1950s and 1960s Nouvelle Vague, began in the country. It is noted for having a strong film industry, due in part to protections afforded by the Government of France. France remains a leader in filmmaking, as of 2015 producing more films than any other European country.[372][373] The nation also hosts the Cannes Festival, one of the most important and famous film festivals in the world.[374][375]
Apart from its strong and innovative film tradition, France has also been a gathering spot for artists from across Europe and the world. For this reason, French cinema is sometimes intertwined with the cinema of foreign nations. Directors from nations such as Poland (Roman Polanski, Krzysztof Kieślowski, Andrzej Żuławski), Argentina (Gaspar Noé, Edgardo Cozarinsky), Russia (Alexandre Alexeieff, Anatole Litvak), Austria (Michael Haneke) and Georgia (Géla Babluani, Otar Iosseliani) are prominent in the ranks of French cinema. Conversely, French directors have had prolific and influential careers in other countries, such as Luc Besson, Jacques Tourneur or Francis Veber in the United States.
Although the French film market is dominated by Hollywood, France is the only nation in the world where American films make up the smallest share of total film revenues, at 50%, compared with 77% in Germany and 69% in Japan.[376] French films account for 35% of the total film revenues of France, which is the highest percentage of national film revenues in the developed world outside the United States, compared to 14% in Spain and 8% in the UK.[376] France is in 2013 the 2nd exporter of films in the world after the United States.[377]
Until recently, France had for centuries been the cultural center of the world,[276] although its dominant position has been surpassed by the United States. Subsequently, France takes steps in protecting and promoting its culture, becoming a leading advocate of the cultural exception.[378] The nation succeeded in convincing all EU members to refuse to include culture and audiovisuals in the list of liberalised sectors of the WTO in 1993.[379] Moreover, this decision was confirmed in a voting in the UNESCO in 2005: the principle of "cultural exception" won an overwhelming victory with 198 countries voting for it and only 2 countries, the United States and Israel, voting against.[380]
Fashion

Fashion has been an important industry and cultural export of France since the 17th century, and modern "haute couture" originated in Paris in the 1860s. Today, Paris, along with London, Milan, and New York City, is considered one of the world's fashion capitals, and the city is home or headquarters to many of the premier fashion houses. The expression Haute couture is, in France, a legally protected name, guaranteeing certain quality standards.
The association of France with fashion and style (French: la mode) dates largely to the reign of Louis XIV[381] when the luxury goods industries in France came increasingly under royal control and the French royal court became, arguably, the arbiter of taste and style in Europe. But France renewed its dominance of the high fashion (French: couture or haute couture) industry in the years 1860–1960 through the establishing of the great couturier houses such as Chanel, Dior, and Givenchy. The French perfume industry is world leader in its sector and is centered on the town of Grasse.[382]
In the 1960s, the elitist "Haute couture" came under criticism from France's youth culture. In 1966, the designer Yves Saint Laurent broke with established Haute Couture norms by launching a prêt-à-porter ("ready to wear") line and expanding French fashion into mass manufacturing. With a greater focus on marketing and manufacturing, new trends were established by Sonia Rykiel, Thierry Mugler, Claude Montana, Jean-Paul Gaultier and Christian Lacroix in the 1970s and 1980s. The 1990s saw a conglomeration of many French couture houses under luxury giants and multinationals such as LVMH.
Media
.jpg)
Best-selling daily national newspapers in France are Le Parisien Aujourd'hui en France (with 460,000 sold daily), Le Monde and Le Figaro, with around 300,000 copies sold daily, but also L'Équipe, dedicated to sports coverage.[384] In the past years, free dailies made a breakthrough, with Metro, 20 Minutes and Direct Plus distributed at more than 650,000 copies respectively.[385] However, the widest circulations are reached by regional daily Ouest France with more than 750,000 copies sold, and the 50 other regional papers have also high sales.[386][387] The sector of weekly magazines is stronger and diversified with more than 400 specialized weekly magazines published in the country.[388]
The most influential news magazines are the left-wing Le Nouvel Observateur, centrist L'Express and right-wing Le Point (more than 400.000 copies),[389] but the highest circulation for weeklies is reached by TV magazines and by women's magazines, among them Marie Claire and ELLE, which have foreign versions. Influential weeklies also include investigative and satirical papers Le Canard Enchaîné and Charlie Hebdo, as well as Paris Match. Like in most industrialized nations, the print media have been affected by a severe crisis in the past decade. In 2008, the government launched a major initiative to help the sector reform and become financially independent,[390][391] but in 2009 it had to give 600,000 euros to help the print media cope with the economic crisis, in addition to existing subsidies.[392]
In 1974, after years of centralised monopoly on radio and television, the governmental agency ORTF was split into several national institutions, but the three already-existing TV channels and four national radio stations[394][395] remained under state-control. It was only in 1981 that the government allowed free broadcasting in the territory, ending state monopoly on radio.[395] French television was partly liberalized in the next two-decade with the creation of several commercial channels, mainly thanks to cable and satellite television. In 2005 the national service Télévision Numérique Terrestre introduced digital television all over the territory, allowing the creation of other channels.
The four existing national channels are owned by state-owned consortium France Télévisions, funded by advertising revenue and TV licence fees. Public broadcasting group Radio France run five national radio stations. Among these public media are Radio France Internationale, which broadcasts programs in French all over the world, and Franco-German TV channel TV5 Monde. In 2006, the government created global news channel France 24. Long-established TV channels TF1 (privatized in 1987), France 2 and France 3 have the highest shares, while radio stations RTL, Europe 1 and state-owned France Inter are the least listened to.
Society
According to a BBC poll in 2010, based on 29,977 responses in 28 countries, France is globally seen as a positive influence in the world's affairs: 49% have a positive view of the country's influence, whereas 19% have a negative view.[396][397] The Nation Brand Index of 2008 suggested that France has the second best international reputation, only behind Germany.[398] A global opinion poll for the BBC saw France ranked the fourth most positively viewed nation in the world (behind Germany, Canada and the United Kingdom) in 2014.[399]
According to a poll in 2011, the French were found to have the highest level of religious tolerance and to be the country where the highest proportion of the population defines its identity primarily in term of nationality and not religion.[400] As of 2011, 75% of French had a favourable view of the United States, making France one of the most pro-American countries in the world.[401] As of 2017, the favourable view of the United States had dropped to 46%.[402] In January 2010, the magazine International Living ranked France as "best country to live in", ahead of 193 other countries, for the fifth year running.[403]
The French Revolution continues to permeate the country's collective memory. The tricolour flag of France,[404] the anthem "La Marseillaise", and the motto Liberté, égalité, fraternité, defined in Title 1 of the Constitution as national symbols, all emerged during the cultural ferment of the early revolution, along with Marianne, a common national personification. In addition, Bastille Day, the national holiday, commemorates the storming of the Bastille on 14 July 1789.[405]
A common and traditional symbol of the French people is the Gallic rooster. Its origins date back to Antiquity, since the Latin word Gallus meant both "rooster" and "inhabitant of Gaul". Then this figure gradually became the most widely shared representation of the French, used by French monarchs, then by the Revolution and under the successive republican regimes as representation of the national identity, used for some stamps and coins.[406]
France is one of the world leaders of gender equality in the workplace: as of 2017, it has 36.8% of its corporate board seats held by women, which makes it the leader of the G20 for that metric;[407] and was ranked in 2019 by the World Bank as one of the only 6 countries in the world where women have the same work rights as men.[408]
France is one of the most liberal countries in the world when it comes to LGBT rights: a 2013 Pew Research Center poll found that 77% of the French think that same-sex relationships should be accepted by society, one of the highest acceptance rates in the world (comparable to that of other Western European nations).[409] France legalized same-sex marriage and adoption in 2013.[410] The government has used its diplomatic clout to support LGBT rights throughout the world, notably in the United Nations.[411]
France is also committed to protecting the environment: in 2018, France was ranked 2nd in the Environmental Performance Index (behind neighboring Switzerland), out of 180 countries ranked by Yale University in that study.[412] Being the host country of the 2015 Paris Climate Change Conference, the French government was instrumental in securing the 2015 Paris agreement, a success that has been credited to its"openness and experience in diplomacy"[413] (though the US, after the election of President Trump in 2016, then announced it will withdraw from the agreement).
Cuisine
French cuisine is renowned for being one of the finest in the world.[414][415] According to the regions, traditional recipes are different, the North of the country prefers to use butter as the preferred fat for cooking, whereas olive oil is more commonly used in the South.[416] Moreover, each region of France has iconic traditional specialities: Cassoulet in the Southwest, Choucroute in Alsace, Quiche in the Lorraine region, Beef bourguignon in the Bourgogne, provençal Tapenade, etc. France's most renowned products are wines,[417] including Champagne, Bordeaux, Bourgogne, and Beaujolais as well as a large variety of different cheeses, such as Camembert, Roquefort and Brie. There are more than 400 different varieties.[418][419]
A meal often consists of three courses, hors d'œuvre or entrée (introductory course, sometimes soup), plat principal (main course), fromage (cheese course) and/or dessert, sometimes with a salad offered before the cheese or dessert. Hors d'œuvres could include terrine de saumon au basilic, lobster bisque, foie gras, French onion soup or a croque monsieur. The plat principal could include a pot au feu or steak frites. The dessert could be mille-feuille pastry, a macaron, an éclair, crème brûlée, mousse au chocolat, crêpes, or Café liégeois.
.jpg)
French cuisine is also regarded as a key element of the quality of life and the attractiveness of France.[403] A French publication, the Michelin guide, awards Michelin stars for excellence to a select few establishments.[420][421] The acquisition or loss of a star can have dramatic effects on the success of a restaurant. By 2006, the Michelin Guide had awarded 620 stars to French restaurants, at that time more than any other country, although the guide also inspects more restaurants in France than in any other country (by 2010, Japan was awarded as many Michelin stars as France, despite having half the number of Michelin inspectors working there).[422][423]
In addition to its wine tradition, France is also a major producer of beer and rum. The three main French brewing regions are Alsace (60% of national production), Nord-Pas-de-Calais and Lorraine. France produces rum via distilleries located on islands such as Reunion Island in the southern Indian Ocean.
Sports

France hosts "the world's biggest annual sporting event", the Tour de France,[425] and other popular sports played in France include: football, judo, tennis,[426] rugby[427] and pétanque. France has hosted events such as the 1938 and 1998 FIFA World Cups,[428] the 2007 Rugby World Cup,[429] and will host the 2023 Rugby World Cup. The country also hosted the 1960 European Nations' Cup, UEFA Euro 1984, UEFA Euro 2016 and 2019 FIFA Women's World Cup. The Stade de France in Saint-Denis is France's largest stadium and was the venue for the 1998 FIFA World Cup and 2007 Rugby World Cup finals. Since 1903, France is famous for its 24 Hours of Le Mans sports car endurance race.[430] Several major tennis tournaments take place in France, including the Paris Masters and the French Open, one of the four Grand Slam tournaments. French martial arts include Savate and Fencing.

France has a close association with the Modern Olympic Games; it was a French aristocrat, Baron Pierre de Coubertin, who suggested the Games' revival, at the end of the 19th century.[431][432] After Athens was awarded the first Games, in reference to the Olympics' Greek origins, Paris hosted the second Games in 1900.[433] Paris was the first home of the International Olympic Committee, before it moved to Lausanne.[434] Since 1900, France has hosted the Olympics on 4 further occasions: the 1924 Summer Olympics, again in Paris[432] and three Winter Games (1924 in Chamonix, 1968 in Grenoble and 1992 in Albertville).[432]
Similar to the Olympics, France introduced Olympics for the deaf people (Deaflympics) in 1924 with the idea of a French deaf car mechanic, Eugène Rubens-Alcais who paved the way to organise the inaugural edition of the Summer Deaflympics in Paris.[435]
Both the national football team and the national rugby union team are nicknamed "Les Bleus" in reference to the team's shirt colour as well as the national French tricolour flag. Football is the most popular sport in France, with over 1,800,000 registered players, and over 18,000 registered clubs.[436] The football team is among the most successful in the world, with two FIFA World Cup victories in 1998 and 2018,[437] one FIFA World Cup second place in 2006,[438] and two UEFA European Championships in 1984[439] and 2000.[440]

The top national football club competition is Ligue 1. France has produced some of the greatest players in the world, including three time FIFA World Player of the Year Zinedine Zidane, three time Ballon d'Or recipient Michel Platini, record holder for most goals scored at a World Cup Just Fontaine, first football player to receive the Légion d'honneur Raymond Kopa, and the record goalscorer for the French national team Thierry Henry.[442]
The French Open, also called Roland-Garros, is a major tennis tournament held over two weeks between late May and early June at the Stade Roland-Garros in Paris. It is the premier clay court tennis championship event in the world and the second of four annual Grand Slam tournaments.[443]
Rugby union is popular, particularly in Paris and the southwest of France.[444] The national rugby union team has competed at every Rugby World Cup, and takes part in the annual Six Nations Championship. Stemming from a strong domestic league, the French rugby team has won 16 Six Nations Championships, including 8 grand slams; and has reached the semi-final of the Rugby World Cup 6 times, going on to the final 3 times. Rugby league in France is mostly played and followed in the South of France, in cities such as Perpignan and Toulouse. The Catalans Dragons and Toulouse Olympique are the most notable clubs currently playing in the Super League and the RFL Championship is the top-tier rugby league competitions in Europe. The Elite One Championship is the professional competition for rugby league clubs in France.
Judo is an important sport in France. It is the second country, after Japan, to have the most gold medals. Teddy Riner has won ten World Championships gold medals, the first and only judoka to do so, and David Douillet has won four, making them respectively the first and third top judokas in the world in terms of gold medals.
In recent decades, France has produced world-elite basketball players, most notably Tony Parker. The French National Basketball Team won gold at the FIBA EuroBasket 2013. The national team has won two Olympic silver medals: in 2000 and 1948.
See also
Footnotes
- For information about regional languages see Languages of France.
- Established the Kingdom of the West Franks (the Kingdom of France) from the Carolingian Empire of Francia.
- European Union since 1993.
- Established the Fifth Republic
- French National Geographic Institute data, which includes bodies of water.
- French Land Register data, which exclude lakes, ponds and glaciers larger than 1 km2 (0.386 sq mi or 247 acres) as well as the estuaries of rivers.
- Whole of the French Republic except the overseas territories in the Pacific Ocean.
- French overseas territories in the Pacific Ocean only.
- Daylight saving time is observed in metropolitan France and Saint Pierre and Miquelon only.
- Time zones across the French Republic span from UTC-10 (French Polynesia) to UTC+12 (Wallis and Futuna).
- The overseas regions and collectivities form part of the French telephone numbering plan, but have their own country calling codes: Guadeloupe +590; Martinique +596; French Guiana +594, Réunion and Mayotte +262; Saint Pierre and Miquelon +508. The overseas territories are not part of the French telephone numbering plan; their country calling codes are: New Caledonia +687, French Polynesia +689; Wallis and Futuna +681.
- In addition to .fr, several other Internet TLDs are used in French overseas départements and territories: .re, .mq, .gp, .tf, .nc, .pf, .wf, .pm, .gf and .yt. France also uses .eu, shared with other members of the European Union. The .cat domain is used in Catalan-speaking territories.
- French Guiana is located in South America; Guadeloupe and Martinique are in the Caribbean Sea; and Réunion and Mayotte are in the Indian Ocean, off the coast of Africa. All five are considered integral parts of the French Republic. France also comprises Saint Pierre and Miquelon in North America; Saint Barthélemy and Saint Martin in the Caribbean; French Polynesia, New Caledonia, Wallis and Futuna and Clipperton Island in the Pacific Ocean; and finally the French Southern and Antarctic Lands.
- The present-day state of Austria did not exist as such, its territory was part of the Habsburg Monarchy which also comprised the present-day states of Hungary, Czech Republic, Slovakia, Belgium, Slovenia and Croatia: that Habsburg Monarchy was usually called 'Austria'.
- The last sacre was that of Charles X, 29 May 1825.
References
- https://appsso.eurostat.ec.europa.eu/nui/submitViewTableAction.do
- Special Eurobarometer 493, European Union: European Commission, September 2019, pages 229-230 Retrieved 17 January 2020. The question asked was "Do you consider yourself to be...?" With a card showing: Catholic, Orthodox Christian, Protestant, Other Christian, Jewish, Muslim - Shia, Muslim - Sunni, Other Muslim, Sikh, Buddhist, Hindu, Atheist, Non believer/Agnostic and Other. Also space was given for Refusal (SPONTANEOUS) and Don't Know. On the other hand, Sikh and Hindu did not reach the 1% threshold.
- "Table 3: Population by sex, rate of population increase, surface area and density" (PDF). Demographic Yearbook. United Nations Statistics Division. 2012. Retrieved 4 September 2017.
- "France Métropolitaine". INSEE. 2011. Archived from the original on 28 August 2015. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - "Demography – Population at the beginning of the month – France". Insee. 2019. Retrieved 31 July 2019.
- "Demography – Population at the beginning of the month – Metropolitan France". Insee. 2019. Retrieved 31 July 2019.
- "World Economic Outlook Database, October 2019". IMF.org. International Monetary Fund. Retrieved 30 October 2019.
- "Gini coefficient of equivalised disposable income – EU-SILC survey". ec.europa.eu/eurostat. Eurostat. Retrieved 15 October 2019.
- "Human Development Report 2019" (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. 10 December 2019. Retrieved 10 December 2019.
- "Field Listing :: Area". The World Factbook. CIA. Retrieved 1 November 2015.
- Tucker, Spencer C. (31 August 2019). Middle East Conflicts from Ancient Egypt to the 21st Century: An Encyclopedia and Document Collection [4 volumes]. ABC-CLIO. p. 999. ISBN 978-1-4408-5353-1.
- Hargreaves, Alan G., ed. (2005). Memory, Empire, and Postcolonialism: Legacies of French Colonialism. Lexington Books. p. 1. ISBN 978-0-7391-0821-5.
- R.R. Palmer; Joel Colton (1978). A History of the Modern World (5th ed.). p. 161.
- https://www.france24.com/en/20190517-france-tourism-record-number-visitors-tourists-despite-yellow-vests-paris
- "Global Wealth Report" (PDF). Credit Suisse. October 2010. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 November 2014. Retrieved 27 October 2014.
"In euro and USD terms, the total wealth of French households is very sizeable. Although it has just 1% of the world's adults, France ranks fourth among nations in aggregate household wealth – behind China and just ahead of Germany. Europe as a whole accounts for 35% of the individuals in the global top 1%, but France itself contributes a quarter of the European contingent.
- "World Health Organization Assesses the World's Health Systems". World Health Organization. 8 December 2010. Retrieved 16 July 2011.
- "World Population Prospects – The 2006 Revision" (PDF). UN. Retrieved 27 April 2010.
- Jack S. Levy, War in the Modern Great Power System, 1495–1975, (2014) p. 29
- "Europa Official Site – France". EU. Retrieved 28 October 2014.
- "History of France". Discoverfrance.net. Archived from the original on 24 August 2011. Retrieved 17 July 2011.
- Perry, Walter Copland (1857). The Franks, from Their First Appearance in History to the Death of King Pepin. London: Longman, Brown, Green, Longmans, and Roberts.
- Examples: "frank". American Heritage Dictionary.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link) "frank". Webster's Third New International Dictionary.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link) And so on.
- Michel Rouche (1987). "The Early Middle Ages in the West". In Paul Veyne (ed.). A History of Private Life: From Pagan Rome to Byzantium. Belknap Press. p. 425. ISBN 978-0-674-39974-7. OCLC 59830199.
- Tarassuk, Leonid; Blair, Claude (1982). The Complete Encyclopedia of Arms and Weapons: the most comprehensive reference work ever published on arms and armor from prehistoric times to the present with over 1,250 illustrations. Simon & Schuster. p. 186. ISBN 978-0-671-42257-8. Retrieved 5 July 2011.
- Isidore of Seville, Etymologiarum sive originum, libri XVIII
- Wells, John C. (2008). Longman Pronunciation Dictionary (3rd ed.). Longman. ISBN 978-1-4058-8118-0.
- Collins, Beverley; Mees, Inger M. (1990). "The Phonetics of Cardiff English". In Coupland, Nikolas; Thomas, Alan Richard (eds.). English in Wales: Diversity, Conflict, and Change. Multilingual Matters Ltd. p. 96. ISBN 1-85359-032-0.
- Jean Carpentier (dir.), François Lebrun (dir.), Alain Tranoy, Élisabeth Carpentier et Jean-Marie Mayeur (préface de Jacques Le Goff), Histoire de France, Points Seuil, coll. " Histoire ", Paris, 2000 (1re éd. 1987), p. 17 ISBN 2-02-010879-8
- Carpentier et al. 2000, pp. 20–24.
- The Cambridge ancient history. Cambridge University Press. 2000. p. 754. ISBN 978-0-521-08691-2. Retrieved 23 January 2011.
- Claude Orrieux (1999). A history of ancient Greece. John Wiley & Sons. p. 62. ISBN 978-0-631-20309-4. Retrieved 23 January 2011.
- Carpentier et al. 2000, p. 29.
- "Cornelius Tacitus, The History, BOOK II, chapter 91". perseus.tufts.edu.
- Polybius, The Histories, 2.18.19
- Cornell, The Beginnings of Rome, p. 325
- "Provence in Stone". Life. 13 July 1953. p. 77. Retrieved 23 January 2011.
- Carpentier et al. 2000, pp. 44–45.
- Carpentier et al. 2000, pp. 53–55.
- Carpentier et al. 2000, pp. 76–77
- Carpentier et al. 2000, pp. 79–82.
- Carpentier et al. 2000, p. 81.
- Carpentier et al. 2000, p. 84.
- Carpentier et al. 2000, pp. 84–88.
- "Faith of the Eldest Daughter – Can France retain her Catholic heritage?". Wf-f.org. Archived from the original on 22 July 2011. Retrieved 17 July 2011.
- "France". Berkley Center for Religion, Peace, and World Affairs. Archived from the original on 6 February 2011. Retrieved 14 December 2011. See drop-down essay on "Religion and Politics until the French Revolution"
- "Treaty of Verdun". History.howstuffworks.com. 27 February 2008. Archived from the original on 16 July 2011. Retrieved 17 July 2011.
- "History of France – The Capetian kings of France: AD 987–1328". Historyworld.net. Archived from the original on 6 August 2011. Retrieved 21 July 2011.
- Jean-Benoit Nadeau; Julie Barlow (8 January 2008). The Story of French. St. Martin's Press. pp. 34–. ISBN 978-1-4299-3240-0.
- "Massacre of the Pure". Time. New York. 28 April 1961.
- Albert Guerard, France: A Modern History (University of Michigan Press: Ann Arbor, 1959) pp. 100, 101.
- "France VII". Microsoft Encarta Online Encyclopedia 2009. Webcitation.org. Archived from the original on 29 August 2009.
- Don O'Reilly. "Hundred Years' War: Joan of Arc and the Siege of Orléans". TheHistoryNet.com.
- Emmanuel Le Roy Ladurie (1987). "The French peasantry, 1450–1660". University of California Press. p. 32. ISBN 0-520-05523-3
- Peter Turchin (2003). Historical dynamics: why states rise and fall. Princeton University Press. p. 179. ISBN 0-691-11669-5
- "Massacre of Saint Bartholomew's Day". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 21 July 2011.
- Rex, Richard (15 November 2014). Tudors: The Illustrated History. Amberley Publishing Limited. ISBN 9781445644035 – via Google Books.
- Clodfelter 2017: 40
- Tilly, Charles (1985). "War making and state making as organized crime," in Bringing the State Back In, eds P.B. Evans, D. Rueschemeyer, & T. Skocpol. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1985. p. 174.
- "Language and Diplomacy". Nakedtranslations.com. Archived from the original on 21 July 2011. Retrieved 21 July 2011.
- "BBC History: Louis XV (1710–1774)". BBC. Retrieved 21 July 2011.
- "Scholarly bibliography by Colin Jones (2002)" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 25 July 2011. Retrieved 21 July 2011.
- (in Dutch) Noah Shusterman – De Franse Revolutie (The French Revolution). Veen Media, Amsterdam, 2015. (Translation of: The French Revolution. Faith, Desire, and Politics. Routledge, London/New York, 2014.) Chapter 5 (p. 187–221) : The end of the monarchy and the September Murders (summer–fall 1792).
- Censer, Jack R. and Hunt, Lynn. Liberty, Equality, Fraternity: Exploring the French Revolution. University Park, Pennsylvania: Pennsylvania State University Press, 2004.
- Doyle, William. The Oxford History of The French Revolution. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1989. pp 191–192.
- Dr Linton, Marisa. "The Terror in the French Revolution" (PDF). Kingston University. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 January 2012.
- Jacques Hussenet (dir.), " Détruisez la Vendée ! " Regards croisés sur les victimes et destructions de la guerre de Vendée, La Roche-sur-Yon, Centre vendéen de recherches historiques, 2007
- Frank W. Thackeray (1996). Events that Changed the World in the Nineteenth Century. p. 6. ISBN 978-0-313-29076-3.
- Blanning, Tim (April 1998). "Napoleon and German identity". History Today. 48. London.
- Ben Kiernan (2007). Blood and Soil: A World History of Genocide and Extermination from Sparta to Darfur. Yale University Press. p. 374. ISBN 978-0-300-10098-3.
- "France's oldest WWI veteran dies". BBC News. London. 20 January 2008.
- Spencer C. Tucker, Priscilla Mary Roberts (2005). Encyclopedia Of World War I: A Political, Social, And Military History. ABC-CLIO. ISBN 1-85109-420-2
- Vichy France and the Jews. Michael Robert Marrus, Robert O. Paxton (1995). Stanford University Press. p. 368. ISBN 0-8047-2499-7
- "The Danish Center for Holocaust and Genocide Studies". Archived from the original on 16 April 2014.
- "BBC - History - World Wars: The Vichy Policy on Jewish Deportation". www.bbc.co.uk.
- France, United States Holocaust Memorial Museum, "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 6 December 2014. Retrieved 16 October 2014.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- Noir sur Blanc: Les premières photos du camp de concentration de Buchenwald après la libération, "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 9 November 2014. Retrieved 14 October 2014.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) (French)
- Norrie Macqueen (22 July 2014). Colonialism. Routledge. p. 131. ISBN 978-1-317-86480-6.
- Kimmelman, Michael (4 March 2009). "In France, a War of Memories Over Memories of War". The New York Times.
- Crozier, Brian; Mansell, Gerard (July 1960). "France and Algeria". International Affairs. 36 (3): 310–321. doi:10.2307/2610008. JSTOR 2610008.
- "From Fourth to Fifth Republic". University of Sunderland. Archived from the original on 23 May 2008.
- A New Paradigm of the African State: Fundi wa Afrika. Springer. 2009. p. 75.
- David P Forsythe (27 August 2009). Encyclopedia of Human Rights. OUP USA. p. 37. ISBN 978-0-19-533402-9.
- Elizabeth Schmidt (25 March 2013). Foreign Intervention in Africa: From the Cold War to the War on Terror. Cambridge University Press. p. 46. ISBN 978-1-107-31065-0.
- "Declaration by the Franco-German Defense and Security Council". Elysee.fr. Archived from the original on 25 October 2005. Retrieved 21 July 2011.
- "France and NATO". La France à l'Otan. Archived from the original on 9 May 2014.
- Marie-Christine Weidmann-Koop, Rosalie Vermette, "France at the dawn of the twenty-first century, trends and transformations", p. 160
- Yvonne Yazbeck Haddad and Michael J. Balz, "The October Riots in France: A Failed Immigration Policy or the Empire Strikes Back?" International Migration (2006) 44#2 pp. 23–34.
- Sylvia Zappi, "French Government Revives Assimilation Policy", in Migration Policy Institute "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 30 January 2015. Retrieved 30 January 2015.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- Hinnant, Lori; Adamson, Thomas (11 January 2015). "Officials: Paris Unity Rally Largest in French History". Associated Press. Archived from the original on 11 January 2015. Retrieved 11 January 2015.
- "Paris attacks: Millions rally for unity in France". BBC News. 12 January 2015. Retrieved 12 January 2015.
- "Parisians throw open doors in wake of attacks, but Muslims fear repercussions". The Guardian. 14 November 2015. Retrieved 19 November 2015.
- Syeed, Nafeesa (15 November 2015). "Yes, Parisians are traumatised, but the spirit of resistance still lingers". The Irish Independent. Retrieved 19 November 2015.
- "Europe's open-border policy may become latest victim of terrorism". The Irish Times. 19 November 2015. Retrieved 19 November 2015.
- "French policies provoke terrorist attacks". The Matador. 14 December 2015.
- Gabriel Goodliffe and Riccardo Brizzi, eds. France After 2012 (Berghahn Books, 2015).
- "Europe :: France". The World Factbook. CIA. 3 January 2018. Archived from the original on 5 February 2010.
- "Mont Blanc shrinks by 45 cm (17.72 in) in two years". The Sydney Morning Herald. 6 November 2009. Retrieved 9 August 2010.
- "Close to ESTUARY".
- "Protection of the Environment". Archived from the original on 25 April 2011.
- "Nuclear Power in France". World Nuclear Association. July 2011. Archived from the original on 19 July 2011. Retrieved 17 July 2011.
- Eia (10 September 2010) [First published: 23 April 2010]. "Energy profile of France". In Cutler J. Cleveland (ed.). Encyclopedia of Earth. Topic editor: Langdon D. Clough. Washington, D.C.: Environmental Information Coalition, National Council for Science and the Environment. Archived from the original on 29 April 2011. Retrieved 17 July 2011.
- Morgane Remy (18 June 2010). "CO2 : la France moins pollueuse grâce au nucléaire" [CO2: France less polluting thanks to nuclear]. L'Usine Nouvelle (in French). Archived from the original on 21 June 2010.
- "L'énergie nucléaire en France" [Nuclear energy in France]. La France en Chine (in French). 7 January 2008. Archived from the original on 1 July 2010.
- "2018 EPI Results | Environmental Performance Index". epi.envirocenter.yale.edu. Archived from the original on 23 July 2019. Retrieved 20 August 2019.
- Hsu, A.; et al. (2016). "2016 Environmental Performance Index" (PDF). New Haven, CT: Yale University. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 October 2017. Retrieved 14 December 2017.
- Ian Traynor and David Gow (21 February 2007). "EU promises 20% reduction in carbon emissions by 2020". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 21 July 2011.
- Marie Verdier (6 December 2009). "Les quatre enjeux de Copenhague". La Croix. Archived from the original on 11 January 2012.
- Kanter, James (1 July 2010). "Per-Capita Emissions Rising in China". The New York Times. Retrieved 21 July 2011.
- "France Sets Carbon Tax at 17 Euros a Ton". The New York Times. France. Reuters. 10 September 2009. Retrieved 21 July 2011.
- "France set to impose carbon tax". BBC News. 10 September 2009. Retrieved 21 July 2011.
- Saltmarsh, Matthew (23 March 2010). "France Abandons Plan for Carbon Tax". The New York Times. Retrieved 21 July 2011.
- "Why France's forests are getting bigger". The Economist. 18 July 2019. ISSN 0013-0613. Retrieved 20 August 2019.
- "Countries Compared by Environment > Forest area > % of land area". Nationmaster.com. International Statistics. Retrieved 7 January 2018.
- "Evolution of the French forest from 1984 to 1996". Inventaire Forestier National [National Forest Inventory]. Archived from the original on 13 May 2011.
- "La forêt en France et dans le monde" [The forest in France and in the world]. lepapier.fr (in French). Archived from the original on 27 July 2010.
- "Parks and other protected areas in France". Parks.it.
- "Fédération des parcs naturels régionaux de France" [Federation of Regional Natural Parks of France] (in French). Archived from the original on 12 July 2010.
- "La France veut créer une Zone Économique Exclusive en Méditérannée" [France wants to create an Exclusive Economic Zone in the Mediterranean]. Actu-Environnement.com (in French). 25 August 2009. Archived from the original on 13 May 2011.
- "The regional nature Parks of France" (PDF). Fédération des Parcs naturels régionaux de France [Federation of the regional nature Parks of France]. 22 July 2013. Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 July 2013. Retrieved 22 June 2014.
- William M. Lafferty (2001). Sustainable communities in Europe. Earthscan. p. 181. ISBN 978-1-85383-791-3.
- "Regional Natural Parks". France Guide. Maison de la France. 2008. Archived from the original on 5 April 2012. Retrieved 27 October 2011.
- "Découvrir les 54 Parcs". Fédération des Parcs naturels régionaux de France.
- "La réforme territoriale" (in French). Government of France. 18 December 2015. Archived from the original on 30 December 2015. Retrieved 1 January 2016.
- "Departments of France" (in French). Myfrenchproperty.com. Archived from the original on 14 July 2011. Retrieved 21 July 2011.
- "Circonscriptions administratives au 1er janvier 2015 : comparaisons régionales" [Administrative constituencies of 1 January 2015: regional comparisons] (in French). INSEE. Archived from the original on 30 April 2014. Retrieved 5 July 2015.
- "Currency and Exchange Rate". Thetahititraveler.com. Archived from the original on 17 July 2011. Retrieved 21 July 2011.
- "2085rank". The World Factbook. CIA.
- "Constitutional Limits on Government: Country Studies – France". Democracy Web: Comparative studies in Freedom. Archived from the original on 28 August 2013. Retrieved 30 September 2013.
- Helen Drake (2011). Contemporary France. Palgrave Macmillan. p. 95. doi:10.1007/978-0-230-36688-6. ISBN 978-0-333-79243-8.
- "Le quinquennat : le référendum du 24 Septembre 2000" [The 5-year term: referendum of 24 September 2000] (in French). Archived from the original on 12 August 2010.
- "The National Assembly and the Senate – General Characteristics of the Parliament". Assemblée Nationale. Archived from the original on 5 December 2008.
- "Election of deputies". Assemblée Nationale. Archived from the original on 4 July 2011.
- "The senatorial elections". Sénate.
- "Le role du Sénat" [What is the purpose of the Senate?] (in French). 18 August 2007. Archived from the original on 18 June 2010.
- "OECD Better Life Index". oecdbetterlifeindex.org. Retrieved 20 August 2019.
- In European countries, legal doctrine has long faced the question of succession of criminal laws in time: Buonomo, Giampiero (2015). "La rivendicazione di Gallo". Mondoperaio Edizione Online. – via Questia (subscription required)
- "François Hollande signs same-sex marriage into law". France 24. 18 May 2013. Retrieved 27 June 2013.
- "France: Strict Defamation and Privacy Laws Limit Free Expression – Index on Censorship | Index on Censorship." France: Strict Defamation and Privacy Laws Limit Free Expression – Index on Censorship | Index on Censorship. N.p., n.d. Web. 26 February 2014. "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 22 September 2013. Retrieved 18 February 2014.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link).
- (in French) La lutte contre le racisme et l'antisémintisme en France. AmbaFrance
- Kenneth Roth Executive Director (26 February 2004). "Human Rights Watch". Human Rights Watch. Retrieved 31 January 2009.
- "France votes to ban full-face veils". Amnesty International. 13 July 2010. Archived from the original on 7 December 2014.
- "L'image de l'islam en France" (PDF). ifop.fr (in French). IFOP. p. 22. Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 March 2014. Retrieved 16 January 2017.
- "Membership of the Security Councils of the UN". 6 July 2010. Archived from the original on 6 July 2010.
- "The Soft Power 30" (PDF). Monocle. Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 November 2015.
- "Members and Observers". World Trade Organization. Retrieved 30 October 2010.
- "History". Secretariate of the Pacific Community. 12 February 2010. Archived from the original on 28 August 2010.
- "Les pays membres de la COI" [IOC member countries]. Commission de l'Océan Indien | Indian Ocean Commission (in French). Archived from the original on 2 April 2012.
- "About the Association of Caribbean States". Association of Caribbean States. 24 July 1994. Archived from the original on 22 August 2012. Retrieved 22 June 2012.
- "84 États et gouvernements" [84 states and governments]. Organisation internationale de la Francophonie.
- "Embassies and consulates". France Diplomatie. The French Ministry of Foreign affairs. Archived from the original on 8 September 2010.
- Pierre-Louis Germain (12 November 2009). "L'alliance Franco-allemande au coeur de la puissance européenne" [The Franco-German alliance at the heart of European power] (in French). Institut Montaigne. Archived from the original on 23 January 2010.
- "De Gaulle says 'non' to Britain – again". BBC News. 27 November 1967. Retrieved 21 July 2011.
- Isabelle Lasserre (11 March 2009). "Quand Mitterrand, déjà, négociait le retour de la France dans l'Otan" [Mitterrand already negotiated the return of France to NATO]. Le Figaro (in French).
- "France ends four-decade Nato rift". BBC News. 12 March 2009. Retrieved 21 July 2011.
- Roger, Patrick (11 March 2009). "Le retour de la France dans l'OTAN suscite un malaise dans les rangs de la Droite" [The return of France to NATO causes discomfort in the ranks of the right]. Le Monde (in French). Paris.
- "Fifth French nuclear test sparks international outrage". CNN. 28 December 1995. Retrieved 21 July 2011.
- "China adds voice to Iraq war doubts". CNN. 23 January 2003. Retrieved 21 July 2011.
- "EU allies unite against Iraq war". BBC News. 22 January 2003. Retrieved 21 July 2011.
- Keith Porter (11 March 2004). "Foreign Policy Implications of the Iraq War". About.com:US Foreign Policy. Archived from the original on 25 February 2010. Retrieved 9 August 2010.
- Sean Loughlin (12 March 2003). "House cafeterias change names for 'french' fries and 'french' toast". CNN. Retrieved 21 July 2011.
- "L'empire colonial français". Archived from the original on 25 April 2011.
- "France involvement in peace-keeping operations". Delegfrance-onu-geneve.org. Archived from the original on 25 April 2011. Retrieved 9 August 2010.
- "Official development assistance (ODA) – Net ODA – OECD Data". theOECD. Retrieved 20 August 2019.
- "Aid to developing countries rebounds in 2013 to reach an all-time high". OECD. Retrieved 3 March 2016.
- France priorities Archived 22 July 2010 at the Wayback Machine – France Diplomatie
- (in French) La fin du service militaire obligatoire Archived 8 August 2010 at the Wayback Machine – La documentation française
- "Status of signature and ratification". CTBTO Preparatory Commission. 26 May 2010. Retrieved 27 May 2010.
- Trends in World Military Expenditure SIPRI. Retrieved 2019-12-18.
- (in French) Centre de Documentation et de Recherche sur la Paix et les Conflits, Etat des forces nucléaires françaises au 15 août 2004 Archived 25 July 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- "90.07.06: The Aerospace Industry: Its History and How it Affects the U.S. Economy". Yale. Archived from the original on 20 September 2011. Retrieved 21 July 2011.
- "Aerospace industry of France". The Translation Company. Archived from the original on 18 February 2016. Retrieved 6 January 2016.
- Thierry Gadault (13 June 2002). "La France demeure un fournisseur d'armes de premier plan" [France stays one of the biggest arms supplier]]. L'express (in French). Archived from the original on 11 March 2012.
En 2001, la France a vendu pour 1,288 milliard de dollars d'équipements militaires, ce qui la met au troisième rang mondial des exportateurs derrière les États-Unis et la Russie. [In 2001, France sold $1,288 billion of military equipment, ranking 3rd in the world for arms exportations behind the USA and Russia
- "Les ventes d'armes explosent en 2009" [Sales of weapons explode in 2009]. 20 minutes (in French). 8 February 2010. Retrieved 6 January 2017.
La France est au 4ème rang mondial des exportateurs d'armes, derrière les Etats-Unis, le Royaume-Uni et la Russie, et devant Israël, selon un rapport du ministère de la Défense publié l'an dernier. [France is 4th biggest arms exporter, behind the United States, the United Kingdom and Russia, and ahead of Israel, according to a report of the Ministry of Defense published a year ago.]
- "Country Comparison :: Public Debt". The World Factbook. CIA. Retrieved 10 January 2018.
- John, Mark (26 October 2012). "Analysis: Low French borrowing costs risk negative reappraisal". Reuters. Retrieved 27 November 2012.
- "GDP, PPP (current international $)". The World Bank Group. Retrieved 1 November 2015.
- "History of the Euro". BBC News. Retrieved 30 October 2010.
- "Entreprises selon le nombre de salariés et l'activité" [Companies by number of employees and activity] (in French). INSEE. July 2008. Archived from the original on 15 November 2009.
- "Entreprises publiques selon l'activité économique" [Public enterprises by economic activity] (in French). INSEE. March 2009. Archived from the original on 2 December 2009.
- "International Trade Statistics 2008" (PDF). WTO. 2009. p. 12. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 June 2011. Retrieved 5 July 2011.
- "Country Comparison :: Exports". The World Factbook. CIA. Retrieved 14 July 2017.
- "Country fact sheet: France" (PDF). World Investment Report 2009. UNCTAD. Archived (PDF) from the original on 4 July 2010. Retrieved 7 October 2010.
- "Country fact sheet: Japan" (PDF). World Investment Report 2009. UNCTAD. Archived (PDF) from the original on 4 July 2010. Retrieved 7 October 2010.
- Gould, Charles. "Global300 Report 2010, International Co-operative Alliance. The world's major co-operatives and mutual businesses" (PDF). ica.coop.
- Audrey Vautherot (19 November 2007). "La Bourse de Paris : une institution depuis 1724" [The Paris Stock Exchange: an institution since 1724]. Gralon (in French).
- Embassy of France. "Embassy of France in Washington: Economy of France". Ambafrance-us.org. Archived from the original on 9 October 2011. Retrieved 16 July 2011.
- Andrews, Edmund L. (1 January 2002). "Germans Say Goodbye to the Mark, a Symbol of Strength and Unity". The New York Times. Retrieved 18 March 2011.
- Taylor Martin, Susan (28 December 1998). "On Jan. 1, out of many arises one Euro". St. Petersburg Times. p. National, 1.A.
- "The 10 Largest Banks in the World". Doughroller.net. 15 June 2010. Archived from the original on 12 July 2011. Retrieved 16 July 2011.
- "France – Agriculture". Nations Encyclopedia. Archived from the original on 4 January 2011.
- "Key figures of the French economy". France Diplomatie. French Ministry of Foreign and European Affairs. Archived from the original on 14 January 2010.
France is the world's fifth largest exporter of goods (mainly durables). The country ranks fourth in services and third in agriculture (especially in cereals and the agri-food sector). It is the leading producer and exporter of farm products in Europe.
- "A Panorama of the agriculture and agri-food industries" (PDF). Ministère de l'Alimentation, de l'Agriculture et de la Pêche. Archived (PDF) from the original on 21 September 2010.
- "Un ministère au service de votre alimentation" [A ministry serving your food] (in French). Ministère de l'Alimentation, de l'Agriculture et de la Pêche. 29 July 2010. Archived from the original on 6 August 2010.
- "Annex 1: Indicative Figures on the Distribution of Aid, by Size-Class of Aid, Received in the Context of Direct Aid Paid to the Producers According to Council Regulation (EC) No 1782/2003 (Financial Year 2007)" (PDF). European Commission. 22 April 2009. Archived from the original (PDF) on 30 April 2011. Retrieved 7 October 2010.
- "Les enjeux des industries agroalimentaires françaises" [The stakes of the French agri-food industries] (in French). Panorama des Industries Agroalimentaires. Archived from the original on 29 December 2011.
- UNWTO Tourism Highlights (2014 ed.). United Nations World Tourism Organization. 2014. doi:10.18111/9789284416226. ISBN 9789284416226.
- Dilorenzo, Sarah (18 July 2013). "France learns to speak 'touriste'". Associated Press. Archived from the original on 22 August 2013. Retrieved 20 July 2013.
- "Fréquentation des musées et des bâtiments historiques" [Frequentation of museums and historic buildings] (in French). 2003. Archived from the original on 24 December 2007.
- Judith Rubin, ed. (2009). "TEA/AECOM Attraction Attendance Report for 2009" (PDF). Themed Entertainment Association. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 June 2010. Retrieved 7 October 2010.
- "The French Riviera Tourist Board". CÔTE D'AZUR. Archived from the original on 25 April 2011. Retrieved 23 January 2011.
- "Présentation de la Côte d'Azur" [Presentation of the French Riviera] (PDF) (in French). Côte d'Azur Economic Development Agency. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 July 2010.
- Foucher, Editors translated by Joséphine. "Tourism: The Loire Valley, an intoxicating destination for visitors". TourMaG.com, 1er journal des professionnels du tourisme francophone (in French). Retrieved 10 October 2018.CS1 maint: extra text: authors list (link)
- "Chateaux deluxe: 5 best Loire Valley castles". CNN. 12 July 2017. Retrieved 10 October 2018.
- "Greenhouse Gas Emissions". Environmental Indicators. United Nations. July 2010. Archived from the original on 10 March 2010. Retrieved 8 January 2017. ♦ Archived: 10 March 2010 ♦ Archived: 11 July 2017
- "Nuclear share figures, 2006–2016". World Nuclear Association. April 2017. Retrieved 8 January 2018.
- "France". IAEA | PRIS Power Reactor Information System. International Atomic Energy Agency. Retrieved 8 January 2018.
- "Chiffres clés du transport Édition 2010" (PDF) (in French). Ministère de l'Écologie, de l'Énergie, du Développement Durable et de la Mer. Archived from the original (PDF) on 1 June 2010. Retrieved 7 October 2010.
- "Country comparison :: railways". The World Factbook. CIA.
- "TGV – The French High-speed Train Service". h2g2 The Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy: Earth Edition. Archived from the original on 16 July 2012. Retrieved 21 July 2011.
- "Country comparison :: roadways". The World Factbook. CIA.
- (in French) L'automobile magazine, hors-série 2003/2004 page 294
- "Guide pratique de l' ADEME, la voiture". Ademe.fr. Archived from the original on 6 October 2008. Retrieved 22 October 2008.
- Bockman, Chris (4 November 2003). "France builds world's tallest bridge". BBC News. Retrieved 21 July 2011.
- "Strikes block French ports". The Journal of Commerce Online. 23 April 2008. Archived from the original on 17 May 2008 – via BDP International.
- "Marseille : un grand port maritime qui ne demande qu'à se montrer" [Marseille: a grand seaport just waiting to show]. La Provence (in French). 27 June 2009.
- Dave Emery (22 February 2010). "Marseille – A French Pearl in the Mediterranean Sea". HotelClub Blog. Archived from the original on 24 February 2010. Retrieved 21 July 2011.
- European Space Agency - Funding
- William Godwin (1876). "Lives of the Necromancers". p. 232.
- André Thuilier, Histoire de l'université de Paris et de la Sorbonne, Paris, Nouvelle librairie de France, 1994
- Burke, Peter, A social history of knowledge: from Gutenberg to Diderot, Malden: Blackwell Publishers Inc., 2000, p. 17
- Lanzetta M; Petruzzo P; Dubernard JM; et al. (July 2007). "Second report (1998–2006) of the International Registry of Hand and Composite Tissue Transplantation". Transpl Immunol. 18 (1): 1–6. doi:10.1016/j.trim.2007.03.002. PMID 17584595.
- Ghodoussi, Dr. "Media Collection". Interface Surgical Technologies, LLC. Retrieved 14 November 2011.
- Austin, Naomi (17 October 2006). "My face transplant saved me". BBC News. Retrieved 25 November 2007.
- "Woman has first face transplant". BBC News. 30 November 2005.
- Pascal Boniface; Barthélémy Courmont (22 November 2006). Le monde nucléaire: Arme nucléaire et relations internationales depuis 1945. Armand Colin. pp. 120–. ISBN 978-2-200-35687-3.
- "Status of World Nuclear Forces". Federation Of American Scientists. Archived from the original on 18 June 2015.
- "Study France's Nuclear-Power Success". TheLedger.com. Archived from the original on 22 May 2015.
- "Stanford Journal of International Relations, "The French Connection: Comparing French and American Civilian Nuclear Energy Programs"" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 May 2015.
- "Countries Generating The Most Nuclear Energy – Business Insider". Business Insider. 6 March 2014.
- Muriel Gargaud; Ricardo Amils; Henderson James Cleaves (2011). Encyclopedia of Astrobiology. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 322–. ISBN 978-3-642-11271-3.
- "France". oecd-ilibrary.org. Archived from the original on 4 October 2015.
- French Ministry of Foreign Affairs and International Development. "France at the heart of the Rosetta space mission: a unique technological challenge". France Diplomatie. Archived from the original on 22 May 2015.
- "French set new rail speed record". BBC News.
- "All Nobel Prizes". Archived from the original on 3 November 2013. Retrieved 10 October 2012.
- "List of Fields Medallists". International Mathematical Union. Retrieved 10 October 2012.
- "Démographie – Population au début du mois – France (inclus Mayotte à partir de 2014)" [Demography – Population at the beginning of the month – France (including Mayotte since 2014)] (in French). Insee.
- "Bilan démographique 2006 : un excédent naturel record" (in French). Insee.
- "People in the EU – statistics on demographic changes – Statistics Explained". European Commission. Retrieved 21 August 2019.
- Max Roser (2014), "Total Fertility Rate around the world over the last centuries", Our World in Data, Gapminder Foundation, archived from the original on 8 July 2019, retrieved 7 May 2019
- "Bilan démographique 2016" (in French). Insee. Retrieved 19 January 2017.
- "Bilan démographique 2010" (in French). Insee. Retrieved 20 January 2011.
- "Tableau 44 – Taux de fécondité générale par âge de la mère" (in French). Insee. Archived from the original on 27 April 2011. Retrieved 20 January 2011.
- "World Factbook EUROPE : FRANCE", The World Factbook, 12 July 2018
- "Évolution générale de la situation démographique, France" (in French). Insee. Retrieved 20 January 2011.
- "WDI – Home". World Bank. Retrieved 27 August 2019.
- "Naissances selon le pays de naissance des parents 2010". Insee. Archived from the original on 27 September 2013.
- Jean-Louis Brunaux (2008). Seuil (ed.). Nos ancêtres les Gaulois [Our ancestors the Gauls]. p. 261.
- Yazid Sabeg; Laurence Méhaignerie (January 2004). Les oubliés de l'égalité des chances [The forgotten of equal opportunities] (PDF) (in French). Institut Montaigne.
- "France's ethnic minorities: To count or not to count". The Economist. 26 March 2009. Retrieved 25 April 2013.
- "'Trajectories and Origins' Survey". Ined. 2008. Archived from the original on 2 December 2011.
♦ - Oppenheimer, David B. (2008). "Why France needs to collect data on racial identity...in a French way". Hastings International and Comparative Law Review. 31 (2): 735–752. SSRN 1236362.
- Robin Cohen (1995). The Cambridge Survey of World Migration. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-44405-7.
- "France's crisis of national identity". The Independent. London. 25 November 2009.
- "Les personnes d'origine maghrébine y sont également au nombre de 5 à 6 millions; 3,5 millions ont la nationalité française (don't 500 000 harkis)", Évelyne Perrin, Identité Nationale, Amer Ministère, L'Harmattan, 2010, p. 112 ISBN 2-296-10839-3
- Falila Gbadamassi. "Les personnes originaires d'Afrique, des Dom-Tom et de la Turquie sont 5,5 millions dans l'Hexagone". Afrik.com. Archived from the original on 2 October 2013.
- Richburg, Keith B. (24 April 2005). "Europe's Minority Politicians in Short Supply". The Washington Post.
- Sachs, Susan (12 January 2007). "In officially colorblind France, blacks have a dream – and now a lobby". The Christian Science Monitor. Boston.
- "National strategy for Roma integration – European Commission – DG Justiceunknown label". Archived from the original on 6 March 2016.
- Astier, Henri (13 February 2014). "France's unwanted Roma". BBC.
- "Paris Riots in Perspective". New York: ABC News. 4 November 2005.
- James E. Hassell (1991). "III. French Government and the Refugees". Transactions of the American Philosophical Society. Volume 81, Part 7: Russian Refugees in France and the United States Between the World Wars. American Philosophical Society. p. 22. ISBN 978-0-87169-817-9.
- Markham, James M. (6 April 1988). "For Pieds-Noirs, the Anger Endures". The New York Times.
- Raimondo Cagiano De Azevedo, ed. (1994). Migration and development co-operation. p. 25. ISBN 978-92-871-2611-5.
- "Flux d'immigration par continent d'origine" [Immigration flow by continent of origin]. Ined (in French). Archived from the original on 23 May 2012.
♦ 3 November 2010: - "Western Europe" (PDF). UNHCR Global Report 2005. UNHCR. Archived (PDF) from the original on 14 June 2007. Retrieved 14 December 2006.
- Kalt, Anne; Hossain, Mazeda; Kiss, Ligia; Zimmerman, Cathy (March 2013). "Asylum Seekers, Violence and Health: A Systematic Review of Research in High-Income Host Countries". American Journal of Public Health. 103 (3): e30–e42. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2012.301136. ISSN 0090-0036. PMC 3673512. PMID 23327250.
- "aida – Asylum Information Database – Country Report: France" (PDF). 2017.
- Catherine Borrel; Bertrand Lhommeau (30 March 2010). "Être né en France d'un parent immigré" [To be born in France of an immigrant parent] (in French). Insee. Archived from the original on 3 February 2012.
- "Répartition des immigrés par pays de naissance" [Distribution of immigrants by country of birth] (in French). Insee. 2008. Archived from the original on 26 October 2011.
- Catherine Borrel (August 2006). "Enquêtes annuelles de recensement 2004 et 2005" [Annual census surveys 2004 and 2005] (in French). Insee. Archived from the original on 12 December 2006. Retrieved 14 December 2006.
- Swalec, Andrea (6 July 2010). "Turks and Moroccans top list of new EU citizens". Reuters. Archived from the original on 12 January 2012.
- "Qui sont les nouveaux immigrés qui vivent en France ?" [Who are the new immigrants living in France?]. SudOuest (in French). 2 December 2014.
- "Aires urbaines" [Urban areas]. Insee (in French). Archived from the original on 6 February 2019. Retrieved 15 May 2019.
- (in French) La Constitution- La Constitution du 4 Octobre 1958 – Légifrance.
- Abalain, Hervé, (2007) Le français et les langues historiques de la France, Éditions Jean-Paul Gisserot, p. 113.
- Joffre Agnes ls the French obsession with "cultural exception" declining? Archived 17 October 2011 at the Wayback Machine. France in London. 5 October 2008
- "Language and Diplomacy – Translation and Interpretation". Diplomacy.edu. Archived from the original on 19 July 2011. Retrieved 10 September 2010.
- "Why Is French Considered the Language of Diplomacy?". Legallanguage.com. Archived from the original on 30 December 2010. Retrieved 23 January 2011.
- "Rapport Grégoire an II". Archived from the original on 5 April 2008.
- "The International Education Site". Intstudy.com. Archived from the original on 27 February 2011. Retrieved 23 January 2011.
- "French: one of the world's main languages". About-france.com. Archived from the original on 16 May 2016. Retrieved 21 July 2011.
- (in French) Qu'est-ce que la Francophonie ? Archived 23 June 2011 at the Wayback Machine – Organisation internationale de la Francophonie
- "GESIS – Leibniz Institute for the Social Sciences". gesis.org. Retrieved 24 April 2018.
- "A French Islam is possible" (PDF). Institut Montaigne. 2016. p. 13. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 September 2017.
- Jon Henley (22 April 2004). "France to train imams in 'French Islam'". The Guardian.
- "France – International Religious Freedom Report 2005". U.S. State Department. Retrieved 30 October 2010.
- "Observatoire du patrimoine religieux". 1 February 2012. Archived from the original on 26 November 2013.
94% des édifices sont catholiques (dont 50% églises paroissiales, 25% chapelles, 25% édifices appartenant au clergé régulier)
- "France". Berkley Center for Religion, Peace, and World Affairs. Archived from the original on 6 February 2011. Retrieved 14 December 2011.
- Joy of Sects, Sam Jordison, 2006, p. 166
- "Commission d'enquête sur les sectes". Assemblee-nationale.fr. Retrieved 30 October 2010.
- "Society2; religion in France; beliefs; secularism (laicité)". Understandfrance.org. Archived from the original on 16 September 2009. Retrieved 20 September 2009.
- How to conduct European clinical trials from the Paris Region ? Clinical Trials. Paris. February 2003
- "World Health Organization Assesses the World's Health Systems". Who.int. 8 December 2010. Retrieved 6 January 2012.
- The ranking, see spreadsheet details for a whole analysis photius.com
- "Measuring Overall Health System Performance for 191 Countries" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 August 2011. Retrieved 21 July 2011.
- "WHO country facts: France". Who.int. Archived from the original on 11 November 2013. Retrieved 11 November 2013.
- The World Health Report 2000: WHO
- "Espérance de vie, taux de mortalité et taux de mortalité infantile dans le monde" (in French). Insee.
- "Evolution de l'espérance de vie à divers âges" (in French). Insee.
- "Nombre de médecins pour 1000 habitants" (in French). Statistiques mondiales. Archived from the original on 5 March 2010.
- "Dépenses de santé par habitants" (in French). Statistiques mondiales. Archived from the original on 12 December 2009.
- Even the French are fighting obesity – The New York Times
- Wahlgren, Eric (14 November 2009). "France's obesity crisis: All those croissants really do add up, after all". Dailyfinance.com. Archived from the original on 8 July 2011. Retrieved 21 July 2011.
- Lambert, Victoria (8 March 2008). "The French children learning to fight obesity". The Daily Telegraph. London. Retrieved 9 August 2010.
- Why So Few French Are Fat Archived 25 January 2010 at the Wayback Machine – Bloomberg Businessweek
- "The French Diet – Eat, Drink, and be Thin". Streetdirectory.com. Retrieved 9 August 2010.
- Mimi Spencer (7 November 2004). "Let them eat cake". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 21 July 2011.
- France heading for US obesity levels says study – Food Navigator
- "New French food guidelines aimed at tackling obesity". Nutraingredients.com. 14 September 2006. Retrieved 9 August 2010.
- Petah Marian (23 May 2008). "France urged to get tough on child obesity". Just-food.com. Retrieved 9 August 2010.
- "Lycée". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 22 July 2011.
- (in French) II. L'évolution du contenu de l'obligation scolaire. Sénat.fr
- (in French) 1881–1882 : Lois Ferry École publique gratuite, laïque et obligatoire. Assemblé Nationale
- "Compare your country - PISA 2018". www.compareyourcountry.org.
- (in French) Les grandes écoles dans la tourmente – Le Figaro
- Ministère de la Culture et de la Communication, "Cultura statistics", Key figures
- "Official properties inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List in France". UNESCO. Retrieved 9 July 2015.
- "Guide to Impressionism". National Gallery. Retrieved 22 July 2011.
- (in French) RFI, Le néo-impressionnisme de Seurat à Paul Klee 15 March 2005
- National Gallery of Art (United States), The Fauves (dossier) Archived 5 November 2010 at the Wayback Machine
- (in French) RFI, Vlaminck, version fauve, 25 February 2008
- Musée d'Orsay (official website), History of the museum – From station to museum
- "History of the painting collection". Musee-orsay.fr. 31 July 2007. Retrieved 22 July 2011.
- (in French) Ministry of Tourism, Sites touristiques en France Archived 11 May 2011 at the Wayback Machine page 2 "Palmarès des 30 premiers sites culturels (entrées comptabilisées)" [Ranking of 30 most visited cultural sites in France]
- "Toulouse's Saint Sernin, Largest Romanesque Church in Europe". Europeupclose.com. 22 February 1999. Archived from the original on 10 July 2011. Retrieved 22 July 2011.
- Brodie, Allan M. (2003). "Opus francigenum". Oxford Art Online. Oxford Art Online. Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/gao/9781884446054.article.t063666. Retrieved 13 January 2019.
- "The Gothic Period". Justfrance.org. Retrieved 22 July 2011.
- (in French) Histoire et Architecture – Site officiel de la Cathedrale de Notre-Dame de Reims
- Loire, Mission Val de. "Charles VII et Louis XI -Know -Val de Loire patrimoine mondial". loirevalley-worldheritage.org. Retrieved 10 October 2018.
- (in French) Claude Lébedel – Les Splendeurs du Baroque en France: Histoire et splendeurs du baroque en France page 9: "Si en allant plus loin, on prononce les mots 'art baroque en France', on provoque alors le plus souvent une moue interrogative, parfois seulement étonnée, parfois franchement réprobatrice: Mais voyons, l'art baroque n'existe pas en France!"
- Hills, Helen (2003). Architecture and the Politics of Gender in Early Modern Europe. Ashgate Publishing. p. 86. ISBN 978-0-7546-0309-2.
- "Fortifications of Vauban". UNESCO. 8 July 2008. Retrieved 9 August 2010.
- "Official site of the UNESCO". UNESCO. Retrieved 9 August 2010.
- Paris: City Guide. Lonely Planet. 2008. p. 48. ISBN 978-1-74059-850-7.
- Henri SECKEL (8 July 2008). "Urbanisme : Des gratte-ciel à Paris : qu'en pensez-vous ?nbsp;– Posez vos questions". MYTF1News. Archived from the original on 29 October 2010.
- In the heart of the main European Business area Archived 29 July 2010 at the Wayback Machine – NCI Business Center
- "Montaigne". Humanistictexts.org. Archived from the original on 25 May 2011. Retrieved 22 July 2011.
- "La Princesse de Cleves by Madame de Lafayette, adapted by Jo Clifford". Radiodramareviews.com. 28 February 2010. Archived from the original on 10 August 2011. Retrieved 22 July 2011.
- Jean de La Fontaine, Fables (1668–1679), I., 21, Les Frelons et les Mouches à miel; reported in Thomas Benfield Harbottle and Philip Hugh Dalbiac, Dictionary of Quotations (French and Italian) (1904), p. 1.
- (in French) Auteurs et répertoires Archived 19 September 2010 at the Wayback Machine – Official site of the Comédie Française
- "Author of some of the finest comedies in the history of the theater". Hartnoll, Phyllis (ed.). The Oxford Companion to the Theatre, 1983, Oxford University Press, p. 554.
- Randall, Colin (25 October 2004). "France looks to the law to save the language of Molière". The Daily Telegraph. London. Retrieved 22 July 2011.
- "Le Symbolisme français". users.skynet.be.
- "Victor Hugo est le plus grand écrivain français" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 July 2013.
- "Victor Hugo 1802–1885". Enotes.com. Retrieved 16 July 2011.
- "All-Time 100 Best Novels List". Adherents.com. Retrieved 22 July 2011.
- (in French) La première Académie Goncourt Archived 25 April 2011 at the Wayback Machine – Site officiel de l'Académie Goncourt Archived 19 November 2008 at the Wayback Machine
- "The Little Prince". Completelynovel.com. Retrieved 22 July 2011.
- Modiano strengthens France's literature Nobel dominance Archived 18 October 2014 at the Wayback Machine, Global Post, 9 October 2014
- "The Beginning of Modern Sciences". Friesian.com. Retrieved 16 July 2011.
- Girdlestone p. 14: "It is customary to couple him with Couperin as one couples Haydn with Mozart or Ravel with Debussy."
- Allen Schrott. "Claude Debussy – Biography – AllMusic". AllMusic.
- Huizenga, Tom (14 October 2005). "Debussy's 'La Mer' Marks 100th Birthday". NPR. Retrieved 22 July 2011.
- "Debussy's Musical Game of Deception". NPR. 12 July 2008. Retrieved 22 July 2011.
- "Biography of Claude Debussy". Classicfm.co.uk. Retrieved 22 July 2011.
- "Biography of Maurice Ravel". Classicfm.co.uk. Retrieved 22 July 2011.
- Schwartz, Lloyd (24 May 2010). "Composer-Conductor Pierre Boulez at 85". NPR. Retrieved 22 July 2011.
- "100人の偉大なアーティスト - No. 62" [The 100 Greatest Artists – No. 62]. ローチケHMV [Roachke HMV] (in Japanese). 21 April 2003.
- "Biography of Noir Désir". rfi Music. RFI Musique. December 2010. Retrieved 11 January 2018.
Rock music doesn't come naturally to the French. A Latin country, with more affinity to poetry and melody, France has very rarely produced talented rock musicians. Rock music has other, more Anglo-Saxon ingredients: fury, excess, electricity.
- "French music has the whole planet singing". France Diplomatie. 22 June 2009. Archived from the original on 22 December 2010.
- "Bureau Export – Les certifications export 2012" (PDF) (in French). IRMA. p. 26. Retrieved 7 March 2015.
- Bernadette McNulty (17 November 2007). "Daft Punk: Behind the robot masks". The Telegraph.
Daft Punk were in many ways responsible for turning the spotlight on a new, cool underground of French music in the late 1990s, including bestselling acts such as Air, and have been a huge influence on the current generation of international star DJs.
- Alex Webb (20 December 2001). "The return of French pop music". BBC News. Retrieved 22 July 2011.
- "About "Fête de la Musique"". French Ministry for Culture. Archived from the original on 15 May 2010.
- "Fête de la Musique". France Diplomatie. 21 June 2007. Archived from the original on 18 January 2012.
- Dargis, Manohla. "Cannes International Film Festival". The New York Times.
- Lim, Dennis (15 May 2012). "They'll Always Have Cannes". The New York Times.
- Woolsey, Matt. "In Pictures: Chic Cannes Hideaways". Forbes.
- "Louis de Funès". IMDb.
- Larousse, Éditions. "Encyclopédie Larousse en ligne – les frères Lumière". larousse.fr.
- Dargis, Manohla; Scott, A.O. (20 September 2018). "You Know These 20 Movies. Now Meet the Women Behind Them". The New York Times. Retrieved 4 December 2018.
- UIS. "UIS Statistics". UNESCO.
- Alan Riding (28 February 1995). "The Birthplace Celebrates Film's Big 1-0-0". The New York Times.
- "Cannes – a festival virgin's guide". Cannesguide.com. 15 February 2007. Retrieved 22 July 2011.
- "Cannes Film Festival | Palais des Festivals, Cannes, France". Whatsonwhen.com. Archived from the original on 10 June 2012.
- (in French) Damien Rousselière Cinéma et diversité culturelle: le cinéma indépendant face à la mondialisation des industries culturelles. Horizons philosophiques Vol. 15 No. 2 2005
- "Enquête sur l'image du cinéma français dans le monde". unifrance.org. Archived from the original on 13 December 2014.
- Joëlle Farchy (1999) La Fin de l'exception culturelle ? CNRS ISBN 978-2-271-05633-7
- The cultural exception is not negotiable by Catherine Trautmann – Ministry of Culture
- (in French) La Convention UNESCO pour la diversité culturelle : vers un droit international culturel contraignant ? Archived 27 April 2011 at the Wayback Machine – http://www.fnsac-cgt.com
- Kelly, 181. DeJean, chapters 2–4.
- "French perfume". About-France.com.
- Agence France-Presse, Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved November, 11th, 2018.
- (in French) OJD, "Observatoire de la Presse", Presse Quotidienne Nationale Archived 7 May 2010 at the Wayback Machine
- (in French) OJD, Presse Gratuite d'Information Archived 4 December 2010 at the Wayback Machine. November 2011
- (in French) Observatoire de la Presse, Presse Quotidienne Régionale et Départementale Archived 7 May 2010 at the Wayback Machine
- (in French) OJD, "Bureau Presse Payante Grand Public", Presse Quotidienne Régionale et Départementale Archived 25 April 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- (in French) Observatoire de la Presse, Presse Magazine – Synthèse Archived 29 September 2010 at the Wayback Machine
- (in French) Observatoire de la Presse, Presse News Archived 29 September 2010 at the Wayback Machine
- The Telegraph, Nicolas Sarkozy: French media faces 'death' without reform 2 October 2008
- French government portal, Lancement des états généraux de la presse Archived 25 June 2010 at the Wayback Machine 2 October 2008 [Launching of General State of written media]
- Angelique Chrisafis in Paris (23 January 2009). "Sarkozy pledges €600m to newspapers". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 21 June 2012.
- "Le Figaro". Encyclopædia Britannica.
- Radio France, "L'entreprise", Repères. Landmarks of Radio France company
- (in French) Vie Publique, Chronologie de la politique de l'audiovisuel Archived 13 May 2011 at the Wayback Machine 20 August 2004 [Chronology of policy for audiovisual]
- "World warming to US under Obama, BBC poll suggests". BBC News. 19 April 2010. Retrieved 21 July 2011.
- "Global Views of United States Improve While Other Countries Decline" (PDF). BBC News. 18 April 2010. Retrieved 26 December 2011.
- "Germany on Top, U.S. Seventh in Nation Brands IndexSM". GfK Group. 24 September 2008. Archived from the original on 25 August 2010. Retrieved 9 August 2010.
- "World Service Global Poll: Negative views of Russia on the rise". BBC. 4 June 2014. Retrieved 17 February 2018.
- "Muslim-Western Tensions Persist" (PDF). Pew Research Center. 21 July 2011. Retrieved 17 November 2011.
- "Opinion of the United States (2011)". Pew Research Center. Retrieved 9 January 2018.
- "Opinion of the United States (2017)". Pew Research Center. Retrieved 9 January 2018.
- Daniela Deane (11 February 2010). "Why France is best place to live in world". CNN. Retrieved 1 October 2013.
- "France". Flags of the World. 12 December 2013. Retrieved 9 January 2018.
- "The Symbols of the French Republic". Government of France. Archived from the original on 7 January 2014. Retrieved 16 January 2014.
- "Le coq" [The rooster]. Élysée – Présidence de la République (in French). Archived from the original on 1 April 2010.
- Women Leaders Index Gender Equality Case Study: France, Global Government Forum, 05 Septembre 2017
- Only 6 countries give women the same work rights as men. The U.S. isn't one of them., The Washington Post
- The Global Divide on Homosexuality- Greater Acceptance in More Secular and Affluent Countries, Pew Research Center, 4 June 2019
- France marks five-year anniversary of same-sex marriage, France 24, 23 April 2018
- Sexual Orientation and Gender Identity, France Diplomatie. Retrieved 3 September 2019
- 2018 Environmental Performance Index. Retrieved 3 September 2019
- Paris climate change agreement: the world's greatest diplomatic success, The Guardian, 14 December 2019
- Amy B. Trubek (2000). Haute Cuisine: How the French Invented the Culinary Profession. University of Pennsylvania Press. ISBN 978-0-8122-1776-6.
- Priscilla Parkhurst Ferguson (2006). Accounting for Taste: The Triumph of French Cuisine. University of Chicago Press. ISBN 978-0-226-24327-6.
- Véronique MARTINACHE (30 November 2009). "La France du beurre et celle de l'huile d'olive maintiennent leurs positions" [France butter and olive oil maintain their positions]. Agence France-Presse. Archived from the original on 25 April 2011.
- "Wines of France". Walter's Web. 17 May 2008. Archived from the original on 11 February 2010. Retrieved 9 August 2010.
- "French Cheese". Goodcooking. Retrieved 22 July 2011.
- "French Cheese". Archived from the original on 27 August 2010.
- Fairburn, Carolyn (29 February 1992). "Fading stars – Michelin Red Guide". The Times.
- Beale, Victoria; Boxell, James (16 July 2011). "Falling stars". Financial Times.
- "Michelin 3 Star Restaurants around the world". Andy Hayler's 3 Star Restaurant Guide. Archived from the original on 24 July 2010. Retrieved 30 October 2010.
- Gilles Campion (25 November 2010). "Japan overtakes France with more Michelin-starred restaurants". Agence France-Presse.
- "Union Cycliste Internationale". Archived from the original on 14 November 2012. Retrieved 19 May 2012.
- "Tour De France 2019: Everything you need to know". BBC. 6 July 2019. Retrieved 15 July 2019.
- (in French) Les licences sportives en France – Insee
- "All you need to know about sport in France". Retrieved 11 February 2012.
- "History of the World Cup Final Draw" (PDF). Retrieved 22 July 2011.
- France wins right to host the 2007 rugby world cup. Associated Press. 11 April 2003
- "Une course légendaire" (in French). Archived from the original on 16 January 2013. – Site officiel du 24 heures du Mans
- Hill, Christopher R. (1996). Olympic Politics. Manchester University Press ND. p. 5. ISBN 978-0-7190-4451-9. Retrieved 5 July 2011.
- Olympic History – World Atlas of Travel
- "Paris 1900 Summer Olympics. Official Site of the Olympic Movement". International Olympic Committee. 27 August 2018.
- Lausanne, olympic capital – Tourism in Lausanne Archived 6 October 2007 at the Wayback Machine
- "Deaflympics lowdown". 29 December 2004. Retrieved 8 July 2018.
- "Licenses of the French Football Federation" (PDF).
- McNulty, Phil (15 July 2018). "World Cup 2018: France beat Croatia 4-2 in World Cup final". BBC Sport. Retrieved 15 July 2018.
- Stevenson, Jonathan (9 July 2006). "Zidane off as Italy win World Cup". BBC News. Retrieved 21 July 2011.
- 1984: Platini shines for flamboyant France. UEFA Archived 7 May 2012 at the Wayback Machine
- 2000: Trezeguet strikes gold for France. UEFA Archived 28 October 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- "Zidane voted Europe's best ever" The Guardian. Retrieved 17 November 2013
- "Thierry Henry calls end to France career". BBC Sport. Retrieved 29 October 2014.
- Clarey, Christopher (30 June 2001). "Change Seems Essential to Escape Extinction: Wimbledon: World's Most Loved Dinosaur". International Herald Tribune. Archived from the original on 16 October 2007. Retrieved 26 February 2018.
- Rugby. 123 Voyage
Further reading
- "France." in Europe, edited by Ferdie McDonald and Claire Marsden, Dorling Kindersley, (Gale, 2010), pp. 144–217. online
- "France." in Worldmark Encyclopedia of the Nations, edited by Timothy L. Gall and Derek M. Gleason, (13th ed., vol. 5: Europe, Gale, 2012), pp. 215–243. online
Topics
- Carls, Alice-Catherine. "France." in World Press Encyclopedia, edited by Amanda C. Quick, (2nd ed., vol. 1, Gale, 2003), pp. 314–337. online coverage of press and media
- Chabal, Emile, ed. France since the 1970s: History, Politics and Memory in an Age of Uncertainty (2015) Excerpt
- Gildea, Robert. France Since 1945 (2nd ed. Oxford University Press, 2002).
- Goodliffe, Gabriel, and Riccardo Brizzi, eds. France After 2012 (Bergham, 2015)
- Haine, W. S. Culture and Customs of France (Greenwood Press, 2006).
- Kelly, Michael, ed. French Culture and Society: The Essentials (Oxford University Press, 2001).
- Raymond, Gino. Historical Dictionary of France (2nd ed. Scarecrow, 2008).
- Jones, Colin. Cambridge Illustrated History of France (Cambridge University Press,1999)
External links
| The Wikibook Wikijunior:Countries A-Z has a page on the topic of: France |
- France at Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development
- France at UCB Libraries GovPubs
- France at Curlie
- France at the EU

- Key Development Forecasts for France from International Futures
Economy
Government
- France.fr (in English) Official French tourism website
- (in French) Official Site of the Government
- Official site of the French public service – Links to various administrations and institutions
- Official site of the National Assembly
Culture
- Contemporary French Civilization, journal, University of Illinois.
- FranceGuide – Official website of the French Government Tourist Office

.svg.png)







.svg.png)
.svg.png)
.svg.png)
.svg.png)