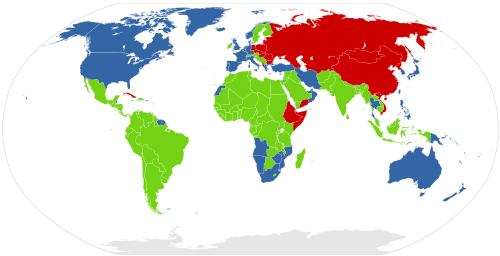
Western Bloc
The Western Bloc, also known as the Capitalist Bloc, was a coalition of countries that were allied with the United States, a member of NATO, and/or opposed the Soviet Union and the Warsaw Pact during the Cold War. The latter were referred to as the Eastern Bloc. The governments and press of the Western Bloc were more inclined to refer to themselves as the "Free World" or the "Western world", whereas the Eastern Bloc was often called the "Communist world or Second world".
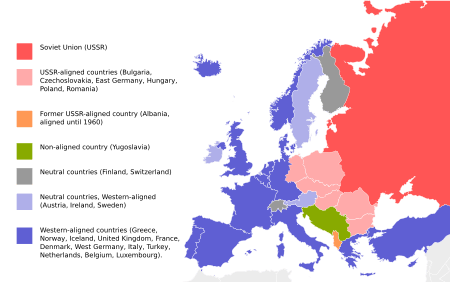
Political situation in Europe during the Cold War
Since the end of the Cold War, until recently, further escalation between China and Russia became tense since the NATO bombing of Yugoslavia in 1999, such as the conflicts in the Middle East (particularly in Iran, Syria and Yemen), Venezuela and Ukraine.[1]
Western Bloc associations
NATO
.svg.png)
.svg.png)











Countries which have become members of the NATO after the end of the Cold War (1991)













Other NATO-affiliated states and partners
Anti-Soviet Communist states during the Sino-Soviet split
Rio Treaty












.svg.png)




.svg.png)




SEATO

Map of SEATO members in 1959, shown in blue
.svg.png)







Southwest Asia/North Africa Region


.svg.png)


















East Asia


gollark: ... wait, what?
gollark: If you don't know where the internet HQ is, you can just make a GUI in visual basic to track their IP.
gollark: Don't know, I use linux.
gollark: `PiNG` or `Tracer-T` (`tracert)`.
gollark: ```I need to build as detailed an operational dossier on Stephen Bannon as possible in a week and a half. If any of y'all got somethin, DM it to me.```
See also
Sources
- Matloff, Maurice. Makers of Modern Strategy. Ed. Peter Paret. Princeton: Princeton UP, 1971. 702.
- Kissinger, Henry. Diplomacy. New York: Simon & Schuster, 1994. 447,454.
- Lewkowicz, Nicolas. The United States, the Soviet Union and the Geopolitical Implications of the Origins of the Cold War New York and London: Anthem Press, 2018.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.