Chambéry
Chambéry (UK: /ˈʃɒ̃bəri/,[2] US: /ˌʃɒ̃beɪˈriː/,[3] French: [ʃɑ̃beʁi]; Arpitan: Chambèri; Italian: Sciamberì; Latin: Camberia) is the prefecture of the Savoie department in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region of Southeastern France. In 2017, the commune had a population of 58,919.
Chambéry Chambèri (Arpitan) | |
|---|---|
Prefecture and commune | |
A general view of Chambéry | |
 Coat of arms | |
Location of Chambéry 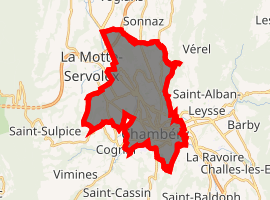
| |
 Chambéry  Chambéry | |
| Coordinates: 45°34′12″N 5°54′42″E | |
| Country | France |
| Region | Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes |
| Department | Savoie |
| Arrondissement | Chambéry |
| Canton | Chambéry-1, 2 and 3 |
| Intercommunality | Chambéry Métropole |
| Government | |
| • Mayor (2020–2026) | Thierry Repentin (PS) |
| Area 1 | 20.99 km2 (8.10 sq mi) |
| Population (2017-01-01)[1] | 58,919 |
| • Rank | 95th in France |
| • Density | 2,800/km2 (7,300/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| INSEE/Postal code | 73065 /73000 |
| Elevation | 245–560 m (804–1,837 ft) (avg. 270 m or 890 ft) |
| Website | www |
| 1 French Land Register data, which excludes lakes, ponds, glaciers > 1 km2 (0.386 sq mi or 247 acres) and river estuaries. | |
It is the capital of the department and has been the historical capital of the Savoy region since the 13th century, when Amadeus V, Count of Savoy, made the city his seat of power. Together with other Alpine towns Chambéry engages in the Alpine Town of the Year Association for the implementation of the Alpine Convention to achieve sustainable development in the Alpine Arc. Chambéry was awarded Alpine Town of the Year 2006.
Geography
Chambéry was founded at a crossroads of ancient routes through the Dauphiné (Dôfenâ), Burgundy, Switzerland, and Italy, in a wide valley between the Bauges and the Chartreuse Mountains on the Leysse River. The metropolitan area has more than 125,000 residents, extending from the vineyard slopes of the fr:Combe de Savoie almost to the shores of the Lac du Bourget, the largest natural lake in France. The city is a major railway hub, at the midpoint of the Franco-Italian Turin–Lyon high-speed railway.
Chambéry is situated in southeast France, 523 kilometres (325 miles) from Paris, 326 kilometres (203 miles) from Marseille, 214 km (133 mi) from Turin, 100 kilometres (62 miles) from Lyon and 85 kilometres (53 miles) from Geneva. It is found in a large valley, surrounded by the Massif des Bauges to the east (dominated by Le Nivolet, upon which La Croix du Nivolet is found), Mont Granier (Chartreuse) and the Chaîne de Belledonne to the south, the Chaîne de l'Épine (the most southern mountain of the Jura) to the west and the Lac du Bourget to the north. If seen as the meeting point of the Jura and the Alps, it is the westernmost point of the Swiss plateau which lies between them.
The towns surrounding Chambéry are Barberaz, Bassens, Cognin, Jacob-Bellecombette, La Motte-Servolex, La Ravoire, Saint-Alban-Leysse and Sonnaz.
History
The history of Chambéry is closely linked to the House of Savoy and was the Savoyard capital from 1295 to 1563. During this time, Savoy encompassed a region that stretched from Bourg-en-Bresse in the west, across the Alps to Turin, north to Geneva, and south to Nice. To insulate Savoy from provocations by France, Duke Emmanuel Philibert moved his capital to Turin in 1563, and, consequently, Chambéry declined.
France annexed the regions that formerly constituted the Duchy of Savoy west of the Alps in 1792; however, the former Duchy and Chambéry were returned to the rulers of the House of Savoy in Turin in 1815 following the defeat of Napoleon Bonaparte. The need for urban revitalization was met by the establishment of the Société Académique de Savoie in 1820, which was devoted to material and ethical progress, now housed in an apartment of the ducal Château. Chambéry and lands of the former Duchy, as well as The County of Nice, were ceded to France by Piedmont in 1860, under the reign of Napoleon III.
 Chambéry in 1645.
Chambéry in 1645.- Around 1780.
 In 1864.
In 1864.
Toponymy
The town known as Lemencum first changed its name in the Middle Ages during the period that the Duc de Savoie erected his castle. It was called Camefriacum in 1016, Camberiaco in 1029, Cambariacum in 1036, and Cambariaco in 1044. In the next century, Cambariaco changed to Chamberium (1233), finally becoming Chamberi in 1603. The actual name supposedly comes from the Gaulois term camboritos (a ford situated in a curve). The Latin name cambarius, meaning beer brewer, may also explain the name. Another hypothesis is that the Gallo-Roman name Camberiacum suggests the idea of currency changing (cambium) or trade (camerinum : market), or perhaps, a room (camera) where the toll taxes are collected.
Climate
Chambéry features an oceanic climate (Köppen : Cfb). In spite of this it is highly influenced by its interior position within France, resulting in quite hot summers and winters with frequent temperatures below freezing, especially at night.
| Climate data for Chambéry (1981–2010 averages) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 17.9 (64.2) |
20.5 (68.9) |
25.1 (77.2) |
29.5 (85.1) |
32.7 (90.9) |
36.1 (97.0) |
38.8 (101.8) |
38.8 (101.8) |
32.0 (89.6) |
29.0 (84.2) |
23.3 (73.9) |
22.7 (72.9) |
38.8 (101.8) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 5.8 (42.4) |
7.9 (46.2) |
12.6 (54.7) |
16.3 (61.3) |
20.8 (69.4) |
24.6 (76.3) |
27.4 (81.3) |
26.6 (79.9) |
22.0 (71.6) |
16.7 (62.1) |
10.1 (50.2) |
6.4 (43.5) |
16.4 (61.6) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 2.2 (36.0) |
3.6 (38.5) |
7.4 (45.3) |
10.7 (51.3) |
15.2 (59.4) |
18.7 (65.7) |
21.0 (69.8) |
20.4 (68.7) |
16.5 (61.7) |
12.1 (53.8) |
6.3 (43.3) |
3.1 (37.6) |
11.4 (52.6) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −1.4 (29.5) |
−0.7 (30.7) |
2.1 (35.8) |
5.1 (41.2) |
9.7 (49.5) |
12.8 (55.0) |
14.7 (58.5) |
14.2 (57.6) |
11.0 (51.8) |
7.4 (45.3) |
2.5 (36.5) |
−0.2 (31.6) |
6.4 (43.6) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −19.0 (−2.2) |
−14.4 (6.1) |
−10.3 (13.5) |
−4.6 (23.7) |
−1.4 (29.5) |
2.8 (37.0) |
5.4 (41.7) |
5.0 (41.0) |
1.0 (33.8) |
−4.3 (24.3) |
−10.8 (12.6) |
−13.5 (7.7) |
−19.0 (−2.2) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 102.6 (4.04) |
91.5 (3.60) |
100.0 (3.94) |
92.2 (3.63) |
104.2 (4.10) |
94.8 (3.73) |
86.6 (3.41) |
91.7 (3.61) |
111.8 (4.40) |
122.6 (4.83) |
105.0 (4.13) |
118.0 (4.65) |
1,221 (48.07) |
| Average precipitation days | 9.8 | 8.2 | 10.4 | 10.3 | 11.5 | 9.7 | 7.9 | 8.9 | 8.6 | 10.8 | 10.0 | 10.5 | 116.6 |
| Average snowy days | 5.4 | 4.6 | 2.2 | 1.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.7 | 3.2 | 18.3 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 77.7 | 104.4 | 156.7 | 172.8 | 202.5 | 234.0 | 260.1 | 232.5 | 176.3 | 121.4 | 71.2 | 60.6 | 1,870.3 |
| Source: Météo France[4][5] | |||||||||||||
Main sights
Château de Chambéry
The first counts of Savoy settled into an existing fortress in 1285 and expanded it in the early-14th century to serve as a residence, seat of power and administration, and as stronghold for the House of Savoy. However, it quickly became obsolete as a serious fortification genuinely capable of resisting a siege. Due to constant French hostilities on the château, Duke Emmanuel Philibert decided to move his capital to Turin.
The château remained purely an administrative centre until Christine Marie of France, Duchess of Savoy, returned to hold court in 1640. It was the site of the 1684 marriage between Victor Amadeus II of Sardinia and Anne Marie d'Orléans, niece of Louis XIV. Victor Amadeus II, having abdicated, lived here with his second wife Anna Canalis di Cumiana before they were imprisoned at the Castle of Rivoli for trying to reclaim the throne.
In 1786, Victor Amadeus III enlarged it, adding a Royal Wing.
Under Napoleon Bonaparte, the Aile du Midi ("South Wing") was rebuilt and redecorated to house the imperial prefecture of the department of Mont-Blanc. Elaborate modification to the structure were made again after Savoy was annexed by France in 1860.
Today, the political administration of the department of Savoie is located in the castle, and it is open for tours and concerts.
.jpg)
Fontaine des Éléphants
The Fontaine des Éléphants ("Elephants Fountain") is the most famous landmark in Chambéry. It was built in 1838 to honour Benoît de Boigne's feats when he was in India. The monumental fountain has strikingly realistic sculptures of the head and forelimbs of four lifesize elephants truncated into the base of a tall column in the shape of the savoyan (savoyarde) cross, topped by a statue of de Boigne. At first, the landmark was mocked by the local residents who were annoyed by it, but it now is accepted as one of the city's symbols. Since the early controversy, the statue kept its nickname of les quatre sans culs, ("the four without arses", which sounds in French similar to the title of the best-known movie by nouvelle vague director François Truffaut: Les quatre cents coups, "The 400 Blows"). A total restoration was done between December 2014 and July 2015.[6]
Others
The Cistercian Abbey of Hautecombe, founded in 1135, is one of the burial places of the rulers of the House of Savoy. Saint Francis de Sales officiated at Notre-Dame de Myans (established before the 12th century). Francis I of France went to Notre-Dame de l'Aumône at Rumilly in the 13th century as a pilgrim. The Sisters of St Joseph, an order founded at Chambéry in 1812, devotes itself to teaching and charitable work, and today, its members are now spread worldwide.
Chambéry is also the administrative headquarters of the Orchestre des Pays de Savoie.
Education
Chambéry is home to a famous engineering graduate school, Arts et Métiers ParisTech (ENSAM), that established an institute of research in 1994. This institute offers doctoral and master programs in the field of mechanical and industrial engineering.
Chambéry is also home to the INSEEC Business School, a French business school which offers Master in Management – Grande école program educational system.
Transport
Chambéry Airport serves Chambéry in the winter. The Chambéry-Challes-les-Eaux station provides rail connections, including a nonstop TGV service to Paris-Gare de Lyon. High-speed rail service also continues east along the Maurienne Valley and through the Fréjus Rail Tunnel to Turin, Italy. STAC is the local bus system.
Military
Chambéry is home to the 13th Battalion of the Chasseurs Alpins.
Demography
| 1793 | 1800 | 1806 | 1822 | 1838 | 1858 | 1861 | 1866 | 1872 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11,425 | 10,800 | 11,991 | 11,236 | 15,916 | 19,035 | 19,953 | 18,835 | 19,144 |
| 1876 | 1881 | 1886 | 1891 | 1896 | 1901 | 1906 | 1911 | 1921 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18,545 | 19,622 | 20,916 | 20,922 | 21,762 | 22,108 | 23,027 | 22,958 | 20,617 |
| 1926 | 1931 | 1936 | 1946 | 1954 | 1962 | 1968 | 1975 | 1982 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 23,400 | 25,407 | 28,073 | 29,975 | 32,139 | 44,246 | 51,066 | 54,415 | 53,427 |
| 1990 | 1999 | 2006 | 2008 | 2014 | - | - | - | - |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 54,120 | 55,786 | 57,543 | 56,835 | 59,490 | - | - | - | - |
Population Over Time
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vermouth
Chambéry is an AOC region for Chambéry vermouth, where the Dolin and Routin brands are made.[7]
Sport
Chambéry is home to SO Chambéry Foot and to Chambéry Savoie Handball.
Notable people
Chambéry was the birthplace of (chronological order):
- Thomas, Count of Savoy (1178-1233), who buys the city, with the exception of the castle, to Viscount Berlion de Chambéry, 15 March 1230.
- Amadeus V, Count of Savoy(v. 1249 - 1323), who buys in 1295 the castle of Chambéry, which will establish itself as the main county residence of the House of Savoy.
- François de Candie, 1st Viscount of Geneva, "Ancien Vidam de Genéve", (c. 1314–1360), nobleman and military commander of the Royal Guard of Savoy, Lord of the Chateau of Rumilly, and Salagine.
- Gauvain de Candie, count of Berruyre, novelist and poet of the House of Candia, who in 1475 at age 28 he composed the famous "Chason d'Amoure" recited poems to the ducal couple of Marguerite of Austria and Philibert II, Duke of Savoy.
- César Vichard de Saint-Réal (1639–1692), novelist
- Amédée-François Frézier (1682–1773), engineer, mathematician, spy, and explorer
- Benoît de Boigne (1751–1830), military adventurer in India
- Joseph de Maistre, (1753–1821) conservative political philosopher and critic of the French Revolution
- Xavier de Maistre (1763–1852), soldier and author
- Luigi Federico, conte Menabrea (1809–1896), Italian prime minister and general
- Pierre Pendaries (1893-????), World War I flying ace
- Michel de Certeau (1925–1986), Jesuit and scholar
- Jean-Michel Roddaz (1948–), historian
- brothers Renaud Capuçon (1976-) and Gautier Capuçon (1981-)
- Pierre-Jules Ginet (1985–), pastry chef at Fauchon
- Olivier Giroud (1986-), French international footballer and striker for English Premier League club Chelsea F.C.
- Grégory Lemarchal (1983-2007), French singer and winner from the reality TV program Star Academy in 2004
International relations
Chambéry is twinned with:[8]

.svg.png)

.svg.png)


See also
- Duchy of Savoy
- House of Savoy
- Archdiocese of Chambéry
- Kingdom of Sardinia
- Arpitan language
- Université de Savoie
- Communes of the Savoie department
- Listing of the works of Alexandre Falguière
References
- "Populations légales 2017". INSEE. Retrieved 6 January 2020.
- "Chambéry". Lexico UK Dictionary. Oxford University Press. Retrieved 31 July 2019.
- "Chambéry". Merriam-Webster Dictionary. Retrieved 31 July 2019.
- "Données climatiques de la station de Chambéry" (in French). Meteo France. Retrieved 26 December 2015.
- "Climat Rhône-Alpes" (in French). Meteo France. Retrieved 26 December 2015.
- "2014 -2015 : Travaux de restauration complets" (in French). Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 22 June 2016.
- "Vermouth boom". punchdrinks.com. Retrieved 5 February 2019.
- "Villes en coopération". chambery.fr (in French). Chambéry. Retrieved 20 November 2019.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Chambéry. |

- Official website
- STAC – the local bus system