Methanol
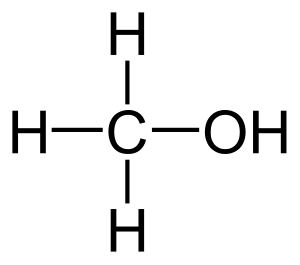
Methanol, also known as methyl alcohol amongst other names, is a chemical with the formula CH3OH (a methyl group linked to a hydroxyl group, often abbreviated MeOH). It is a light, volatile, colourless, flammable liquid with a distinctive alcoholic odour similar to that of ethanol.[2] A polar solvent, methanol acquired the name wood alcohol because it was once produced chiefly by the destructive distillation of wood. Today, methanol is mainly produced industrially by hydrogenation of carbon monoxide.[18]
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˈmɛθənɒl/ | ||
| Preferred IUPAC name
Methanol[1] | |||
| Other names
Carbinol Columbian spirits Hydroxymethane MeOH Methyl Hydrate Methyl alcohol Methyl hydroxide Methylic alcohol Methylol Methylene hydrate Pyroligneous spirit Wood alcohol Wood naphtha Wood spirit | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| 3DMet | |||
| 1098229 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.599 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| 449 | |||
| KEGG | |||
| MeSH | Methanol | ||
PubChem CID |
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1230 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| CH 3OH or CH 4O | |||
| Molar mass | 32.04 g mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colourless liquid | ||
| Odor | Ethanol-like[2] | ||
| Density | 0.792 g/cm3[3] | ||
| Melting point | −97.6 °C (−143.7 °F; 175.6 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 64.7 °C (148.5 °F; 337.8 K) | ||
| miscible | |||
| log P | −0.69 | ||
| Vapor pressure | 13.02 kPa (at 20 °C) | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | 15.5[4] | ||
| Conjugate acid | Methyloxonium[5] | ||
| Conjugate base | Methanolate[6] | ||
| −21.40·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
Refractive index (nD) |
1.33141[7] | ||
| Viscosity | 0.545 mPa·s (at 25 °C) [8] | ||
| 1.69 D | |||
| Hazards[9][10] | |||
| Main hazards | Methanol and its vapours are flammable.
Moderately Toxic for small animals – Highly Toxic to large animals and humans — May be fatal/lethal or cause blindness and damage to the liver, kidneys, and heart if swallowed – Toxic effects from repeated over exposure have an accumulative effect on the central nervous system, especially the optic nerve – Symptoms may be delayed, become severe after 12 to 18 hours, and linger for several days after exposure [11] | ||
| Safety data sheet | See: data page | ||
| GHS pictograms |    | ||
| GHS Signal word | Danger[12] | ||
GHS hazard statements |
H225, H301, H311, H331, H370[12] | ||
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P260, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+330+331, P310, P302+352, P312, P303+361+353, P304+340, P311, P305+351+338, P307+311, P337+313, P361, P363, P370+378, P403+233[12] | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | 11 to 12 °C (52 to 54 °F; 284 to 285 K) | ||
| 470 °C (878 °F; 743 K)[14] 385 °C (725 °F; 658 K)[15] | |||
| Explosive limits | 6–36%[16] | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LD50 (median dose) |
5628 mg/kg (rat, oral) 7300 mg/kg (mouse, oral) 12880 mg/kg (rat, oral) 14200 mg/kg (rabbit, oral)[17] | ||
LC50 (median concentration) |
64,000 ppm (rat, 4 h)[17] | ||
LCLo (lowest published) |
33,082 ppm (cat, 6 h) 37,594 ppm (mouse, 2 h)[17] | ||
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |||
PEL (Permissible) |
TWA 200 ppm (260 mg/m3)[16] | ||
REL (Recommended) |
TWA 200 ppm (260 mg/m3) ST 250 ppm (325 mg/m3) [skin][16] | ||
IDLH (Immediate danger) |
6000 ppm[16] | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds |
Methanethiol Silanol Ethanol | ||
| Supplementary data page | |||
| Refractive index (n), Dielectric constant (εr), etc. | |||
Thermodynamic data |
Phase behaviour solid–liquid–gas | ||
| UV, IR, NMR, MS | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Methanol consists of a methyl group linked to a hydroxyl group. With more than 20 million tons produced annually, it is used as a precursor to other commodity chemicals, including formaldehyde, acetic acid, methyl tert-butyl ether, as well as a host of more specialised chemicals.[18]
Occurrence
Small amounts of methanol are present in normal, healthy human individuals. One study found a mean of 4.5 ppm in the exhaled breath of test subjects.[19] The mean endogenous methanol in humans of 0.45 g/d may be metabolized from pectin found in fruit; one kilogram of apple produces up to 1.4 g methanol.[20]
Methanol is produced by anaerobic bacteria and phytoplankton.[21][22]
Interstellar medium
Methanol is also found in abundant quantities in star-forming regions of space and is used in astronomy as a marker for such regions. It is detected through its spectral emission lines.[23]
In 2006, astronomers using the MERLIN array of radio telescopes at Jodrell Bank Observatory discovered a large cloud of methanol in space, 288 billion miles (463 billion km) across.[24][25] In 2016, astronomers detected methanol in a planet-forming disc around the young star TW Hydrae using ALMA radio telescope.[26]
Toxicity
As little as 10 mL (0.34 US fl oz) of pure methanol can cause permanent blindness by destruction of the optic nerve. 30 mL (1.0 US fl oz) is potentially fatal.[27] The median lethal dose is 100 mL (3.4 US fl oz), i.e., 1–2 mL/kg body weight of pure methanol.[28] The reference dose for methanol is 0.5 mg/kg in a day.[29][30] Toxic effects begin hours after ingestion, and antidotes can often prevent permanent damage.[27] Because of its similarities in both appearance and odor to ethanol (the alcohol in beverages), it is difficult to differentiate between the two; such is also the case with denatured alcohol, adulterated liquors or very low quality alcoholic beverages.
Methanol is toxic by two mechanisms. First, methanol can be fatal due to effects on the central nervous system, acting as a central nervous system depressant in the same manner as ethanol poisoning. Second, in a process of toxication, it is metabolised to formic acid (which is present as the formate ion) via formaldehyde in a process initiated by the enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase in the liver.[31] Methanol is converted to formaldehyde via alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) and formaldehyde is converted to formic acid (formate) via aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH). The conversion to formate via ALDH proceeds completely, with no detectable formaldehyde remaining.[32] Formate is toxic because it inhibits mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase, causing hypoxia at the cellular level, and metabolic acidosis, among a variety of other metabolic disturbances.[33]
Outbreaks of methanol poisoning have occurred primarily due to contamination of drinking alcohol. This is more common in the developing world.[34] In 2013 more than 1700 cases nonetheless occurred in the United States. Those affected are often adult men.[35] Outcomes may be good with early treatment.[36] Toxicity to methanol was described as early as 1856.[37]
Because of its toxic properties, methanol is frequently used as a denaturant additive for ethanol manufactured for industrial uses. This addition of methanol exempts industrial ethanol (commonly known as "denatured alcohol" or "methylated spirit") from liquor excise taxation in the US and some other countries.
Applications
Formaldehyde, acetic acid, methyl tert-butylether
Methanol is primarily converted to formaldehyde, which is widely used in many areas, especially polymers. The conversion entails oxidation:
- 2 CH3OH + O2 → 2 CH2O + 2 H2O
Acetic acid can be produced from methanol.
Methanol and isobutene are combined to give methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE). MTBE is a major octane booster in gasoline.
Methanol to hydrocarbons, olefins, gasoline
Condensation of methanol to produce hydrocarbons and even aromatic systems is the basis of several technologies related to gas to liquids. These include methanol-to-hydrocarbons (MTH), methanol to gasoline (MTG), and methanol to olefins (MTO), and methanol to propylene (MTP). These conversions are catalyzed by zeolites as heterogeneous catalysts. The MTG process was once commercialized at Motunui in New Zealand.[39][40]
Gasoline additive
The European Fuel Quality Directive allows fuel producers to blend up to 3% methanol, with an equal amount of cosolvent, with gasoline sold in Europe. China uses more than 4.5 billion liters of methanol per year as a transportation fuel in low level blends for conventional vehicles, and high level blends in vehicles designed for methanol fuels.
Other chemicals
Methanol is the precursor to most simple methylamines, methyl halides, and methyl ethers.[18] Methyl esters are produced from methanol, including the transesterification of fats and production of biodiesel via transesterification.[41][42]
Niche and potential uses
Energy carrier
Methanol is a promising energy carrier because, as a liquid, it is easier to store than hydrogen and natural gas. Its energy density is however low reflecting the fact that it represents partially combusted methane. Its energy density is 15.6 MJ/L, whereas ethanol's is 24 and gasoline's is 33 MJ/L.
Further advantages for methanol is its ready biodegradability and low toxicity. It does not persist in either aerobic (oxygen-present) or anaerobic (oxygen-absent) environments. The half-life for methanol in groundwater is just one to seven days, while many common gasoline components have half-lives in the hundreds of days (such as benzene at 10–730 days). Since methanol is miscible with water and biodegradable, it is unlikely to accumulate in groundwater, surface water, air or soil.[43]
Fuel for vehicles
Methanol is occasionally used to fuel internal combustion engines. It burns forming carbon dioxide and water:
- 2 CH3OH + 3 O2 → 2 CO2 + 4 H2O
One problem with high concentrations of methanol in fuel is that alcohols corrode some metals, particularly aluminium. Methanol fuel has been proposed for ground transportation. The chief advantage of a methanol economy is that it could be adapted to gasoline internal combustion engines with minimum modification to the engines and to the infrastructure that delivers and stores liquid fuel. Its energy density is however only half that of gasoline, meaning that twice the volume of methanol would be required.
Other applications
Methanol was used as a denaturant (intentional toxin) for ethanol, the product being known as "denatured alcohol" or "methylated spirit". This was commonly used during the Prohibition to discourage consumption of bootlegged liquor, and ended up causing several deaths.[44] These types of practices are illegal in modern times, being considered homicide. [45]
Methanol is used as a solvent and as an antifreeze in pipelines and windshield washer fluid. Methanol was used as an automobile coolant antifreeze in the early 1900s.[46] As of May 2019, methanol was banned in the EU for use in windscreen washing or defrosting due to its risk of human consumption.[47][48]
In some wastewater treatment plants, a small amount of methanol is added to wastewater to provide a carbon food source for the denitrifying bacteria, which convert nitrates to nitrogen gas and reduce the nitrification of sensitive aquifers.
Methanol is used as a destaining agent in polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis.
Direct-methanol fuel cells are unique in their low temperature, atmospheric pressure operation, which lets them be greatly miniaturized.[49][50] This, combined with the relatively easy and safe storage and handling of methanol, may open the possibility of fuel cell-powered consumer electronics, such as laptop computers and mobile phones.[51]
Methanol is also a widely used fuel in camping and boating stoves. Methanol burns well in an unpressurized burner, so alcohol stoves are often very simple, sometimes little more than a cup to hold fuel. This lack of complexity makes them a favorite of hikers who spend extended time in the wilderness. Similarly, the alcohol can be gelled to reduce risk of leaking or spilling, as with the brand "Sterno".
Methanol is mixed with water and injected into high performance diesel and gasoline engines for an increase of power and a decrease in intake air temperature in a process known as water methanol injection.
Production
From synthesis gas
Carbon monoxide and hydrogen react over a catalyst to produce methanol. Today, the most widely used catalyst is a mixture of copper and zinc oxides, supported on alumina, as first used by ICI in 1966. At 5–10 MPa (50–100 atm) and 250 °C (482 °F), the reaction is characterized by high selectivity (>99.8%):
- CO + 2 H2 → CH3OH
The production of synthesis gas from methane produces three moles of hydrogen for every mole of carbon monoxide, whereas the synthesis consumes only two moles of hydrogen gas per mole of carbon monoxide. One way of dealing with the excess hydrogen is to inject carbon dioxide into the methanol synthesis reactor, where it, too, reacts to form methanol according to the equation:
- CO2 + 3 H2 → CH3OH + H2O
In terms of mechanism, the process occurs via initial conversion of CO into CO2, which is then hydrogenated:[52]
- CO2 + 3 H2 → CH3OH + H2O
where the H2O byproduct is recycled via the water-gas shift reaction
- CO + H2O → CO2 + H2,
This gives an overall reaction, which is the same as listed above.
- CO + 2 H2 → CH3OH
Biosynthesis
The catalytic conversion of methane to methanol is effected by enzymes including methane monooxygenases. These enzymes are mixed-function oxygenases, i.e. oxygenation is coupled with production of water[53] and NAD+.[54]
CH4 + O2 + NADPH + H+ → CH3OH + H2O + NAD+
Both Fe- and Cu-dependent enzymes have been characterized.[54] Intense but largely fruitless efforts have been undertaken to emulate this reactivity.[55][56] Methanol is more easily oxidized than is the feedstock methane, so the reactions tend not to be selective. Some strategies exist to circumvent this problem. Examples include Shilov systems and Fe- and Cu containing zeolites.[57] These systems do not necessarily mimick the mechanisms employed by metalloenzymes, but draw some inspiration from them. Active sites can vary substantially from those known in the enzymes. For example, a dinuclear active site is proposed in the sMMO enzyme, whereas a mononuclear iron (alpha-oxygen) is proposed in the Fe-zeolite.[58]
Safety
Methanol is highly flammable. Its vapours are heavier than air, can travel and ignite. Methanol fires should be extinguished with dry chemical, carbon dioxide, water spray or alcohol-resistant foam.[9]
Quality specifications and analysis
Methanol is available commercially in various purity grades. Commercial methanol is generally classified according to ASTM purity grades A and AA. Methanol for chemical use normally corresponds to Grade AA. In addition to water, typical impurities include acetone and ethanol (which are very difficult to separate by distillation). UV-vis spectroscopy is a convenient method for detecting aromatic impurities. Water content can be determined by the Karl-Fischer titration.
History
In their embalming process, the ancient Egyptians used a mixture of substances, including methanol, which they obtained from the pyrolysis of wood. Pure methanol, however, was first isolated in 1661 by Robert Boyle, when he produced it via the distillation of buxus (boxwood).[59] It later became known as "pyroxylic spirit". In 1834, the French chemists Jean-Baptiste Dumas and Eugene Peligot determined its elemental composition.[60] They also introduced the word "methylène" to organic chemistry, forming it from Greek methy = "alcoholic liquid" + hȳlē = "forest, wood, timber, material". "Methylène" designated a "radical" that was about 14% hydrogen by weight and contained one carbon atom. This would be CH2, but at the time carbon was thought to have an atomic weight only six times that of hydrogen, so they gave the formula as CH.[60] They then called wood alcohol (l'esprit de bois) "bihydrate de méthylène" (bihydrate because they thought the formula was C4H8O4 = (CH)4(H2O)2). The term "methyl" was derived in about 1840 by back-formation from "methylene", and was then applied to describe "methyl alcohol". This was shortened to "methanol" in 1892 by the International Conference on Chemical Nomenclature.[61] The suffix -yl, which, in organic chemistry, forms names of carbon groups, is from the word methyl.
In 1923, the German chemists Alwin Mittasch and Mathias Pier, working for Badische-Anilin & Soda-Fabrik (BASF), developed a means to convert synthesis gas (a mixture of carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, and hydrogen) into methanol. US patent 1,569,775 (US 1569775) was applied for on 4 Sep 1924 and issued on 12 January 1926; the process used a chromium and manganese oxide catalyst with extremely vigorous conditions: pressures ranging from 50 to 220 atm, and temperatures up to 450 °C. Modern methanol production has been made more efficient through use of catalysts (commonly copper) capable of operating at lower pressures. The modern low pressure methanol (LPM) process was developed by ICI in the late 1960s US 3326956 with the technology patent since long expired.
During World War II, methanol was used as a fuel in several German military rocket designs, under the name M-Stoff, and in a roughly 50/50 mixture with hydrazine, known as C-Stoff.
The use of methanol as a motor fuel received attention during the oil crises of the 1970s. By the mid-1990s, over 20,000 methanol "flexible fuel vehicles" (FFV) capable of operating on methanol or gasoline were introduced in the U.S. In addition, low levels of methanol were blended in gasoline fuels sold in Europe during much of the 1980s and early-1990s. Automakers stopped building methanol FFVs by the late-1990s, switching their attention to ethanol-fueled vehicles. While the methanol FFV program was a technical success, rising methanol pricing in the mid- to late-1990s during a period of slumping gasoline pump prices diminished interest in methanol fuels.[62]
In the early 1970s, a process was developed by Mobil for producing gasoline fuel from methanol.[63]
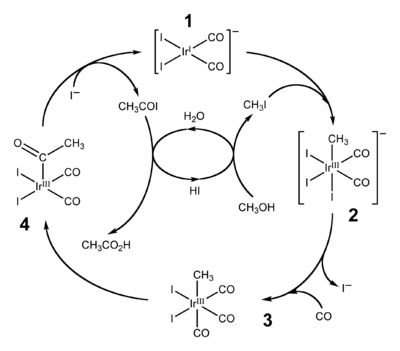
Between the 1960s and 1980s methanol emerged as a precursor to the feedstock chemicals acetic acid and acetic anhydride. These processes include the Monsanto acetic acid synthesis, Cativa process, and Tennessee Eastman acetic anhydride process.
References
- Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry : IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. p. 692. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-00648. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (22 August 2008). "The Emergency Response Safety and Health Database: Methanol". Retrieved 17 March 2009.
- Lide, D. R., ed. (2005). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (86th ed.). Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press. ISBN 0-8493-0486-5.
- Ballinger, P.; Long, F. A. (1960). "Acid Ionization Constants of Alcohols. II. Acidities of Some Substituted Methanols and Related Compounds". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 82 (4): 795–798. doi:10.1021/ja01489a008.
- "Methyloxonium". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 21 December 2018.
- "Methanolate". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 21 December 2018.
Methoxide is an organic anion that is the conjugate base of methanol. … It is a conjugate base of a methanol.
- "RefractiveIndex.INFO - Refractive index database".
- González, Begoña (2007). "Density, dynamic viscosity, and derived properties of binary mixtures of methanol or ethanol with water, ethyl acetate, and methyl acetate at T = (293.15, 298.15, and 303.15) K". The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics. 39 (12): 1578–1588. doi:10.1016/j.jct.2007.05.004.
- "The Emergency Response Safety and Health Database: Systematic Agent: METHANOL". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved 3 August 2018.
- "PubChem: Safety and Hazards - GHS Classification". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Toxicity on PubChem
- "Methanol" (PDF). Lab Chem. Valtech. Retrieved 10 March 2016.
- "Methanol Safe Handling Manual" (PDF). Methanol Institute. 2017. p. 253. Retrieved 3 August 2018.
- "Technical Information & Safe Handling Guide for Methanol". Methanex Corporation. Archived from the original on 11 March 2012.
- "Methanol Safe Handling Manual" (PDF). Methanol Institute. 2017. p. 243. Retrieved 3 August 2018.
- NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0397". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- "Methanol". Immediately Dangerous to Life and Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- Fiedler, E.; Grossmann, G.; Burkhard Kersebohm, D.; Weiss, G. and Witte, C. (2005). "Methanol". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a16_465. ISBN 978-3527306732.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
- Turner C (2006). "A longitudinal study of methanol in the exhaled breath of 30 healthy volunteers using selected ion flow tube mass spectrometry, SIFT-MS". Physiological Measurement. 27 (7): 637–48. Bibcode:2006PhyM...27..637T. doi:10.1088/0967-3334/27/7/007. PMID 16705261.
- Lindinger W (1997). "Endogenous production of methanol after the consumption of fruit". Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research. 21 (5): 939–43. doi:10.1111/j.1530-0277.1997.tb03862.x. PMID 9267548.
- "Major Source of Methanol in the Ocean Identified". Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution. 10 March 2016. Retrieved 30 March 2016.
- Mincer, Tracy J.; Aicher, Athena C. (2016). "Methanol Production by a Broad Phylogenetic Array of Marine Phytoplankton". PLOS ONE. 11 (3): e0150820. Bibcode:2016PLoSO..1150820M. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0150820. PMC 4786210. PMID 26963515.
- Brooks Hays (17 April 2015). "Why astronomers hate the lawn-mowing Roomba". Space Daily.
- "Upgraded MERLIN spies cloud of alcohol spanning 288 billion miles" (Press release). Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophysics. 19 April 2006. Archived from the original on 20 July 2011.
- Amos, Jonathan (5 April 2006). "Merlin sees vast alcohol stream". BBC News.
- "First Detection of Methyl Alcohol in a Planet-forming Disc". Retrieved 22 June 2016.
- Vale A (2007). "Methanol". Medicine. 35 (12): 633–4. doi:10.1016/j.mpmed.2007.09.014.
- "Methanol Poisoning Overview". Antizol. Archived from the original on 5 October 2011.
- "Integrated Risk Information System". US EPA, ORD, NCEA, IRISD. 15 March 2013.
- "Toxicological Review of Methanol (Noncancer) (CAS No. 67-56-1) In Support of Summary Information on the Integrated Risk Information System (IRIS)" (PDF). EPA. September 2013. EPA/635/R-11/001Fa. Retrieved 4 September 2017. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - Schep LJ, Slaughter RJ, Vale JA, Beasley DM (2009). "A seaman with blindness and confusion". BMJ. 339: b3929. doi:10.1136/bmj.b3929. PMID 19793790. S2CID 6367081.
- McMartin KE, Martin-Amat G, Noker PE, Tephly TR (1979). "Lack of a role for formaldehyde in methanol poisoning in the monkey". Biochem. Pharmacol. 28 (5): 645–9. doi:10.1016/0006-2952(79)90149-7. PMID 109089.
- Liesivuori J, Savolainen H (September 1991). "Methanol and formic acid toxicity: biochemical mechanisms". Pharmacol. Toxicol. 69 (3): 157–63. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0773.1991.tb01290.x. PMID 1665561.
- Beauchamp, GA; Valento, M (September 2016). "Toxic Alcohol Ingestion: Prompt Recognition And Management In The Emergency Department". Emergency Medicine Practice. 18 (9): 1–20. PMID 27538060.
- Ferri, Fred F. (2016). Ferri's Clinical Advisor 2017: 5 Books in 1. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 794. ISBN 9780323448383.
- Kruse, JA (October 2012). "Methanol and ethylene glycol intoxication". Critical Care Clinics. 28 (4): 661–711. doi:10.1016/j.ccc.2012.07.002. PMID 22998995.
- Clary, John J. (2013). The Toxicology of Methanol. John Wiley & Sons. p. 3.4.1. ISBN 9781118353103.
- Sunley, G. J.; Watson, D. J. (2000). "High productivity methanol carbonylation catalysis using iridium - The Cativa process for the manufacture of acetic acid". Catalysis Today. 58 (4): 293–307. doi:10.1016/S0920-5861(00)00263-7.
- Olsbye, U.; Svelle, S.; Bjorgen, M.; Beato, P.; Janssens, T. V. W.; Joensen, F.; Bordiga, S.; Lillerud, K. P. (2012). "Conversion of Methanol to Hydrocarbons: How Zeolite Cavity and Pore Size Controls Product Selectivity". Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 51 (24): 5810–5831. doi:10.1002/anie.201103657. PMID 22511469.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
- Tian, P.; Wei, Y.; Ye, M.; Liu, Z. (2015). "Methanol to Olefins (MTO): From Fundamentals to Commercialization". ACS Catal. 5 (3): 1922–1938. doi:10.1021/acscatal.5b00007.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
- "Biodiesel - METHANOL INSTITUTE". METHANOL INSTITUTE. Retrieved 24 March 2018.
- "Biodiesel Production Principles and Processes - eXtension". Retrieved 24 March 2018.
- Evaluation of the Fate and Transport of Methanol in the Environment Archived 16 May 2016 at the Portuguese Web Archive, Malcolm Pirnie, Inc., January 1999.
- Blum, Deborah (19 February 2010). "The little-told story of how the U.S. government poisoned alcohol during Prohibition". Slate Magazine. Retrieved 10 June 2010.
- https://uscode.house.gov/view.xhtml?path=/prelim@title22/chapter75&edition=prelim
- Yant, W. P.; Schrenk, H. H.; Sayers, R. R. (1931). "Methanol Antifreeze and Methanol Poisoning". Industrial & Engineering Chemistry. 23 (5): 551. doi:10.1021/ie50257a020.
- "EUR-Lex - 32018R0589 - EN - EUR-Lex". eur-lex.europa.eu. Retrieved 28 November 2018.
- Corrigendum to Commission Regulation (EU) 2018/589 of 18 April 2018 amending Annex XVII to Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council concerning the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) as regards methanol (OJ L 99, 19.4.2018), 23 April 2018, retrieved 7 July 2020
- Kamitani, A.; Morishita, S.; Kotaki, H.; Arscott, S. (2008). "Miniaturized microDMFC using silicon microsystems techniques: Performances at low fuel flow rates". Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering. 18 (12): 125019. Bibcode:2008JMiMi..18l5019K. doi:10.1088/0960-1317/18/12/125019.
- Kamitani, A.; Morishita, S.; Kotaki, H.; Arscott, S. (2011). "Microfabricated microfluidic fuel cells". Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical. 154 (2): 174. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2009.11.014.
- Berger, Sandy (30 September 2006). "Methanol Laptop Fuel". Compu·Kiss. Retrieved 22 May 2007.
- Deutschmann, Olaf; Knözinger, Helmut; Kochloefl, Karl and Turek, Thomas (2012) "Heterogeneous Catalysis and Solid Catalysts, 3. Industrial Applications" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.o05_o03
- Mu-Hyun Baik, Martin Newcomb, Richard A. Friesner, Stephen J. Lippard (2003). "Mechanistic Studies on the Hydroxylation of Methane by Methane Monooxygenase". Chem. Rev. 103 (6): 2385–2420. doi:10.1021/cr950244f. PMID 12797835.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
- Lawton, T. J.; Rosenzweig, A. C. (2016). "Biocatalysts for methane conversion: big progress on breaking a small substrate". Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 35: 142–149. doi:10.1016/j.cbpa.2016.10.001. PMC 5161620. PMID 27768948.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
- Alayon, E. M. C.; Nachtegaal, M.; Ranocchiari, M.; Van Bokhoven, J. A. (2012). "Catalytic Conversion of Methane to Methanol Using Cu-Zeolites". CHIMIA International Journal for Chemistry. 66 (9): 668–674. doi:10.2533/chimia.2012.668. PMID 23211724.
- Hammond, C.; Jenkins, R. L.; Dimitratos, N.; Lopez-Sanchez, J. A.; Ab Rahim, M. H.; Forde, M. M.; Thetford, A.; Murphy, D. M.; Hagen, H.; Stangland, E. E.; Moulijn, J. M.; Taylor, S. H.; Willock, D. J.; Hutchings, G. J. (2012). "Catalytic and Mechanistic Insights of the Low-Temperature Selective Oxidation of Methane over Cu-Promoted Fe-ZSM-5". Chemistry: A European Journal. 18 (49): 15735–45. doi:10.1002/chem.201202802. PMID 23150452.
- Snyder, Benjamin E. R.; Bols, Max L.; Schoonheydt, Robert A.; Sels, Bert F.; Solomon, Edward I. (19 December 2017). "Iron and Copper Active Sites in Zeolites and Their Correlation to Metalloenzymes". Chemical Reviews. 118 (5): 2718–2768. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00344. PMID 29256242.
- Snyder, Benjamin E. R.; Vanelderen, Pieter; Bols, Max L.; Hallaert, Simon D.; Böttger, Lars H.; Ungur, Liviu; Pierloot, Kristine; Schoonheydt, Robert A.; Sels, Bert F. (2016). "The active site of low-temperature methane hydroxylation in iron-containing zeolites". Nature. 536 (7616): 317–321. Bibcode:2016Natur.536..317S. doi:10.1038/nature19059. PMID 27535535. S2CID 4467834.
- Boyle discusses the distillation of liquids from the wood of the box shrub in: Robert Boyle, The Sceptical Chymist (London, England: J. Cadwell, 1661), pp. 192–195.
- A report on methanol to the French Academy of Sciences by J. Dumas and E. Péligot began during the Academy's meeting of 27 October 1834 and finished during the meeting of 3 November 1834. See: Procès-verbaux des séances de l'Académie, 10 : 600–601. Available on: Gallica. The complete report appears in: J. Dumas and E. Péligot (1835) "Mémoire sur l'espirit de bois et sur les divers composés ethérés qui en proviennent" (Memoir on spirit of wood and on the various ethereal compounds that derive therefrom), Annales de chimie et de physique, 58 : 5–74; from page 9: Nous donnerons le nom de méthylène (1) à un radical … (1) Μεθυ, vin, et υλη, bois; c'est-à-dire vin ou liqueur spiritueuse du bois. (We will give the name methylene (1) to a radical … (1) methy, wine, and hulē, wood; that is, wine or spirit of wood.)
- For a report on the International Conference on Chemical Nomenclature that was held in April 1892 in Geneva, Switzerland, see:
- Armstrong, Henry E (1892). "The International Conference on Chemical Nomenclature". Nature. 46 (1177): 56–9. Bibcode:1892Natur..46...56A. doi:10.1038/046056c0.
- Armstrong's report is reprinted with the resolutions in English in: Armstrong, Henry (1892). "The International Conference on Chemical Nomenclature". The Journal of Analytical and Applied Chemistry. 6 (1177): 390–400. Bibcode:1892Natur..46...56A. doi:10.1038/046056c0.
p. 398: 15. The alcohols and the phenols are named after the hydrocarbon from which they derive, terminated with the suffix ol (ex. pentanol, pentenol, etc.).
- Halderman, James D.; Martin, Tony (2009). Hybrid and alternative fuel vehicles. Pearson/Prentice Hall. ISBN 978-0-13-504414-8.
- Ronald Smith (1 December 2011). "Methanol to Gasoline: A Private Report by the Process Economics Program" (PDF). Retrieved 4 December 2019.
Further reading
- Robert Boyle, The Sceptical Chymist (1661) – contains account of distillation of wood alcohol.
External links
- International Chemical Safety Card 0057
- Methyl Alcohol (Methanol) CDC/NIOSH, links to safety information
- CDC – NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards – Methyl Alcohol
- Methanol Fact Sheet – National Pollutant Inventory