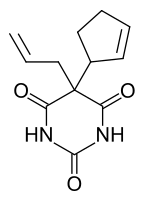
Cyclopentobarbital
Cyclopentobarbital sodium (Cyclopal, Dormisan) is a barbiturate derivative invented in the 1940s.[1] It has sedative and anticonvulsant properties, and was used primarily as an anaesthetic in veterinary medicine.[2] Cyclopal is considered similar in effects to phenobarbital but lasts almost three times as long, and is considered a long-acting barbiturate with a fairly slow onset of action.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Allylpental, Cyclopental, 5-Allyl-5-Δ2-Cyclopentenyl Barbituric Acid |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.891 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C12H14N2O3 |
| Molar mass | 234.255 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
See also
References
- Martin, J. R.; Godel, T.; Hunkeler, W.; Jenck, F.; Moreau, J.-L.; Sleight, A. J.; Widmer, U. (2000). "Psychopharmacological Agents". doi:10.1002/0471238961.1619250313011820.a01. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - Vander Brook MJ, Cartland GF. A Pharmacologic Study of 5-Allyl-5-Cyclopentenyl Barbituric Acid (Cyclopal). Journal of Pharmacology And Experimental Therapeutics, 1944, 80(2): 119-125
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.