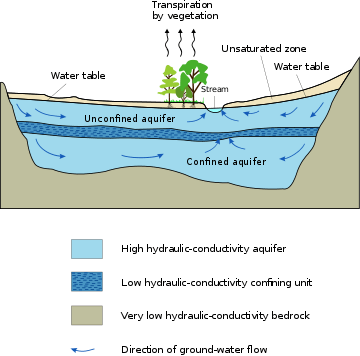
Aquifer
An aquifer is an underground layer of water-bearing permeable rock, rock fractures or unconsolidated materials (gravel, sand, or silt). Groundwater can be extracted using a water well. The study of water flow in aquifers and the characterization of aquifers is called hydrogeology. Related terms include aquitard, which is a bed of low permeability along an aquifer,[1] and aquiclude (or aquifuge), which is a solid, impermeable area underlying or overlying an aquifer, the pressure of which could create a confined aquifer.
Depth
Aquifers occur from near surface to deeper than 9,000 metres (30,000 ft).[2] Those closer to the surface are not only more likely to be used for water supply and irrigation, but are also more likely to be topped up by the local rainfall. Many desert areas have limestone hills or mountains within them or close to them that can be exploited as groundwater resources. Part of the Atlas Mountains in North Africa, the Lebanon and Anti-Lebanon ranges between Syria and Lebanon, the Jebel Akhdar in Oman, parts of the Sierra Nevada and neighboring ranges in the United States' Southwest, have shallow aquifers that are exploited for their water. Overexploitation can lead to the exceeding of the practical sustained yield; i.e., more water is taken out than can be replenished. Along the coastlines of certain countries, such as Libya and Israel, increased water usage associated with population growth has caused a lowering of the water table and the subsequent contamination of the groundwater with saltwater from the sea.
A beach provides a model to help visualize an aquifer. If a hole is dug into the sand, very wet or saturated sand will be located at a shallow depth. This hole is a crude well, the wet sand represents an aquifer, and the level to which the water rises in this hole represents the water table.
In 2013 large freshwater aquifers were discovered under continental shelves off Australia, China, North America and South Africa. They contain an estimated half a million cubic kilometers of "low salinity" water that could be economically processed into potable water. The reserves formed when ocean levels were lower and rainwater made its way into the ground in land areas that were not submerged until the ice age ended 20,000 years ago. The volume is estimated to be 100 times the amount of water extracted from other aquifers since 1900.[3][4]
Classification
An aquitard is a zone within the Earth that restricts the flow of groundwater from one aquifer to another. An aquitard can sometimes, if completely impermeable, be called an aquiclude or aquifuge. Aquitards are composed of layers of either clay or non-porous rock with low hydraulic conductivity.
Saturated versus unsaturated
Groundwater can be found at nearly every point in the Earth's shallow subsurface to some degree, although aquifers do not necessarily contain fresh water. The Earth's crust can be divided into two regions: the saturated zone or phreatic zone (e.g., aquifers, aquitards, etc.), where all available spaces are filled with water, and the unsaturated zone (also called the vadose zone), where there are still pockets of air that contain some water, but can be filled with more water.
Saturated means the pressure head of the water is greater than atmospheric pressure (it has a gauge pressure > 0). The definition of the water table is the surface where the pressure head is equal to atmospheric pressure (where gauge pressure = 0).
Unsaturated conditions occur above the water table where the pressure head is negative (absolute pressure can never be negative, but gauge pressure can) and the water that incompletely fills the pores of the aquifer material is under suction. The water content in the unsaturated zone is held in place by surface adhesive forces and it rises above the water table (the zero-gauge-pressure isobar) by capillary action to saturate a small zone above the phreatic surface (the capillary fringe) at less than atmospheric pressure. This is termed tension saturation and is not the same as saturation on a water-content basis. Water content in a capillary fringe decreases with increasing distance from the phreatic surface. The capillary head depends on soil pore size. In sandy soils with larger pores, the head will be less than in clay soils with very small pores. The normal capillary rise in a clayey soil is less than 1.8 m (6 ft) but can range between 0.3 and 10 m (1 and 33 ft).[5]
The capillary rise of water in a small-diameter tube involves the same physical process. The water table is the level to which water will rise in a large-diameter pipe (e.g., a well) that goes down into the aquifer and is open to the atmosphere.
Aquifers versus aquitards
Aquifers are typically saturated regions of the subsurface that produce an economically feasible quantity of water to a well or spring (e.g., sand and gravel or fractured bedrock often make good aquifer materials).
An aquitard is a zone within the Earth that restricts the flow of groundwater from one aquifer to another. A completely impermeable aquitard is called an aquiclude or aquifuge. Aquitards comprise layers of either clay or non-porous rock with low hydraulic conductivity.
In mountainous areas (or near rivers in mountainous areas), the main aquifers are typically unconsolidated alluvium, composed of mostly horizontal layers of materials deposited by water processes (rivers and streams), which in cross-section (looking at a two-dimensional slice of the aquifer) appear to be layers of alternating coarse and fine materials. Coarse materials, because of the high energy needed to move them, tend to be found nearer the source (mountain fronts or rivers), whereas the fine-grained material will make it farther from the source (to the flatter parts of the basin or overbank areas—sometimes called the pressure area). Since there are less fine-grained deposits near the source, this is a place where aquifers are often unconfined (sometimes called the forebay area), or in hydraulic communication with the land surface.
Confined versus unconfined
There are two end members in the spectrum of types of aquifers; confined and unconfined (with semi-confined being in between). Unconfined aquifers are sometimes also called water table or phreatic aquifers, because their upper boundary is the water table or phreatic surface. (See Biscayne Aquifer.) Typically (but not always) the shallowest aquifer at a given location is unconfined, meaning it does not have a confining layer (an aquitard or aquiclude) between it and the surface. The term "perched" refers to ground water accumulating above a low-permeability unit or strata, such as a clay layer. This term is generally used to refer to a small local area of ground water that occurs at an elevation higher than a regionally extensive aquifer. The difference between perched and unconfined aquifers is their size (perched is smaller). Confined aquifers are aquifers that are overlain by a confining layer, often made up of clay. The confining layer might offer some protection from surface contamination.
If the distinction between confined and unconfined is not clear geologically (i.e., if it is not known if a clear confining layer exists, or if the geology is more complex, e.g., a fractured bedrock aquifer), the value of storativity returned from an aquifer test can be used to determine it (although aquifer tests in unconfined aquifers should be interpreted differently than confined ones). Confined aquifers have very low storativity values (much less than 0.01, and as little as 10−5), which means that the aquifer is storing water using the mechanisms of aquifer matrix expansion and the compressibility of water, which typically are both quite small quantities. Unconfined aquifers have storativities (typically then called specific yield) greater than 0.01 (1% of bulk volume); they release water from storage by the mechanism of actually draining the pores of the aquifer, releasing relatively large amounts of water (up to the drainable porosity of the aquifer material, or the minimum volumetric water content).
Isotropic versus anisotropic
In isotropic aquifers or aquifer layers the hydraulic conductivity (K) is equal for flow in all directions, while in anisotropic conditions it differs, notably in horizontal (Kh) and vertical (Kv) sense.
Semi-confined aquifers with one or more aquitards work as an anisotropic system, even when the separate layers are isotropic, because the compound Kh and Kv values are different (see hydraulic transmissivity and hydraulic resistance).
When calculating flow to drains [6] or flow to wells [7] in an aquifer, the anisotropy is to be taken into account lest the resulting design of the drainage system may be faulty.
Porous versus karst
To properly manage an aquifer its properties must be understood. Many properties must be known to predict how an aquifer will respond to rainfall, drought, pumping, and contamination. Where and how much water enters the groundwater from rainfall and snowmelt? How fast and what direction does the groundwater travel? How much water leaves the ground as springs. How much water can be sustainably pumped out? How quickly will a contamination incident reach a well or spring? Computer models can be used to test how accurately the understanding of the aquifer properties matches the actual aquifer performance.[8]:192–193, 233–237 Environmental regulations require sites with potential sources of contamination to demonstrate that the hydrology has been characterized.[8]:3
Porous

Porous aquifers typically occur in sand and sandstone. Porous aquifer properties depend on the depositional sedimentary environment and later natural cementation of the sand grains. The environment where a sand body was deposited controls the orientation of the sand grains, the horizontal and vertical variations, and the distribution of shale layers. Even thin shale layers are important barriers to groundwater flow. All these factors affect the porosity and permeability of sandy aquifers.[9]:413 Sandy deposits formed in shallow marine environments and in windblown sand dune environments have moderate to high permeability while sandy deposits formed in river environments have low to moderate permeability.[9]:418 Rainfall and snowmelt enter the groundwater where the aquifer is near the surface. Groundwater flow directions can be determined from potentiometric surface maps of water levels in wells and springs. Aquifer tests and well tests can be used with Darcy's law flow equations to determine the ability of a porous aquifer to convey water.[8]:177–184 Analyzing this type of information over an area gives an indication how much water can be pumped without overdrafting and how contamination will travel.[8]:233 In porous aquifers groundwater flows as slow seepage in pores between sand grains. A groundwater flow rate of 1 foot per day (0.3 m/d) is considered to be a high rate for porous aquifers,[10] as illustrated by the water slowly seeping from sandstone in the accompanying image to the left.
Karst

Karst aquifers typically develop in limestone. Surface water containing natural carbonic acid moves down into small fissures in limestone. This carbonic acid gradually dissolves limestone thereby enlarging the fissures. The enlarged fissures allow a larger quantity of water to enter which leads to a progressive enlargement of openings. Abundant small openings store a large quantity of water. The larger openings create a conduit system that drains the aquifer to springs.[11] Characterization of karst aquifers requires field exploration to locate sinkholes, swallets, sinking streams, and springs in addition to studying geologic maps.[12]:4 Conventional hydrogeologic methods such as aquifer tests and potentiometric mapping are insufficient to characterize the complexity of karst aquifers. These conventional investigation methods need to be supplemented with dye traces, measurement of spring discharges, and analysis of water chemistry.[13] U.S. Geological Survey dye tracing has determined that conventional groundwater models that assume a uniform distribution of porosity are not applicable for karst aquifers.[14] Linear alignment of surface features such as straight stream segments and sinkholes develop along fracture traces. Locating a well in a fracture trace or intersection of fracture traces increases the likelihood to encounter good water production.[15] Voids in karst aquifers can be large enough to cause destructive collapse or subsidence of the ground surface that can create a catastrophic release of contaminants.[8]:3–4 Groundwater flow rate in karst aquifers is much more rapid than in porous aquifers as shown in the accompanying image to the left. For example, in the Barton Springs Edwards aquifer, dye traces measured the karst groundwater flow rates from 0.5 to 7 miles per day (0.8 to 11.3 km/d).[16] The rapid groundwater flow rates make karst aquifers much more sensitive to groundwater contamination than porous aquifers.[12]:1
Transboundary aquifer
When an aquifer transcends international boundaries, the term transboundary aquifer applies.[17]
Transboundariness is a concept, a measure and an approach first introduced in 2017.[18] The relevance of this approach is that the physical features of the aquifers become just additional variables among the broad spectrum of considerations of the transboundary nature of an aquifer:
- social (population);
- economic (groundwater productivity);
- political (as transboundary);
- available research or data;
- water quality and quantity;
- other issues governing the agenda (security, trade, immigration and so on).
The discussion changes from the traditional question of “is the aquifer transboundary?” to “how transboundary is the aquifer?”.
The socio-economic and political contexts effectively overwhelm the aquifer's physical features adding its corresponding geostrategic value (its transboundariness)[19]
The criteria proposed by this approach attempt to encapsulate and measure all potential variables that play a role in defining the transboundary nature of an aquifer and its multidimensional boundaries.
Groundwater in rock formations
Groundwater may exist in underground rivers (e.g., caves where water flows freely underground). This may occur in eroded limestone areas known as karst topography, which make up only a small percentage of Earth's area. More usual is that the pore spaces of rocks in the subsurface are simply saturated with water—like a kitchen sponge—which can be pumped out for agricultural, industrial, or municipal uses.
If a rock unit of low porosity is highly fractured, it can also make a good aquifer (via fissure flow), provided the rock has a hydraulic conductivity sufficient to facilitate movement of water. Porosity is important, but, alone, it does not determine a rock's ability to act as an aquifer. Areas of the Deccan Traps (a basaltic lava) in west central India are good examples of rock formations with high porosity but low permeability, which makes them poor aquifers. Similarly, the micro-porous (Upper Cretaceous) Chalk Group of south east England, although having a reasonably high porosity, has a low grain-to-grain permeability, with its good water-yielding characteristics mostly due to micro-fracturing and fissuring.
Human dependence on groundwater

Most land areas on Earth have some form of aquifer underlying them, sometimes at significant depths. In some cases, these aquifers are rapidly being depleted by the human population.
Fresh-water aquifers, especially those with limited recharge by snow or rain, also known as meteoric water, can be over-exploited and depending on the local hydrogeology, may draw in non-potable water or saltwater intrusion from hydraulically connected aquifers or surface water bodies. This can be a serious problem, especially in coastal areas and other areas where aquifer pumping is excessive. In some areas, the ground water can become contaminated by arsenic and other mineral poisons.
Aquifers are critically important in human habitation and agriculture. Deep aquifers in arid areas have long been water sources for irrigation (see Ogallala below). Many villages and even large cities draw their water supply from wells in aquifers.
Municipal, irrigation, and industrial water supplies are provided through large wells. Multiple wells for one water supply source are termed "wellfields", which may withdraw water from confined or unconfined aquifers. Using ground water from deep, confined aquifers provides more protection from surface water contamination. Some wells, termed "collector wells", are specifically designed to induce infiltration of surface (usually river) water.
Aquifers that provide sustainable fresh groundwater to urban areas and for agricultural irrigation are typically close to the ground surface (within a couple of hundred metres) and have some recharge by fresh water. This recharge is typically from rivers or meteoric water (precipitation) that percolates into the aquifer through overlying unsaturated materials.
Occasionally, sedimentary or "fossil" aquifers are used to provide irrigation and drinking water to urban areas. In Libya, for example, Muammar Gaddafi's Great Manmade River project has pumped large amounts of groundwater from aquifers beneath the Sahara to populous areas near the coast.[20] Though this has saved Libya money over the alternative, desalination, the aquifers are likely to run dry in 60 to 100 years.[20] Aquifer depletion has been cited as one of the causes of the food price rises of 2011.[21]
Subsidence
In unconsolidated aquifers, groundwater is produced from pore spaces between particles of gravel, sand, and silt. If the aquifer is confined by low-permeability layers, the reduced water pressure in the sand and gravel causes slow drainage of water from the adjoining confining layers. If these confining layers are composed of compressible silt or clay, the loss of water to the aquifer reduces the water pressure in the confining layer, causing it to compress from the weight of overlying geologic materials. In severe cases, this compression can be observed on the ground surface as subsidence. Unfortunately, much of the subsidence from groundwater extraction is permanent (elastic rebound is small). Thus, the subsidence is not only permanent, but the compressed aquifer has a permanently reduced capacity to hold water.
Saltwater intrusion
Aquifers near the coast have a lens of freshwater near the surface and denser seawater under freshwater. Seawater penetrates the aquifer diffusing in from the ocean and is denser than freshwater. For porous (i.e., sandy) aquifers near the coast, the thickness of freshwater atop saltwater is about 12 metres (40 ft) for every 0.3 m (1 ft) of freshwater head above sea level. This relationship is called the Ghyben-Herzberg equation. If too much ground water is pumped near the coast, salt-water may intrude into freshwater aquifers causing contamination of potable freshwater supplies. Many coastal aquifers, such as the Biscayne Aquifer near Miami and the New Jersey Coastal Plain aquifer, have problems with saltwater intrusion as a result of overpumping and sea level rise.
Salination
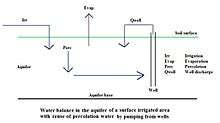
Aquifers in surface irrigated areas in semi-arid zones with reuse of the unavoidable irrigation water losses percolating down into the underground by supplemental irrigation from wells run the risk of salination.[22]
Surface irrigation water normally contains salts in the order of 0.5 g/l or more and the annual irrigation requirement is in the order of 10,000 m3/ha or more so the annual import of salt is in the order of 5,000 kg/ha or more.[23]
Under the influence of continuous evaporation, the salt concentration of the aquifer water may increase continually and eventually cause an environmental problem.
For salinity control in such a case, annually an amount of drainage water is to be discharged from the aquifer by means of a subsurface drainage system and disposed of through a safe outlet. The drainage system may be horizontal (i.e. using pipes, tile drains or ditches) or vertical (drainage by wells). To estimate the drainage requirement, the use of a groundwater model with an agro-hydro-salinity component may be instrumental, e.g. SahysMod.
Examples
The Great Artesian Basin situated in Australia is arguably the largest groundwater aquifer in the world[24] (over 1.7 million km2 or 0.66 million sq mi). It plays a large part in water supplies for Queensland, and some remote parts of South Australia.
The Guarani Aquifer, located beneath the surface of Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay, and Uruguay, is one of the world's largest aquifer systems and is an important source of fresh water.[25] Named after the Guarani people, it covers 1,200,000 km2 (460,000 sq mi), with a volume of about 40,000 km3 (9,600 cu mi), a thickness of between 50 and 800 m (160 and 2,620 ft) and a maximum depth of about 1,800 m (5,900 ft).
Aquifer depletion is a problem in some areas, and is especially critical in northern Africa, for example the Great Manmade River project of Libya. However, new methods of groundwater management such as artificial recharge and injection of surface waters during seasonal wet periods has extended the life of many freshwater aquifers, especially in the United States.
The Ogallala Aquifer of the central United States is one of the world's great aquifers, but in places it is being rapidly depleted by growing municipal use, and continuing agricultural use. This huge aquifer, which underlies portions of eight states, contains primarily fossil water from the time of the last glaciation. Annual recharge, in the more arid parts of the aquifer, is estimated to total only about 10 percent of annual withdrawals. According to a 2013 report by research hydrologist Leonard F. Konikow[26] at the United States Geological Survey (USGS), the depletion between 2001–2008, inclusive, is about 32 percent of the cumulative depletion during the entire 20th century (Konikow 2013:22)."[26] In the United States, the biggest users of water from aquifers include agricultural irrigation and oil and coal extraction.[27] "Cumulative total groundwater depletion in the United States accelerated in the late 1940s and continued at an almost steady linear rate through the end of the century. In addition to widely recognized environmental consequences, groundwater depletion also adversely impacts the long-term sustainability of groundwater supplies to help meet the Nation’s water needs."[26]
An example of a significant and sustainable carbonate aquifer is the Edwards Aquifer[28] in central Texas. This carbonate aquifer has historically been providing high quality water for nearly 2 million people, and even today, is full because of tremendous recharge from a number of area streams, rivers and lakes. The primary risk to this resource is human development over the recharge areas.
Discontinuous sand bodies at the base of the McMurray Formation in the Athabasca Oil Sands region of northeastern Alberta, Canada, are commonly referred to as the Basal Water Sand (BWS) aquifers.[29] Saturated with water, they are confined beneath impermeable bitumen-saturated sands that are exploited to recover bitumen for synthetic crude oil production. Where they are deep-lying and recharge occurs from underlying Devonian formations they are saline, and where they are shallow and recharged by surface water they are non-saline. The BWS typically pose problems for the recovery of bitumen, whether by open-pit mining or by in situ methods such as steam-assisted gravity drainage (SAGD), and in some areas they are targets for waste-water injection.[30][31][32]
See also
- Aquifer storage and recovery
- Aquifer properties
- Artesian aquifer – A confined aquifer containing groundwater under positive pressure
- Cistern – Waterproof receptacle for holding liquids, usually water
- Groundwater – Water located beneath the ground surface
- Groundwater model
- Groundwater pollution – Pollution that occurs when pollutants are released to the ground and seep down into groundwater
- Hydraulic tomography
- Overexploitation – Depleting a renewable resource
- Rock (geology) – Naturally occurring mineral aggregate
- Seasonal thermal energy storage – storage of heat or cold for periods of up to several months - aquifers may be used for storing heat between opposing seasons and for ecologically heating/cooling greenhouses, buildings, and district systems
- Spring (hydrology) – Point at which water emerges from an aquifer to the surface
- Surficial aquifer
References
- "aquitard: Definition from". Answers.com. Archived from the original on 29 September 2010. Retrieved 6 September 2010.
- "Aquifers and Groundwater". USGS.
...more than 30,000 feet. On the average, however, the porosity and permeability of rocks decrease as their depth below land surface increases; the pores and cracks in rocks at great depths are closed or greatly reduced in size because of the weight of overlying rocks.
- "Huge reserves of freshwater lie beneath the ocean floor". Gizmag.com. 11 December 2013. Retrieved 15 December 2013.
- Post, V. E. A.; Groen, J.; Kooi, H.; Person, M.; Ge, S.; Edmunds, W. M. (2013). "Offshore fresh groundwater reserves as a global phenomenon". Nature. 504 (7478): 71–78. doi:10.1038/nature12858. PMID 24305150.
- "Morphological Features of Soil Wetness". Ces.ncsu.edu. Archived from the original on 9 August 2010. Retrieved 6 September 2010.
- The energy balance of groundwater flow applied to subsurface drainage in anisotropic soils by pipes or ditches with entrance resistance. International Institute for Land Reclamation and Improvement (ILRI), Wageningen, The Netherlands. On line : Archived 2009-02-19 at the Wayback Machine . Paper based on: R.J. Oosterbaan, J. Boonstra and K.V.G.K. Rao, 1996, "The energy balance of groundwater flow". Published in V.P.Singh and B.Kumar (eds.), Subsurface-Water Hydrology, pp. 153–60, Vol. 2 of Proceedings of the International Conference on Hydrology and Water Resources, New Delhi, India, 1993. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands. ISBN 978-0-7923-3651-8 . On line : . The corresponding "EnDrain" software can be downloaded from : , or from :
- ILRI (2000), Subsurface drainage by (tube)wells: Well spacing equations for fully and partially penetrating wells in uniform or layered aquifers with or without anisotropy and entrance resistance, 9 pp. Principles used in the "WellDrain" model. International Institute for Land Reclamation and Improvement (ILRI), Wageningen, The Netherlands. On line : . Download "WellDrain" software from : , or from :
- Assaad, Fakhry; LaMoreaux, Philip; Hughes, Travis (2004). Field methods for geologists and hydrogeologists. Berlin, Germany: Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg. doi:10.1007/978-3-662-05438-3. ISBN 978-3-540-40882-6.
- Pettijohn, Francis; Potter, Paul; Siever, Raymond (1987). Sand and Sandstone. New York: Springer Science+Business Media. doi:10.1007/978-1-4612-1066-5. ISBN 978-0-387-96350-1.
- Alley, William; Reilly, Thomas; Franke, O. (1999). Sustainability of ground-water resources. Circular 1186. Denver, Colorado: U.S. Geological Survey. p. 8. doi:10.3133/cir1186. ISBN 978-0-607-93040-5.
- Dreybrodt, Wolfgang (1988). Processes in karst systems: physics, chemistry, and geology. Springer Series in Physical Environment. 4. Berlin: Springer. pp. 2–3. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-83352-6. ISBN 978-3-642-83354-0.
- Taylor, Charles (1997). Delineation of ground-water basins and recharge areas for municipal water-supply springs in a karst aquifer system in the Elizabethtown area, Northern Kentucky (PDF). Water-Resources Investigations Report 96-4254. Denver, Colorado: U.S. Geological Survey. doi:10.3133/wri964254.
- Taylor, Charles; Greene, Earl (2008). "Hydrogeologic characterization and methods used in the investigation of karst hydrology." (PDF). Field Techniques for Estimating Water Fluxes Between Surface Water and Ground Water. Techniques and Methods 4–D2. U.S. Geological Survey. p. 107.
- Renken, R.; Cunningham, K.; Zygnerski, M.; Wacker, M.; Shapiro, A.; Harvey, R.; Metge, D.; Osborn, C.; Ryan, J. (November 2005). "Assessing the Vulnerability of a Municipal Well Field to Contamination in a Karst Aquifer". Environmental and Engineering Geoscience. GeoScienceWorld. 11 (4): 320. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.372.1559. doi:10.2113/11.4.319.
- Fetter, Charles (1988). Applied Hydrology. Columbus, Ohio: Merrill. pp. 294–295. ISBN 978-0-675-20887-1.
- Scanlon, Bridget; Mace, Robert; Barrett, Michael; Smith, Brian (2003). "Can we simulate regional groundwater flow in a karst system using equivalent porous media models? Case study, Barton Springs Edwards aquifer, USA". Journal of Hydrology. Elsevier Science. 276 (1–4): 142. doi:10.1016/S0022-1694(03)00064-7.
- "International Waters". United Nations Development Programme. Archived from the original on 27 January 2009.
- Sanchez, Rosario; Eckstein, Gabriel (2017). "Aquifers Shared Between Mexico and the United States: Management Perspectives and Their Transboundary Nature" (PDF). Groundwater. 55 (4): 495–505. doi:10.1111/gwat.12533.
- https://transboundary.tamu.edu/media/1385/2018_awras_impact.pdf
- Scholl, Adam. "Map Room: Hidden Waters". World Policy journal. Retrieved 19 December 2012.
- Brown, Lester. "The Great Food Crisis of 2011." Foreign Policy Magazine, 10 January 2011.
- ILRI (1989), Effectiveness and Social/Environmental Impacts of Irrigation Projects: a Review (PDF), In: Annual Report 1988 of the International Institute for Land Reclamation and Improvement (ILRI), Wageningen, The Netherlands, pp. 18–34
- ILRI (2003), Drainage for Agriculture: Drainage and hydrology/salinity - water and salt balances. Lecture notes International Course on Land Drainage, International Institute for Land Reclamation and Improvement (ILRI), Wageningen, The Netherlands. Download from : , or directly as PDF :
- "The Great Artesian Basin" (PDF). Facts: Water Series. Queensland Department of Natural Resources and Water. Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 November 2006. Retrieved 3 January 2007.
- Brittain, John (22 June 2015). "The International Atomic Energy Agency: Linking Nuclear Science and Diplomacy". Science and Diplomacy.
- Konikow, Leonard F. Groundwater Depletion in the United States (1900–2008) (PDF) (Report). Scientific Investigations Report. Reston, VA: U.S. Department of the Interior, U.S. Geological Survey. p. 63.
- Zabarenko, Deborah (20 May 2013). "Drop in U.S. underground water levels has accelerated: USGS". Reuters. Washington, DC.
- "Edwards Aquifer Authority". Edwardsaquifer.org. Retrieved 15 December 2013.
- Joslyn North Mine Project: Environmental Impact Assessment Hydrologeology (PDF) (Report). Edmonton, Alberta: Deer Creek Energy. December 2005. p. 4. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 December 2013.
- Barson, D., Bachu, S. and Esslinger, P. 2001. Flow systems in the Mannville Group in the east-central Athabasca area and implications for steam-assisted gravity drainage (SAGD) operations for in situ bitumen production. Bulletin of Canadian Petroleum Geology, vol. 49, no. 3, pp. 376–92.
- Griffiths, Mary; Woynillowicz, Dan (April 2003). Oil and Troubled Waters: Reducing the impact of the oil and gas industry on Alberta’s water resources (PDF) (Report). Edmonton, Alberta: Pembina Institute.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- FMFN (June 2012). Fort McKay’s Review of Teck Resources Ltd. – Frontier Oil Sands Mine Project Integrated Application (PDF) (Report). Fort McKay First Nation.
