Carbonyl sulfide
Carbonyl sulfide is the chemical compound with the linear formula OCS. Normally written as COS as a chemical formula that does not imply its structure, it is a colourless flammable gas with an unpleasant odor. It is a linear molecule consisting of a carbonyl group double bonded to a sulfur atom. Carbonyl sulfide can be considered to be intermediate between carbon dioxide and carbon disulfide, both of which are valence isoelectronic with it.
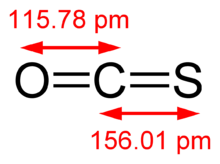 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC names | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.674 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2204 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| COS | |
| Molar mass | 60.075 g/mol |
| Appearance | colorless gas |
| Odor | sulfide-like |
| Density | 2.51 g/L |
| Melting point | −138.8 °C (−217.8 °F; 134.3 K) |
| Boiling point | −50.2 °C (−58.4 °F; 223.0 K) |
| 0.376 g/100 mL (0 °C) 0.125 g/100 mL (25 °C) | |
| Solubility | very soluble in KOH, CS2 soluble in alcohol, toluene |
| -32.4·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| 0.65 D | |
| Thermochemistry | |
Heat capacity (C) |
41.5 J/mol K |
Std molar entropy (S |
231.5 J/mol K |
Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
-141.8 kJ/mol |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | Carbonyl sulfide MSDS |
| GHS pictograms |     |
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
GHS hazard statements |
H220, H280, H315, H319, H331, H335 |
| P210, P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+352, P304+340, P305+351+338, P311, P312, P321, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P377, P381, P403, P403+233, P405, P410+403, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Explosive limits | 12-29% |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds |
Carbon dioxide Carbon disulfide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Carbonyl sulfide decomposes in the presence of humidity and bases to carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide.[2][3][4]
This compound is found to catalyze the formation of peptides from amino acids. This finding is an extension of the Miller–Urey experiment and it is suggested that carbonyl sulfide played a significant role in the origin of life.[5]
Occurrence
Carbonyl sulfide is the most abundant sulfur compound naturally present in the atmosphere, at 0.5±0.05 ppb, because it is emitted from oceans, volcanoes and deep sea vents. As such, it is a significant compound in the global sulfur cycle. Measurements on the Antarctica ice cores and from air trapped in snow above glaciers (firn air) have provided a detailed picture of OCS concentrations from 1640 to the present day and allow an understanding of the relative importance of anthropogenic and non-anthropogenic sources of this gas to the atmosphere.[6] Some carbonyl sulfide that is transported into the stratospheric sulfate layer is oxidized to sulfuric acid.[7] Sulfuric acid forms particulate which affects energy balance due to light scattering.[8] The long atmospheric lifetime of COS makes it the major source of stratospheric sulfate, though sulfur dioxide from volcanic activity can be significant too.[8] Carbonyl sulfide is also removed from the atmosphere by terrestrial vegetation by enzymes associated with the uptake of carbon dioxide during photosynthesis, and by hydrolysis in ocean waters.[9][10] Loss processes, such as these, limit the persistence (or lifetime) of a molecule of COS in the atmosphere to a few years.
The largest man-made sources of carbonyl sulfide release include its primary use as a chemical intermediate and as a byproduct of carbon disulfide production; however, it is also released from automobiles and their tire wear,[11] coal-fired power plants, coking ovens, biomass combustion, fish processing, combustion of refuse and plastics, petroleum manufacture, and manufacture of synthetic fibers, starch, and rubber.[2] The average total worldwide release of carbonyl sulfide to the atmosphere has been estimated at about 3 million tons/year, of which less than one third was related to human activity.[2] It is also a significant sulfur-containing impurity in synthesis gas.
Carbonyl sulfide is present in foodstuffs, such as cheese and prepared vegetables of the cabbage family. Traces of COS are naturally present in grains and seeds in the range of 0.05–0.1 mg·kg−1.
Carbonyl sulfide has been observed in the interstellar medium (see also List of molecules in interstellar space), in comet 67P[12] and in the atmosphere of Venus, where, because of the difficulty of producing COS inorganically, it is considered a possible indicator of life.[13]
Applications
Carbonyl sulfide is used as an intermediate in the production of thiocarbamate herbicides.[3] Carbonyl sulfide is a potential alternative fumigant[14] to methyl bromide and phosphine. In some cases, however, residues on the grain result in flavours that are unacceptable to consumers, e.g. barley used for brewing. Carbonyl sulfide is readily converted to the gaseous signaling molecule hydrogen sulfide by carbonic anhydrase enzymes in plants and mammals. Because of this chemistry, the release of carbonyl sulfide from small organic molecules has been identified as a strategy for delivering hydrogen sulfide in different biological contexts.[15] In ecosystem science, carbonyl sulfide is increasingly often being used to describe the rate of the photosynthesis.[16]
Synthesis
Carbonyl sulfide was first described in 1841,[17] but was apparently mischaracterized as a mixture of carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide. Carl von Than first characterized the substance in 1867. It forms when carbon monoxide reacts with molten sulfur. This reaction reverses above 1200 K (930 °C; 1700 °F). A laboratory synthesis entails the reaction potassium thiocyanate and sulfuric acid. The resulting gas contains significant amounts of byproducts and requires purification.[18]
- KSCN + 2 H
2SO
4 + H
2O → KHSO
4 + NH
4HSO
4 + COS
Hydrolysis of isothiocyanates in hydrochloric acid solution also affords COS.
Toxicity
As of 1994, limited information existed on the acute toxicity of carbonyl sulfide in humans and in animals.[3] High concentrations (>1000 ppm) can cause sudden collapse, convulsions, and death from respiratory paralysis.[2][3] Occasional fatalities have been reported, practically without local irritation or olfactory warning.[3] In tests with rats, 50% animals died when exposed to 1400 ppm of COS for 90 minutes, or at 3000 ppm for 9 minutes.[3] Limited studies with laboratory animals also suggest that continued inhalation of low concentrations (~50 ppm for up to 12 weeks) does not affect the lungs or the heart.[3]
References
- International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (2005). Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry (IUPAC Recommendations 2005). Cambridge (UK): RSC–IUPAC. ISBN 0-85404-438-8. p. 292. Electronic version.
- "Carbonyl Sulfide CASRN: 463-58-1". Hazardous Substances Data Bank. National Library of Medicine.
- "Chemical Summary for Carbonyl Sulfide". U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. 2013-07-19.
- Protoschill-Krebs, G.; Wilhelm, C.; Kesselmeier, J. (1996). "Consumption of carbonyl sulphide (COS) by higher plant carbonic anhydrase (CA)". Atmospheric Environment. 30 (18): 3151–3156. Bibcode:1996AtmEn..30.3151P. doi:10.1016/1352-2310(96)00026-X.
- Leman L, Orgel L, Ghadiri MR (2004). "Carbonyl sulfide-mediated prebiotic formation of peptides". Science. 306 (5694): 283–6. Bibcode:2004Sci...306..283L. doi:10.1126/science.1102722. PMID 15472077.
- Montzka, S. A.; Aydin, M.; Battle, M.; Butler, J. H.; Saltzman, E. S.; Hall, B. D.; Clarke, A. D.; Mondeel, D.; Elkins, J. W. (2004). "A 350-year atmospheric history for carbonyl sulfide inferred from Antarctic firn air and air trapped in ice" (PDF). Journal of Geophysical Research. 109 (D18): 22302. Bibcode:2004JGRD..10922302M. doi:10.1029/2004JD004686. eid D22302.
- Crutzen, P. (1976). "The possible importance of COS for the sulfate layer of the stratosphere". Geophysical Research Letters. 3 (2): 73–76. Bibcode:1976GeoRL...3...73C. doi:10.1029/GL003i002p00073.
- Seinfeld, J. (2006). Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics. London: J. Wiley. ISBN 978-1-60119-595-1.
- Kettle, A. J.; Kuhn, U.; von Hobe, M.; Kesselmeier, J.; Andreae, M. O. (2002). "Global budget of atmospheric carbonyl sulfide: Temporal and spatial variations of the dominant sources and sinks". Journal of Geophysical Research. 107 (D22): 4658. Bibcode:2002JGRD..107.4658K. doi:10.1029/2002JD002187.
- Montzka, S. A.; Calvert, P.; Hall, B. D.; Elkins, J. W.; Conway, T. J.; Tans, P. P.; Sweeney, C. (2007). "On the global distribution, seasonality, and budget of atmospheric carbonyl sulfide (COS) and some similarities to CO2". Journal of Geophysical Research. 112 (D9): 9302. Bibcode:2007JGRD..11209302M. doi:10.1029/2006JD007665. eid D09302.
- Pos W, Berreshein B (1993). "Automotive tire wear as a source for atmospheric OCS and CS2". Geophysical Research Letters. 1 (9): 815–818. Bibcode:1993GeoRL..20..815P. doi:10.1029/93GL00972.
- Rosetta Blog. "OMET'S FIREWORK DISPLAY AHEAD OF PERIHELION". blogs.esa.int. European Space Agency. Retrieved 11 August 2015.
- Landis, G. A. (2003). "Astrobiology: the Case for Venus" (PDF). Journal of the British Interplanetary Society. 56 (7–8): 250–254. Bibcode:2003JBIS...56..250L.
- Bartholomaeus, Andrew; Haritos, Victoria (2005). "Review of the toxicology of carbonyl sulfide, a new grain fumigant". Food and Chemical Toxicology. 43 (12): 1687–1701. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2005.06.016. PMID 16139940.
- Steiger, Andrea K.; Pardue, Sibile; Kevil, Christopher G.; Pluth, Michael D. (2016-06-15). "Self-Immolative Thiocarbamates Provide Access to Triggered H2S Donors and Analyte Replacement Fluorescent Probes". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 138 (23): 7256–7259. doi:10.1021/jacs.6b03780. ISSN 0002-7863. PMC 4911618. PMID 27218691.
- Yakir, Dan; Montzka, Stephen A.; Uri Dicken; Tatarinov, Fyodor; Rotenberg, Eyal; Asaf, David (March 2013). "Ecosystem photosynthesis inferred from measurements of carbonyl sulphide flux". Nature Geoscience. 6 (3): 186–190. Bibcode:2013NatGe...6..186A. doi:10.1038/ngeo1730. ISSN 1752-0908.
- Couërbe, J. P. (1841). "Ueber den Schwefelkohlenstoff". Journal für Praktische Chemie. 23 (1): 83–124. doi:10.1002/prac.18410230105.
- Ferm R. J. (1957). "The Chemistry of Carbonyl Sulfide". Chemical Reviews. 57 (4): 621–640. doi:10.1021/cr50016a002.
Further reading
- Beck, M. T.; Kauffman, G. B. (1985). "COS and C3S2: The Discovery and Chemistry of Two Important Inorganic Sulfur Compounds". Polyhedron. 4 (5): 775–781. doi:10.1016/S0277-5387(00)87025-4.
- Svoronos P. D. N.; Bruno T. J. (2002). "Carbonyl sulfide: A review of its chemistry and properties". Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research. 41 (22): 5321–5336. doi:10.1021/ie020365n.
External links
- Carbonyl sulfide and origins of life
- Carbonyl sulfide as a potential fumigant
- Carbonyl sulfide in the atmosphere

