Brilaroxazine
Brilaroxazine, also known by the developmental code names RP-5063 and RP-5000, is an investigational atypical antipsychotic which is under development by Reviva Pharmaceuticals for the treatment of schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder.[1][2][3][4] Reviva Pharmaceuticals also intends to investigate brilaroxazine for the treatment of bipolar disorder, major depressive disorder, psychosis/agitation associated with Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease psychosis, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADD/ADHD), and autism.[5][6] As of May 2015, it is in phase III clinical trials for schizophrenia.[5][6]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | RP-5063; RP-5000; Oxaripiprazole |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
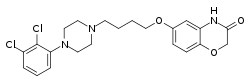
| Formula | C22H25Cl2N3O3 |
| Molar mass | 450.36 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics
Brilaroxazine is described as a so-called "dopamine-serotonin system stabilizer" due to its unique actions on the dopamine and serotonin neurotransmitter systems compared to other antipsychotics.[4][7] Specifically, it acts as a partial agonist of the D2, D3, and D4 receptors and of the 5-HT1A and 5-HT2A receptors, and as an antagonist of the 5-HT6 and 5-HT7 receptors.[3][4][7] Brilaroxazine has high affinity for the D2S, D2L, D3, D4.4, 5-HT1A, 5-HT2A, 5-HT7, and H1 receptors, and moderate affinity for the D1, D5, 5-HT3, 5-HT6 receptors, the serotonin transporter, and the α1B-adrenergic receptor.[7] It lacks significant affinity for the 5-HT1B, 5-HT2C, α2-adrenergic, and muscarinic acetylcholine receptors, as well as for the norepinephrine and dopamine transporters.[7][8]
Chemistry
Brilaroxazine is identical to aripiprazole in chemical structure except for the replacement of one of the carbon atoms in aripiprazole's quinolinone ring system with an oxygen atom, resulting instead in a benzoxazinone ring system. The drug is also closely related structurally to brexpiprazole and cariprazine.
References
- Medicines in Development for Mental Health (PDF) (Report). Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America. 2014. p. 20. Retrieved 2015-05-19.
- Köster, Luisa-Sophie; Carbon, Maren; Correll, Christoph U (2014). "Emerging drugs for schizophrenia: an update". Expert Opinion on Emerging Drugs. 19 (4): 511–531. doi:10.1517/14728214.2014.958148. ISSN 1472-8214. PMID 25234340.
- "Drug Development in Schizophrenia: Summary and Table". Pharmaceutical Medicine. 28 (5): 265–271. 2014. doi:10.1007/s40290-014-0070-6. ISSN 1178-2595.
- Cantillon, Marc (2014). "Efficacy and Safety of Novel Dopamine Serotonin Stabilizer RP 5063 in Acute Schizophrenia and Schizoaffective Disorder". Schizophrenia Research. 153: S22. doi:10.1016/S0920-9964(14)70070-2. ISSN 0920-9964.
- "About Us". Reviva Pharmaceuticals. Retrieved 2015-05-19.
- "Product Pipeline". Reviva Pharmaceuticals. Retrieved 2015-05-19.
- Marc Cantillon, M.D., Mike Li, MS, Sarath Kanekal, Ph.D., DABT, RAC, Robert M.J. Ings, Ph.D., Grace Tung, RAC, Laxminarayan Bhat (2013). "Refresh: A Phase 2 RP5063 Efficacy and Safety in Schizophrenia and Schizoaffective Disorder" (PDF). American Society of Clinical Psychopharmacology. Retrieved 2015-05-19.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- Reviva Pharmaceuticals (2012). "Reviva Pharmaceuticals Announces Enrollment of Patients in Phase 2 Clinical Study of RP5063 for the Treatment of Schizophrenia and Schizoaffective Disorder". PipelineReview.
External links