Broxaterol
Broxaterol is a β2 adrenoreceptor agonist.[1] It is part of a class of drugs that affect the smooth muscle receptors in the body, often in use cases for respiratory disease that respond to this type of treatment.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
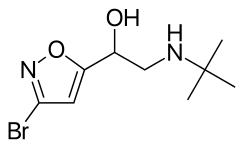
| IUPAC name
1-(3-Bromo-5-isoxazolyl)-2-(tert-butylamino)ethanol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.071.338 |
| MeSH | Broxaterol |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H15BrN2O2 | |
| Molar mass | 263.135 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- Nava S, Crotti P, Gurrieri G, Fracchia C, Rampulla C (January 1992). "Effect of a beta 2-agonist (broxaterol) on respiratory muscle strength and endurance in patients with COPD with irreversible airway obstruction". Chest. 101 (1): 133–40. doi:10.1378/chest.101.1.133. PMID 1345900. Archived from the original on 2013-04-14.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.