Eticlopride
Eticlopride is a selective dopamine antagonist that acts on D2 dopamine receptor. It is primarily used in pharmacological research.[1][2][3][4]
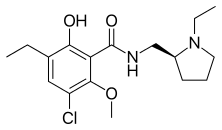 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H25ClN2O3 |
| Molar mass | 340.85 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| | |
References
- "Eticlopride hydrochloride".
- Renee Claytora, Joshua A. Lilea, 1, Michael A. Nader (2006). "The effects of eticlopride and the selective D3-antagonist PNU 99194-A on food- and cocaine-maintained responding in rhesus monkeys". Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior. 83 (3): 456–464. doi:10.1016/j.pbb.2006.03.007. PMID 16631246.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- Hemby, Scott; Smith, James; Dworkin, Steven (1996). "The effects of eticlopride and naltrexone on responding maintained by food, cocaine, heroin and cocaine/heroin combinations in rats". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 277 (3): 1247–1258. PMID 8667185.
- Haile, Colin; Kosten, Therese (2001). "Differential effects of D1- and D2-like compounds on cocaine self-administration in Lewis and Fischer 344 inbred rats". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 299 (2): 509–518. PMID 11602661.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.