Serotonin
Serotonin (/ˌsɛrəˈtoʊnɪn, ˌsɪərə-/[6][7][8]) or 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) is a monoamine neurotransmitter. Its biological function is complex and multifaceted, modulating mood, cognition, reward, learning, memory, and numerous physiological processes such as vomiting and vasoconstriction.[9]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | 5-HT, 5-Hydroxytryptamine, Enteramine, Thrombocytin, 3-(β-Aminoethyl)-5-hydroxyindole, Thrombotonin |
| Physiological data | |
| Source tissues | raphe nuclei, enterochromaffin cells |
| Target tissues | system-wide |
| Receptors | 5-HT1, 5-HT2, 5-HT3, 5-HT4, 5-HT5, 5-HT6, 5-HT7 |
| Agonists | Indirectly: SSRIs, MAOIs |
| Precursor | 5-HTP |
| Biosynthesis | Aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase |
| Metabolism | MAO |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
| PDB ligand | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.054 |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC names
5-Hydroxytryptamine or 3-(2-Aminoethyl)indol-5-ol | |
| Other names
5-Hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT, Enteramine; Thrombocytin, 3-(β-Aminoethyl)-5-hydroxyindole, Thrombotonin | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.054 |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | Serotonin |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H12N2O | |
| Molar mass | 176.215 g/mol |
| Appearance | White powder |
| Melting point | 167.7 °C (333.9 °F; 440.8 K) 121–122 °C (ligroin)[1] |
| Boiling point | 416 ± 30 °C (at 760 Torr)[2] |
| slightly soluble | |
| Acidity (pKa) | 10.16 in water at 23.5 °C[3] |
| 2.98 D | |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | External MSDS |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose) |
750 mg/kg (subcutaneous, rat),[4] 4500 mg/kg (intraperitoneal, rat),[5] 60 mg/kg (oral, rat) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Biochemically, the indoleamine molecule derives from the amino acid tryptophan, via the (rate-limiting) hydroxylation of the 5 position on the ring (forming the intermediate 5-hydroxytryptophan), and then decarboxylation to produce serotonin.[10] Serotonin is primarily found in the enteric nervous system located in the gastrointestinal tract (GI tract). However, it is also produced in the central nervous system (CNS), specifically in the Raphe nuclei located in the brainstem and Merkel cells located in the skin. Additionally, serotonin is stored in blood platelets and is released during agitation and vasoconstriction, where it then acts as an agonist to other platelets.[11]
Approximately 90% of the human body's total serotonin is located in the enterochromaffin cells in the GI tract, where it regulates intestinal movements.[12][13] The serotonin is secreted luminally and basolaterally, which leads to increased serotonin uptake by circulating platelets and activation after stimulation, which gives increased stimulation of myenteric neurons and gastrointestinal motility.[14] The remainder is synthesized in serotonergic neurons of the CNS, where it has various functions. These include the regulation of mood, appetite, and sleep. Serotonin also has some cognitive functions, including memory and learning.
Several classes of antidepressants, such as the SSRIs and the SNRIs among others, interfere with the normal reabsorption of serotonin after it is done with the transmission of the signal, therefore augmenting the neurotransmitter levels in the synapses.
Serotonin secreted from the enterochromaffin cells eventually finds its way out of tissues into the blood. There, it is actively taken up by blood platelets, which store it. When the platelets bind to a clot, they release serotonin, where it can serve as a vasoconstrictor or a vasodilator while regulating hemostasis and blood clotting. In high concentrations, serotonin acts as a vasoconstrictor by contracting endothelial smooth muscle directly or by potentiating the effects of other vasoconstrictors (e.g. angiotensin II, norepinephrine). The vasoconstrictive property is mostly seen in pathologic states affecting the endothelium – such as atherosclerosis or chronic hypertension. In physiologic states, vasodilation occurs through the serotonin mediated release of nitric oxide from endothelial cells. Additionally, it inhibits the release of norepinephrine from adrenergic nerves.[15] Serotonin is also a growth factor for some types of cells, which may give it a role in wound healing. There are various serotonin receptors.
Serotonin is metabolized mainly to 5-HIAA, chiefly by the liver. Metabolism involves first oxidation by monoamine oxidase to the corresponding aldehyde. There follows oxidation by aldehyde dehydrogenase to 5-HIAA, the indole acetic-acid derivative. The latter is then excreted by the kidneys.
Besides mammals, serotonin is found in all bilateral animals including worms and insects,[16] as well as in fungi and in plants. Serotonin's presence in insect venoms and plant spines serves to cause pain, which is a side-effect of serotonin injection.[17] Serotonin is produced by pathogenic amoebae, and its effect in the human gut is diarrhea.[18] Its widespread presence in many seeds and fruits may serve to stimulate the digestive tract into expelling the seeds.[19]
Serotonin is also present in plants as phytoserotonin.[20]
Perception of resource availability
Serotonin mediates the animal's perceptions of resources; in less complex animals, such as some invertebrates, resources simply mean food availability.[21] In plants serotonin synthesis seems to be associated with stress signals.[20] In more complex animals, such as arthropods and vertebrates, resources also can mean social dominance.[22] In response to the perceived abundance or scarcity of resources, an animal's growth, reproduction or mood may be elevated or lowered. This may somewhat depend on how much serotonin the organism has at its disposal.
Cellular effects
In humans, serotonin is a neurotransmitter used throughout the body having action of 14 variants of the serotonin receptor to have diverse effects on mood, anxiety, sleep, appetite, temperature, eating behaviour, sexual behaviour, movements, and gastrointestinal motility.[23] Serotonin is not administered clinically as a drug itself as it is not specific enough. However, drugs that selectively target specific serotonin receptor subtypes are used therapeutically for antidepressant effects; these are called selective serotonin re-uptake inhibitors. They are dependent on serotonin availability in the synapse.[24]
Receptors
The 5-HT receptors, the receptors for serotonin, are located on the cell membrane of nerve cells and other cell types in animals, and mediate the effects of serotonin as the endogenous ligand and of a broad range of pharmaceutical and psychedelic drugs. Except for the 5-HT3 receptor, a ligand-gated ion channel, all other 5-HT receptors are G-protein-coupled receptors (also called seven-transmembrane, or heptahelical receptors) that activate an intracellular second messenger cascade.[25]
Termination
Serotonergic action is terminated primarily via uptake of 5-HT from the synapse. This is accomplished through the specific monoamine transporter for 5-HT, SERT, on the presynaptic neuron. Various agents can inhibit 5-HT reuptake, including cocaine, dextromethorphan (an antitussive), tricyclic antidepressants and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). A 2006 study conducted by the University of Washington suggested that a newly discovered monoamine transporter, known as PMAT, may account for "a significant percentage of 5-HT clearance".[26]
Contrasting with the high-affinity SERT, the PMAT has been identified as a low-affinity transporter, with an apparent Km of 114 micromoles/l for serotonin; approximately 230 times higher than that of SERT. However, the PMAT, despite its relatively low serotonergic affinity, has a considerably higher transport 'capacity' than SERT, "resulting in roughly comparable uptake efficiencies to SERT in heterologous expression systems.”[26] The study also suggests some SSRIs, such as fluoxetine and sertraline anti-depressants, inhibit PMAT but at IC50 values which surpass the therapeutic plasma concentrations by up to four orders of magnitude. Therefore, SSRI monotherapy is "ineffective" in PMAT inhibition. At present, no known pharmaceuticals are known to appreciably inhibit PMAT at normal therapeutic doses. The PMAT also suggestively transports dopamine and norepinephrine, albeit at Km values even higher than that of 5-HT (330–15,000 μmoles/L).[26]
Serotonylation
Serotonin can also signal through a nonreceptor mechanism called serotonylation, in which serotonin modifies proteins.[27] This process underlies serotonin's effects upon platelet-forming cells (thrombocytes) in which it links to the modification of signaling enzymes called GTPases that then trigger the release of vesicle contents by exocytosis.[28] A similar process underlies the pancreatic release of insulin.[27]
The effects of serotonin upon vascular smooth muscle tone (this is the biological function from which serotonin originally got its name) depend upon the serotonylation of proteins involved in the contractile apparatus of muscle cells.[29]
| Receptor | Ki (nM)[30] | Receptor function[Note 1] |
|---|---|---|
| 5-HT1 receptor family signals via Gi/o inhibition of adenylyl cyclase. | ||
| 5-HT1A | 3.17 | Memory (agonists ↓); learning (agonists ↓); anxiety (agonists ↓); depression (agonists ↓); positive, negative, and cognitive symptoms of schizophrenia (partial agonists ↓); analgesia (agonists ↑); aggression (agonists ↓); dopamine release in the prefrontal cortex (agonists ↑); serotonin release and synthesis (agonists ↓) |
| 5-HT1B | 4.32 | Vasoconstriction (agonists ↑); aggression (agonists ↓); bone mass (↓). Serotonin autoreceptor. |
| 5-HT1D | 5.03 | Vasoconstriction (agonists ↑) |
| 5-HT1E | 7.53 | |
| 5-HT1F | 10 | |
| 5-HT2 receptor family signals via Gq activation of phospholipase C. | ||
| 5-HT2A | 11.55 | Psychedelia (agonists ↑); depression (agonists & antagonists ↓); anxiety (antagonists ↓); positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia (antagonists ↓); norepinephrine release from the locus coeruleus (antagonists ↑); glutamate release in the prefrontal cortex (agonists ↑); dopamine in the prefrontal cortex (agonists ↑);[31] urinary bladder contractions (agonists ↑)[32] |
| 5-HT2B | 8.71 | Cardiovascular functioning (agonists increase risk of pulmonary hypertension), empathy (via von Economo neurons[33]) |
| 5-HT2C | 5.02 | Dopamine release into the mesocorticolimbic pathway (agonists ↓); acetylcholine release in the prefrontal cortex (agonists ↑); dopaminergic and noradrenergic activity in the frontal cortex (antagonists ↑);[34] appetite (agonists ↓); antipsychotic effects (agonists ↑); antidepressant effects (agonists & antagonists ↑) |
| Other 5-HT receptors | ||
| 5-HT3 | 593 | Emesis (agonists ↑); anxiolysis (antagonists ↑). |
| 5-HT4 | 125.89 | Movement of food across the GI tract (agonists ↑); memory & learning (agonists ↑); antidepressant effects (agonists ↑). Signalling via Gαs activation of adenylyl cyclase. |
| 5-HT5A | 251.2 | Memory consolidation.[35] Signals via Gi/o inhibition of adenylyl cyclase. |
| 5-HT6 | 98.41 | Cognition (antagonists ↑); antidepressant effects (agonists & antagonists ↑); anxiogenic effects (antagonists ↑[36]). Gs signalling via activating adenylyl cyclase. |
| 5-HT7 | 8.11 | Cognition (antagonists ↑); antidepressant effects (antagonists ↑). Acts by Gs signalling via activating adenylyl cyclase. |
Nervous system
The neurons of the raphe nuclei are the principal source of 5-HT release in the brain.[37] There are nine raphe nuclei, designated B1-B9, which contain the majority of serotonin-containing neurons (some scientists chose to group the nuclei raphes lineares into one nucleus), all of which are located along the midline of the brainstem, and centered on the reticular formation.[38][39] Axons from the neurons of the raphe nuclei form a neurotransmitter system reaching almost every part of the central nervous system. Axons of neurons in the lower raphe nuclei terminate in the cerebellum and spinal cord, while the axons of the higher nuclei spread out in the entire brain.
Ultrastructure and function
The serotonin nuclei may also be divided into two main groups, the rostral and caudal containing three and four nuclei respectively. The rostral group consists of the caudal linear nuclei (B8), the dorsal raphe nuclei (B6 and B7) and the median raphe nuclei (B5, B8 and B9), that project into multiple cortical and subcortical structures. The caudal group consists of the nucleus raphe magnus (B3), raphe obscurus nucleus (B2), raphe pallidus nucleus (B1), and lateral medullary reticular formation, that project into the brainstem.[40]
The serotonergic pathway is involved in sensorimotor function, with pathways projecting both into cortical (Dorsal and Median Raphe Nuclei), subcortical, and spinal areas involved in motor activity. Pharmacological manipulation suggests that serotonergic activity increases with motor activity while firing rates of serotonergic neurons increase with intense visual stimuli. The descending projections form a pathway that inhibits pain called the "descending inhibitory pathway" that may be relevant to a disorder such as fibromyalgia, migraine, and other pain disorders, and the efficacy of antidepressants in them.[41]
Serotonergic projections from the caudal nuclei are involved in regulating mood and emotion, and hypo-[42] or hyper-serotonergic[43] states may be involved in depression and sickness behavior.
Microanatomy
Serotonin is released into the synapse, or space between neurons, and diffuses over a relatively wide gap (>20 nm) to activate 5-HT receptors located on the dendrites, cell bodies, and presynaptic terminals of adjacent neurons.
When humans smell food, dopamine is released to increase the appetite. But, unlike in worms, serotonin does not increase anticipatory behaviour in humans; instead, the serotonin released while consuming activates 5-HT2C receptors on dopamine-producing cells. This halts their dopamine release, and thereby serotonin decreases appetite. Drugs that block 5-HT2C receptors make the body unable to recognize when it is no longer hungry or otherwise in need of nutrients, and are associated with weight gain,[44] especially in people with a low number of receptors.[45] The expression of 5-HT2C receptors in the hippocampus follows a diurnal rhythm,[46] just as the serotonin release in the ventromedial nucleus, which is characterised by a peak at morning when the motivation to eat is strongest.[47]
In macaques, alpha males have twice the level of serotonin in the brain as subordinate males and females (measured by the concentration of 5-HIAA in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)). Dominance status and CSF serotonin levels appear to be positively correlated. When dominant males were removed from such groups, subordinate males begin competing for dominance. Once new dominance hierarchies were established, serotonin levels of the new dominant individuals also increased to double those in subordinate males and females. The reason why serotonin levels are only high in dominant males, but not dominant females has not yet been established.[48]
In humans, levels of 5-HT1A receptor inhibition in the brain show negative correlation with aggression,[49] and a mutation in the gene that codes for the 5-HT2A receptor may double the risk of suicide for those with that genotype.[50] Serotonin in the brain is not usually degraded after use, but is collected by serotonergic neurons by serotonin transporters on their cell surfaces. Studies have revealed nearly 10% of total variance in anxiety-related personality depends on variations in the description of where, when and how many serotonin transporters the neurons should deploy.[51]
Psychological influences
Serotonin has been implicated in cognition, mood, anxiety and psychosis, but strong clarity has not been achieved.[52][53]
Serotonin and its role in autism spectrum disorder (ASD)
In regards to research for neurotransmitters and effects on patients with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), 5-HT has been studied the most in terms of research efforts and investigations.[54] As noted, 5-HT signaling does facilitate many neural processes including that of neurogenesis, cell migration and survival, synaptogenesis, and synaptic plasticity.[54] It was noted that 45% of tested ASD subjects contained high levels of 5-HT in their blood.[54] In addition, investigations performed on ASD-like animal models reported that hyperserotonemia significantly reduced the motivation for social interest through inhibition of separation distress, which could be related in the ASD patients that have social impairments.[54]
Outside the nervous system
In the digestive tract (emetic)
Serotonin regulates gastrointestinal function. The gut is surrounded by enterochromaffin cells, which release serotonin in response to food in the lumen. This makes the gut contract around the food. Platelets in the veins draining the gut collect excess serotonin. There are often serotonin abnormalities in gastrointestinal disorders such as constipation and irritable bowel syndrome.[23]
If irritants are present in the food, the enterochromaffin cells release more serotonin to make the gut move faster, i.e., to cause diarrhea, so the gut is emptied of the noxious substance. If serotonin is released in the blood faster than the platelets can absorb it, the level of free serotonin in the blood is increased. This activates 5-HT3 receptors in the chemoreceptor trigger zone that stimulate vomiting.[55] Thus, drugs and toxins stimulate serotonin release from enterochromaffin cells in the gut wall. The enterochromaffin cells not only react to bad food but are also very sensitive to irradiation and cancer chemotherapy. Drugs that block 5HT3 are very effective in controlling the nausea and vomiting produced by cancer treatment, and are considered the gold standard for this purpose.[56]
Bone metabolism
In mice and humans, alterations in serotonin levels and signalling have been shown to regulate bone mass.[57][58][59][60] Mice that lack brain serotonin have osteopenia, while mice that lack gut serotonin have high bone density. In humans, increased blood serotonin levels have been shown to be significant negative predictor of low bone density. Serotonin can also be synthesized, albeit at very low levels, in the bone cells. It mediates its actions on bone cells using three different receptors. Through 5-HT1B receptors, it negatively regulates bone mass, while it does so positively through 5-HT2B receptors and 5-HT2C receptors. There is very delicate balance between physiological role of gut serotonin and its pathology. Increase in the extracellular content of serotonin results in a complex relay of signals in the osteoblasts culminating in FoxO1/ Creb and ATF4 dependent transcriptional events.[61] Very recently following the seminal finidings that gut serotonin regulates bone mass in 2008, the mechanistic investigations into what regulates serotonin synthesis from the gut in the regulation of bone mass have started. Piezzo1 has been shown to sense RNA in the gut and relay this information through serotonin synthesis to the bone. This study by Sugisawa et al., showed that cation channel Piezo1 in the gut acts as a sensor of single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) governing 5-HT production. Intestinal epithelium-specific deletion of mouse Piezo1 profoundly disturbed gut peristalsis, impeded experimental colitis, and suppressed serum 5-HT levels. Because of systemic 5-HT deficiency, conditional knockout of Piezo1 increased bone formation. Notably, fecal ssRNA was identified as a natural Piezo1 ligand, and ssRNA-stimulated 5-HT synthesis from the gut was evoked in a MyD88/TRIF-independent manner. Colonic infusion of RNase A suppressed gut motility and increased bone mass. These findings suggest gut ssRNA as a master determinant of systemic 5-HT levels, indicating the ssRNA-Piezo1 axis as a potential prophylactic target for treatment of bone and gut disorders. These studies of Yadav et al., Cell 2008, Nat Med 2010 and more recently Sugisawa et al., Cell 2019 have opened a new area of serotonin research in bone metabolism that can be potentially harnessed to treat bone mass disorders.[62]
Organ development
Since serotonin signals resource availability it is not surprising that it affects organ development. Many human and animal studies have shown that nutrition in early life can influence, in adulthood, such things as body fatness, blood lipids, blood pressure, atherosclerosis, behavior, learning, and longevity.[63][64][65] Rodent experiment shows that neonatal exposure to SSRIs makes persistent changes in the serotonergic transmission of the brain resulting in behavioral changes,[66][67] which are reversed by treatment with antidepressants.[68] By treating normal and knockout mice lacking the serotonin transporter with fluoxetine scientists showed that normal emotional reactions in adulthood, like a short latency to escape foot shocks and inclination to explore new environments were dependent on active serotonin transporters during the neonatal period.[69][70]
Human serotonin can also act as a growth factor directly. Liver damage increases cellular expression of 5-HT2A and 5-HT2B receptors, mediating liver compensatory regrowth (see Liver § Regeneration and transplantation)[71] Serotonin present in the blood then stimulates cellular growth to repair liver damage.[72] 5HT2B receptors also activate osteocytes, which build up bone[73] However, serotonin also inhibits osteoblasts, through 5-HT1B receptors.[74]
Cardiovascular growth factor
Serotonin, in addition, evokes endothelial nitric oxide synthase activation and stimulates, through a 5-HT1B receptor-mediated mechanism, the phosphorylation of p44/p42 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in bovine aortic endothelial cell cultures.[75] In blood, serotonin is collected from plasma by platelets, which store it. It is thus active wherever platelets bind in damaged tissue, as a vasoconstrictor to stop bleeding, and also as a fibrocyte mitotic (growth factor), to aid healing.[76]
Skin
Serotonin is also produced by Merkel cells which are part of the somatosensory system.[77]
Pharmacology
Several classes of drugs target the 5-HT system, including some antidepressants, antipsychotics, anxiolytics, antiemetics, and antimigraine drugs, as well as, the psychedelic drugs and empathogens.
Mechanism of action
At rest, serotonin is stored within the vesicles of presynaptic neurons. When stimulated by nerve impulses, serotonin is released as a neurotransmitter into the synapse, reversibly binding to the postsynaptic receptor to induce a nerve impulse on the postsynaptic neuron. Serotonin can also bind to auto-receptors on the presynaptic neuron to regulate the synthesis and release of serotonin. Normally serotonin is taken back into the presynaptic neuron to stop its action, then reused or broken down by monoamine oxidase.[78]
Psychedelic drugs
The serotonergic psychedelic drugs psilocin/psilocybin, DMT, mescaline, psychedelic mushroom and LSD are agonists, primarily at 5HT2A/2C receptors.[79][80][81] The empathogen-entactogen MDMA releases serotonin from synaptic vesicles of neurons.[82]
Antidepressants
Drugs that alter serotonin levels are used in treating depression, generalized anxiety disorder, and social phobia. Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) prevent the breakdown of monoamine neurotransmitters (including serotonin), and therefore increase concentrations of the neurotransmitter in the brain. MAOI therapy is associated with many adverse drug reactions, and patients are at risk of hypertensive emergency triggered by foods with high tyramine content, and certain drugs. Some drugs inhibit the re-uptake of serotonin, making it stay in the synaptic cleft longer. The tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) inhibit the reuptake of both serotonin and norepinephrine. The newer selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) have fewer side-effects and fewer interactions with other drugs.[83]
Certain SSRI medications have been shown to lower serotonin levels below the baseline after chronic use, despite initial increases.[84] The 5-HTTLPR gene codes for the number of serotonin transporters in the brain, with more serotonin transporters causing decreased duration and magnitude of serotonergic signaling.[85] The 5-HTTLPR polymorphism (l/l) causing more serotonin transporters to be formed is also found to be more resilient against depression and anxiety.[86][87]
Serotonin syndrome
Extremely high levels of serotonin can cause a condition known as serotonin syndrome, with toxic and potentially fatal effects. In practice, such toxic levels are essentially impossible to reach through an overdose of a single antidepressant drug, but require a combination of serotonergic agents, such as an SSRI with an MAOI.[88] The intensity of the symptoms of serotonin syndrome vary over a wide spectrum, and the milder forms are seen even at nontoxic levels.[89]
Antiemetics
Some 5-HT3 antagonists, such as ondansetron, granisetron, and tropisetron, are important antiemetic agents. They are particularly important in treating the nausea and vomiting that occur during anticancer chemotherapy using cytotoxic drugs. Another application is in the treatment of postoperative nausea and vomiting.
Other
Some serotonergic agonist drugs cause fibrosis anywhere in the body, particularly the syndrome of retroperitoneal fibrosis, as well as cardiac valve fibrosis.[90] In the past, three groups of serotonergic drugs have been epidemiologically linked with these syndromes. These are the serotonergic vasoconstrictive antimigraine drugs (ergotamine and methysergide),[90] the serotonergic appetite suppressant drugs (fenfluramine, chlorphentermine, and aminorex), and certain anti-Parkinsonian dopaminergic agonists, which also stimulate serotonergic 5-HT2B receptors. These include pergolide and cabergoline, but not the more dopamine-specific lisuride.[91]
As with fenfluramine, some of these drugs have been withdrawn from the market after groups taking them showed a statistical increase of one or more of the side effects described. An example is pergolide. The drug was declining in use since it was reported in 2003 to be associated with cardiac fibrosis.[92]
Two independent studies published in The New England Journal of Medicine in January 2007 implicated pergolide, along with cabergoline, in causing valvular heart disease.[93][94] As a result of this, the FDA removed pergolide from the United States market in March 2007.[95] (Since cabergoline is not approved in the United States for Parkinson's Disease, but for hyperprolactinemia, the drug remains on the market. Treatment for hyperprolactinemia requires lower doses than that for Parkinson's Disease, diminishing the risk of valvular heart disease).[96]
Methyl-tryptamines and hallucinogens
Several plants contain serotonin together with a family of related tryptamines that are methylated at the amino (NH2) and (OH) groups, are N-oxides, or miss the OH group. These compounds do reach the brain, although some portion of them are metabolized by monoamine oxidase enzymes (mainly MAO-A) in the liver. Examples are plants from the genus Anadenanthera that are used in the hallucinogenic yopo snuff. These compounds are widely present in the leaves of many plants, and may serve as deterrents for animal ingestion. Serotonin occurs in several mushrooms of the genus Panaeolus.[97]
Comparative biology and evolution
Unicellular organisms
Serotonin is used by a variety of single-cell organisms for various purposes. SSRIs have been found to be toxic to algae.[98] The gastrointestinal parasite Entamoeba histolytica secretes serotonin, causing a sustained secretory diarrhea in some people.[18][99] Patients infected with E. histolytica have been found to have highly elevated serum serotonin levels, which returned to normal following resolution of the infection.[100] E. histolytica also responds to the presence of serotonin by becoming more virulent.[101] This means serotonin secretion not only serves to increase the spread of enteamoebas by giving the host diarrhea but also serves to coordinate their behaviour according to their population density, a phenomenon known as quorum sensing. Outside the gut of a host, there is nothing that the entoamoebas provoke to release serotonin, hence the serotonin concentration is very low. Low serotonin signals to the entoamoebas they are outside a host and they become less virulent to conserve energy. When they enter a new host, they multiply in the gut, and become more virulent as the enterochromaffine cells get provoked by them and the serotonin concentration increases.
Plants
In drying seeds, serotonin production is a way to get rid of the buildup of poisonous ammonia. The ammonia is collected and placed in the indole part of L-tryptophan, which is then decarboxylated by tryptophan decarboxylase to give tryptamine, which is then hydroxylated by a cytochrome P450 monooxygenase, yielding serotonin.[102]
However, since serotonin is a major gastrointestinal tract modulator, it may be produced by plants in fruits as a way of speeding the passage of seeds through the digestive tract, in the same way as many well-known seed and fruit associated laxatives. Serotonin is found in mushrooms, fruits, and vegetables. The highest values of 25–400 mg/kg have been found in nuts of the walnut (Juglans) and hickory (Carya) genera. Serotonin concentrations of 3–30 mg/kg have been found in plantains, pineapples, banana, kiwifruit, plums, and tomatoes. Moderate levels from 0.1–3 mg/kg have been found in a wide range of tested vegetables.[19]
Serotonin is one compound of the poison contained in stinging nettles (Urtica dioica), where it causes pain on injection in the same manner as its presence in insect venoms (see below). It is also naturally found in Paramuricea clavata, or the Red Sea Fan.[103]
Serotonin and tryptophan have been found in chocolate with varying cocoa contents. The highest serotonin content (2.93 µg/g) was found in chocolate with 85% cocoa, and the highest tryptophan content (13.27–13.34 µg/g) was found in 70–85% cocoa. The intermediate in the synthesis from tryptophan to serotonin, 5-hydroxytryptophan, was not found.[104]
Invertebrates
Serotonin functions as a neurotransmitter in the nervous systems of most animals. For example, in the roundworm Caenorhabditis elegans, which feeds on bacteria, serotonin is released as a signal in response to positive events, such as finding a new source of food or in male animals finding a female with which to mate.[105] When a well-fed worm feels bacteria on its cuticle, dopamine is released, which slows it down; if it is starved, serotonin also is released, which slows the animal down further. This mechanism increases the amount of time animals spend in the presence of food.[106] The released serotonin activates the muscles used for feeding, while octopamine suppresses them.[107] Serotonin diffuses to serotonin-sensitive neurons, which control the animal's perception of nutrient availability.
If lobsters are injected with serotonin, they behave like dominant individuals whereas octopamine causes subordinate behavior.[22] A crayfish that is frightened may flip its tail to flee, and the effect of serotonin on this behavior depends largely on the animal's social status. Serotonin inhibits the fleeing reaction in subordinates, but enhances it in socially dominant or isolated individuals. The reason for this is social experience alters the proportion between serotonin receptors (5-HT receptors) that have opposing effects on the fight-or-flight response. The effect of 5-HT1 receptors predominates in subordinate animals, while 5-HT2 receptors predominates in dominants.[108]
Insects
Serotonin is evolutionarily conserved and appears across the animal kingdom. It is seen in insect processes in roles similar to in the human central nervous system, such as memory, appetite, sleep, and behavior.[109][16] Locust swarming is mediated by serotonin, by transforming social preference from aversion to a gregarious state that enables coherent groups.[110] Learning in flies and honeybees is affected by the presence of serotonin.[111][112] Insect 5-HT receptors have similar sequences to the vertebrate versions, but pharmacological differences have been seen. Invertebrate drug response has been far less characterized than mammalian pharmacology and the potential for species selective insecticides has been discussed.[113]
Wasps and hornets have serotonin in their venom,[114] which causes pain and inflammation.[17] as do scorpions.[115]
If flies are fed serotonin, they are more aggressive; flies depleted of serotonin still exhibit aggression, but they do so much less frequently.[116]
Growth and reproduction
In the nematode C. elegans, artificial depletion of serotonin or the increase of octopamine cues behavior typical of a low-food environment: C. elegans becomes more active, and mating and egg-laying are suppressed, while the opposite occurs if serotonin is increased or octopamine is decreased in this animal.[21] Serotonin is necessary for normal nematode male mating behavior,[117] and the inclination to leave food to search for a mate.[118] The serotonergic signaling used to adapt the worm's behaviour to fast changes in the environment affects insulin-like signaling and the TGF beta signaling pathway,[119] which control long-term adaption.
In the fruit fly insulin both regulates blood sugar as well as acting as a growth factor. Thus, in the fruit fly, serotonergic neurons regulate the adult body size by affecting insulin secretion.[120][121] Serotonin has also been identified as the trigger for swarm behavior in locusts.[122] In humans, though insulin regulates blood sugar and IGF regulates growth, serotonin controls the release of both hormones, modulating insulin release from the beta cells in the pancreas through serotonylation of GTPase signaling proteins.[27] Exposure to SSRIs during Pregnancy reduces fetal growth.[123]
Genetically altered C. elegans worms that lack serotonin have an increased reproductive lifespan, may become obese, and sometimes present with arrested development at a dormant larval state.[124][125]
Aging and age-related phenotypes
Serotonin is known to regulate aging, learning and memory. The first evidence comes from the study of longevity in C. elegans.[119] During early phase of aging, the level of serotonin increases, which alters locomotory behaviors and associative memory.[126] The effect is restored by mutations and drugs (including mianserin and methiothepin) that inhibit serotonin receptors. The observation does not contradict with the notion that the serotonin level goes down in mammals and humans, which is typically seen in late but not early phase of aging.
Biochemical mechanisms
Biosynthesis
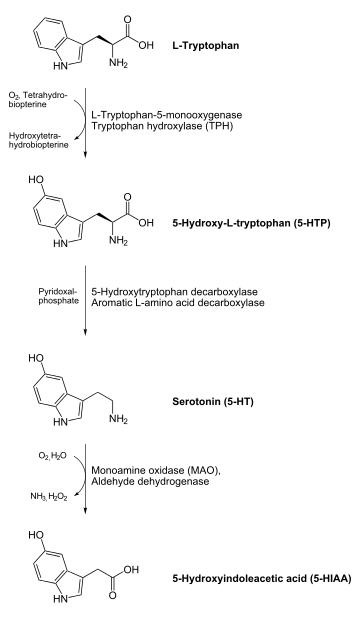
In animals including humans, serotonin is synthesized from the amino acid L-tryptophan by a short metabolic pathway consisting of two enzymes, tryptophan hydroxylase (TPH) and aromatic amino acid decarboxylase (DDC), and the coenzyme pyridoxal phosphate. The TPH-mediated reaction is the rate-limiting step in the pathway. TPH has been shown to exist in two forms: TPH1, found in several tissues, and TPH2, which is a neuron-specific isoform.[127]
Serotonin can be synthesized from tryptophan in the lab using Aspergillus niger and Psilocybe coprophila as catalysts. The first phase to 5-hydroxytryptophan would require letting tryptophan sit in ethanol and water for 7 days, then mixing in enough HCl (or other acid) to bring the pH to 3, and then adding NaOH to make a pH of 13 for 1 hour. Asperigillus niger would be the catalyst for this first phase. The second phase to synthesizing tryptophan itself from the 5-hydroxytryptophan intermediate would require adding ethanol and water, and letting sit for 30 days this time. The next two steps would be the same as the first phase: adding HCl to make the pH = 3, and then adding NaOH to make the pH very basic at 13 for 1 hour. This phase uses the Psilocybe coprophila as the catalyst for the reaction.[128]
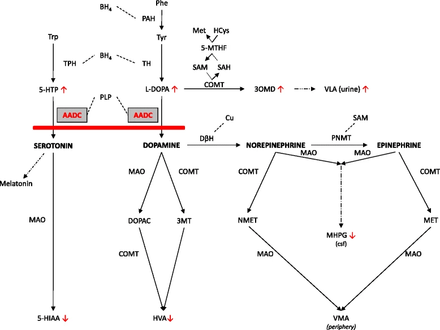
Serotonin taken orally does not pass into the serotonergic pathways of the central nervous system, because it does not cross the blood–brain barrier.[9] However, tryptophan and its metabolite 5-hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP), from which serotonin is synthesized, does cross the blood–brain barrier. These agents are available as dietary supplements, and may be effective serotonergic agents. One product of serotonin breakdown is 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA), which is excreted in the urine. Serotonin and 5-HIAA are sometimes produced in excess amounts by certain tumors or cancers, and levels of these substances may be measured in the urine to test for these tumors.
Effects of food content
Consuming purified tryptophan increases brain serotonin whereas eating foods containing tryptophan does not.[129] This is because the transport system which brings tryptophan across the blood-brain barrier is also selective for the other amino acids contained in protein sources.[9] High plasma levels of other large neutral amino acids compete for transport and prevent the elevated plasma tryptophan from increasing serotonin synthesis.
History and etymology
In 1935, Italian Vittorio Erspamer showed an extract from enterochromaffin cells made intestines contract. Some believed it contained adrenaline, but two years later, Erspamer was able to show it was a previously unknown amine, which he named "enteramine".[130] In 1948, Maurice M. Rapport, Arda Green, and Irvine Page of the Cleveland Clinic discovered a vasoconstrictor substance in blood serum, and since it was a serum agent affecting vascular tone, they named it serotonin.[131]
In 1952, enteramine was shown to be the same substance as serotonin, and as the broad range of physiological roles was elucidated, the abbreviation 5-HT of the proper chemical name 5-hydroxytryptamine became the preferred name in the pharmacological field.[132] Synonyms of serotonin include: 5-hydroxytriptamine, thrombotin, enteramin, substance DS, and 3-(β-Aminoethyl)-5-hydroxyindole.[133] In 1953, Betty Twarog and Page discovered serotonin in the central nervous system.[134]
See also
Notes
- References for the functions of these receptors are available on the wikipedia pages for the specific receptor in question
References
- Pietra S (1958). "[Indolic derivatives. II. A new way to synthesize serotonin]". Il Farmaco; Edizione Scientifica (in Italian). 13 (1): 75–9. PMID 13524273.
- Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software V11.02 (©1994–2011 ACD/Labs)
- Mazák K, Dóczy V, Kökösi J, Noszál B (April 2009). "Proton speciation and microspeciation of serotonin and 5-hydroxytryptophan". Chemistry & Biodiversity. 6 (4): 578–90. doi:10.1002/cbdv.200800087. PMID 19353542.
- Erspamer V (1952). "Ricerche preliminari sulle indolalchilamine e sulle fenilalchilamine degli estratti di pelle di Anfibio". Ricerca Scientifica. 22: 694–702.
- Tammisto T (1967). "Increased toxicity of 5-hydroxytryptamine by ethanol in rats and mice". Annales Medicinae Experimentalis et Biologiae Fenniae. 46 (3, Pt. 2): 382–4.
- Jones D (2003) [1917], Roach P, Hartmann J, Setter J (eds.), English Pronouncing Dictionary, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-3-12-539683-8
- "Serotonin". Dictionary.com Unabridged. Random House.
- "Serotonin". Merriam-Webster Dictionary.
- Young SN (November 2007). "How to increase serotonin in the human brain without drugs". Journal of Psychiatry & Neuroscience. 32 (6): 394–9. PMC 2077351. PMID 18043762.
- González-Flores D, Velardo B, Garrido M, González-Gómez D, Lozano M, Ayuso MC, Barriga C, Paredes SD, Rodríguez AB (2011). "Ingestion of Japanese plums (Prunus salicina Lindl. cv. Crimson Globe) increases the urinary 6-sulfatoxymelatonin and total antioxidant capacity levels in young, middle-aged and elderly humans: Nutritional and functional characterization of their content". Journal of Food and Nutrition Research. 50 (4): 229–236.
- Schlienger RG, Meier CR (2003). "Effect of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors on platelet activation: can they prevent acute myocardial infarction?". American Journal of Cardiovascular Drugs : Drugs, Devices, and Other Interventions. 3 (3): 149–62. doi:10.2165/00129784-200303030-00001. PMID 14727927.
- King MW. "Serotonin". The Medical Biochemistry Page. Indiana University School of Medicine. Retrieved 1 December 2009.
- Berger M, Gray JA, Roth BL (2009). "The expanded biology of serotonin". Annual Review of Medicine. 60: 355–66. doi:10.1146/annurev.med.60.042307.110802. PMC 5864293. PMID 19630576.
- Yano JM, Yu K, Donaldson GP, Shastri GG, Ann P, Ma L, Nagler CR, Ismagilov RF, Mazmanian SK, Hsiao EY (April 2015). "Indigenous bacteria from the gut microbiota regulate host serotonin biosynthesis". Cell. 161 (2): 264–76. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2015.02.047. PMC 4393509. PMID 25860609.
- Vanhoutte PM (February 1987). "Serotonin and the vascular wall". International Journal of Cardiology. 14 (2): 189–203. doi:10.1016/0167-5273(87)90008-8. PMID 3818135.
- Huser A, Rohwedder A, Apostolopoulou AA, Widmann A, Pfitzenmaier JE, Maiolo EM, Selcho M, Pauls D, von Essen A, Gupta T, Sprecher SG, Birman S, Riemensperger T, Stocker RF, Thum AS (2012). "The serotonergic central nervous system of the Drosophila larva: anatomy and behavioral function". PLOS One. 7 (10): e47518. Bibcode:2012PLoSO...747518H. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0047518. PMC 3474743. PMID 23082175.
- Chen J, Lariviere WR (2010). "The nociceptive and anti-nociceptive effects of bee venom injection and therapy: a double-edged sword". Progress in Neurobiology. 92 (2): 151–83. doi:10.1016/j.pneurobio.2010.06.006. PMC 2946189. PMID 20558236.
- McGowan K, Kane A, Asarkof N, Wicks J, Guerina V, Kellum J, Baron S, Gintzler AR, Donowitz M (August 1983). "Entamoeba histolytica causes intestinal secretion: role of serotonin". Science. 221 (4612): 762–4. Bibcode:1983Sci...221..762M. doi:10.1126/science.6308760. PMID 6308760.
- Feldman JM, Lee EM (October 1985). "Serotonin content of foods: effect on urinary excretion of 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid". The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 42 (4): 639–43. doi:10.1093/ajcn/42.4.639. PMID 2413754.
- Ramakrishna A, Giridhar P, Ravishankar GA (2011). "Phytoserotonin: a review". Plant Signaling & Behavior. 6 (6): 800–9. doi:10.4161/psb.6.6.15242. PMC 3218476. PMID 21617371.
- Srinivasan S, Sadegh L, Elle IC, Christensen AG, Faergeman NJ, Ashrafi K (June 2008). "Serotonin regulates C. elegans fat and feeding through independent molecular mechanisms". Cell Metabolism. 7 (6): 533–44. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2008.04.012. PMC 2495008. PMID 18522834.
- Kravitz EA (September 1988). "Hormonal control of behavior: amines and the biasing of behavioral output in lobsters". Science. 241 (4874): 1775–81. Bibcode:1988Sci...241.1775K. doi:10.1126/science.2902685. PMID 2902685.
- Beattie, D. T.; Smith, J. A. M. (9 April 2008). "Serotonin pharmacology in the gastrointestinal tract: a review". Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology. 377 (3): 181–203. doi:10.1007/s00210-008-0276-9. PMID 18398601.
- Sangkuhl, K; Klein, TE; Altman, RB (November 2009). "Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors pathway". Pharmacogenetics and Genomics. 19 (11): 907–9. doi:10.1097/FPC.0b013e32833132cb. PMC 2896866. PMID 19741567.
- Hannon J, Hoyer D (December 2008). "Molecular biology of 5-HT receptors". Behavioural Brain Research. 195 (1): 198–213. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2008.03.020. PMID 18571247.
- Zhou M, Engel K, Wang J (January 2007). "Evidence for significant contribution of a newly identified monoamine transporter (PMAT) to serotonin uptake in the human brain". Biochemical Pharmacology. 73 (1): 147–54. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2006.09.008. PMC 1828907. PMID 17046718.
- Paulmann N, Grohmann M, Voigt JP, Bert B, Vowinckel J, Bader M, Skelin M, Jevsek M, Fink H, Rupnik M, Walther DJ (October 2009). O'Rahilly S (ed.). "Intracellular serotonin modulates insulin secretion from pancreatic beta-cells by protein serotonylation". PLOS Biology. 7 (10): e1000229. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1000229. PMC 2760755. PMID 19859528.
- Walther DJ, Peter JU, Winter S, Höltje M, Paulmann N, Grohmann M, Vowinckel J, Alamo-Bethencourt V, Wilhelm CS, Ahnert-Hilger G, Bader M (December 2003). "Serotonylation of small GTPases is a signal transduction pathway that triggers platelet alpha-granule release". Cell. 115 (7): 851–62. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(03)01014-6. PMID 14697203.
- Watts SW, Priestley JR, Thompson JM (May 2009). "Serotonylation of vascular proteins important to contraction". PLOS One. 4 (5): e5682. Bibcode:2009PLoSO...4.5682W. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0005682. PMC 2682564. PMID 19479059.
- Roth BL, Driscol J (12 January 2011). "PDSP Ki Database". Psychoactive Drug Screening Program (PDSP). University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and the United States National Institute of Mental Health. Archived from the original on 8 November 2013. Retrieved 17 December 2013.
- Bortolozzi A, Díaz-Mataix L, Scorza MC, Celada P, Artigas F (December 2005). "The activation of 5-HT receptors in prefrontal cortex enhances dopaminergic activity". Journal of Neurochemistry. 95 (6): 1597–607. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2005.03485.x. hdl:10261/33026. PMID 16277612.
- Moro C, Edwards L, Chess-Williams R (November 2016). "2Areceptor enhancement of contractile activity of the porcine urothelium and lamina propria". International Journal of Urology. 23 (11): 946–951. doi:10.1111/iju.13172. PMID 27531585.
- "Von Economo neuron – NeuronBank". neuronbank.org.
- Millan MJ, Gobert A, Lejeune F, et al. (September 2003). "The novel melatonin agonist agomelatine (S20098) is an antagonist at 5-hydroxytryptamine2C receptors, blockade of which enhances the activity of frontocortical dopaminergic and adrenergic pathways". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 306 (3): 954–64. doi:10.1124/jpet.103.051797. PMID 12750432.
- Gonzalez R, Chávez-Pascacio K, Meneses A (September 2013). "Role of 5-HT5A receptors in the consolidation of memory". Behavioural Brain Research. 252: 246–51. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2013.05.051. PMID 23735322.
- Nautiyal KM, Hen R (2017). "Serotonin receptors in depression: from A to B". F1000Research. 6: 123. doi:10.12688/f1000research.9736.1. PMC 5302148. PMID 28232871.
- Frazer A, Hensler JG (1999). "Understanding the neuroanatomical organization of serotonergic cells in the brain provides insight into the functions of this neurotransmitter". In Siegel GJ, Agranoff, Bernard W, Fisher SK, Albers RW, Uhler MD (eds.). Basic Neurochemistry (Sixth ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 978-0-397-51820-3.
In 1964, Dahlstrom and Fuxe (discussed in [2]), using the Falck-Hillarp technique of histofluorescence, observed that the majority of serotonergic soma are found in cell body groups, which previously had been designated as the Raphe nuclei.
- Binder MD, Hirokawa N (2009). encyclopedia of neuroscience. Berlin: Springer. p. 705. ISBN 978-3-540-23735-8.
- The raphe nuclei group of neurons are located along the brain stem from the labels 'Mid Brain' to 'Oblongata', centered on the pons. (See relevant image.)
- Jacobs, edited by Christian P. Müller, Barry (2009). Handbook of the behavioral neurobiology of serotonin (1st ed.). London: Academic. pp. 51–59. ISBN 9780123746344.CS1 maint: extra text: authors list (link)
- Sommer C (2009). "Serotonin in Pain and Pain Control". In Jacobs CP, Müller B (eds.). Handbook of the behavioral neurobiology of serotonin (1st ed.). London: Academic. pp. 457–460. ISBN 9780123746344.
- Hensler JG (2009). "Serotonin in Mode and Emotions". In Jacobs CP, Müller B (eds.). Handbook of the behavioral neurobiology of serotonin (1st ed.). London: Academic. pp. 367–399. ISBN 9780123746344.
- Andrews PW, Bharwani A, Lee KR, Fox M, Thomson JA (April 2015). "Is serotonin an upper or a downer? The evolution of the serotonergic system and its role in depression and the antidepressant response". Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews. 51: 164–88. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2015.01.018. PMID 25625874.
- Stahl SM, Mignon L, Meyer JM (March 2009). "Which comes first: atypical antipsychotic treatment or cardiometabolic risk?". Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica. 119 (3): 171–9. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0447.2008.01334.x. PMID 19178394.
- Buckland PR, Hoogendoorn B, Guy CA, Smith SK, Coleman SL, O'Donovan MC (March 2005). "Low gene expression conferred by association of an allele of the 5-HT2C receptor gene with antipsychotic-induced weight gain". The American Journal of Psychiatry. 162 (3): 613–5. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.162.3.613. PMID 15741483.
- Holmes MC, French KL, Seckl JR (June 1997). "Dysregulation of diurnal rhythms of serotonin 5-HT2C and corticosteroid receptor gene expression in the hippocampus with food restriction and glucocorticoids". The Journal of Neuroscience. 17 (11): 4056–65. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-11-04056.1997. PMC 6573558. PMID 9151722.
- Leibowitz SF (1990). "The role of serotonin in eating disorders". Drugs. 39 Suppl 3: 33–48. doi:10.2165/00003495-199000393-00005. PMID 2197074.
- McGuire, Michael (2013) "Believing, the neuroscience of fantasies, fears, and confictions" (Prometius Books)
- Caspi N, Modai I, Barak P, Waisbourd A, Zbarsky H, Hirschmann S, Ritsner M (March 2001). "Pindolol augmentation in aggressive schizophrenic patients: a double-blind crossover randomized study". International Clinical Psychopharmacology. 16 (2): 111–5. doi:10.1097/00004850-200103000-00006. PMID 11236069.
- Ito Z, Aizawa I, Takeuchi M, Tabe M, Nakamura T (December 1975). "[Proceedings: Study of gastrointestinal motility using an extraluminal force transducer. 6. Observation of gastric and duodenal motility using synthetic motilin]". Nihon Heikatsukin Gakkai Zasshi. 11 (4): 244–6. PMID 1232434.
- Lesch KP, Bengel D, Heils A, Sabol SZ, Greenberg BD, Petri S, Benjamin J, Müller CR, Hamer DH, Murphy DL (November 1996). "Association of anxiety-related traits with a polymorphism in the serotonin transporter gene regulatory region". Science. 274 (5292): 1527–31. Bibcode:1996Sci...274.1527L. doi:10.1126/science.274.5292.1527. PMID 8929413.
- Chilmonczyk Z, Bojarski AJ, Pilc A, Sylte I (August 2015). "Functional Selectivity and Antidepressant Activity of Serotonin 1A Receptor Ligands". International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 16 (8): 18474–506. doi:10.3390/ijms160818474. PMC 4581256. PMID 26262615.
- Blier P, El Mansari M (2013). "Serotonin and beyond: therapeutics for major depression". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences. 368 (1615): 20120536. doi:10.1098/rstb.2012.0536. PMC 3638389. PMID 23440470.
- Eissa, Nermin; Al-Houqani, Mohammed; Sadeq, Adel; Ojha, Shreesh K.; Sasse, Astrid; Sadek, Bassem (16 May 2018). "Current Enlightenment About Etiology and Pharmacological Treatment of Autism Spectrum Disorder". Frontiers in Neuroscience. 12. doi:10.3389/fnins.2018.00304. ISSN 1662-4548. PMC 5964170. PMID 29867317.
- Rang HP (2003). Pharmacology. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone. p. 187. ISBN 978-0-443-07145-4.
- de Wit R, Aapro M, Blower PR (September 2005). "Is there a pharmacological basis for differences in 5-HT3-receptor antagonist efficacy in refractory patients?". Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology. 56 (3): 231–8. doi:10.1007/s00280-005-1033-0. PMID 15838653.
- Frost M, Andersen TE, Yadav V, Brixen K, Karsenty G, Kassem M (March 2010). "Patients with high-bone-mass phenotype owing to Lrp5-T253I mutation have low plasma levels of serotonin". Journal of Bone and Mineral Research. 25 (3): 673–5. doi:10.1002/jbmr.44. PMID 20200960.
- Rosen CJ (February 2009). "Breaking into bone biology: serotonin's secrets". Nature Medicine. 15 (2): 145–6. doi:10.1038/nm0209-145. PMID 19197289.
- Mödder UI, Achenbach SJ, Amin S, Riggs BL, Melton LJ, Khosla S (February 2010). "Relation of serum serotonin levels to bone density and structural parameters in women". Journal of Bone and Mineral Research. 25 (2): 415–22. doi:10.1359/jbmr.090721. PMC 3153390. PMID 19594297.
- Frost M, Andersen T, Gossiel F, Hansen S, Bollerslev J, van Hul W, Eastell R, Kassem M, Brixen K (August 2011). "Levels of serotonin, sclerostin, bone turnover markers as well as bone density and microarchitecture in patients with high-bone-mass phenotype due to a mutation in Lrp5". Journal of Bone and Mineral Research. 26 (8): 1721–8. doi:10.1002/jbmr.376. PMID 21351148.
- Kode A, Mosialou I, Silva BC, Rached MT, Zhou B, Wang J, Townes TM, Hen R, DePinho RA, Guo XE, Kousteni S (October 2012). "FOXO1 orchestrates the bone-suppressing function of gut-derived serotonin". The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 122 (10): 3490–503. doi:10.1172/JCI64906. PMC 3461930. PMID 22945629.
- Yadav VK, Balaji S, Suresh PS, Liu XS, Lu X, Li Z, Guo XE, Mann JJ, Balapure AK, Gershon MD, Medhamurthy R, Vidal M, Karsenty G, Ducy P (March 2010). "Pharmacological inhibition of gut-derived serotonin synthesis is a potential bone anabolic treatment for osteoporosis". Nature Medicine. 16 (3): 308–12. doi:10.1038/nm.2098. PMC 2836724. PMID 20139991.
- Ozanne SE, Hales CN (January 2004). "Lifespan: catch-up growth and obesity in male mice". Nature. 427 (6973): 411–2. Bibcode:2004Natur.427..411O. doi:10.1038/427411b. PMID 14749819.
- Lewis DS, Bertrand HA, McMahan CA, McGill HC, Carey KD, Masoro EJ (October 1986). "Preweaning food intake influences the adiposity of young adult baboons". J. Clin. Invest. 78 (4): 899–905. doi:10.1172/JCI112678. PMC 423712. PMID 3760191.
- Hahn P (July 1984). "Effect of litter size on plasma cholesterol and insulin and some liver and adipose tissue enzymes in adult rodents". J. Nutr. 114 (7): 1231–4. doi:10.1093/jn/114.7.1231. PMID 6376732.
- Popa D, Léna C, Alexandre C, Adrien J (April 2008). "Lasting syndrome of depression produced by reduction in serotonin uptake during postnatal development: evidence from sleep, stress, and behavior". The Journal of Neuroscience. 28 (14): 3546–54. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4006-07.2008. PMC 6671102. PMID 18385313.
- Maciag D, Simpson KL, Coppinger D, Lu Y, Wang Y, Lin RC, Paul IA (January 2006). "Neonatal antidepressant exposure has lasting effects on behavior and serotonin circuitry". Neuropsychopharmacology. 31 (1): 47–57. doi:10.1038/sj.npp.1300823. PMC 3118509. PMID 16012532.
- Maciag D, Williams L, Coppinger D, Paul IA (February 2006). "Neonatal citalopram exposure produces lasting changes in behavior which are reversed by adult imipramine treatment". European Journal of Pharmacology. 532 (3): 265–9. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2005.12.081. PMC 2921633. PMID 16483567.
- Holden C (October 2004). "Neuroscience. Prozac treatment of newborn mice raises anxiety". Science. 306 (5697): 792. doi:10.1126/science.306.5697.792. PMID 15514122.
- Ansorge MS, Zhou M, Lira A, Hen R, Gingrich JA (October 2004). "Early-life blockade of the 5-HT transporter alters emotional behavior in adult mice". Science. 306 (5697): 879–81. Bibcode:2004Sci...306..879A. doi:10.1126/science.1101678. PMID 15514160.
- Lesurtel M, Graf R, Aleil B, Walther DJ, Tian Y, Jochum W, Gachet C, Bader M, Clavien PA (April 2006). "Platelet-derived serotonin mediates liver regeneration". Science. 312 (5770): 104–7. Bibcode:2006Sci...312..104L. doi:10.1126/science.1123842. PMID 16601191.
- Matondo RB, Punt C, Homberg J, Toussaint MJ, Kisjes R, Korporaal SJ, Akkerman JW, Cuppen E, de Bruin A (April 2009). "Deletion of the serotonin transporter in rats disturbs serotonin homeostasis without impairing liver regeneration". American Journal of Physiology. Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology. 296 (4): G963–8. doi:10.1152/ajpgi.90709.2008. PMID 19246633.
- Collet C, Schiltz C, Geoffroy V, Maroteaux L, Launay JM, de Vernejoul MC (February 2008). "The serotonin 5-HT2B receptor controls bone mass via osteoblast recruitment and proliferation". FASEB Journal. 22 (2): 418–27. doi:10.1096/fj.07-9209com. PMC 5409955. PMID 17846081.
- Yadav VK, Ryu JH, Suda N, Tanaka KF, Gingrich JA, Schütz G, Glorieux FH, Chiang CY, Zajac JD, Insogna KL, Mann JJ, Hen R, Ducy P, Karsenty G (November 2008). "Lrp5 controls bone formation by inhibiting serotonin synthesis in the duodenum". Cell. 135 (5): 825–37. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2008.09.059. PMC 2614332. PMID 19041748. Lay summary – Science Daily.
- McDuffie JE, Motley ED, Limbird LE, Maleque MA (March 2000). "5-hydroxytryptamine stimulates phosphorylation of p44/p42 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in bovine aortic endothelial cell cultures". Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology. 35 (3): 398–402. doi:10.1097/00005344-200003000-00008. PMID 10710124.
- Marieb EN (2009). Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology (Eighth ed.). San Francisco: Pearson/Benjamin Cummings. p. 336. ISBN 978-0-321-51342-7.
- Chang, Weipang; Kanda, Hirosato; Ikeda, Ryo; Ling, Jennifer; DeBerry, Jennifer J.; Gu, Jianguo G. (13 September 2016). "Merkel disc is a serotonergic synapse in the epidermis for transmitting tactile signals in mammals". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 113 (37): E5491–E5500. doi:10.1073/pnas.1610176113. ISSN 0027-8424. PMID 27573850.
- Fuller, RW (1980). "Pharmacology of central serotonin neurons". Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology. 20: 111–27. doi:10.1146/annurev.pa.20.040180.000551. PMID 6992697.
- Titeler M, Lyon RA, Glennon RA (1988). "Radioligand binding evidence implicates the brain 5-HT2 receptor as a site of action for LSD and phenylisopropylamine hallucinogens". Psychopharmacology. 94 (2): 213–6. doi:10.1007/BF00176847. PMID 3127847.
- Nichols DE (2000). "Role of serotonergic neurons and 5-HT receptors in the action of hallucinogens". In Baumgarten HG, Gothert M (eds.). Serotoninergic Neurons and 5-HT Receptors in the CNS. Santa Clara, CA: Springer-Verlag TELOS. ISBN 978-3-540-66715-5.
- Kapur S, Seeman P (2002). "NMDA receptor antagonists ketamine and PCP have direct effects on the dopamine D(2) and serotonin 5-HT(2)receptors-implications for models of schizophrenia". Molecular Psychiatry. 7 (8): 837–44. doi:10.1038/sj.mp.4001093. PMID 12232776.
- Johnson MP, Hoffman AJ, Nichols DE (December 1986). "Effects of the enantiomers of MDA, MDMA and related analogues on [3H]serotonin and [3H]dopamine release from superfused rat brain slices". European Journal of Pharmacology. 132 (2–3): 269–76. doi:10.1016/0014-2999(86)90615-1. PMID 2880735.
- Goodman LS, Brunton LL, Chabner B, Knollmann BC (2001). Goodman and Gilman's pharmacological basis of therapeutics. New York: McGraw-Hill. pp. 459–461. ISBN 978-0-07-162442-8.
- Benmansour S, Cecchi M, Morilak DA, Gerhardt GA, Javors MA, Gould GG, Frazer A (December 1999). "Effects of chronic antidepressant treatments on serotonin transporter function, density, and mRNA level". The Journal of Neuroscience. 19 (23): 10494–501. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-23-10494.1999. PMC 6782424. PMID 10575045.
- Beitchman JH, Baldassarra L, Mik H, De Luca V, King N, Bender D, Ehtesham S, Kennedy JL (June 2006). "Serotonin transporter polymorphisms and persistent, pervasive childhood aggression". The American Journal of Psychiatry. 163 (6): 1103–5. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.163.6.1103. PMID 16741214.
- Pezawas L, Meyer-Lindenberg A, Drabant EM, Verchinski BA, Munoz KE, Kolachana BS, Egan MF, Mattay VS, Hariri AR, Weinberger DR (June 2005). "5-HTTLPR polymorphism impacts human cingulate-amygdala interactions: a genetic susceptibility mechanism for depression". Nature Neuroscience. 8 (6): 828–34. doi:10.1038/nn1463. PMID 15880108.
- Schinka JA, Busch RM, Robichaux-Keene N (February 2004). "A meta-analysis of the association between the serotonin transporter gene polymorphism (5-HTTLPR) and trait anxiety". Molecular Psychiatry. 9 (2): 197–202. doi:10.1038/sj.mp.4001405. PMID 14966478.
- Isbister GK, Bowe SJ, Dawson A, Whyte IM (2004). "Relative toxicity of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) in overdose". Journal of Toxicology. Clinical Toxicology. 42 (3): 277–85. doi:10.1081/CLT-120037428. PMID 15362595.
- Dunkley EJ, Isbister GK, Sibbritt D, Dawson AH, Whyte IM (September 2003). "The Hunter Serotonin Toxicity Criteria: simple and accurate diagnostic decision rules for serotonin toxicity". QJM. 96 (9): 635–42. doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcg109. PMID 12925718.
- Baskin SI (1991). Principles of cardiac toxicology. Boca Raton: CRC Press. ISBN 978-0-8493-8809-5. Retrieved 3 February 2010.
- Jähnichen S, Horowski R, Pertz H. "Pergolide and Cabergoline But not Lisuride Exhibit Agonist Efficacy at Serotonin 5-HT2B Receptors" (PDF). Retrieved 3 February 2010.
- Adverse Drug Reactions Advisory Committee, Australia (2004). "Cardiac valvulopathy with pergolide". Aust Adv Drug React Bull. 23 (4). Archived from the original on 27 June 2012.
- Schade R, Andersohn F, Suissa S, Haverkamp W, Garbe E (January 2007). "Dopamine agonists and the risk of cardiac-valve regurgitation". The New England Journal of Medicine. 356 (1): 29–38. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa062222. PMID 17202453.
- Zanettini R, Antonini A, Gatto G, Gentile R, Tesei S, Pezzoli G (January 2007). "Valvular heart disease and the use of dopamine agonists for Parkinson's disease". The New England Journal of Medicine. 356 (1): 39–46. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa054830. PMID 17202454.
- "Food and Drug Administration Public Health Advisory". 29 March 2007. Retrieved 7 February 2010.
- "MedWatch – 2007 Safety Information Alerts. Permax (pergolide) and generic equivalents". United States Food and Drug Administration. 29 March 2007. Retrieved 30 March 2007.
- Tyler VE (September 1958). "Occurrence of serotonin in a hallucinogenic mushroom". Science. 128 (3326): 718. Bibcode:1958Sci...128..718T. doi:10.1126/science.128.3326.718. PMID 13580242.
- Johnson DJ, Sanderson H, Brain RA, Wilson CJ, Solomon KR (May 2007). "Toxicity and hazard of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor antidepressants fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, and sertraline to algae". Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety. 67 (1): 128–39. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2006.03.016. PMID 16753215.
- McGowan K, Guerina V, Wicks J, Donowitz M (1985). Secretory hormones of Entamoeba histolytica. Ciba Foundation Symposium. Novartis Foundation Symposia. 112. pp. 139–54. doi:10.1002/9780470720936.ch8. ISBN 9780470720936. PMID 2861068.
- Banu N, Zaidi KR, Mehdi G, Mansoor T (July 2005). "Neurohumoral alterations and their role in amoebiasis". Indian Journal of Clinical Biochemistry. 20 (2): 142–5. doi:10.1007/BF02867414. PMC 3453840. PMID 23105547.
- Acharya DP, Sen MR, Sen PC (August 1989). "Effect of exogenous 5-hydroxytryptamine on pathogenicity of Entamoeba histolytica in experimental animals". Indian Journal of Experimental Biology. 27 (8): 718–20. PMID 2561282.
- Schröder P, Abele C, Gohr P, Stuhlfauth-Roisch U, Grosse W (1999). "Latest on enzymology of serotonin biosynthesis in walnut seeds". Tryptophan, Serotonin, and Melatonin. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. 467. pp. 637–44. doi:10.1007/978-1-4615-4709-9_81. ISBN 978-0-306-46204-7. PMID 10721112.
- Pénez N, Culioli G, Pérez T, Briand JF, Thomas OP, Blache Y (October 2011). "Antifouling properties of simple indole and purine alkaloids from the Mediterranean gorgonian Paramuricea clavata". Journal of Natural Products. 74 (10): 2304–8. doi:10.1021/np200537v. PMID 21939218.
- Guillén-Casla V, Rosales-Conrado N, León-González ME, Pérez-Arribas LV, Polo-Díez LM (April 2012). "Determination of serotonin and its precursors in chocolate samples by capillary liquid chromatography with mass spectrometry detection". Journal of Chromatography A. 1232: 158–65. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2011.11.037. PMID 22186492.
- Jonz MG, EkateriniMercier A, JoffrePotter JW (2001). "Effects Of 5-HT (Serotonin) On Reproductive Behaviour In Heterodera Schachtii (Nematoda)". Canadian Journal of Zoology. 79 (9): 1727. doi:10.1139/z01-135.
- Sawin ER, Ranganathan R, Horvitz HR (June 2000). "C. elegans locomotory rate is modulated by the environment through a dopaminergic pathway and by experience through a serotonergic pathway". Neuron. 26 (3): 619–31. doi:10.1016/S0896-6273(00)81199-X. PMID 10896158.
- Niacaris T, Avery L (January 2003). "Serotonin regulates repolarization of the C. elegans pharyngeal muscle". The Journal of Experimental Biology. 206 (Pt 2): 223–31. doi:10.1242/jeb.00101. PMC 4441752. PMID 12477893.
- Yeh SR, Fricke RA, Edwards DH (January 1996). "The effect of social experience on serotonergic modulation of the escape circuit of crayfish" (PDF). Science. 271 (5247): 366–9. Bibcode:1996Sci...271..366Y. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.470.6528. doi:10.1126/science.271.5247.366. PMID 8553075.
- "Serotonin, serotonin receptors and their actions in insects". Neurotransmitter. 2: 1–14. 2015. doi:10.14800/nt.314.
- Anstey ML, Rogers SM, Ott SR, Burrows M, Simpson SJ (January 2009). "Serotonin mediates behavioral gregarization underlying swarm formation in desert locusts". Science. 323 (5914): 627–30. Bibcode:2009Sci...323..627A. doi:10.1126/science.1165939. PMID 19179529.
- Sitaraman D, LaFerriere H, Birman S, Zars T (June 2012). "Serotonin is critical for rewarded olfactory short-term memory in Drosophila". Journal of Neurogenetics. 26 (2): 238–44. doi:10.3109/01677063.2012.666298. PMID 22436011.
- Bicker G, Menzel R (January 1989). "Chemical codes for the control of behaviour in arthropods". Nature. 337 (6202): 33–9. Bibcode:1989Natur.337...33B. doi:10.1038/337033a0. PMID 2562906.
- Cai M, Li Z, Fan F, Huang Q, Shao X, Song G (March 2010). "Design and synthesis of novel insecticides based on the serotonergic ligand 1-[(4-aminophenyl)ethyl]-4-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]piperazine (PAPP)". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 58 (5): 2624–9. doi:10.1021/jf902640u. PMID 20000410.
- Manahan SE (2002). Toxicological Chemistry and Biochemistry (3rd ed.). CRC Press. p. 393. ISBN 978-1-4200-3212-3.
- Postma TL (2009). "Neurotoxic Animal Poisons and Venoms". In Dobbs MR (ed.). Clinical Neurotoxicology. pp. 463–89. ISBN 978-0-323-05260-3.
- Dierick HA, Greenspan RJ (May 2007). "Serotonin and neuropeptide F have opposite modulatory effects on fly aggression". Nature Genetics. 39 (5): 678–82. doi:10.1038/ng2029. PMID 17450142.
- Loer CM, Kenyon CJ (December 1993). "Serotonin-deficient mutants and male mating behavior in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans". The Journal of Neuroscience. 13 (12): 5407–17. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-12-05407.1993. PMC 6576401. PMID 8254383.
- Lipton J, Kleemann G, Ghosh R, Lints R, Emmons SW (August 2004). "Mate searching in Caenorhabditis elegans: a genetic model for sex drive in a simple invertebrate". The Journal of Neuroscience. 24 (34): 7427–34. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1746-04.2004. PMC 6729642. PMID 15329389.
- Murakami H, Murakami S (August 2007). "Serotonin receptors antagonistically modulate Caenorhabditis elegans longevity". Aging Cell. 6 (4): 483–8. doi:10.1111/j.1474-9726.2007.00303.x. PMID 17559503.
- Kaplan DD, Zimmermann G, Suyama K, Meyer T, Scott MP (July 2008). "A nucleostemin family GTPase, NS3, acts in serotonergic neurons to regulate insulin signaling and control body size". Genes & Development. 22 (14): 1877–93. doi:10.1101/gad.1670508. PMC 2492735. PMID 18628395.
- Ruaud AF, Thummel CS (July 2008). "Serotonin and insulin signaling team up to control growth in Drosophila". Genes & Development. 22 (14): 1851–5. doi:10.1101/gad.1700708. PMC 2735276. PMID 18628391.
- Anstey ML, Rogers SM, Ott SR, Burrows M, Simpson SJ (January 2009). "Serotonin mediates behavioral gregarization underlying swarm formation in desert locusts". Science. 323 (5914): 627–30. Bibcode:2009Sci...323..627A. doi:10.1126/science.1165939. PMID 19179529. Lay summary – BBC News.
- Davidson S, Prokonov D, Taler M, Maayan R, Harell D, Gil-Ad I, Weizman A (February 2009). "Effect of exposure to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in utero on fetal growth: potential role for the IGF-I and HPA axes". Pediatric Research. 65 (2): 236–41. doi:10.1203/PDR.0b013e318193594a. PMID 19262294.
- Ben Arous J, Laffont S, Chatenay D (October 2009). Brezina V (ed.). "Molecular and sensory basis of a food related two-state behavior in C. elegans". PLOS One. 4 (10): e7584. Bibcode:2009PLoSO...4.7584B. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0007584. PMC 2762077. PMID 19851507.
- Sze JY, Victor M, Loer C, Shi Y, Ruvkun G (February 2000). "Food and metabolic signalling defects in a Caenorhabditis elegans serotonin-synthesis mutant". Nature. 403 (6769): 560–4. Bibcode:2000Natur.403..560S. doi:10.1038/35000609. PMID 10676966.
- Murakami H, Bessinger K, Hellmann J, Murakami S (July 2008). "Manipulation of serotonin signal suppresses early phase of behavioral aging in Caenorhabditis elegans". Neurobiology of Aging. 29 (7): 1093–100. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2007.01.013. PMID 17336425.
- Côté F, Thévenot E, Fligny C, Fromes Y, Darmon M, Ripoche MA, Bayard E, Hanoun N, Saurini F, Lechat P, Dandolo L, Hamon M, Mallet J, Vodjdani G (November 2003). "Disruption of the nonneuronal tph1 gene demonstrates the importance of peripheral serotonin in cardiac function". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 100 (23): 13525–30. Bibcode:2003PNAS..10013525C. doi:10.1073/pnas.2233056100. PMC 263847. PMID 14597720.
- Alarcon J (2008). "Biotransformation of indole derivatives by mycelial cultures". Zeitschrift für Naturforschung C. 63 (1–2): 82–4. doi:10.1515/znc-2008-1-215. PMID 18386493.
- Wurtman RJ, Hefti F, Melamed E (December 1980). "Precursor control of neurotransmitter synthesis". Pharmacological Reviews. 32 (4): 315–35. PMID 6115400.
- Negri L (2006). "[Vittorio Erspamer (1909–1999)]". Medicina Nei Secoli. 18 (1): 97–113. PMID 17526278.
- Rapport MM, Green AA, Page IH (December 1948). "Serum vasoconstrictor, serotonin; isolation and characterization". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 176 (3): 1243–51. PMID 18100415.
- Feldberg W, Toh CC (February 1953). "Distribution of 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin, enteramine) in the wall of the digestive tract". The Journal of Physiology. 119 (2–3): 352–62. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004850. PMC 1392800. PMID 13035756.
- SciFinder – Serotonin Substance Detail. Accessed (4 November 2012).
- Twarog BM, Page IH (October 1953). "Serotonin content of some mammalian tissues and urine and a method for its determination". The American Journal of Physiology. 175 (1): 157–61. doi:10.1152/ajplegacy.1953.175.1.157. PMID 13114371.
Further reading
- Gutknecht L, Jacob C, Strobel A, Kriegebaum C, Müller J, Zeng Y, Markert C, Escher A, Wendland J, Reif A, Mössner R, Gross C, Brocke B, Lesch KP (June 2007). "Tryptophan hydroxylase-2 gene variation influences personality traits and disorders related to emotional dysregulation". The International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology. 10 (3): 309–20. doi:10.1017/S1461145706007437. PMID 17176492.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Serotonin. |
- 5-Hydroxytryptamine MS Spectrum
- Serotonin bound to proteins in the PDB
- PsychoTropicalResearch Extensive reviews on serotonergic drugs and Serotonin Syndrome.
- Molecule of the Month: Serotonin at University of Bristol
- 60-Second Psych: No Fair! My Serotonin Level Is Low, Scientific American
- Serotonin Test Interpretation on ClinLab Navigator.