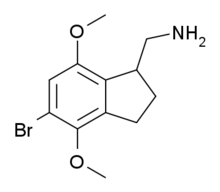
2CB-Ind
2CB-Ind is a conformationally-restricted derivative of the phenethylamine hallucinogen 2C-B, discovered in 1974 by Alexander Shulgin. It acts as a moderately potent and selective agonist for the 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors, but unlike the corresponding benzocyclobutene derivative TCB-2 which is considerably more potent than the parent compound 2C-B, 2CB-Ind is several times weaker, with racemic 2CB-Ind having a Ki of 47nM at the human 5-HT2A receptor, only slightly more potent than the mescaline analogue (R)-jimscaline.[1][2]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C12H16BrNO2 |
| Molar mass | 286.169 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Analogues and derivatives
Analogues and derivatives of 2C-B:
- 2C-B-FLY
- 2CBFly-NBOMe (NBOMe-2CB-Fly)
Other:
- 2C-B-AN
- 2C-B-BUTTERFLY
- 2C-B-DragonFLY
- 2CB-5-hemifly
- 2CB-Ind
- βk-2C-B (beta-keto 2C-B)
- TCB-2 (2C-BCB)
gollark: Then that's just weird.
gollark: Use a JSON parser? It looks vaguely jsony, if that's the aa/bb/cc.
gollark: Roblox devs aren't everyone.
gollark: And?
gollark: Maybe people don't know of it, or maybe they just find it bad style, but it's quite uncommon, at least.
See also
References
- McLean TH, Parrish JC, Braden MR, Marona-Lewicka D, Gallardo-Godoy A, Nichols DE (September 2006). "1-Aminomethylbenzocycloalkanes: conformationally restricted hallucinogenic phenethylamine analogues as functionally selective 5-HT2A receptor agonists". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 49 (19): 5794–803. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.688.9849. doi:10.1021/jm060656o. PMID 16970404.
- Braden MR (2007). Towards a biophysical understanding of hallucinogen action (PhD.). Purdue University. ProQuest 304838368.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.