Oral administration
Oral administration is a route of administration where a substance is taken through the mouth. Per os abbreviated to P.O. is sometimes used as a direction for medication to be taken orally. Many medications are taken orally because they are intended to have a systemic effect, reaching different parts of the body via the bloodstream, for example.[1]
| Oral administration | |
|---|---|
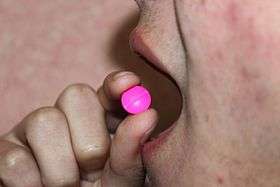 Oral administration of a tablet | |
| Other names | By mouth, per os (PO) |

.jpg)
Terminology
Per os (/ˌpɜːrˈoʊs/; P.O.) is an adverbial phrase meaning literally from Latin "by opening" or "by way of the opening." The expression is used in medicine to describe a treatment that is taken orally. The abbreviation P.O. is often used on medical prescriptions. P.O. is also occasionally alternatively rendered per orem.
Scope
Oral administration includes:
- Buccal, dissolved inside the cheek
- Sublabial, dissolved under the lip
- Sublingual administration (SL), dissolved under the tongue, but due to rapid absorption many consider SL a parenteral route
Enteral medications come in various forms, including[1] Oral solid dosage (OSD) forms:[2]
- Tablets to swallow, chew or dissolve in water or under the tongue
- Capsules and chewable capsules (with a coating that dissolves in the stomach or bowel to release the medication there)
- Time-release or sustained-release tablets and capsules (which release the medication gradually)
- Powders or granules
and oral liquid dosage forms:[3]
- Teas
- Drops
- Liquid medications or syrups
Facilitating methods
Concomitant ingestion of water facilitates in swallowing tablets and capsules.[4] If the substance has disagreeable taste, addition of a flavor may facilitate ingestion.[4] Substances that are harmful to the teeth are preferably given through a straw.[4]
See also
References
- Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care. "Oral medications". Informed Health Online. Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care. Retrieved 22 June 2013.
- Jacobs, Terry; Signore, Andrew A. (2016-08-19). Good Design Practices for GMP Pharmaceutical Facilities. CRC Press. ISBN 978-1-4822-5891-2.
- McCabe-Sellers, Beverly; Frankel, Eric H.; Wolfe, Jonathan J. (2003-04-29). Handbook of Food-Drug Interactions. CRC Press. ISBN 978-0-203-49024-2.
- TheFreeDictionary > oral administration of medication Citing: Mosby's Medical Dictionary, 8th edition. 2009
-solution.jpg)