25I-NBMD
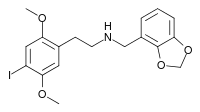
25I-NBMD (NBMD-2C-I, Cimbi-29) is a derivative of the phenethylamine hallucinogen 2C-I, discovered in 2006 by a team at Purdue University led by David Nichols. It acts as a potent partial agonist for the 5HT2A receptor with a Ki of 0.049nM at the human 5HT2A receptor.[1][2][3] The corresponding 4-bromo analogue 25B-NBMD has been used for molecular dynamics studies on the shape of the 5-HT2A receptor.[4]
 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H20INO4 |
| Molar mass | 441.265 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Legality
Sweden
The Riksdag added 25I-NBMD to Narcotic Drugs Punishments Act under swedish schedule I ("substances, plant materials and fungi which normally do not have medical use") as of January 16, 2015, published by Medical Products Agency (MPA) in regulation LVFS 2014:11 listed as 25I-NBMD, and 2-(4-jodo-2,5-dimetoxifenyl)-N-[(2,3-metylendioxifenyl)metyl]etanamin.[5]
United Kingdom
This substance is a Class A drug in the United Kingdom as a result of the N-benzylphenethylamine catch-all clause in the Misuse of Drugs Act 1971.[6]
Analogues and derivatives
Analogues and derivatives of 2C-I:
25I-NB*:
- 25I-NBF
- 25I-NBMD
- 25I-NB34MD
- 25I-NBOH
- 25I-NBOMe (NBOMe-2CI)
- 25I-NB3OMe
- 25I-NB4OMe
References
- Braden, MR; Parrish, JC; Naylor, JC; Nichols, DE (2006). "Molecular interaction of serotonin 5-HT2A receptor residues Phe339(6.51) and Phe340(6.52) with superpotent N-benzyl phenethylamine agonists". Molecular Pharmacology. 70 (6): 1956–64. doi:10.1124/mol.106.028720. PMID 17000863. S2CID 15840304.
- Michael Robert Braden PhD. Towards a biophysical understanding of hallucinogen action. Purdue University 2007.
- Ettrup, A.; Hansen, M.; Santini, M. A.; Paine, J.; Gillings, N.; Palner, M.; Lehel, S.; Herth, M. M.; Madsen, J.; et al. (2010). "Radiosynthesis and in vivo evaluation of a series of substituted 11C-phenethylamines as 5-HT2A agonist PET tracers". European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging. 38 (4): 681–93. doi:10.1007/s00259-010-1686-8. PMID 21174090.
- Isberg V, Balle T, Sander T, Jørgensen FS, Gloriam DE (February 2011). "G protein- and agonist-bound serotonin 5-HT2A receptor model activated by steered molecular dynamics simulations". Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling. 51 (2): 315–25. doi:10.1021/ci100402f. PMID 21261291.
- "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-03-16. Retrieved 2017-04-21.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "The Misuse of Drugs Act 1971 (Ketamine etc.) (Amendment) Order 2014". www.legislation.gov.uk.
| 5-HT1 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-HT2 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-HT3–7 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phenethylamines |
|
|---|---|
| Amphetamines |
|
| Phentermines |
|
| Cathinones |
|
| Phenylisobutylamines | |
| Phenylalkylpyrrolidines | |
| Catecholamines (and close relatives) |
|
| Miscellaneous |
|