Triprolidine
Triprolidine is an over-the-counter antihistamine with anticholinergic properties.[1] It is used to combat the symptoms associated with allergies and is sometimes combined with other cold medications designed to provide general relief for flu-like symptoms.[2] As with many antihistamines, the most common side effect is drowsiness.[1]
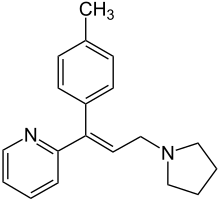 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Actidil, Myidil, Actifed (in the latter combined with pseudoephedrine and either dextromethorphan or guaifenesin) |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 4% oral |
| Protein binding | 90% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic (CYP2D6) |
| Elimination half-life | 4–6 hours |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| KEGG |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.934 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H22N2 |
| Molar mass | 278.399 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 60 °C (140 °F) |
| Solubility in water | 500 mg/mL (20 °C) |
| |
| |
| | |
It was patented in 1948 and came into medical use in 1953.[3]
References
- Goldsmith P, Dowd PM (January 1993). "The new H1 antihistamines. Treatment of urticaria and other clinical problems". Dermatologic Clinics. 11 (1): 87–95. PMID 8094649.
- Williams BO, Liao SH, Lai AA, Arnold JD, Perkins JG, Blum MR, Findlay JW (1984). "Bioavailability of pseudoephedrine and triprolidine from combination and single-ingredient products". Clinical Pharmacy. 3 (6): 638–43. PMID 6509877.
- Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 546. ISBN 9783527607495.
| Benzimidazoles (*) | |
|---|---|
| Diarylmethanes |
|
| Ethylenediamines | |
| Tricyclics | |
| Others |
|
| For topical use | |
| H1 |
|
|---|---|
| H2 |
|
| H3 |
|
| H4 |
|
See also: Receptor/signaling modulators • Monoamine metabolism modulators • Monoamine reuptake inhibitors | |
| mAChRs |
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precursors (and prodrugs) | |||||
See also: Receptor/signaling modulators • Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor modulators • Acetylcholine metabolism/transport modulators | |||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.