MCOLN3
Mucolipin-3 also known as TRPML3 (transient receptor potential cation channel, mucolipin subfamily, member 3) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MCOLN3 gene.[5] It is a member of the small family of the TRPML channels, a subgroup of the large protein family of TRP ion channels.[6]
Gene
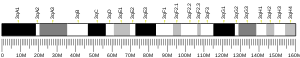
In human, the MCOLN3 gene resides on the short arm of chromosome 1 at 1p22.3. The gene is split in 12 exons, which entail the open reading frame of 1659 nucleotides. The encoded protein, TRPML3, has 553 amino acid with a predicted molecular weight of ≈64 kDa. Computational analyses of the secondary structure predict the presence of six transmembrane domains, an ion transport motif (PF00520) and a transient receptor potential motif (PS50272). In the mouse, Mcoln3, is located on the distal end of chromosome 3 at cytogenetic band qH2. Human and mouse TRPML3 proteins share 91% sequence identity.[7] All vertebrate species, for which a genomic sequence is available, harbor the MCOLN3 gene. Homologs of MCOLN3 are also present in the genome of insects (Drosophila melanogaster), nematodes (Caenorhabditis elegans), sea urchin (Strongylocentrotus purpuratus) and lower organisms including Hydra and Dictyostelium.
Expression
Genetics
Phenotypes
Mutations of the MCOLN3 gene in mice result in auditory hair cell death and deafness.[8]
See also
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000055732 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000036853 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Clapham DE, Julius D, Montell C, Schultz G (December 2005). "International Union of Pharmacology. XLIX. Nomenclature and structure-function relationships of transient receptor potential channels". Pharmacol. Rev. 57 (4): 427–50. doi:10.1124/pr.57.4.6. PMID 16382100.
- Noben-Trauth K (January 2011). "Chapter 13: TRPML3". In Islam MS (ed.). Transient Receptor Potential Channels. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. 704. Berlin: Springer. p. 700. ISBN 978-94-007-0264-6.
- Noben-Trauth, Konrad (2011). "The TRPML3 Channel: From Gene to Function". Transient Receptor Potential Channels. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. 704. pp. 229–237. doi:10.1007/978-94-007-0265-3_13. ISBN 978-94-007-0264-6. PMID 21290299.
- Nagata K, Zheng L, Madathany T, Castiglioni AJ, Bartles JR, García-Añoveros J (January 2008). "The varitint-waddler (Va) deafness mutation in TRPML3 generates constitutive, inward rectifying currents and causes cell degeneration". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 105 (1): 353–8. doi:10.1073/pnas.0707963105. PMC 2224216. PMID 18162548.
Further reading
- Venkatachalam K, Hofmann T, Montell C (2006). "Lysosomal localization of TRPML3 depends on TRPML2 and the mucolipidosis-associated protein TRPML1". J. Biol. Chem. 281 (25): 17517–27. doi:10.1074/jbc.M600807200. PMC 4196876. PMID 16606612.
- Fares H, Greenwald I (2001). "Regulation of endocytosis by CUP-5, the Caenorhabditis elegans mucolipin-1 homolog". Nat. Genet. 28 (1): 64–8. doi:10.1038/88281. PMID 11326278.
- Kim HJ, Li Q, Tjon-Kon-Sang S, et al. (2008). "A novel mode of TRPML3 regulation by extracytosolic pH absent in the varitint-waddler phenotype". EMBO J. 27 (8): 1197–205. doi:10.1038/emboj.2008.56. PMC 2367400. PMID 18369318.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Grimm C, Jörs S, Heller S (2009). "Life and Death of Sensory Hair Cells Expressing Constitutively Active TRPML3". J. Biol. Chem. 284 (20): 13823–31. doi:10.1074/jbc.M809045200. PMC 2679483. PMID 19299509.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2002). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Kim HJ, Li Q, Tjon-Kon-Sang S, et al. (2007). "Gain-of-function mutation in TRPML3 causes the mouse Varitint-Waddler phenotype". J. Biol. Chem. 282 (50): 36138–42. doi:10.1074/jbc.C700190200. PMID 17962195.
- Di Palma F, Belyantseva IA, Kim HJ, et al. (2002). "Mutations in Mcoln3 associated with deafness and pigmentation defects in varitint-waddler (Va) mice". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (23): 14994–9. doi:10.1073/pnas.222425399. PMC 137533. PMID 12403827.
- Gregory SG, Barlow KF, McLay KE, et al. (2006). "The DNA sequence and biological annotation of human chromosome 1". Nature. 441 (7091): 315–21. doi:10.1038/nature04727. PMID 16710414.
External links
- MCOLN3+protein,+human at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)