Homodihydrocapsaicin
Homodihydrocapsaicin is a capsaicinoid and analog and congener of capsaicin in chili peppers (Capsicum). Like capsaicin it is an irritant. Homodihydrocapsaicin accounts for about 1% of the total capsaicinoids mixture[2] and has about half the pungency of capsaicin. Pure homodihydrocapsaicin is a lipophilic colorless odorless crystalline to waxy compound. It produces "numbing burn" in the throat and is one of the most prolonged and difficult to rinse out. On the Scoville scale it has 8,600,000 SHU (Scoville heat units).[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
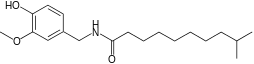
| IUPAC name
N-(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxybenzyl)-9-methyldecanamide | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C19H31NO3 | |
| Molar mass | 321.461 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
| Homodihydrocapsaicin | |
|---|---|
| Heat | Above peak |
| Scoville scale | 8,600,000[1] SHU |
See also
References
- Govindarajan, Sathyanarayana (1991). "Capsicum — Production, Technology, Chemistry, and Quality. Part V. Impact on Physiology, Pharmacology, Nutrition, and Metabolism; Structure, Pungency, Pain, and Desensitization Sequences". Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition. 29 (6): 435–474. doi:10.1080/10408399109527536. PMID 2039598.
- Bennett DJ, Kirby GW (1968). "Constitution and biosynthesis of capsaicin". J. Chem. Soc. C: 442. doi:10.1039/j39680000442.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.