Carvacrol
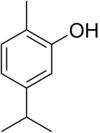
Carvacrol, or cymophenol, C6H3(CH3)(OH)C3H7, is a monoterpenoid phenol. It has a characteristic pungent, warm odor of oregano.[4]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Methyl-5-(propan-2-yl)phenol[2] | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
2-Methyl-5-(propan-2-yl)benzenol | |
| Other names
Carvacrol 5-Isopropyl-2-methylphenol 2-Methyl-5-(1-methylethyl)phenol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.173 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H14O | |
| Molar mass | 150.217 g/mol |
| Density | 0.9772 g/cm3 at 20 °C |
| Melting point | 1 °C (34 °F; 274 K) |
| Boiling point | 237.7 °C (459.9 °F; 510.8 K) |
| insoluble | |
| Solubility | soluble in ethanol, diethyl ether, carbon tetrachloride, acetone[3] |
| −1.091×10−4 cm3/mol | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Natural occurrence
Carvacrol is present in the essential oil of Origanum vulgare (oregano), oil of thyme, oil obtained from pepperwort, and wild bergamot. The essential oil of thyme subspecies contains between 5% and 75% of carvacrol, while Satureja (savory) subspecies have a content between 1% and 45%.[5] Origanum majorana (marjoram) and Dittany of Crete are rich in carvacrol, 50% and 60–80% respectively.[6]
It is also found in tequila[7] and Lippia graveolens (Mexican oregano) in the verbena family.
Synthesis and derivatives
Carvacrol may be synthetically prepared by the fusion of cymol sulfonic acid with caustic potash; by the action of nitrous acid on 1-methyl-2-amino-4-propyl benzene; by prolonged heating of five parts of camphor with one part of iodine; or by heating carvol with glacial phosphoric acid or by performing a dehydrogenation of carvone with a palladium-carbon catalyst. It is extracted from Origanum oil by means of a 50% potash solution. It is a thick oil that sets at 20 °C to a mass of crystals of melting point 0 °C, and boiling point 236–237 °C. Oxidation with ferric chloride converts it into dicarvacrol, whilst phosphorus pentachloride transforms it into chlorcymol.
List of the plants that contain the chemical
- Monarda didyma[8]
- Nigella sativa[9]
- Origanum compactum[10]
- Origanum dictamnus[11]
- Origanum microphyllum[12]
- Origanum onites[13][14]
- Origanum scabrum[12]
- Origanum syriacum[15]
- Origanum vulgare[16][17]
- Plectranthus amboinicus
- Thymus glandulosus[10]
- Lavandula multifida
- Origanum minutiflorum
- Satureja thymbra
Toxicology
In vitro, carvacrol has antimicrobial activity against 25 different periodontopathic bacteria and strains, [18] Cladosporium herbarum,[18] Penicillium glabrum,[18] and fungi such as F. moniliforme, R. solani, S. sclerotirum, and P. capisci.[18]
Compendial status
See also
Notes and references
- "Carvacrol data sheet from Sigma-Aldrich".
- "Front Matter". Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry : IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. p. 691. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- Lide, David R. (1998). Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (87 ed.). Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press. pp. 3–346. ISBN 978-0-8493-0594-8.
- Ultee, A.; Slump, R. A.; Steging, G.; Smid, E. J. (2000). "Antimicrobial activity of carvacrol toward Bacillus cereus on rice". Journal of Food Protection. 63 (5): 620–624. doi:10.4315/0362-028x-63.5.620. PMID 10826719.
- Vladić, J.; Zeković, Z.; Jokić, S.; Svilović, S.; Kovačević, S.; Vidović, S. (November 2016). "Winter savory: Supercritical carbon dioxide extraction and mathematical modeling of extraction process". The Journal of Supercritical Fluids. 117: 89–97. doi:10.1016/j.supflu.2016.05.027.
- De Vincenzi, M.; Stammati, A.; De Vincenzi, A.; Silano, M. (2004). "Constituents of aromatic plants: Carvacrol". Fitoterapia. 75 (7–8): 801–804. doi:10.1016/j.fitote.2004.05.002. PMID 15567271.
- De León Rodríguez, A.; Escalante Minakata, P.; Jiménez García, M. I.; Ordóñez Acevedo, L. G.; Flores Flores, J. L.; Barba de la Rosa, A. P. (2008). "Characterization of volatile compounds from ethnic Agave alcoholic beverages by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry". Food Technology and Biotechnology. 46 (4): 448–455.
- Mazza, G.; Kiehn, F. A.; Marshall, H. H. (1993). "Monarda: A source of geraniol, linalool, thymol and carvacrol-rich essential oils". In Janick, J.; Simon, J. E. (eds.). New Crops. New York: Wiley. pp. 628–631. ISBN 0-471-59374-5.
- Zawirska-Wojtasiak, R.; Mildner-Szkudlarz, S.; Wąsowicz, E.; Pacyński, M. (2010). "Gas chromatography, sensory analysis and electronic nose in the evaluation of black cumin (Nigella sativa L.) aroma quality" (PDF). Herba Polonica.
- Bouchra, C.; Achouri, M.; Idrissi Hassani, L. M.; Hmamouchi, M. (2003). "Chemical composition and antifungal activity of essential oils of seven Moroccan Labiatae against Botrytis cinerea Pers: Fr". Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 89 (1): 165–169. doi:10.1016/S0378-8741(03)00275-7. PMID 14522450.
- Liolios, C. C.; Gortzi, O.; Lalas, S.; Tsaknis, J.; Chinou, I. (2009). "Liposomal incorporation of carvacrol and thymol isolated from the essential oil of Origanum dictamnus L. and in vitro antimicrobial activity". Food Chemistry. 112 (1): 77–83. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.05.060.
- Aligiannis, N.; Kalpoutzakis, E.; Mitaku, S.; Chinou, I. B. (2001). "Composition and antimicrobial activity of the essential oils of two Origanum species". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 49 (9): 4168–4170. doi:10.1021/jf001494m. PMID 11559104.
- Coşkun, Ş.; Girişgin, O.; Kürkçüoğlu, M.; Malyer, H.; Girişgin, A. O.; Kırımer, N.; Başer, K. H. (2008). "Acaricidal efficacy of Origanum onites L. essential oil against Rhipicephalus turanicus (Ixodidae)". Parasitology Research. 103 (2): 259–261. doi:10.1007/s00436-008-0956-x. PMID 18438729.
- Ruberto, G.; Biondi, D.; Meli, R.; Piattelli, M. (1993). "Volatile flavour components of Sicilian Origanum onites L.". Flavour and Fragrance Journal. 8 (4): 197–200. doi:10.1002/ffj.2730080406.
- Ghasemi Pirbalouti, A.; Rahimmalek, M.; Malekpoor, F.; Karimi, A. (2011). "Variation in antibacterial activity, thymol and carvacrol contents of wild populations of Thymus daenensis subsp. daenensis Celak" (PDF). Plant Omics. 4: 209–214.
- Kanias, G. D.; Souleles, C.; Loukis, A.; Philotheou-Panou, E. (1998). "Trace elements and essential oil composition in chemotypes of the aromatic plant Origanum vulgare". Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry. 227 (1–2): 23–31. doi:10.1007/BF02386426.
- Figiel, A.; Szumny, A.; Gutiérrez Ortiz, A.; Carbonell Barrachina, Á. A. (2010). "Composition of oregano essential oil (Origanum vulgare) as affected by drying method". Journal of Food Engineering. 98 (2): 240–247. doi:10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2010.01.002.
- Andersen, A. (2006). "Final report on the safety assessment of sodium p-chloro-m-cresol, p-chloro-m-cresol, chlorothymol, mixed cresols, m-cresol, o-cresol, p-cresol, isopropyl cresols, thymol, o-cymen-5-ol, and carvacrol". International Journal of Toxicology. 25: 29–127. doi:10.1080/10915810600716653. PMID 16835130.
- "Index" (PDF). British Pharmacopoeia. 2009. Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 April 2009. Retrieved 29 March 2010.
