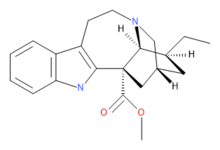
Coronaridine
Coronaridine, also known as 18-carbomethoxyibogamine, is an alkaloid found in Tabernanthe iboga and related species, including Tabernaemontana divaricata for which (under the now obsolete synonym Ervatamia coronaria) it was named.[1]
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ChEBI | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.727 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C21H26N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 338.451 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Pharmacology
Coronaridine has been reported to bind to an assortment of molecular sites, including: μ-opioid (Ki = 2.0 μM), δ-opioid (Ki = 8.1 μM), and κ-opioid receptors (Ki = 4.3 μM), NMDA receptor (Ki = 6.24 μM) (as an antagonist),[2] and nAChRs (as an antagonist).[3] It has also been found to inhibit the enzyme acetylcholinesterase, act as a voltage-gated sodium channel blocker,[4] and displays estrogenic activity in rodents.[2][3] In contrast to ibogaine and other iboga alkaloids, coronaridine does not bind to either the σ1 or σ2 receptor.[4]
Sources
| Family | Plants |
|---|---|
| Apocynaceae | Tabernaemontana catharinensis, Tabernaemontana ternifolia, Tabernaemontana pandacaqui, Tabernaemontana heyneana, Tabernaemontana litoralis, Tabernaemontana divaricata, Tabernaemontana penduliflora.[5] |
See also
References
- Delorenzi JC, Freire-de-Lima L, Gattass CR, et al. (July 2002). "In vitro activities of iboga alkaloid congeners coronaridine and 18-methoxycoronaridine against Leishmania amazonensis". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 46 (7): 2111–5. doi:10.1128/aac.46.7.2111-2115.2002. PMC 127312. PMID 12069962.
- Christophe Wiart (16 December 2013). Lead Compounds from Medicinal Plants for the Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases. Academic Press. pp. 67–69, 73. ISBN 978-0-12-398383-1.
- Gideon Polya (15 May 2003). Biochemical Targets of Plant Bioactive Compounds: A Pharmacological Reference Guide to Sites of Action and Biological Effects. CRC Press. pp. 203–. ISBN 978-0-203-01371-7.
- Chemistry and Biology. Academic Press. 21 September 1998. pp. 222–. ISBN 978-0-08-086576-8.
- European Bioinformatics Institute
Treatment of drug dependence (N07B) | |
|---|---|
| Nicotine dependence | |
| Alcohol dependence |
|
| Opioid dependence | |
| Benzodiazepine dependence | |
| Research | |