Pempidine
Pempidine is a ganglion-blocking drug, first reported in 1958 by two research groups working independently, and introduced as an oral treatment for hypertension.[1][2]
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.102 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
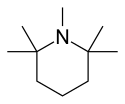
| Formula | C10H21N |
| Molar mass | 155.285 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
Pharmacology
Reports on the "classical" pharmacology of pempidine have been published.[3][4] The Spinks group, at ICI, compared pempidine, its N-ethyl analogue, and mecamylamine in considerable detail, with additional data related to several structurally simpler compounds.[3]
Toxicology
LD50 for the HCl salt of pempidine in mice: 74 mg/kg (i.v.); 125 mg/kg (i.p.); 413 mg/kg (p.o.).[3]
Chemistry
Pempidine is an aliphatic, sterically hindered, cyclic, tertiary amine, which is a weak base: in its protonated form it has a pKa of 11.25.[5]
Pempidine is a liquid with a boiling point of 187–188 °C and a density of 0.858 g/cm3.[3]
Two early syntheses of this compound are those of Leonard and Hauck,[6] and Hall.[5] These are very similar in principle: Leonard and Hauck reacted phorone with ammonia, to produce 2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-4-piperidone,[7] which was then reduced by means of the Wolff–Kishner reduction to 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine; this secondary amine was then N-methylated using methyl iodide and potassium carbonate.[8]
Hall's method involved reacting acetone with ammonia in the presence of calcium chloride to give 2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-4-piperidone, which was then reduced under Wolff-Kishner conditions, followed by N-methylation of the resulting 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine with methyl p-toluenesulfonate.
References
- A. Spinks and E. H. P. Young (1958) Nat. 181 1397
- G. E. Lee et al. (1958) Nat. 181 1717.
- A. Spinks et al. (1958) Br. J. Pharmacol. Chemother. 13 501-520.
- D. F. Muggleton and H. W.Reading (1959) Br. J. Pharmacol. Chemother. 14 202
- H. K. Hall (1957) J. Am. Chem. Soc. 79 5447-5451.
- N. J. Leonard and F. P. Hauck (1957) J. Am. Chem. Soc. 79 5279-5292.
- The "trivial" name of this compound is triacetonamine.
- The boiling point of 147 °C given by these authors for their N,2,2,6,6-pentamethylpiperidine (pempidine) is significantly below the range of ~182–188 °C reported by other chemists.