Carbosulfan
Carbosulfan is an organic compound adherent to the carbamate class. At normal conditions, it is brown viscous liquid. It is not very stable; it decomposes slowly at room temperature. Its solubility in water is low but it is miscible with xylene, hexane, chloroform, dichloromethane, methanol and acetone. Carbosulfan is used as an insecticide.[1] The European Union banned use of carbosulfan in 2007.[2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
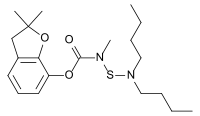
| IUPAC name
2,2-Dimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1-benzofuran-7-yl [(dibutylamino)sulfanyl]methylcarbamate | |
| Other names
2,3-Dihydro-2,2-dimethyl-7-benzofuranyl[(dibutylamino)thio] methylcarbamate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.054.132 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H32N2O3S | |
| Molar mass | 380.55 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Its oral LD50 for rats is 90 to 250 mg/kg bw, inhalation LC50 is 0.61 mg/L. Carbosulfan is only slightly absorbed through skin (LD50 >2000 mg/kg for rabbits). The mechanism of toxicity is based on reversible inhibition of acetylcholinesterase (as for carbamates generally).[3] Carbosulfan has very low maximum residue limits for use in the EU and UK examples of this can be seen in apples and oranges, where it is 0.05 mg/kg.
See also
- Carbofuran
- Carbosulfan in the Pesticide Properties DataBase (PPDB)
References
- CARBOSULFAN – Pesticide residues in food – 1984
- COMMISSION DECISION of 13 June 2007 concerning the non-inclusion of carbosulfan in Annex I to Council Directive 91/414/EEC and the withdrawal of authorisations for plant protection products containing that substance
- CARBOSULFAN – Pesticide residues in food – 2003