Pinacidil
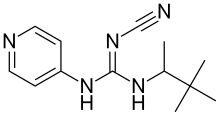
Pinacidil is a cyanoguanidine drug that opens ATP-sensitive potassium channels producing peripheral vasodilatation of arterioles.[1] It reduces blood pressure and peripheral resistance and produces fluid retention.[2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
N-cyano-N'-pyridin-4-yl-N''-(1,2,2-trimethylpropyl)guanidine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.056.614 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C13H19N5 | |
| Molar mass | 245.32346 |
| Pharmacology | |
| C02DG01 (WHO) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- Gollasch M, Bychkov R, Ried C, Behrendt F, Scholze S, Luft FC, Haller H (1995). "Pinacidil relaxes porcine and human coronary arteries by activating ATP-dependent potassium channels in smooth muscle cells". J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 275 (2): 681–92. PMID 7473155.
- Reynolds, James Blair; Martindale, William L. (1996). The extra pharmacopoeia (31st ed.). London: Royal Pharmaceutical Society. pp. 2739 pages. ISBN 0-85369-342-0.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.