Darodipine
Darodipine is an experimental calcium channel blocker that based on animal models may reduce neuronal cytoskeletal alterations during aging and in neurodegenerative disorders. Studies performed on rats have shown darodipine to have an effect on brain serotonergic systems. Darodipine increased the 5-HIAA/5-HT ratio within various parts of the brain.[1] Darodipine has also been shown to impair memory and learning processes on mice.[2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
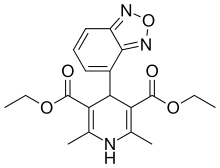
| IUPAC name
4-(2,1,3-Benzoxadiazol-7-yl)-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic acid diethyl ester | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C19H21N3O5 | |
| Molar mass | 371.393 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
See also
- Isradipine, a structural isomer of darodipine
References
- Gaggi, Renato (June–July 1995). "Effects of isradipine and darodipine on serotonergic system of the rat brain". Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior. 51 (2): 183–187.
- Lamberti, C. (Dec 1994). "Effects of the calcium-channel blockers darodipine and nimodipine on amnesia induced by three different hypoxic methods". Pharmacological Research. 30: 359.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.