Enterodiol
Enterodiol is a lignan formed by the action of intestinal bacteria on lignan precursors found in plants.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
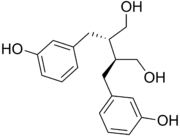
| IUPAC name
(2R,3R)-2,3-bis[(3-hydroxyphenyl)methyl]butane-1,4-diol | |
| Other names
(−)-Enterodiol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.162.704 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C18H22O4 | |
| Molar mass | 302.370 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- Lampe JW (2003). "Isoflavonoid and lignan phytoestrogens as dietary biomarkers". J Nutr. 133 (Suppl 3): 956S–964S. doi:10.1093/jn/133.3.956S. PMID 12612182.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.