EA-2613
EA-2613 is an extremely toxic organophosphate nerve agent. It's an extremely potent acetylcholinesterase inhibitor that is resistant to atropine and oxime treatment.[1]
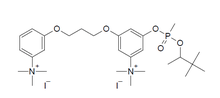 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| Properties | |
| C28H47I2N2O5P | |
| Molar mass | 776.476 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Solid |
| Melting point | 124–126 °C (255–259 °F; 397–399 K) |
| Soluble | |
| Solubility | Soluble in alcohol, acetone and chloroform |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Extremely toxic |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose) |
100 μg/kg (Rats, IV) 12 μg/kg (Rabbits, IV) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
See also
References
| Animal | |
|---|---|
| Bacterial | |
| Cyanotoxins | |
| Plant | |
| Mycotoxins | |
| Pesticides | |
| Nerve agents | |
| Bicyclic phosphates | |
| Other | |
| Enzyme (modulators) |
| ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transporter (modulators) |
| ||||||
| Release (modulators) |
| ||||||
See also: Receptor/signaling modulators • Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor modulators • Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor modulators | |||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.