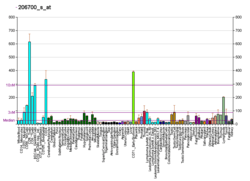
KDM5D
Lysine-specific demethylase 5D is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the KDM5D gene.[5][6][7] KDM5D belongs to the alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent hydroxylases superfamily.
This gene encodes a protein containing zinc finger domains. A short peptide derived from this protein is a minor histocompatibility antigen which can lead to graft rejection of male donor cells in a female recipient.[7]
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000012817 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000056673 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Froggatt P (Feb 1977). "The foundation of the "Inst" medical department and its association with the Belfast Fever Hospital". The Ulster Medical Journal. 45 (2): 107–45. PMC 2385577. PMID 795123.
- Kent-First MG, Maffitt M, Muallem A, Brisco P, Shultz J, Ekenberg S, Agulnik AI, Agulnik I, Shramm D, Bavister B, Abdul-Mawgood A, VandeBerg J (October 1996). "Gene sequence and evolutionary conservation of human SMCY". Nature Genetics. 14 (2): 128–9. doi:10.1038/ng1096-128. PMID 8841177.
- "Entrez Gene: JARID1D jumonji, AT rich interactive domain 1D".
Further reading
- Simpson E, Scott D, Chandler P (1997). "The male-specific histocompatibility antigen, H-Y: a history of transplantation, immune response genes, sex determination and expression cloning". Annual Review of Immunology. 15: 39–61. doi:10.1146/annurev.immunol.15.1.39. PMID 9143681.
- Wolf U (1998). "The serologically detected H-Y antigen revisited". Cytogenetics and Cell Genetics. 80 (1–4): 232–5. doi:10.1159/000014986. PMID 9678364.
- Agulnik AI, Mitchell MJ, Lerner JL, Woods DR, Bishop CE (June 1994). "A mouse Y chromosome gene encoded by a region essential for spermatogenesis and expression of male-specific minor histocompatibility antigens". Human Molecular Genetics. 3 (6): 873–8. doi:10.1093/hmg/3.6.873. PMID 7524912.
- Wang W, Meadows LR, den Haan JM, Sherman NE, Chen Y, Blokland E, Shabanowitz J, Agulnik AI, Hendrickson RC, Bishop CE (September 1995). "Human H-Y: a male-specific histocompatibility antigen derived from the SMCY protein". Science. 269 (5230): 1588–90. doi:10.1126/science.7667640. hdl:1887/2988. PMID 7667640.
- Nagase T, Seki N, Ishikawa K, Ohira M, Kawarabayasi Y, Ohara O, Tanaka A, Kotani H, Miyajima N, Nomura N (October 1996). "Prediction of the coding sequences of unidentified human genes. VI. The coding sequences of 80 new genes (KIAA0201-KIAA0280) deduced by analysis of cDNA clones from cell line KG-1 and brain". DNA Research. 3 (5): 321–9, 341–54. doi:10.1093/dnares/3.5.321. PMID 9039502.
- Agulnik AI, Bishop CE, Lerner JL, Agulnik SI, Solovyev VV (February 1997). "Analysis of mutation rates in the SMCY/SMCX genes shows that mammalian evolution is male driven". Mammalian Genome. 8 (2): 134–8. doi:10.1007/s003359900372. PMID 9060413.
- Rufer N, Wolpert E, Helg C, Tiercy JM, Gratwohl A, Chapuis B, Jeannet M, Goulmy E, Roosnek E (October 1998). "HA-1 and the SMCY-derived peptide FIDSYICQV (H-Y) are immunodominant minor histocompatibility antigens after bone marrow transplantation". Transplantation. 66 (7): 910–6. doi:10.1097/00007890-199810150-00016. PMID 9798702.
- Lau YF, Zhang J (April 2000). "Expression analysis of thirty one Y chromosome genes in human prostate cancer". Molecular Carcinogenesis. 27 (4): 308–21. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1098-2744(200004)27:4<308::AID-MC9>3.0.CO;2-R. PMID 10747295.
- Shen P, Wang F, Underhill PA, Franco C, Yang WH, Roxas A, Sung R, Lin AA, Hyman RW, Vollrath D, Davis RW, Cavalli-Sforza LL, Oefner PJ (June 2000). "Population genetic implications from sequence variation in four Y chromosome genes". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 97 (13): 7354–9. doi:10.1073/pnas.97.13.7354. PMC 16549. PMID 10861003.
- Skaletsky H, Kuroda-Kawaguchi T, Minx PJ, Cordum HS, Hillier L, Brown LG, Repping S, Pyntikova T, Ali J, Bieri T, Chinwalla A, Delehaunty A, Delehaunty K, Du H, Fewell G, Fulton L, Fulton R, Graves T, Hou SF, Latrielle P, Leonard S, Mardis E, Maupin R, McPherson J, Miner T, Nash W, Nguyen C, Ozersky P, Pepin K, Rock S, Rohlfing T, Scott K, Schultz B, Strong C, Tin-Wollam A, Yang SP, Waterston RH, Wilson RK, Rozen S, Page DC (June 2003). "The male-specific region of the human Y chromosome is a mosaic of discrete sequence classes". Nature. 423 (6942): 825–37. doi:10.1038/nature01722. PMID 12815422.
- Agate RJ, Choe M, Arnold AP (February 2004). "Sex differences in structure and expression of the sex chromosome genes CHD1Z and CHD1W in zebra finches". Molecular Biology and Evolution. 21 (2): 384–96. doi:10.1093/molbev/msh027. PMID 14660691.
- Miklos DB, Kim HT, Miller KH, Guo L, Zorn E, Lee SJ, Hochberg EP, Wu CJ, Alyea EP, Cutler C, Ho V, Soiffer RJ, Antin JH, Ritz J (April 2005). "Antibody responses to H-Y minor histocompatibility antigens correlate with chronic graft-versus-host disease and disease remission". Blood. 105 (7): 2973–8. doi:10.1182/blood-2004-09-3660. PMC 1350982. PMID 15613541.
- Piper KP, McLarnon A, Arrazi J, Horlock C, Ainsworth J, Kilby MD, Martin WL, Moss PA (January 2007). "Functional HY-specific CD8+ T cells are found in a high proportion of women following pregnancy with a male fetus". Biology of Reproduction. 76 (1): 96–101. doi:10.1095/biolreprod.106.055426. PMID 16988213.
- Iwase S, Lan F, Bayliss P, de la Torre-Ubieta L, Huarte M, Qi HH, Whetstine JR, Bonni A, Roberts TM, Shi Y (March 2007). "The X-linked mental retardation gene SMCX/JARID1C defines a family of histone H3 lysine 4 demethylases". Cell. 128 (6): 1077–88. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.02.017. PMID 17320160.
- Lee MG, Norman J, Shilatifard A, Shiekhattar R (March 2007). "Physical and functional association of a trimethyl H3K4 demethylase and Ring6a/MBLR, a polycomb-like protein". Cell. 128 (5): 877–87. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.02.004. PMID 17320162.
External links
- JARID1D+protein,+human at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- Overview of all the structural information available in the PDB for UniProt: Q9BY66 (Lysine-specific demethylase 5D) at the PDBe-KB.
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.