Projections of population growth
Population projections are attempts to show how the human population living today will change in the future.[1] These projections are an important input to forecasts of the population’s impact on this planet and humanity’s future well-being.[2]
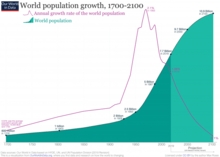
The 2019 forecast from the United Nation’s Population Division shows that world population growth peaked at 2.1% per year in 1962, has since dropped to 1.0%, and could drop even further to 0.1% by 2100, a growth rate not seen since pre-industrial revolution days.[3]
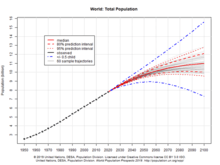
Based on this, the UN Population Division expects world population, currently (2020) at 7.8 billion, to level out at or soon after the end of the 21st Century at 10.9 billion (the median line),[4][5] assuming a continuing decrease in the global average fertility rate from 2.5 births per woman during the 2015–2020 period to 1.9 in 2095–2100, according to the medium-variant projection.[6]
About two thirds of the predicted growth in population between 2020 and 2050 will take place in Africa.[7]
Because of population momentum the global population will continue to grow, although at a steadily slower rate, for the remainder of this century, but the main driver of long-term future population growth will be the evolution of the global average fertility rate.[6]
Growth regions
The table below shows that from 2020 to 2050, the bulk of the world's population growth is predicted to take place in Africa: of the additional 1.9 billion people projected between 2020 and 2050, 1.2 billion will be added in Africa, 0.7 billion in Asia and zero in the rest of the world. Africa's share of global population is projected to grow from 17% in 2020 to 26% in 2050 and 39% by 2100, while the share of Asia will fall from 59% in 2020 to 55% in 2050 and 43% in 2100.[8][7]The strong growth of the African population will happen regardless of the rate of decrease of fertility, because of the exceptional proportion of young people already living today. For example, the UN projects that the population of Nigeria will surpass that of the United States by about 2050.[5]
| Region | Pop
2020 |
% of
Total |
Pop
2050 |
% of
Total |
Chg
2020–50 |
Pop
2100 |
% of
Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Africa | 1.3 | 17 | 2.5 | 26 | 1.2 | 4.3 | 39 |
| Asia | 4.6 | 59 | 5.3 | 55 | 0.7 | 4.7 | 43 |
| Other | 1.9 | 24 | 1.9 | 20 | 0.0 | 1.9 | 17 |
| World | 7.8 | 100 | 9.7 | 100 | 1.9 | 10.9 | 100 |
The population of the More Developed regions is slated to remain mostly unchanged, at 1.3 billion for the remainder of the 21st century. All population growth comes from the Less Developed regions.[8][9]
| Region | Pop
2020 |
% of
Total |
Pop
2050 |
% of
Total |
Chg
2020–50 |
Pop
2100 |
% of
Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| More Developed | 1.3 | 17 | 1.3 | 13 | 0.0 | 1.3 | 12 |
| Less Developed | 6.5 | 83 | 8.4 | 87 | 1.9 | 9.6 | 88 |
| World | 7.8 | 100 | 9.7 | 100 | 1.9 | 10.9 | 100 |
The table below breaks out the UN’s future population growth predictions by region[7]
| Region | 2020–25
% chg/yr
|
2045–50
% chg/yr |
2095–2100
% chg/yr |
|---|---|---|---|
| Africa | 2.4 | 1.8 | 0.6 |
| Asia | 0.8 | 0.1 | -0.4 |
| Europe | 0.0 | -0.3 | -0.1 |
| Latin America & the Caribbean | 0.8 | 0.2 | -0.5 |
| Northern America | 0.6 | 0.3 | 0.2 |
| Oceania | 1.2 | 0.8 | 0.4 |
| World | 1.0 | 0.5 | 0.0 |
Between 2020 and the end of this century, the UN predicts that all six regions will experience declines in population growth, that by the end of the century three of them will be experiencing population decline, and the world will have reached zero population growth.
World population in 2050
.svg.png)
Asia Africa Europe Latin America Northern America Oceania
The median scenario of the UN 2019 World Population Prospects[8] predicts the following populations per region in 2050 (compared to population in 2000), in billions:
| 2000 | 2050 | growth | %/yr | |
| Asia | 3.74 | 5.29 | +41% | +0.7% |
| Africa | 0.81 | 2.49 | +207% | +2.3% |
| Europe | 0.73 | 0.71 | -3% | -0.1% |
| South/Central America +Caribbean | 0.52 | 0.76 | +46% | +0.8% |
| Northern America | 0.31 | 0.43 | +39% | +0.7% |
| Oceania | 0.03 | 0.06 | +100% | +1.4% |
| World | 6.14 | 9.74 | +60% | +0.9% |
After 2050
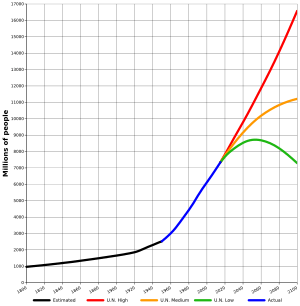
Projections of population reaching more than one generation into the future are highly speculative: Thus, the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs report of 2004 projected the world population to peak at 9.22 billion in 2075 and then stabilise at a value close to 9 billion;[11] By contrast, a 2014 projection by the United Nations Population Division predicts a population close to 11 billion by 2100 without any declining trend in the foreseeable future.[12] On the other hand, a conservative scenario published in 2012 assumes that a maximum of 8 billion will be reached before 2040.[13]
Projections for after 2050 have usually assumed that fertility rates will have declined by then and the population will be stable or will decrease. However, a study in 2014 found that fertility rates in Africa have leveled off at around 4.6 instead of continuing to decline, and that consequently world population may be as high as 12 billion by 2100. Reasons for the continuing high birth rate include better survival rates with respect to HIV, and contraception shortage.[14][15] Evolutionary biology also suggests the demographic transition may reverse itself and global population may continue to grow in the long term.[16] In addition, recent evidence suggests birth rates may be rising in the 21st century in the developed world.[17]
UN projections published in 2019 estimate the world population in 2100 to be 10.9 billion.[8]
Year by year
The following table shows projections of world population for the 21st century.
| Year | United States Census Bureau
(2015)[18] |
Population Reference Bureau
(1973–2015)[19] |
United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs
(2015)[20] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 7,334,771,614 | 7,432,663,280 | |
| 2017 | 7,412,778,971 | ||
| 2018 | 7,490,427,640 | ||
| 2019 | 7,567,402,977 | ||
| 2020 | 7,643,402,123 | 7,758,157,000 | |
| 2021 | 7,718,256,830 | ||
| 2022 | 7,792,021,317 | ||
| 2023 | 7,864,725,370 | ||
| 2024 | 7,936,271,554 | ||
| 2025 | 8,006,580,553 | 8,000,000,000 | 8,141,661,000 |
| 2026 | 8,075,716,000 | ||
| 2027 | 8,143,729,466 | ||
| 2028 | 8,210,559,895 | ||
| 2029 | 8,276,190,519 | ||
| 2030 | 8,340,606,590 | 8,505,000,000 | 8,500,766,000 |
| 2031 | 8,403,880,343 | ||
| 2032 | 8,466,094,022 | ||
| 2033 | 8,527,246,205 | ||
| 2034 | 8,587,325,154 | ||
| 2035 | 8,646,304,704 | 8,838,908,000 | |
| 2036 | 8,704,239,274 | ||
| 2037 | 8,761,189,197 | ||
| 2038 | 8,817,138,785 | ||
| 2039 | 8,872,066,537 | ||
| 2040 | 8,925,949,679 | 9,157,234,000 | |
| 2041 | 8,978,822,945 | ||
| 2042 | 9,030,723,366 | ||
| 2043 | 9,081,617,002 | ||
| 2044 | 9,131,462,326 | ||
| 2045 | 9,180,225,214 | 9,453,892,000 | |
| 2046 | 9,227,935,007 | ||
| 2047 | 9,274,616,811 | ||
| 2048 | 9,320,232,984 | ||
| 2049 | 9,364,750,182 | ||
| 2050 | 9,408,141,302 | 9,804,000,000 | 9,725,148,000 |
| 2055 | 9,968,809,000 | ||
| 2060 | 10,184,290,000 | ||
| 2065 | 10,375,719,000 | ||
| 2070 | 10,547,989,000 | ||
| 2075 | 10,701,653,000 | ||
| 2080 | 10,836,635,000 | ||
| 2085 | 10,953,525,000 | ||
| 2090 | 11,055,270,000 | ||
| 2095 | 11,142,461,000 | ||
| 2100 | 11,213,317,000 | ||
Drivers of population change
The population of a country or area grows or declines through the interaction of three demographic drivers: fertility, mortality, and migration.[2]
Fertility
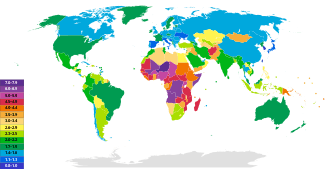
Fertility is expressed as the total fertility rate (TFR), a measure of the number of children on average that a woman will bear in her lifetime. With longevity trending towards uniform and stable values worldwide, the main driver of future population growth will be the evolution of the fertility rate.[6]
Where fertility is high, demographers generally assume that fertility will decline and eventually stabilize at about two children per woman.[2]
From 2015 to 2020, the average world fertility rate was 2.5 children per woman,[6] about half the level in 1950–1955 (5 children per woman). In the medium variant, global fertility is projected to decline further to 2.2 in 2045 to 2050 and to 1.9 in 2095–2100.[6]
Mortality
If the mortality rate is relatively high and the resulting life expectancy is therefore relatively low, changes in mortality can have a material impact on population growth. Where the mortality rate is low and life expectancy has therefore risen, a change in mortality will have much less an effect.[2]
Because child mortality has declined substantially over the last several decades,[2] Global life expectancy at birth, which is estimated to have risen from 47 years in 1950–1955 to 67 years in 2000–2005,[21] is expected to keep rising to reach 77 years in 2045–2050.[22] In the More Developed regions, the projected increase is from 79 years today[21] to 83 years by mid-century.[22] Among the Least Developed countries, where life expectancy today is just under 65 years,[21] it is expected to be 71 years in 2045–2050.[22]
The population of 31 countries or areas, including Ukraine, Romania, Japan and most of the successor states of the Soviet Union, is expected to be lower in 2050 than in 2005.
Migration
Migration can have a significant effect on population change. To this, Global South-South migration accounts for 38% of total migration, as opposed to only 34% for Global South-North.[23] For example, the United Nations reports that during the period 2010–2020, fourteen countries will have seen a net inflow of more than one million migrants, while ten countries will have seen a net outflow of similar proportions. The largest migratory outflows have been in response to demand for workers in other countries (Bangladesh, Nepal and the Philippines) or to insecurity in the home country (Myanmar, Syria and Venezuela). Belarus, Estonia, Germany, Hungary, Italy, Japan, the Russian Federation, Serbia and Ukraine have experienced a net inflow of migrants over the decade, helping to offset population losses caused by a negative natural increase (births minus deaths).[24]
History of population projections
Walter Greiling projected in the 1950s that world population would reach a peak of about nine billion, in the 21st century, and then stop growing after a readjustment of the Third World and a sanitation of the tropics.[25]
Estimates published in the 2000s tended to predict that the population of Earth would stop increasing around 2070;[26]In a 2004 long-term prospective report, the United Nations Population Division projected the world population would peak at 9.22 billion in 2075. After reaching this maximum, it would decline slightly and then resume a slow increase, reaching a level of 8.97 billion by 2300, about the same as the projected 2050 figure.[27]
This prediction was revised in the 2010s, to the effect that no maximum will likely be reached in the 21st century.[28] The main reason for the revision was that the ongoing rapid population growth in Africa had been underestimated. A 2014 paper by demographers from several universities and the United Nations Population Division forecast that the world's population would reach about 10.9 billion in 2100 and continue growing thereafter.[12] In 2017 the UN predicted a decline of global population growth rate from +1.0% in 2020 to +0.5% in 2050 and to +0.1% in 2100.[10]
Jørgen Randers, one of the authors of the seminal 1972 long-term simulations in The Limits to Growth, offered an alternative scenario in a 2012 book, arguing that traditional projections insufficiently take into account the downward impact of global urbanization on fertility. Randers' "most likely scenario" predicts a peak in the world population in the early 2040s at about 8.1 billion people, followed by decline.[29]
Some of the authors of the 2004 UN report say that life expectancy is assumed to rise slowly and continuously. The projections in the report assume this with no upper limit, though at a slowing pace depending on circumstances in individual countries. By 2100, the report assumed life expectancy to be from 66 to 97 years, and by 2300 from 87 to 106 years, depending on the country. Based on that assumption, they said that rising life expectancy will produce small but continuing population growth by the end of the projections, ranging from 0.03 to 0.07 percent annually. The hypothetical feasibility (and wide availability) of life extension by technological means would further exacerbate the overpopulation problem.[30][31][32]
Most populous nations by 2050 and 2100
The UN Population Division has calculated the future population of the world's countries, based on current demographic trends. Current population is around 7.7-7.8 billion people living in the world so far. The 2019 report projects the world population in 2050 to be 9.7 billion people, and possibly as high to 11 billion by the next century, with the following estimates for the top 14 countries in 2020, 2050,and 2100:[8]
| Country | Pop
2020 (mil) |
Pop
2050 (mil) |
Pop
2100 (mil) |
2020
Rank |
2050
Rank |
2100
Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| China | 1,439 | 1,402 | 1,065 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| India | 1,380 | 1,639 | 1,447 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| United States | 331 | 379 | 434 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Indonesia | 273 | 331 | 321 | 4 | 6 | 7 |
| Pakistan | 221 | 338 | 403 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Brazil | 212 | 229 | 181 | 6 | 7 | 12 |
| Nigeria | 206 | 401 | 733 | 7 | 3 | 3 |
| Bangladesh | 165 | 192 | 151 | 8 | 10 | 14 |
| Russian Federation | 146 | 136 | 126 | 9 | 14 | 19 |
| Mexico | 129 | 155 | 141 | 10 | 12 | 17 |
| Japan | 126 | 106 | 75 | 11 | 17 | 36 |
| Ethiopia | 115 | 205 | 294 | 12 | 8 | 8 |
| Philippines | 110 | 144 | 146 | 13 | 13 | 15 |
| Egypt | 102 | 160 | 225 | 14 | 11 | 10 |
| Dem Republic of Congo | 90 | 194 | 362 | 16 | 9 | 6 |
| Tanzania | 60 | 129 | 286 | 24 | 15 | 9 |
| Angola | 33 | 77 | 188 | 44 | 24 | 11 |
| Niger | 24 | 66 | 165 | 56 | 30 | 13 |
| World | 7,795 | 9,735 | 10,875 |
From 2017 to 2050, the nine highlighted countries are expected to account for half of the world's projected population increase: India, Nigeria, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Pakistan, Ethiopia, Tanzania, the United States, Uganda, and Indonesia, listed according to the expected size of their contribution to that projected population growth.[24]
Population projections of the 101 largest metropolitan areas in the 21st century
Large urban areas are hubs of economic development and innovation, with larger cities underpinning regional economies and local and global sustainability initiatives. Currently, 757 million humans live in the 101 largest cities;[33] these cities are home to 11% of the world's population.[33] By the end of the century, the world population is projected to grow, with estimates ranging from 6.9 billion to 13.1 billion;[33] the percentage of people living in the 101 largest cities is estimated to be 15% to 23%.[33]
The following 101 metropolitan areas with the largest population projections for the years 2025, 2050, 2075, and 2100 are listed below.[33]
See also
- Population projection
- Population growth
- World population estimates
- Human overpopulation
- Pledge two or fewer (campaign for smaller families)
- List of countries and territories by fertility rate
- List of countries by number of births
References
- "Population Projections". United States Census Bureau.
- Kaneda, Toshiko (June 2014). "Understanding Population Projections: Assumptions Behind the Numbers" (PDF). Population Reference Bureau.
- Roser, Max (June 18, 2019). "Two centuries of rapid global population growth will come to an end". Our World in Data.
- "World Population Prospects 2019". United Nations, Dept of Economic and Social Affairs. 2019.
- "World Population Prospects 2019, Population Data, File: Total Population Both Sexes, Medium Variant tab". United Nations Population Division. 2019.
- "World Population Prospects 2019, Dept of Economic and Social Affairs, File: Total Fertility". United Nations Population Division. 2019.
- "World Population Prospects 2019, Population Data, File: Population Growth Rate, Median Variant tab". United Nations Population Division. 2019.
- "World Population Prospects 2019, Population Data, File: Total Population-Both Sexes, Estimates tab". United Nations Population Division. 2019.
- "Standard country or area codes for statistical use (the M49 standard)". United Nations, Dept of Economics and Social Affairs, Statistics Division. 1999.
- "World Population Prospects 2017, Archive, File: 2017 Revision". United Nations Population Division. 2017. Retrieved 2017-11-29.
- United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs. World Population to 2300. 2004. Executive Summary, p. 2.
- Gerland, P.; Raftery, A. E.; Ev Ikova, H.; Li, N.; Gu, D.; Spoorenberg, T.; Alkema, L.; Fosdick, B. K.; Chunn, J.; Lalic, N.; Bay, G.; Buettner, T.; Heilig, G. K.; Wilmoth, J. (September 14, 2014). "World population stabilization unlikely this century". Science. AAAS. 346 (6206): 234–7. doi:10.1126/science.1257469. ISSN 1095-9203. PMC 4230924. PMID 25301627.
- Randers, Jorgen (2012). 2052: A Global Forecast for the Next Forty Years. Vermont: Chelsea Green Publishing. p. 62.
- Andy Coghlan (27 Sep 2014). "Global population may boom well beyond the year 2050". New Scientist: 11.
- Patrick Gerland, Adrian Raftery; et al. (18 Sep 2014). "World population stabilization unlikely this century". Science. 346 (6206): 234–7. doi:10.1126/science.1257469. PMC 4230924. PMID 25301627.
- Jason Collins (January 2019). "The heritability of fertility makes world population stabilization unlikely in the foreseeable future". Evolution and Human Behavior. 40 (1): 105–111. doi:10.1016/j.evolhumbehav.2018.09.001.
- Can we be sure the world's population will stop rising?, BBC News, 13 October 2012
- Data from U.S. Census Bureau, International Data Base Retrieved on 28 Oct, 2017
- Data from Population Reference Bureau.
- Data from United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. Archived 2014-03-20 at the Wayback Machine
1950–2100 estimates (only medium variants shown): (a) World Population Prospects: The 2008 Revision. Archived 2007-03-21 at the Wayback Machine
Estimates prior to 1950: (b) "The World at Six Billion", 1999.
Estimates from 1950 to 2100: (c) "Population of the entire world, yearly, 1950 - 2100", 2013. Archived November 19, 2016, at the Wayback Machine
2014: (d) http://esa.un.org/unpd/wup/Highlights/WUP2014-Highlights.pdf Archived 2014-11-02 at the Wayback Machine "2014 World Urbanization Prospects", 2014.]
2015: (e) http://esa.un.org/unpd/wpp/Publications/Files/Key_Findings_WPP_2015.pdf"2015 World Urbanization Prospects", 2015.] Archived March 20, 2014, at the Wayback Machine - "World Population Prospects 2019, Mortality Data, File: Life Expectancy at Birth – Both Sexes, Estimates tab". United Nations Population Division. 2019.
- "World Population Prospects, Mortality Data, File: Life Expectancy at Birth – Both Sexes, Median Variant tab". United Nations Population Division. 2019.
- "World Bank Migration and Remittances Factbook 2016" (PDF). World Bank Open Knowledge Archive. 2016.
- "Growing at a slower pace, world population is expected to reach 9.7 billion in 2050 and could peak at nearly 11 billion around 2100". United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs. June 17, 2019.
- Walter Greiling: Wie werden wir leben? ("How are we going to live?") Econ publishers, Munich 1954
- Ciro Pabón y Ciro Pabón, Manual de Urbanismo, Editorial Leyer, Bogotá, 2007, ISBN 978-958-711-296-2
- World Population to 2300. 2004. ISBN 9789211514018.
- "World Population Prospects 2105, Archive, File: 2015 Revision". United Nations Population Division. 2015.
- Randers, Jørgen (2012). 2052: A Global Forecast for the Next Forty Years. Vermont: Chelsea Green Publishing. p. 62.
- Newmark, PA; Sánchez Alvarado, A (2002). "Not your father's planarian: a classic model enters the era of functional genomics". Nat Rev Genet. 3 (3): 210–219. doi:10.1038/nrg759. PMID 11972158.
- Bavestrello, Giorgio; Sommer, Christian; Sarà, Michele (1992). "Bi-directional conversion in Turritopsis nutricula (Hydrozoa)". Scientia Marina. 56 (2–3): 137–140.
- Martínez, DE (1998). "Mortality patterns suggest lack of senescence in hydra". Exp Gerontol. 33 (3): 217–225. doi:10.1016/S0531-5565(97)00113-7. PMID 9615920. In an essay within the 2004 U.N. report, Tim Dyson said: "A rapid increase in life expectancy, which would raise the population pyramids, seems within reach, since it responds to an old and powerful demand for longevity."
- Hoornweg, Daniel; Pope, Kevin (January 2014). "Population predictions of the 101 largest cities in the 21st century" (PDF). Global Cities Institute (Working Paper No. 4).