Organelle
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit, usually within a cell, that has a specific function. The name organelle comes from the idea that these structures are parts of cells, as organs are to the body, hence organelle, the suffix -elle being a diminutive. Organelles are either separately enclosed within their own lipid bilayers (also called membrane-bound organelles) or are spatially distinct functional units without a surrounding lipid bilayer (non-membrane bound organelles). Although most organelles are functional units within cells, some functional units that extend outside of cells are often termed organelles, such as cilia, the flagellum and archaellum, and the trichocyst.
| Organelle | |
|---|---|
| Details | |
| Pronunciation | /ɔːrɡəˈnɛl/ |
| Part of | Cell |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | organella |
| MeSH | D015388 |
| TH | H1.00.01.0.00009 |
| FMA | 63832 |
| Anatomical terms of microanatomy | |
Organelles are identified by microscopy, and can also be purified by cell fractionation. There are many types of organelles, particularly in eukaryotic cells. They include structures that make up the internal endomembrane system (such as the nuclear envelope, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi apparatus), and other structures such as mitochondria and plastids. While prokaryotes do not possess eukaryotic organelles, some do contain protein-shelled bacterial microcompartments, which are thought to act as primitive prokaryotic organelles,[1] and there is also evidence of membrane-bounded structures. Also, the prokaryotic flagellum which protrudes outside the cell, and its motor, as well as the largely extracellular pilus, are often spoken of as organelles.
History and terminology
| Cell biology | |
|---|---|
| The animal cell | |
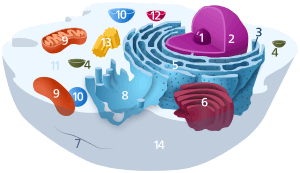 Components of a typical animal cell:
|
In biology organs are defined as confined functional units within an organism.[2] The analogy of bodily organs to microscopic cellular substructures is obvious, as from even early works, authors of respective textbooks rarely elaborate on the distinction between the two.
In the 1830s, Félix Dujardin refuted Ehrenberg theory which said that microorganisms have the same organs of multicellular animals, only minor.[3]
Credited as the first[4][5][6] to use a diminutive of organ (i.e., little organ) for cellular structures was German zoologist Karl August Möbius (1884), who used the term organula (plural of organulum, the diminutive of Latin organum).[7] In a footnote, which was published as a correction in the next issue of the journal, he justified his suggestion to call organs of unicellular organisms "organella" since they are only differently formed parts of one cell, in contrast to multicellular organs of multicellular organisms.[7][8]
Types
While most cell biologists consider the term organelle to be synonymous with cell compartment, a space often bound by one or two lipid bilayers, some cell biologists choose to limit the term to include only those cell compartments that contain deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), having originated from formerly autonomous microscopic organisms acquired via endosymbiosis.[9][10][11]
Under this definition, there would only be two broad classes of organelles (i.e. those that contain their own DNA, and have originated from endosymbiotic bacteria):
- mitochondria (in almost all eukaryotes)
- plastids[12] (e.g. in plants, algae, and some protists).
Other organelles are also suggested to have endosymbiotic origins, but do not contain their own DNA (notably the flagellum – see evolution of flagella).
A second, less restrictive definition of organelles is that they are membrane-bound structures. However, even by using this definition, some parts of the cell that have been shown to be distinct functional units do not qualify as organelles. Therefore, the use of organelle to also refer to non-membrane bound structures such as ribosomes is common and accepted.[13][14][15] This has led many texts to delineate between membrane-bound and non-membrane bound organelles.[16] The non-membrane bound organelles, also called large biomolecular complexes, are large assemblies of macromolecules that carry out particular and specialized functions, but they lack membrane boundaries. Many of these are referred to as "proteinaceous organelles" as there many structure is made of proteins. Such cell structures include:
- large RNA and protein complexes: ribosome, spliceosome, vault
- large protein complexes: proteasome, DNA polymerase III holoenzyme, RNA polymerase II holoenzyme, symmetric viral capsids, complex of GroEL and GroES; membrane protein complexes: photosystem I, ATP synthase
- large DNA and protein complexes: nucleosome
- centriole and microtubule-organizing center (MTOC)
- cytoskeleton
- flagellum
- nucleolus
- stress granule
- germ cell granule
- neuronal transport granule
The mechanisms by which such non-membrane bound organelles form and retain their spatial integrity have been likened to liquid-liquid phase separation.[17]
Eukaryotic organelles
Eukaryotic cells are structurally complex, and by definition are organized, in part, by interior compartments that are themselves enclosed by lipid membranes that resemble the outermost cell membrane. The larger organelles, such as the nucleus and vacuoles, are easily visible with the light microscope. They were among the first biological discoveries made after the invention of the microscope.
Not all eukaryotic cells have each of the organelles listed below. Exceptional organisms have cells that do not include some organelles that might otherwise be considered universal to eukaryotes (such as mitochondria).[18] There are also occasional exceptions to the number of membranes surrounding organelles, listed in the tables below (e.g., some that are listed as double-membrane are sometimes found with single or triple membranes). In addition, the number of individual organelles of each type found in a given cell varies depending upon the function of that cell.
| Organelle | Main function | Structure | Organisms | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| cell membrane | separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment (the extracellular space) which protects the cell from its environment. | two-dimensional liquid | all eukaryotes | |
| cell wall | The cell wall is composed of peptidoglycan and is rigid, provides shape to the cell, helps to keeps the organelles inside the cell, and does not let the cell burst due to changes in osmotic pressure. | cellulose | plants, protists, rare kleptoplastic organisms | |
| chloroplast (plastid) | photosynthesis, traps energy from sunlight | double-membrane compartment | plants, protists, rare kleptoplastic organisms | has own DNA; theorized to be engulfed by the ancestral eukaryotic cell (endosymbiosis) |
| endoplasmic reticulum | translation and folding of new proteins (rough endoplasmic reticulum), expression of lipids (smooth endoplasmic reticulum) | single-membrane compartment | all eukaryotes | rough endoplasmic reticulum is covered with ribosomes, has folds that are flat sacs; smooth endoplasmic reticulum has folds that are tubular |
| flagellum | locomotion, sensory | protein | some eukaryotes | |
| Golgi apparatus | sorting, packaging, processing and modification of proteins | single-membrane compartment | all eukaryotes | cis-face (convex) nearest to rough endoplasmic reticulum; trans-face (concave) farthest from rough endoplasmic reticulum |
| mitochondrion | energy production from the oxidation of glucose substances and the release of adenosine triphosphate | double-membrane compartment | most eukaryotes | constituting element of the chondriome; has own DNA; theorized to have been engulfed by an ancestral eukaryotic cell (endosymbiosis)[19] |
| nucleus | DNA maintenance, controls all activities of the cell, RNA transcription | double-membrane compartment | all eukaryotes | contains bulk of genome |
| vacuole | storage, transportation, helps maintain homeostasis | single-membrane compartment | eukaryotes | |
Mitochondria and plastids, including chloroplasts, have double membranes and their own DNA. According to the endosymbiotic theory, they are believed to have originated from incompletely consumed or invading prokaryotic organisms.
| Organelle/Macromolecule | Main function | Structure | Organisms |
|---|---|---|---|
| acrosome | helps spermatozoa fuse with ovum | single-membrane compartment | most animals |
| autophagosome | vesicle that sequesters cytoplasmic material and organelles for degradation | double-membrane compartment | all eukaryotes |
| centriole | anchor for cytoskeleton, organizes cell division by forming spindle fibers | Microtubule protein | animals |
| cilium | movement in or of external medium; "critical developmental signaling pathway".[20] | Microtubule protein | animals, protists, few plants |
| cnidocyst | stinging | coiled hollow tubule | cnidarians |
| eyespot apparatus | detects light, allowing phototaxis to take place | green algae and other unicellular photosynthetic organisms such as euglenids | |
| glycosome | carries out glycolysis | single-membrane compartment | Some protozoa, such as Trypanosomes. |
| glyoxysome | conversion of fat into sugars | single-membrane compartment | plants |
| hydrogenosome | energy & hydrogen production | double-membrane compartment | a few unicellular eukaryotes |
| lysosome | breakdown of large molecules (e.g., proteins + polysaccharides) | single-membrane compartment | animals |
| melanosome | pigment storage | single-membrane compartment | animals |
| mitosome | probably plays a role in Iron-sulfur cluster (Fe-S) assembly | double-membrane compartment | a few unicellular eukaryotes that lack mitochondria |
| myofibril | myocyte contraction | bundled filaments | animals |
| nucleolus | pre-ribosome production | protein-DNA-RNA | most eukaryotes |
| ocelloid | detects light and possibly shapes, allowing phototaxis to take place | double-membrane compartment | members of the family Warnowiaceae |
| parenthesome | not characterized | not characterized | fungi |
| peroxisome | breakdown of metabolic hydrogen peroxide | single-membrane compartment | all eukaryotes |
| proteasome | degradation of unneeded or damaged proteins by proteolysis | very large protein complex | all eukaryotes, all archaea, and some bacteria |
| ribosome (80S) | translation of RNA into proteins | RNA-protein | all eukaryotes |
| stress granule | mRNA storage[21] | membraneless
(mRNP complexes) |
most eukaryotes |
| TIGER domain | mRNA encoding proteins | membraneless | most organisms |
| vesicle | material transport | single-membrane compartment | all eukaryotes |
Other related structures:
Prokaryotic organelles

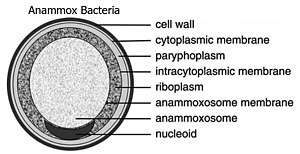
Prokaryotes are not as structurally complex as eukaryotes, and were once thought not to have any internal structures enclosed by lipid membranes. In the past, they were often viewed as having little internal organization, and lack cellular compartments; but slowly, details are emerging about prokaryotic internal structures. An early false turn was the idea developed in the 1970s that bacteria might contain cell membrane folds termed mesosomes, but these were later shown to be artifacts produced by the chemicals used to prepare the cells for electron microscopy.[23]
However, there is increasing evidence of compartmentalization in at least some prokaryotes.[24] Recent research has revealed that at least some prokaryotes have microcompartments, such as carboxysomes. These subcellular compartments are 100–200 nm in diameter and are enclosed by a shell of proteins.[1] Even more striking is the description of membrane-bound magnetosomes in bacteria, reported in 2006.[25][26]
In the bacterial phylum Planctomycetes, internal membrane-bound structures have been found. Plancomycetes species have an intracytoplasmic membranes that separates the cytoplasm into paryphoplasm (an outer ribosome-free space) and pirellulosome (or riboplasm, an inner ribosome-containing space).[27] Membrane-bound anammoxosomes have been discovered in five Plancomycetes anammox genera.[28] In the Plancomycetes Gemmata obscuriglobus, a nucleus-like structure surrounded by lipid membranes has been reported.[27][29]
Compartmentalization is a feature of prokaryotic photosynthetic structures.[24] Purple bacteria have "chromatophores", which are reaction centers found in invaginations of the cell membrane.[24] Green sulfur bacteria have chlorosomes, which are photosynthetic antenna complexes found bonded to cell membranes.[24] Cyanobacteria have internal thylakoid membranes for light-dependent photosynthesis; studies have revealed that the cell membrane and the thylakoid membranes are not continuous with each other.[24]
| Organelle/macromolecule | Main function | Structure | Organisms |
|---|---|---|---|
| anammoxosome | anaerobic ammonium oxidation | ladderane lipid membrane | "Candidatus" bacteria within Planctomycetes |
| carboxysome | carbon fixation | protein-shell bacterial microcompartment | some bacteria |
| chlorosome | photosynthesis | light harvesting complex attached to cell membrane | green sulfur bacteria |
| flagellum | movement in external medium | protein filament | some prokaryotes and eukaryotes |
| magnetosome | magnetic orientation | inorganic crystal, lipid membrane | magnetotactic bacteria |
| nucleoid | DNA maintenance, transcription to RNA | DNA-protein | prokaryotes |
| pilus | Adhesion to other cells for conjugation or to a solid substrate to create motile forces. | a hair-like appendage sticking out (though partially embedded into) the plasma membrane | prokaryotic cells |
| plasmid | DNA exchange | circular DNA | some bacteria |
| ribosome (70S) | translation of RNA into proteins | RNA-protein | bacteria and archaea |
| thylakoid membranes | photosynthesis | photosystem proteins and pigments | mostly cyanobacteria |
See also
- CoRR hypothesis
- Ejectosome
- Endosymbiotic theory
- Organelle biogenesis
- Membrane vesicle trafficking
- Host-pathogen interface
References
- Kerfeld CA, Sawaya MR, Tanaka S, Nguyen CV, Phillips M, Beeby M, Yeates TO (August 2005). "Protein structures forming the shell of primitive organelles". Science. 309 (5736): 936–8. Bibcode:2005Sci...309..936K. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.1026.896. doi:10.1126/science.1113397. PMID 16081736.
- Peterson L (April 17, 2010). "Mastering the Parts of a Cell". Lesson Planet. Retrieved 2010-04-19.
- Di Gregorio MA (2005). From Here to Eternity: Ernst Haeckel and Scientific Faith. Gottingen: Vandenhoeck & Ruprecht. p. 218.
- Bütschli O (1888). Dr. H. G. Bronn's Klassen u. Ordnungen des Thier-Reichs wissenschaftlich dargestellt in Wort und Bild. Erster Band. Protozoa. Dritte Abtheilung: Infusoria und System der Radiolaria. p. 1412.
Die Vacuolen sind demnach in strengem Sinne keine beständigen Organe oder O r g a n u l a (wie Möbius die Organe der Einzelligen im Gegensatz zu denen der Vielzelligen zu nennen vorschlug).
- Ryder JA, ed. (February 1889). "Embryology: The Structure of the Human Spermatozoon". American Naturalist. 23: 184.
It may possibly be of advantage to use the word organula here instead of organ, following a suggestion by Möbius. Functionally differentiated multicellular aggregates in multicellular forms or metazoa are in this sense organs, while, for functionally differentiated portions of unicellular organisms or for such differentiated portions of the unicellular germ-elements of metazoa, the diminutive organula is appropriate.
- Robin C, Pouchet G, Duval MM, Retterrer E, Tourneux F (1891). Journal de l'anatomie et de la physiologie normales et pathologiques de l'homme et des animaux. F. Alcan.
-
Möbius K (September 1884). "Das Sterben der einzelligen und der vielzelligen Tiere. Vergleichend betrachtet". Biologisches Centralblatt. 4 (13, 14): 389–392, 448.
Während die Fortpflanzungszellen der vielzelligen Tiere unthätig fortleben bis sie sich loslösen, wandern und entwickeln, treten die einzelligen Tiere auch durch die an der Fortpflanzung beteiligten Leibesmasse in Verkehr mit der Außenwelt und viele bilden sich dafür auch besondere Organula". Footnote on p. 448: "Die Organe der Heteroplastiden bestehen aus vereinigten Zellen. Da die Organe der Monoplastiden nur verschieden ausgebildete Teile e i n e r Zelle sind schlage ich vor, sie „Organula“ zu nennen
- Walker, Patrick (2009). Nuclear import of histone fold motif containing heterodimers by importin 13. Niedersächsische Staats-und Universitätsbibliothek Göttingen.
- Keeling PJ, Archibald JM (April 2008). "Organelle evolution: what's in a name?". Current Biology. 18 (8): R345-7. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2008.02.065. PMID 18430636.
- Imanian B, Carpenter KJ, Keeling PJ (March–April 2007). "Mitochondrial genome of a tertiary endosymbiont retains genes for electron transport proteins". The Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology. 54 (2): 146–53. doi:10.1111/j.1550-7408.2007.00245.x. PMID 17403155.
- Mullins C (2004). "Theory of Organelle Biogenesis: A Historical Perspective". The Biogenesis of Cellular Organelles. Springer Science+Business Media, National Institutes of Health. ISBN 978-0-306-47990-8.
- Alberts B, Johnson A, Lewis J, Raff M, Roberts K, Walter P. "The Genetic Systems of Mitochondria and Plastids". Molecular Biology of the Cell (4th ed.). ISBN 978-0-8153-3218-3.
- Campbell NA, Reece JB, Mitchell LG (2002). Biology (6th ed.). Benjamin Cummings. ISBN 978-0-8053-6624-2.
- Nott TJ, Petsalaki E, Farber P, Jervis D, Fussner E, Plochowietz A, Craggs TD, Bazett-Jones DP, Pawson T, Forman-Kay JD, Baldwin AJ (March 2015). "Phase transition of a disordered nuage protein generates environmentally responsive membraneless organelles". Molecular Cell. 57 (5): 936–947. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2015.01.013. PMC 4352761. PMID 25747659.
- Banani SF, Lee HO, Hyman AA, Rosen MK (May 2017). "Biomolecular condensates: organizers of cellular biochemistry". Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology. 18 (5): 285–298. doi:10.1038/nrm.2017.7. PMID 28225081.
- Cormack DH (1984). Introduction to Histology. Lippincott. ISBN 978-0-397-52114-2.
- Brangwynne CP, Eckmann CR, Courson DS, Rybarska A, Hoege C, Gharakhani J, Jülicher F, Hyman AA (June 2009). "Germline P granules are liquid droplets that localize by controlled dissolution/condensation". Science. 324 (5935): 1729–32. Bibcode:2009Sci...324.1729B. doi:10.1126/science.1172046. PMID 19460965.
- Fahey RC, Newton GL, Arrick B, Overdank-Bogart T, Aley SB (April 1984). "Entamoeba histolytica: a eukaryote without glutathione metabolism". Science. 224 (4644): 70–2. Bibcode:1984Sci...224...70F. doi:10.1126/science.6322306. PMID 6322306.
- Alberts B, Johnson A, Lewis J, Morgan D, Raff MC, Roberts K, Walter P, Wilson JH, Hunt T (2014-11-18). Molecular biology of the cell (Sixth ed.). Garland Science. p. 679. ISBN 978-0815345244.
- Badano JL, Mitsuma N, Beales PL, Katsanis N (September 2006). "The ciliopathies: an emerging class of human genetic disorders". Annual Review of Genomics and Human Genetics. 7: 125–48. doi:10.1146/annurev.genom.7.080505.115610. PMID 16722803.
- Anderson P, Kedersha N (March 2008). "Stress granules: the Tao of RNA triage". Trends in Biochemical Sciences. 33 (3): 141–50. doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2007.12.003. PMID 18291657.
- Tsai Y, Sawaya MR, Cannon GC, Cai F, Williams EB, Heinhorst S, Kerfeld CA, Yeates TO (June 2007). "Structural analysis of CsoS1A and the protein shell of the Halothiobacillus neapolitanus carboxysome". PLoS Biology. 5 (6): e144. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0050144. PMC 1872035. PMID 17518518.
- Ryter A (January–February 1988). "Contribution of new cryomethods to a better knowledge of bacterial anatomy". Annales de l'Institut Pasteur. Microbiology. 139 (1): 33–44. doi:10.1016/0769-2609(88)90095-6. PMID 3289587.
- Murat, Dorothee; Byrne, Meghan; Komeili, Arash (2010-10-01). "Cell Biology of Prokaryotic Organelles". Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a000422. PMC 2944366. PMID 20739411. Retrieved 2020-07-11.
- Komeili A, Li Z, Newman DK, Jensen GJ (January 2006). "Magnetosomes are cell membrane invaginations organized by the actin-like protein MamK" (PDF). Science. 311 (5758): 242–5. Bibcode:2006Sci...311..242K. doi:10.1126/science.1123231. PMID 16373532.
- Scheffel A, Gruska M, Faivre D, Linaroudis A, Plitzko JM, Schüler D (March 2006). "An acidic protein aligns magnetosomes along a filamentous structure in magnetotactic bacteria". Nature. 440 (7080): 110–4. Bibcode:2006Natur.440..110S. doi:10.1038/nature04382. PMID 16299495.
- Lindsay, M. R.; Webb, R. I.; Strous, M; Jetten, M. S.; Butler, M. K.; Forde, R. J.; Fuerst, J. A. (2001). "Cell compartmentalisation in planctomycetes: Novel types of structural organisation for the bacterial cell". Archives of Microbiology. 175 (6): 413–29. doi:10.1007/s002030100280. PMID 11491082.
- Jetten, Mike S. M.; Niftrik, Laura van; Strous, Marc; Kartal, Boran; Keltjens, Jan T.; Op den Camp, Huub J. M. (2009-06-01). "Biochemistry and molecular biology of anammox bacteria". Critical Reviews in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. pp. 65–84. doi:10.1080/10409230902722783. PMID 19247843. Retrieved 2020-08-03.
- Fuerst JA (October 13, 2005). "Intracellular compartmentation in planctomycetes". Annual Review of Microbiology. 59: 299–328. doi:10.1146/annurev.micro.59.030804.121258. PMID 15910279.
External links
| Library resources about Organelle |

- Tree of Life project: Eukaryotes
- Organelle Databases