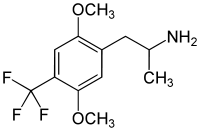
2,5-Dimethoxy-4-trifluoromethylamphetamine
2,5-Dimethoxy-4-trifluoromethylamphetamine (DOTFM) is a psychedelic drug of the phenethylamine and amphetamine chemical classes. It was first synthesized in 1994 by a team at Purdue University led by David E. Nichols.[1] DOTFM is the alpha-methylated analogue of 2C-TFM, and is around twice as potent in animal studies. It acts as an agonist at the 5HT2A and 5HT2C receptors.[1] In drug-substitution experiments in rats, DOTFM fully substituted for LSD and was slightly more potent than DOI.[1]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-trifluoromethylamphetamine |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C12H16F3NO2 |
| Molar mass | 263.260 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
See also
References
- Nichols DE, Frescas S, Marona-Lewicka D, Huang X, Roth BL, Gudelsky GA, Nash JF (1994). "1-(2,5-Dimethoxy-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-2-aminopropane: a potent serotonin 5-HT2A/2C agonist". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 37 (25): 4346–4351. doi:10.1021/jm00051a011. PMID 7996545.
| 5-HT1 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-HT2 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-HT3–7 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phenethylamines |
|
|---|---|
| Amphetamines |
|
| Phentermines |
|
| Cathinones |
|
| Phenylisobutylamines | |
| Phenylalkylpyrrolidines | |
| Catecholamines (and close relatives) |
|
| Miscellaneous |
|
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.