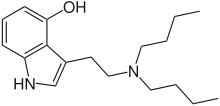
4-HO-DBT
4-Hydroxy-N,N-dibutyltryptamine (4-HO-DBT) is a psychedelic drug belonging to the tryptamine family. It is found either as its crystalline hydrochloride salt or as an oily or crystalline base. 4-HO-DBT was first made by the chemist Alexander Shulgin and reported in his book TiHKAL. Shulgin reported a dosage of 20 mg orally to be without effects. However this compound has subsequently been sold as a "research chemical" and anecdotal reports suggest that at higher doses 4-HO-DBT is indeed an active hallucinogen, although somewhat weaker than other similar tryptamine derivatives.
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H28N2O |
| Molar mass | 288.435 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 74 to 75 °C (165 to 167 °F) |
| |
| |
| | |
Several different isomers of this compound could be made (see DBT for a fuller discussion) but of these only the isobutyl isomer 4-HO-DIBT has been synthesised (mp 152-154 °C) and was also found to be inactive at a 20 mg dose.
External links
|