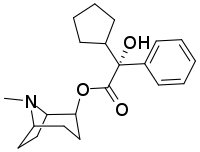
CAR-226,086
CAR-226,086 is a potent anticholinergic deliriant drug with a fairly long duration of action, related to the chemical warfare agent 3-quinuclidinyl benzilate (QNB). It was developed under contract to Edgewood Arsenal during the 1960s as part of the US military chemical weapons program, during research to improve upon the properties of earlier agents such as QNB.
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C21H29NO3 |
| Molar mass | 343.467 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
CAR-226,086 was relatively poorly researched compared to other compounds in the series, but notably was found to have the highest central to peripheral effects ratio out of all compounds tested, even higher than that of other CNS-selective agents such as EA-3443.[1][2]
References
- Commission on Life Sciences (1982). Possible Long-Term Health Effects of Short-Term Exposure to Chemical Agents. Volume 1. The National Academies Press. pp. 196–199.
- Ketchum JS (2006). Chemical Warfare Secrets Almost Forgotton. A Personal Story of Medical Testing of Army Volunteers with Incapacitating Chemical Agents During the Cold War. ChemBooks Inc. ISBN 978-1-4243-0080-8.
| mAChRs |
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precursors (and prodrugs) | |||||
See also: Receptor/signaling modulators • Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor modulators • Acetylcholine metabolism/transport modulators | |||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.