Corbadrine
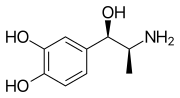
Corbadrine (INN; marketed as Neo-Cobefrine), also known as levonordefrin (USAN) and α-methylnorepinephrine, is a catecholamine sympathomimetic used as a topical nasal decongestant and vasoconstrictor in dentistry in the United States,[1][2] (usually in a pre-mixed solution with local anesthetics, such as mepivacaine).[3]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| KEGG |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.113.606 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C9H13NO3 |
| Molar mass | 183.207 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Corbadrine is also a metabolite of the antihypertensive drug methyldopa,[4] and plays a role in its pharmacology and effects.
See also
References
- Morton I, Morton IK, Hall JM (31 October 1999). Concise Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents: Properties and Synonyms. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 164–. ISBN 978-0-7514-0499-9.
- Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory. Taylor & Francis. January 2000. pp. 275–. ISBN 978-3-88763-075-1.
- "DailyMed — Search results for levonordefrin". DailyMed. Retrieved 20 February 2016.
- Sjoerdsma A, Vendsalu A, Engelman K (October 1963). "Studies on the Metabolism and Mechanism of Action of Methyldopa". Circulation. 28 (4): 492–502. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.28.4.492. PMID 14068757.
External links
- Nordefrin at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
Decongestants and other nasal preparations (R01) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Topical |
| ||||||||||
| Systemic use: Sympathomimetics | |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.