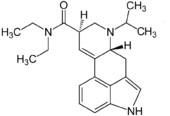
6-Isopropyl-6-nor-lysergic acid diethylamide
6-Isopropyl-6-nor-lysergic acid diethylamide (IP-LAD) is an analog of lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) developed by the team of David E. Nichols. In studies on mice, it was found to be approximately 40% the potency of LSD, compared to the 60% increase in potency seen with ETH-LAD and roughly equivalent potency in AL-LAD and PRO-LAD.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| (verify) | |
References
- Hoffman AJ, Nichols DE (September 1985). "Synthesis and LSD-like discriminative stimulus properties in a series of N(6)-alkyl norlysergic acid N,N-diethylamide derivatives". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 28 (9): 1252–5. doi:10.1021/jm00147a022. PMID 4032428.
| Lysergic acid derivatives |
|
|---|---|
| Psychedelic lysergamides |
|
| Clavines | |
| Other ergolines | |
| Natural sources |
Morning glory: Argyreia nervosa (Hawaiian Baby Woodrose), Ipomoea spp.(Morning Glory, Tlitliltzin, Badoh Negro), Rivea corymbosa (Coaxihuitl, Ololiúqui) |
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.