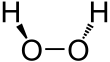Hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula H
2O
2. In its pure form, it is a very pale blue[5] liquid, slightly more viscous than water. Hydrogen peroxide is the simplest peroxide (a compound with an oxygen–oxygen single bond). It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic. Concentrated hydrogen peroxide, or "high-test peroxide", is a reactive oxygen species and has been used as a propellant in rocketry.[6] Its chemistry is dominated by the nature of its unstable peroxide bond.
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Hydrogen peroxide | |||
| Other names
Dioxidane Oxidanyl Perhydroxic acid 0-hydroxyol Dihydrogen dioxide Oxygenated water Peroxaan | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.028.878 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID |
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 2015 (>60% soln.) 2014 (20–60% soln.) 2984 (8–20% soln.) | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| H2O2 | |||
| Molar mass | 34.0147 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | Very light blue color; colorless in solution | ||
| Odor | slightly sharp | ||
| Density | 1.11 g/cm3 (20 °C, 30% (w/w) solution )[1] 1.450 g/cm3 (20 °C, pure) | ||
| Melting point | −0.43 °C (31.23 °F; 272.72 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 150.2 °C (302.4 °F; 423.3 K) (decomposes) | ||
| Miscible | |||
| Solubility | soluble in ether, alcohol insoluble in petroleum ether | ||
| log P | -0.43[2] | ||
| Vapor pressure | 5 mmHg (30 °C)[3] | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | 11.75 | ||
| −17.7·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
Refractive index (nD) |
1.4061 | ||
| Viscosity | 1.245 cP (20 °C) | ||
| 2.26 D | |||
| Thermochemistry | |||
Heat capacity (C) |
1.267 J/(g·K) (gas) 2.619 J/(g·K) (liquid) | ||
Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−187.80 kJ/mol | ||
| Pharmacology | |||
| A01AB02 (WHO) D08AX01 (WHO), D11AX25 (WHO), S02AA06 (WHO) | |||
| Hazards | |||
| Safety data sheet | ICSC 0164 (>60% soln.) | ||
| GHS pictograms |    | ||
| GHS Signal word | Danger | ||
GHS hazard statements |
H271, H302, H314, H332, H335, H412 | ||
| P280, P305+351+338, P310 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | Non-flammable | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LD50 (median dose) |
1518 mg/kg 2000 mg/kg (oral, mouse)[4] | ||
LC50 (median concentration) |
1418 ppm (rat, 4 hr)[4] | ||
LCLo (lowest published) |
227 ppm (mouse)[4] | ||
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |||
PEL (Permissible) |
TWA 1 ppm (1.4 mg/m3)[3] | ||
REL (Recommended) |
TWA 1 ppm (1.4 mg/m3)[3] | ||
IDLH (Immediate danger) |
75 ppm[3] | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds |
Water Ozone Hydrazine Hydrogen disulfide Dioxygen difluoride | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Hydrogen peroxide is unstable and slowly decomposes in the presence of light. Because of its instability, hydrogen peroxide is typically stored with a stabilizer in a weakly acidic solution in a dark coloured bottle. Hydrogen peroxide is found in biological systems including the human body. Enzymes that use or decompose hydrogen peroxide are classified as peroxidases.
Properties
The boiling point of H
2O
2 has been extrapolated as being 150.2 °C (302.4 °F), approximately 50 °C (90 °F) higher than water. In practice, hydrogen peroxide will undergo potentially explosive thermal decomposition if heated to this temperature. It may be safely distilled at lower temperatures under reduced pressure.[7]
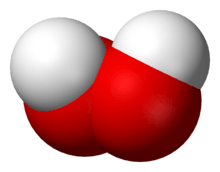
Structure
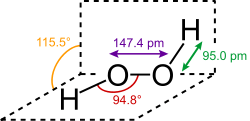
Hydrogen peroxide (H
2O
2) is a nonplanar molecule with (twisted) C2 symmetry; this was first shown by Paul-Antoine Giguère in 1950 using infrared spectroscopy.[8][9] Although the O−O bond is a single bond, the molecule has a relatively high rotational barrier of 2460 cm−1 (29.45 kJ/mol);[10] for comparison, the rotational barrier for ethane is 1040 cm−1 (12.5 kJ/mol). The increased barrier is ascribed to repulsion between the lone pairs of the adjacent oxygen atoms and results in hydrogen peroxide displaying atropisomerism.
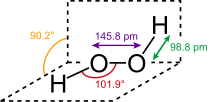
The molecular structures of gaseous and crystalline H
2O
2 are significantly different. This difference is attributed to the effects of hydrogen bonding, which is absent in the gaseous state.[11] Crystals of H
2O
2 are tetragonal with the space group D4
4P4121.[12]
Aqueous solutions
In aqueous solutions, hydrogen peroxide differs from the pure substance due to the effects of hydrogen bonding between water and hydrogen peroxide molecules. Hydrogen peroxide and water form a eutectic mixture, exhibiting freezing-point depression down as low as –56 °C; pure water has a freezing point of 0 °C and pure hydrogen peroxide of −0.43 °C. The boiling point of the same mixtures is also depressed in relation with the mean of both boiling points (125.1 °C). It occurs at 114 °C. This boiling point is 14 °C greater than that of pure water and 36.2 °C less than that of pure hydrogen peroxide.[13]
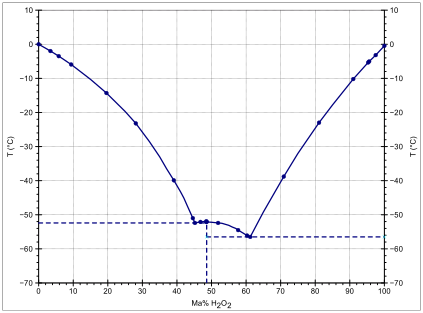
2O
2 and water: Area above blue line is liquid. Dotted lines separate solid–liquid phases from solid–solid phases.
| H2O2 (w/w) | Density (g/cm3) | Temp. (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| 3% | 1.0095 | 15 |
| 27% | 1.10 | 20 |
| 35% | 1.13 | 20 |
| 50% | 1.20 | 20 |
| 70% | 1.29 | 20 |
| 75% | 1.33 | 20 |
| 96% | 1.42 | 20 |
| 98% | 1.43 | 20 |
| 100% | 1.45 | 20 |
Comparison with analogues
Hydrogen peroxide has several structural analogues with Hm−X−X−Hn bonding arrangements (water also shown for comparison). It has the highest (theoretical) boiling point of this series (X = O, N, S). Its melting point is also fairly high, being comparable to that of hydrazine and water, with only hydroxylamine crystallising significantly more readily, indicative of particularly strong hydrogen bonding. Diphosphane and hydrogen disulfide exhibit only weak hydrogen bonding and have little chemical similarity to hydrogen peroxide. All of these analogues are thermodynamically unstable. Structurally, the analogues all adopt similar skewed structures, due to repulsion between adjacent lone pairs.
| Name | Formula | Molar mass (g/mol) | Melting point (°C) | Boiling point (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen peroxide | HOOH | 34.01 | −0.43 | 150.2* |
| Water | HOH | 18.02 | 0.00 | 99.98 |
| Hydrogen disulfide | HSSH | 66.15 | −89.6 | 70.7 |
| Hydrazine | H2NNH2 | 32.05 | 2 | 114 |
| Hydroxylamine | NH2OH | 33.03 | 33 | 58* |
| Diphosphane | H2PPH2 | 65.98 | −99 | 63.5* |
Discovery
Alexander von Humboldt reported one of the first synthetic peroxides, barium peroxide, in 1799 as a by-product of his attempts to decompose air.
Nineteen years later Louis Jacques Thénard recognized that this compound could be used for the preparation of a previously unknown compound, which he described as eau oxygénée ("oxygenated water") – subsequently known as hydrogen peroxide.[14][15][16] Today this term refers instead to water containing dissolved oxygen (O2).
An improved version of Thénard's process used hydrochloric acid, followed by addition of sulfuric acid to precipitate the barium sulfate byproduct. This process was used from the end of the 19th century until the middle of the 20th century.[17]
Thénard and Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac synthesized sodium peroxide in 1811. The bleaching effect of peroxides and their salts on natural dyes became known around that time, but early attempts of industrial production of peroxides failed. The first plant producing hydrogen peroxide was built in 1873 in Berlin. The discovery of the synthesis of hydrogen peroxide by electrolysis with sulfuric acid introduced the more efficient electrochemical method. It was first commercialized in 1908 in Weißenstein, Carinthia, Austria. The anthraquinone process, which is still used, was developed during the 1930s by the German chemical manufacturer IG Farben in Ludwigshafen. The increased demand and improvements in the synthesis methods resulted in the rise of the annual production of hydrogen peroxide from 35,000 tonnes in 1950, to over 100,000 tonnes in 1960, to 300,000 tonnes by 1970; by 1998 it reached 2.7 million tonnes.[18]
Pure hydrogen peroxide was long believed to be unstable, as early attempts to separate it from the water, which is present during synthesis, all failed. This instability was due to traces of impurities (transition-metal salts), which catalyze the decomposition of the hydrogen peroxide. Pure hydrogen peroxide was first obtained in 1894—almost 80 years after its discovery—by Richard Wolffenstein, who produced it by vacuum distillation.[19]
Determination of the molecular structure of hydrogen peroxide proved to be very difficult. In 1892, the Italian physical chemist Giacomo Carrara (1864–1925) determined its molecular mass by freezing-point depression, which confirmed that its molecular formula is H2O2.[20] At least half a dozen hypothetical molecular structures seemed to be consistent with the available evidence.[21] In 1934, the English mathematical physicist William Penney and the Scottish physicist Gordon Sutherland proposed a molecular structure for hydrogen peroxide that was very similar to the presently accepted one.[22][23]
Previously, hydrogen peroxide was prepared industrially by hydrolysis of ammonium persulfate, which was itself obtained by the electrolysis of a solution of ammonium bisulfate (NH
4HSO
4) in sulfuric acid:[24]
Production
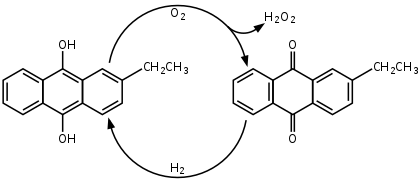
Today, hydrogen peroxide is manufactured almost exclusively by the anthraquinone process, which was formalized in 1936 and patented in 1939. It begins with the reduction of an anthraquinone (such as 2-ethylanthraquinone or the 2-amyl derivative) to the corresponding anthrahydroquinone, typically by hydrogenation on a palladium catalyst. In the presence of oxygen, the anthrahydroquinone then undergoes autoxidation: the labile hydrogen atoms of the hydroxy groups transfer to the oxygen molecule, to give hydrogen peroxide and regenerating the anthraquinone. Most commercial processes achieve oxidation by bubbling compressed air through a solution of the anthrahydroquinone, with the hydrogen peroxide then extracted from the solution and the anthraquinone recycled back for successive cycles of hydrogenation and oxidation.[25][26]
The net reaction for the anthraquinone-catalyzed process is :[25]
- H
2 + O
2 → H
2O
2
The economics of the process depend heavily on effective recycling of the extraction solvents, the hydrogenation catalyst and the expensive quinone.


Other sources
Small, but detectable, amounts of hydrogen peroxide can be formed by several methods. Small amounts are formed by electrolysis of dilute acid around the cathode where hydrogen evolves if oxygen is bubbled around it. It is also produced by exposing water to ultraviolet rays from a mercury lamp, or an electric arc while confining it in a UV transparent vessel (e.g. quartz). It is detectable in ice water after burning a hydrogen gas stream aimed towards it and is also detectable on floating ice. Rapidly cooling humid air blown through an approximately 2,000 °C spark gap results in detectable amounts.[27]
A commercially viable process to produce hydrogen peroxide directly from the environment has been of interest for many years. Efficient direct synthesis is difficult to achieve, as the reaction of hydrogen with oxygen thermodynamically favours production of water. Systems for direct synthesis have been developed, most of which employ finely dispersed metal catalysts similar to those used for hydrogenation of organic substrates.[28][29] None of these has yet reached a point where they can be used for industrial-scale synthesis.
Availability
Hydrogen peroxide is most commonly available as a solution in water. For consumers, it is usually available from pharmacies at 3 and 6 wt% concentrations. The concentrations are sometimes described in terms of the volume of oxygen gas generated; one milliliter of a 20-volume solution generates twenty milliliters of oxygen gas when completely decomposed. For laboratory use, 30 wt% solutions are most common. Commercial grades from 70% to 98% are also available, but due to the potential of solutions of more than 68% hydrogen peroxide to be converted entirely to steam and oxygen (with the temperature of the steam increasing as the concentration increases above 68%) these grades are potentially far more hazardous and require special care in dedicated storage areas. Buyers must typically allow inspection by commercial manufacturers.
In 1994, world production of H
2O
2 was around 1.9 million tonnes and grew to 2.2 million in 2006,[30] most of which was at a concentration of 70% or less. In that year, bulk 30% H
2O
2 sold for around 0.54 USD/kg, equivalent to US$1.50/kg (US$0.68/lb) on a "100% basis".[25]
Hydrogen peroxide occurs in surface water, groundwater and in the atmosphere. It forms upon illumination or natural catalytic action by substances contained in water. Sea water contains 0.5 to 14 μg/L of hydrogen peroxide, freshwater 1 to 30 μg/L and air 0.1 to 1 parts per billion.[18]
Reactions
Decomposition
Hydrogen peroxide is thermodynamically unstable and decomposes to form water and oxygen with a ΔHo of –2884.5 kJ/kg[31] and a ΔS of 70.5 J/(mol·K):
- 2 H
2O
2 → 2 H
2O + O
2
The rate of decomposition increases with rise in temperature, concentration, and pH, with cool, dilute, acidic solutions showing the best stability. Decomposition is catalysed by various compounds, including most transition metals and their compounds (e.g. manganese dioxide (MnO2), silver, and platinum).[32] Certain metal ions, such as Fe2+
or Ti3+
, can cause the decomposition to take a different path, with free radicals such as the hydroxyl radical (HO·) and hydroperoxyl (HOO·) being formed. Non-metallic catalysts include potassium iodide, which reacts particularly rapidly and forms the basis of the elephant toothpaste demonstration. Hydrogen peroxide can also be decomposed biologically by the enzyme catalase. The decomposition of hydrogen peroxide liberates oxygen and heat; this can be dangerous, as spilling high-concentration hydrogen peroxide on a flammable substance can cause an immediate fire.
Redox reactions
The redox properties of hydrogen peroxide depend on pH.
In acidic solutions, H
2O
2 is a powerful oxidizer, stronger than chlorine, chlorine dioxide, and potassium permanganate. When used for cleaning laboratory glassware, a solution of hydrogen peroxide and sulfuric acid is referred to as Piranha solution.
H
2O
2 is a source of hydroxyl radicals (·OH), which are highly reactive. H
2O
2 is used in the Briggs–Rauscher[33][34] and Bray–Liebhafsky[35][36] oscillating reactions.
| Oxidant | Reduced product |
Oxidation potential (V) |
|---|---|---|
| F2 | HF | 3.0 |
| O3 | O2 | 2.1 |
| H2O2 | H2O | 1.8 |
| KMnO4 | MnO2 | 1.7 |
| ClO2 | HClO | 1.5 |
| Cl2 | Cl− | 1.4 |
In acidic solutions Fe2+
is oxidized to Fe3+
(hydrogen peroxide acting as an oxidizing agent):
and sulfite (SO2−
3) is oxidized to sulfate (SO2−
4). However, potassium permanganate is reduced to Mn2+
by acidic H
2O
2. Under alkaline conditions, however, some of these reactions reverse; for example, Mn2+
is oxidized to Mn4+
(as MnO
2).
In basic solution, hydrogen peroxide can reduce a variety of inorganic ions. When it acts as a reducing agent, oxygen gas is also produced. For example, hydrogen peroxide will reduce sodium hypochlorite and potassium permanganate, which is a convenient method for preparing oxygen in the laboratory:
- NaOCl + H
2O
2 → O
2 + NaCl + H
2O - 2 KMnO
4 + 3 H
2O
2 → 2 MnO
2 + 2 KOH + 2 H
2O + 3 O
2
Organic reactions
Hydrogen peroxide is frequently used as an oxidizing agent. Illustrative is oxidation of thioethers to sulfoxides:[37][38]
- Ph−S−CH
3 + H
2O
2 → Ph−S(O)−CH
3 + H
2O
Alkaline hydrogen peroxide is used for epoxidation of electron-deficient alkenes such as acrylic acid derivatives,[39] and for the oxidation of alkylboranes to alcohols, the second step of hydroboration-oxidation. It is also the principal reagent in the Dakin oxidation process.
Precursor to other peroxide compounds
Hydrogen peroxide is a weak acid, forming hydroperoxide or peroxide salts with many metals.
It also converts metal oxides into the corresponding peroxides. For example, upon treatment with hydrogen peroxide, chromic acid (CrO
3 + H
2SO
4) forms an unstable blue peroxide CrO(O
2)
2.
This kind of reaction is used industrially to produce peroxoanions. For example, reaction with borax leads to sodium perborate, a bleach used in laundry detergents:
- Na
2B
4O
7 + 4 H
2O
2 + 2 NaOH → 2 Na
2B
2O
4(OH)
4 + H
2O
H
2O
2 converts carboxylic acids (RCO2H) into peroxy acids (RC(O)O2H), which are themselves used as oxidizing agents. Hydrogen peroxide reacts with acetone to form acetone peroxide and with ozone to form trioxidane. Hydrogen peroxide forms stable adducts with urea (Hydrogen peroxide - urea), sodium carbonate (sodium percarbonate) and other compounds.[40] An acid-base adduct with triphenylphosphine oxide is a useful "carrier" for H
2O
2 in some reactions.
Hydrogen peroxide is both an oxidizing agent and reducing agent. The oxidation of hydrogen peroxide by sodium hypochlorite yields singlet oxygen. The net reaction of a ferric ion with hydrogen peroxide is a ferrous ion and oxygen. This proceeds via single electron oxidation and hydroxyl radicals. This is used in some organic chemistry oxidations, e.g. in the Fenton's reagent. Only catalytic quantities of iron ion is needed since peroxide also oxidizes ferrous to ferric ion. The net reaction of hydrogen peroxide and permanganate or manganese dioxide is manganous ion; however, until the peroxide is spent some manganese ions are reoxidized to make the reaction catalytic. This forms the basis for common monopropellant rockets.
Biological function
Hydrogen peroxide is formed in humans and other animals as a short-lived product in biochemical processes and is toxic to cells. The toxicity is due to oxidation of proteins, membrane lipids and DNA by the peroxide ions.[41] The class of biological enzymes called superoxide dismutase (SOD) is developed in nearly all living cells as an important antioxidant agent. They promote the disproportionation of superoxide into oxygen and hydrogen peroxide, which is then rapidly decomposed by the enzyme catalase to oxygen and water.[42]
- 2 O−
2 + 2 H+
→ H
2O
2 + O
2
Peroxisomes are organelles found in virtually all eukaryotic cells.[43] They are involved in the catabolism of very long chain fatty acids, branched chain fatty acids, D-amino acids, polyamines, and biosynthesis of plasmalogens, ether phospholipids critical for the normal function of mammalian brains and lungs.[44] Upon oxidation, they produce hydrogen peroxide in the following process:[45]
Catalase, another peroxisomal enzyme, uses this H2O2 to oxidize other substrates, including phenols, formic acid, formaldehyde, and alcohol, by means of the peroxidation reaction:
- , thus eliminating the poisonous hydrogen peroxide in the process.
This reaction is important in liver and kidney cells, where the peroxisomes neutralize various toxic substances that enter the blood. Some of the ethanol humans drink is oxidized to acetaldehyde in this way.[46] In addition, when excess H2O2 accumulates in the cell, catalase converts it to H2O through this reaction:
Another origin of hydrogen peroxide is the degradation of adenosine monophosphate which yields hypoxanthine. Hypoxanthine is then oxidatively catabolized first to xanthine and then to uric acid, and the reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme xanthine oxidase:[47]

The degradation of guanosine monophosphate yields xanthine as an intermediate product which is then converted in the same way to uric acid with the formation of hydrogen peroxide.[47]
Eggs of sea urchin, shortly after fertilization by a sperm, produce hydrogen peroxide. It is then quickly dissociated to OH· radicals. The radicals serve as initiator of radical polymerization, which surrounds the eggs with a protective layer of polymer.[48]
The bombardier beetle has a device which allows it to shoot corrosive and foul-smelling bubbles at its enemies. The beetle produces and stores hydroquinone and hydrogen peroxide, in two separate reservoirs in the rear tip of its abdomen. When threatened, the beetle contracts muscles that force the two reactants through valved tubes into a mixing chamber containing water and a mixture of catalytic enzymes. When combined, the reactants undergo a violent exothermic chemical reaction, raising the temperature to near the boiling point of water. The boiling, foul-smelling liquid partially becomes a gas (flash evaporation) and is expelled through an outlet valve with a loud popping sound.[49][50][51]
Hydrogen peroxide is a signaling molecule of plant defense against pathogens.[52]
Hydrogen peroxide has roles as a signalling molecule in the regulation of a wide variety of biological processes.[53] The compound is a major factor implicated in the free-radical theory of aging, based on how readily hydrogen peroxide can decompose into a hydroxyl radical and how superoxide radical byproducts of cellular metabolism can react with ambient water to form hydrogen peroxide.[54] These hydroxyl radicals in turn readily react with and damage vital cellular components, especially those of the mitochondria.[55][56][57] At least one study has also tried to link hydrogen peroxide production to cancer.[58] These studies have frequently been quoted in fraudulent treatment claims.
The amount of hydrogen peroxide in biological systems can be assayed using a fluorometric assay.[59]
Uses
Bleaching
About 60% of the world's production of hydrogen peroxide is used for pulp- and paper-bleaching.[30] The second major industrial application is the manufacture of sodium percarbonate and sodium perborate, which are used as mild bleaches in laundry detergents. Sodium percarbonate, which is an adduct of sodium carbonate and hydrogen peroxide, is the active ingredient in such laundry products as OxiClean and Tide laundry detergent. When dissolved in water, it releases hydrogen peroxide and sodium carbonate,[17] By themselves these bleaching agents are only effective at wash temperatures of 60 °C (140 °F) or above and so, often are used in conjunction with bleach activators, which facilitate cleaning at lower temperatures.
Production of organic compounds
It is used in the production of various organic peroxides with dibenzoyl peroxide being a high volume example. It is used in polymerisations, as a flour bleaching agent, and as a treatment for acne. Peroxy acids, such as peracetic acid and meta-chloroperoxybenzoic acid also are produced using hydrogen peroxide. Hydrogen peroxide has been used for creating organic peroxide-based explosives, such as acetone peroxide.
Disinfectant

2O
2

Hydrogen peroxide is used in certain waste-water treatment processes to remove organic impurities. In advanced oxidation processing, the Fenton reaction[60][61] gives the highly reactive hydroxyl radical (·OH). This degrades organic compounds, including those that are ordinarily robust, such as aromatic or halogenated compounds.[62] It can also oxidize sulfur based compounds present in the waste; which is beneficial as it generally reduces their odour.[63]
Hydrogen peroxide may be used for the sterilization of various surfaces,[64] including surgical tools,[65] and may be deployed as a vapour (VHP) for room sterilization.[66] H2O2 demonstrates broad-spectrum efficacy against viruses, bacteria, yeasts, and bacterial spores.[67][68] In general, greater activity is seen against Gram-positive than Gram-negative bacteria; however, the presence of catalase or other peroxidases in these organisms may increase tolerance in the presence of lower concentrations.[69] Lower levels of concentration (3%) will work against most spores; higher concentrations (7 to 30%) and longer contact times will improve sporicidal activity.[68][70]
Hydrogen peroxide is seen as an environmentally safe alternative to chlorine-based bleaches, as it degrades to form oxygen and water and it is generally recognized as safe as an antimicrobial agent by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).[71]
Hydrogen peroxide may be used to treat acne,[72] although benzoyl peroxide is a more common treatment.
Niche uses
Hydrogen peroxide has various domestic uses, primarily as a cleaning and disinfecting agent.
- Hair bleaching
Diluted H
2O
2 (between 1.9% and 12%) mixed with aqueous ammonia has been used to bleach human hair. The chemical's bleaching property lends its name to the phrase "peroxide blonde".[73]
Hydrogen peroxide is also used for tooth whitening. It may be found in most whitening toothpastes. Hydrogen peroxide has shown positive results involving teeth lightness and chroma shade parameters. It works by oxidizing colored pigments onto the enamel where the shade of the tooth may become lighter. Hydrogen peroxide may be mixed with baking soda and salt to make a homemade toothpaste.[74]
- Propellant
High-concentration H
2O
2 is referred to as "high-test peroxide" (HTP). It can be used either as a monopropellant (not mixed with fuel) or as the oxidizer component of a bipropellant rocket. Use as a monopropellant takes advantage of the decomposition of 70–98% concentration hydrogen peroxide into steam and oxygen. The propellant is pumped into a reaction chamber, where a catalyst, usually a silver or platinum screen, triggers decomposition, producing steam at over 600 °C (1,112 °F), which is expelled through a nozzle, generating thrust. H
2O
2 monopropellant produces a maximal specific impulse (Isp) of 161 s (1.6 kN·s/kg). Peroxide was the first major monopropellant adopted for use in rocket applications. Hydrazine eventually replaced hydrogen-peroxide monopropellant thruster applications primarily because of a 25% increase in the vacuum specific impulse.[75] Hydrazine (toxic) and hydrogen peroxide (less-toxic [ACGIH TLV 0.01 and 1 ppm respectively]) are the only two monopropellants (other than cold gases) to have been widely adopted and utilized for propulsion and power applications. The Bell Rocket Belt, reaction control systems for X-1, X-15, Centaur, Mercury, Little Joe, as well as the turbo-pump gas generators for X-1, X-15, Jupiter, Redstone and Viking used hydrogen peroxide as a monopropellant.[76]
As a bipropellant, H
2O
2 is decomposed to burn a fuel as an oxidizer. Specific impulses as high as 350 s (3.5 kN·s/kg) can be achieved, depending on the fuel. Peroxide used as an oxidizer gives a somewhat lower Isp than liquid oxygen, but is dense, storable, non-cryogenic and can be more easily used to drive gas turbines to give high pressures using an efficient closed cycle. It may also be used for regenerative cooling of rocket engines. Peroxide was used very successfully as an oxidizer in World War II German rocket motors (e.g. T-Stoff, containing oxyquinoline stabilizer, for both the Walter HWK 109-500 Starthilfe RATO externally podded monopropellant booster system, and for the Walter HWK 109-509 rocket motor series used for the Me 163B), most often used with C-Stoff in a self-igniting hypergolic combination, and for the low-cost British Black Knight and Black Arrow launchers.
In the 1940s and 1950s, the Hellmuth Walter KG-conceived turbine used hydrogen peroxide for use in submarines while submerged; it was found to be too noisy and require too much maintenance compared to diesel-electric power systems. Some torpedoes used hydrogen peroxide as oxidizer or propellant. Operator error in the use of hydrogen-peroxide torpedoes was named as possible causes for the sinking of HMS Sidon and the Russian submarine Kursk.[77] SAAB Underwater Systems is manufacturing the Torpedo 2000. This torpedo, used by the Swedish Navy, is powered by a piston engine propelled by HTP as an oxidizer and kerosene as a fuel in a bipropellant system.[78][79]
- Glow sticks
Hydrogen peroxide reacts with certain di-esters, such as phenyl oxalate ester (cyalume), to produce chemiluminescence; this application is most commonly encountered in the form of glow sticks.
- Horticulture
Some horticulturalists and users of hydroponics advocate the use of weak hydrogen peroxide solution in watering solutions. Its spontaneous decomposition releases oxygen that enhances a plant's root development and helps to treat root rot (cellular root death due to lack of oxygen) and a variety of other pests.[80][81]
- Fishkeeping
Hydrogen peroxide is used in aquaculture for controlling mortality caused by various microbes. In 2019, the U.S. FDA approved it for control of Saprolegniasis in all coldwater finfish and all fingerling and adult coolwater and warmwater finfish, for control of external columnaris disease in warm-water finfish, and for control of Gyrodactylus spp. in freshwater-reared salmonids.[82] Laboratory tests conducted by fish culturists have demonstrated that common household hydrogen peroxide may be used safely to provide oxygen for small fish. The hydrogen peroxide releases oxygen by decomposition when it is exposed to catalysts such as manganese dioxide.
Safety
Regulations vary, but low concentrations, such as 5%, are widely available and legal to buy for medical use. Most over-the-counter peroxide solutions are not suitable for ingestion. Higher concentrations may be considered hazardous and typically are accompanied by a safety data sheet (SDS). In high concentrations, hydrogen peroxide is an aggressive oxidizer and will corrode many materials, including human skin. In the presence of a reducing agent, high concentrations of H
2O
2 will react violently.[83]
High-concentration hydrogen peroxide streams, typically above 40%, should be considered hazardous due to concentrated hydrogen peroxide's meeting the definition of a DOT oxidizer according to U.S. regulations, if released into the environment. The EPA Reportable Quantity (RQ) for D001 hazardous wastes is 100 pounds (45 kg), or approximately 10 US gallons (38 L), of concentrated hydrogen peroxide.
Hydrogen peroxide should be stored in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area and away from any flammable or combustible substances. It should be stored in a container composed of non-reactive materials such as stainless steel or glass (other materials including some plastics and aluminium alloys may also be suitable).[84] Because it breaks down quickly when exposed to light, it should be stored in an opaque container, and pharmaceutical formulations typically come in brown bottles that block light.[85]
Hydrogen peroxide, either in pure or diluted form, may pose several risks, the main one being that it forms explosive mixtures upon contact with organic compounds.[86] Highly concentrated hydrogen peroxide is unstable and may cause a boiling liquid expanding vapour explosion (BLEVE) of the remaining liquid. Consequently, distillation of hydrogen peroxide at normal pressures is highly dangerous. It is also corrosive, especially when concentrated, but even domestic-strength solutions may cause irritation to the eyes, mucous membranes, and skin.[87] Swallowing hydrogen peroxide solutions is particularly dangerous, as decomposition in the stomach releases large quantities of gas (ten times the volume of a 3% solution), leading to internal bloating. Inhaling over 10% can cause severe pulmonary irritation.[88]
With a significant vapour pressure (1.2 kPa at 50 °C[89]), hydrogen-peroxide vapour is potentially hazardous. According to U.S. NIOSH, the immediately dangerous to life and health (IDLH) limit is only 75 ppm.[90] The U.S. Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has established a permissible exposure limit of 1.0 ppm calculated as an 8-hour time-weighted average (29 CFR 1910.1000, Table Z-1).[86] Hydrogen peroxide also has been classified by the American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists (ACGIH) as a "known animal carcinogen, with unknown relevance on humans".[91] For workplaces where there is a risk of exposure to the hazardous concentrations of the vapours, continuous monitors for hydrogen peroxide should be used. Information on the hazards of hydrogen peroxide is available from OSHA [86] and from the ATSDR.[92]
Adverse effects on wounds
Historically hydrogen peroxide was used for disinfecting wounds, partly because of its low cost and prompt availability compared to other antiseptics. Now it is thought to inhibit healing and to induce scarring, because it destroys newly formed skin cells.[93] One study found that only very low concentrations (0.03% solution, this is a dilution of typical 3% Peroxide by 100 times) may induce healing, and only if not applied repeatedly. A 0.5% solution was found to impede healing.[94] Surgical use can lead to gas embolism formation.[95][96] Despite this, it is still used for wound treatment in many countries, and, in the United States, is prevalent as a major first aid antiseptic.[97][98]
Dermal exposure to dilute solutions of hydrogen peroxide causes whitening or bleaching of the skin due to microembolism caused by oxygen bubbles in the capillaries.[99]
Use in alternative medicine
Practitioners of alternative medicine have advocated the use of hydrogen peroxide for various conditions, including emphysema, influenza, AIDS, and in particular cancer.[100] There is no evidence of effectiveness and in some cases it has proved fatal.[101][102][103][104][105]
The practice calls for the daily consumption of hydrogen peroxide, either orally or by injection, and is based on two precepts. First, that hydrogen peroxide is produced naturally by the body to combat infection; and second, that human pathogens (including cancer: See Warburg hypothesis) are anaerobic and cannot survive in oxygen-rich environments. The ingestion or injection of hydrogen peroxide therefore is believed to kill disease by mimicking the immune response in addition to increasing levels of oxygen within the body. This makes the practice similar to other oxygen-based therapies, such as ozone therapy and hyperbaric oxygen therapy.
Both the effectiveness and safety of hydrogen peroxide therapy is scientifically questionable. Hydrogen peroxide is produced by the immune system, but in a carefully controlled manner. Cells called phagocytes engulf pathogens and then use hydrogen peroxide to destroy them. The peroxide is toxic to both the cell and the pathogen and so is kept within a special compartment, called a phagosome. Free hydrogen peroxide will damage any tissue it encounters via oxidative stress, a process that also has been proposed as a cause of cancer.[106] Claims that hydrogen peroxide therapy increases cellular levels of oxygen have not been supported. The quantities administered would be expected to provide very little additional oxygen compared to that available from normal respiration. It is also difficult to raise the level of oxygen around cancer cells within a tumour, as the blood supply tends to be poor, a situation known as tumor hypoxia.
Large oral doses of hydrogen peroxide at a 3% concentration may cause irritation and blistering to the mouth, throat, and abdomen as well as abdominal pain, vomiting, and diarrhea.[101] Intravenous injection of hydrogen peroxide has been linked to several deaths.[103][104][105] The American Cancer Society states that "there is no scientific evidence that hydrogen peroxide is a safe, effective, or useful cancer treatment."[102] Furthermore, the therapy is not approved by the U.S. FDA.
Historical incidents
- On 16 July 1934, in Kummersdorf, Germany, a propellant tank containing an experimental monopropellant mixture consisting of hydrogen peroxide and ethanol exploded during a test, killing three people.[107]
- During the Second World War, doctors in German concentration camps experimented with the use of hydrogen peroxide injections in the killing of human subjects.[108]
- In April 1992, an explosion occurred at the hydrogen peroxide plant at Jarrie in France, due to technical failure of the computerised control system and resulting in one fatality and wide destruction of the plant.[109]
- Several people received minor injuries after a hydrogen peroxide spill on board a flight between the U.S. cities of Orlando and Memphis on 28 October 1998.[110]
- The Russian submarine K-141 Kursk sailed to perform an exercise of firing dummy torpedoes at the Pyotr Velikiy, a Kirov-class battlecruiser. On 12 August 2000, at 11:28 local time (07:28 UTC), there was an explosion while preparing to fire the torpedoes. The only credible report to date is that this was due to the failure and explosion of one of the Kursk's hydrogen peroxide-fueled torpedoes. It is believed that HTP, a form of highly concentrated hydrogen peroxide used as propellant for the torpedo, seeped through its container, damaged either by rust or in the loading procedure back on land where an incident involving one of the torpedoes accidentally touching ground went unreported. The vessel was lost with all hands. A similar incident was responsible for the loss of HMS Sidon in 1955.
- On 15 August 2010, a spill of about 30 US gallons (110 L) of cleaning fluid occurred on the 54th floor of 1515 Broadway, in Times Square, New York City. The spill, which a spokesperson for the New York City fire department said was of hydrogen peroxide, shut down Broadway between West 42nd and West 48th streets as fire engines responded to the hazmat situation. There were no reported injuries.[111]
See also
- FOX reagent, used to measure levels of hydrogen peroxide in biological systems.
- Hydrogen chalcogenide
- Retr0bright, a process utilizing hydrogen peroxide to restore yellowed items such as plastic computer cases and game consoles.
References
Notes
- Easton, M. F.; Mitchell, A. G.; Wynne-Jones, W. F. K. (1952). "The behaviour of mixtures of hydrogen peroxide and water. Part 1.?Determination of the densities of mixtures of hydrogen peroxide and water". Transactions of the Faraday Society. 48: 796–801. doi:10.1039/TF9524800796.
- "Hydrogen peroxide". www.chemsrc.com.
- NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0335". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- "Hydrogen peroxide". Immediately Dangerous to Life and Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- Housecroft, Catherine E.; Sharpe, Alan G. (2005). Inorganic Chemistry (2nd ed.). Pearson Prentice-Hall. p. 443. ISBN 0130-39913-2.
- Hill, C. N. (2001). A Vertical Empire: The History of the UK Rocket launch and Space Programme, 1950–1971. Imperial College Press. ISBN 978-1-86094-268-6.
- Brauer, Georg, ed. (1963). Handbook of preparative inorganic chemistry. 1. Translation editing by Reed F. (2nd ed.). New York, N.Y.: Academic Press. p. 140. ISBN 978-0-12-126601-1.
- Giguère, Paul A. (1950). "The Infra‐Red Spectrum of Hydrogen Peroxide" (PDF). Journal of Chemical Physics. 18 (1): 88. Bibcode:1950JChPh..18...88G. doi:10.1063/1.1747464. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2 December 2017. Retrieved 31 December 2018.
- Giguère, Paul A. (1983). "Molecular association and structure of hydrogen peroxide". Journal of Chemical Education. 60 (5): 399–401. Bibcode:1983JChEd..60..399G. doi:10.1021/ed060p399.
- Hunt, Robert H.; Leacock, Robert A.; Peters, C. Wilbur; Hecht, Karl T. (1965). "Internal-Rotation in Hydrogen Peroxide: The Far-Infrared Spectrum and the Determination of the Hindering Potential" (PDF). The Journal of Chemical Physics. 42 (6): 1931. Bibcode:1965JChPh..42.1931H. doi:10.1063/1.1696228. hdl:2027.42/71115. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 April 2014. Retrieved 9 April 2014.
- Dougherty, Dennis A.; Anslyn, Eric V. (2005). Modern Physical Organic Chemistry. University Science. p. 122. ISBN 978-1-891389-31-3.
- Abrahams, S. C.; Collin, R. L.; Lipscomb, W. N. (1 January 1951). "The crystal structure of hydrogen peroxide". Acta Crystallographica. 4 (1): 15–20. doi:10.1107/S0365110X51000039.
- "Hydrogen Peroxide Technical Library" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 29 December 2009. Retrieved 3 March 2016.
- Gilbert, L. W. (1820). "Der tropfbar flüssige Sauerstoff, oder das oxygenierte Wasser". Annals of Physics (in German). 65–66 (1): 3. Bibcode:1820AnP....64....1T. doi:10.1002/andp.18200640102.
- Thénard, L. J. (1818). "Observations sur des nouvelles combinaisons entre l'oxigène et divers acides". Annales de chimie et de physique. 2nd series. 8: 306–312. Archived from the original on 3 September 2016. Retrieved 9 February 2016.
- Giguère, Paul A. "Hydrogen peroxide". Access Science. McGraw-Hill Education. doi:10.1036/1097-8542.329200. Archived from the original on 30 November 2018. Retrieved 28 November 2018.
Hydrogen peroxide was discovered in 1818 by the French chemist Louis-Jacques Thenard, who named it eau oxygénée (oxygenated water).
- Jones, C. W.; Clark, J. H. (1999). Applications of Hydrogen Peroxide and Derivatives. Royal Society of Chemistry. ISBN 978-0-85404-536-5.
- Offermanns, Heribert; Dittrich, Gunther; Steiner, Norbert (2000). "Wasserstoffperoxid in Umweltschutz und Synthese". Chemie in Unserer Zeit. 34 (3): 150. doi:10.1002/1521-3781(200006)34:3<150::AID-CIUZ150>3.0.CO;2-A.
- Wolffenstein, Richard (October 1894). "Concentration und Destillation von Wasserstoffsuperoxyd". Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft (in German). 27 (3): 3307–3312. doi:10.1002/cber.189402703127. Archived from the original on 13 February 2016. Retrieved 29 June 2014.
- G. Carrara (1892) "Sul peso molecolare e sul potere rifrangente dell' acqua ossigenata" Archived 4 September 2016 at the Wayback Machine (On the molecular weight and on the refractive power of oxygenated water [i.e., hydrogen peroxide]), Atti della Reale Accademia dei Lincei, series 5, 1 (2) : 19–24.
Carrara's findings were confirmed by: W. R. Orndorff and John White (1893) "The molecular weight of hydrogen peroxide and of benzoyl peroxide," Archived 4 September 2016 at the Wayback Machine American Chemical Journal, 15 : 347–356. - See, for example:
- In 1882, Kingzett proposed as a structure H2O=O. See: Thomas Kingzett, Charles (29 September 1882). "On the activity of oxygen and the mode of formation of hydrogen dioxide". The Chemical News. 46 (1192): 141–142. Archived from the original on 3 September 2016. Retrieved 9 February 2016.
- In his 1922 textbook, Joseph Mellor considered three hypothetical molecular structures for hydrogen peroxide, admitting (p. 952): "... the constitution of this compound has not been yet established by unequivocal experiments". See: Joseph William Mellor, A Comprehensive Treatise on Inorganic and Theoretical Chemistry, vol. 1 (London, England: Longmans, Green and Co., 1922), p. 952–956. Archived 3 September 2016 at the Wayback Machine
- W. C. Schumb, C. N. Satterfield, and R. L. Wentworth (1 December 1953) "Report no. 43: Hydrogen peroxide, Part two" Archived 26 February 2015 at the Wayback Machine, Office of Naval Research, Contract No. N5ori-07819 On p. 178, the authors present six hypothetical models for hydrogen peroxide's molecular structure. On p. 184, the present structure is considered almost certainly correct—although a small doubt remained. (Note: The report by Schumb et al. was reprinted as: W. C. Schumb, C. N. Satterfield, and R. L. Wentworth, Hydrogen Peroxide (New York, New York: Reinhold Publishing Corp. (American Chemical Society Monograph), 1955).)
- Penney, W. G.; Sutherland, G. B. B. M. (1934). "The theory of the structure of hydrogen peroxide and hydrazine". Journal of Chemical Physics. 2 (8): 492–498. Bibcode:1934JChPh...2..492P. doi:10.1063/1.1749518.
- Penney, W. G.; Sutherland, G. B. B. M. (1934). "A note on the structure of H2O2 and H4N2 with particular reference to electric moments and free rotation". Transactions of the Faraday Society. 30: 898–902. doi:10.1039/tf934300898b.
- "Preparing to manufacture hydrogen peroxide" (PDF). IDC Technologies.
- Campos-Martin, Jose M.; Blanco-Brieva, Gema; Fierro, Jose L. G. (2006). "Hydrogen Peroxide Synthesis: An Outlook beyond the Anthraquinone Process". Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 45 (42): 6962–6984. doi:10.1002/anie.200503779. PMID 17039551.
- H. Riedl and G. Pfleiderer, U.S. Patent 2,158,525 (2 October 1936 in USA, and 10 October 1935 in Germany) to I. G. Farbenindustrie, Germany
- Mellor, Joseph William (1922). Modern Inorganic Chemistry. Longmans, Green and Co. pp. 192–195.
- Noritaka Mizuno Gabriele Centi, Siglinda Perathoner, Salvatore Abate "Direct Synthesis of Hydrogen Peroxide: Recent Advances" in Modern Heterogeneous Oxidation Catalysis: Design, Reactions and Characterization 2009, Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/9783527627547.ch8
- Edwards, Jennifer K.; Solsona, Benjamin; N, Edwin Ntainjua; Carley, Albert F.; Herzing, Andrew A.; Kiely, Christopher J.; Hutchings, Graham J. (20 February 2009). "Switching Off Hydrogen Peroxide Hydrogenation in the Direct Synthesis Process". Science. 323 (5917): 1037–1041. Bibcode:2009Sci...323.1037E. doi:10.1126/science.1168980. PMID 19229032.
- Ronald Hage, Achim Lienke; Lienke (2005). "Applications of Transition-Metal Catalysts to Textile and Wood-Pulp Bleaching". Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 45 (2): 206–222. doi:10.1002/anie.200500525. PMID 16342123.
- "Decomposition of Hydrogen Peroxide - Kinetics and Review of Chosen Catalysts" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 22 December 2018. Retrieved 30 August 2019.
- Petrucci, Ralph H. (2007). General Chemistry: Principles & Modern Applications (9th ed.). Prentice Hall. p. 606. ISBN 978-0-13-149330-8.
- Csepei, L.I.; Bolla, Cs. (2015). "Is starch only a visual indicator for iodine in the Briggs-Rauscher oscillating reaction?" (PDF). Studia UBB Chemia. 60 (2): 187–199.
- Csepei, L.I.; Bolla, Cs (2011). "The Effect of Salicylic Acid on the Briggs-Rauscher Oscillating Reaction". Studia UBB Chemia. 53 (1): 285–300.
- Pejić, Nataša; Kolar-Anić, Ljiljana; Maksimović, Jelena; Janković, Marija; Vukojević, Vladana; Anić, Slobodan (1 June 2016). "Dynamic transitions in the Bray–Liebhafsky oscillating reaction. Effect of hydrogen peroxide and temperature on bifurcation". Reaction Kinetics, Mechanisms and Catalysis. 118 (1): 15–26. doi:10.1007/s11144-016-0984-y. ISSN 1878-5204.
- Maćešić, Stevan; Čupić, Željko; Ivanović-Šašić, Ana; Anić, Slobodan; Radenković, Mirjana; Pejić, Nataša; Kolar-Anić, Ljiljana (1 February 2018). "Bifurcation analysis: a tool for determining model parameters of the considered process". Reaction Kinetics, Mechanisms and Catalysis. 123 (1): 31–45. doi:10.1007/s11144-017-1324-6. ISSN 1878-5204.
- Ravikumar, Kabayadi S.; Kesavan, Venkitasamy; Crousse, Benoit; Bonnet-Delpon, Danièle; Bégué, Jean-Pierre (2003). "Mild and Selective Oxidation of Sulfur Compounds in Trifluoroethanol: Diphenyldisulfide and Methyl phenyl Sulfoxide". Org. Synth. 80: 184. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.080.0184.
- Xu, W. L.; Li, Y. Z.; Zhang, Q. S.; Zhu, H. S. (2004). "A Selective, Convenient, and Efficient Conversion of Sulfides to Sulfoxides". Synthesis (2): 227–232. doi:10.1055/s-2004-44387.
- Mayer, Robert J.; Ofial, Armin R. (22 February 2018). "Nucleophilic Reactivities of Bleach Reagents". Organic Letters. 20 (10): 2816–2820. doi:10.1021/acs.orglett.8b00645. PMID 29741385.
- Chernyshov, Ivan Yu.; Vener, Mikhail V.; Prikhodchenko, Petr V.; Medvedev, Alexander G.; Lev, Ovadia; Churakov, Andrei V. (4 January 2017). "Peroxosolvates: Formation Criteria, H2O2 Hydrogen Bonding, and Isomorphism with the Corresponding Hydrates". Crystal Growth & Design. 17 (1): 214–220. doi:10.1021/acs.cgd.6b01449. ISSN 1528-7483.
- Löffler G. and Petrides, P. E. Physiologische Chemie. 4 ed., p. 288, Springer, Berlin 1988, ISBN 3-540-18163-6 (in German)
- Löffler G. and Petrides, P. E. Physiologische Chemie. 4 ed., pp. 321–322, Springer, Berlin 1988, ISBN 3-540-18163-6 (in German)
- Gabaldón T (2010). "Peroxisome diversity and evolution". Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 365 (1541): 765–73. doi:10.1098/rstb.2009.0240. PMC 2817229. PMID 20124343.
- Wanders RJ, Waterham HR (2006). "Biochemistry of mammalian peroxisomes revisited". Annu. Rev. Biochem. 75 (1): 295–332. doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.74.082803.133329. PMID 16756494.
- Nelson, David; Cox, Michael; Lehninger, Albert L. and Cox, Michael M. Lehninger Biochemie Archived 28 February 2017 at the Wayback Machine, pp. 663–664, Springer, 2001, ISBN 3-540-41813-X (in German)
- Riley, Edward P. et al. (ed.) Fetal Alcoholspectrum Disorder Fasd: Management and Policy Perspectives Archived 28 February 2017 at the Wayback Machine, Wiley-VCH, 2010, ISBN 3-527-32839-4 p. 112
- Nelson, David; Cox, Michael; Lehninger, Albert L. and Cox, Michael M. Lehninger Biochemie, p. 932, Springer, 2001, ISBN 3-540-41813-X (in German)
- Kröger, M. (1989). "History". Chemie in Unserer Zeit. 23: 34–35. doi:10.1002/ciuz.19890230106.
- Schildknecht, H.; Holoubek, K. (1961). "The bombardier beetle and its chemical explosion". Angewandte Chemie. 73: 1–7. doi:10.1002/ange.19610730102.
- Weber CG (Winter 1981). "The Bombadier Beetle Myth Exploded". Creation/Evolution. 2 (1): 1–5. Archived from the original on 29 September 2017. Retrieved 12 November 2017.
- Isaak, Mark (30 May 2003). "Bombardier Beetles and the Argument of Design". TalkOrigins Archive. Archived from the original on 16 November 2017. Retrieved 12 November 2017.
- Wie Pflanzen sich schützen, Helmholtz-Institute of Biochemical Plant Pathology (in German)
- Veal EA, Day AM, Morgan BA (April 2007). "Hydrogen peroxide sensing and signaling". Mol. Cell. 26 (1): 1–14. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2007.03.016. PMID 17434122.
- Weindruch, Richard (January 1996). "Calorie Restriction and Aging". Scientific American: 49–52.
- Giorgio M, Trinei M, Migliaccio E, Pelicci PG (September 2007). "Hydrogen peroxide: a metabolic by-product or a common mediator of ageing signals?". Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 8 (9): 722–8. doi:10.1038/nrm2240. PMID 17700625.
- González, D.; Bejarano, I.; Barriga, C.; Rodríguez, A.B.; Pariente, J.A. (2010). "Oxidative Stress-Induced Caspases are Regulated in Human Myeloid HL-60 Cells by Calcium Signal". Current Signal Transduction Therapy. 5 (2): 181–186. doi:10.2174/157436210791112172.
- Bejarano, I; Espino, J; González-Flores, D; Casado, JG; Redondo, PC; Rosado, JA; Barriga, C; Pariente, JA; Rodríguez, AB (2009). "Role of Calcium Signals on Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced Apoptosis in Human Myeloid HL-60 Cells". International Journal of Biomedical Science. 5 (3): 246–256. PMC 3614781. PMID 23675144.
- López-Lázaro M (July 2007). "Dual role of hydrogen peroxide in cancer: possible relevance to cancer chemoprevention and therapy". Cancer Lett. 252 (1): 1–8. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2006.10.029. PMID 17150302.
- Rapoport, R.; Hanukoglu, I.; Sklan, D. (May 1994). "A fluorometric assay for hydrogen peroxide, suitable for NAD(P)H-dependent superoxide generating redox systems". Anal Biochem. 218 (2): 309–13. doi:10.1006/abio.1994.1183. PMID 8074285.
- Tarr, Matthew A., ed. (2003). Chemical degradation methods for wastes and pollutants environmental and industrial applications. New York: M. Dekker. p. 165. ISBN 978-0-203-91255-3.
- Pignatello, Joseph J.; Oliveros, Esther; MacKay, Allison (January 2006). "Advanced Oxidation Processes for Organic Contaminant Destruction Based on the Fenton Reaction and Related Chemistry". Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology. 36 (1): 1–84. doi:10.1080/10643380500326564.
- Pera-Titus, Marc; Garcı́a-Molina, Verónica; Baños, Miguel A; Giménez, Jaime; Esplugas, Santiago (February 2004). "Degradation of chlorophenols by means of advanced oxidation processes: a general review". Applied Catalysis B: Environmental. 47 (4): 219–256. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2003.09.010.
- Goor, G.; Glenneberg, J.; Jacobi, S. (2007). "Hydrogen Peroxide". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a13_443.pub2. ISBN 978-3-527-30673-2.
- Ascenzi, Joseph M., ed. (1996). Handbook of disinfectants and antiseptics. New York: M. Dekker. p. 161. ISBN 978-0-8247-9524-5.
- Rutala, W. A.; Weber, D. J. (1 September 2004). "Disinfection and Sterilization in Health Care Facilities: What Clinicians Need to Know". Clinical Infectious Diseases. 39 (5): 702–709. doi:10.1086/423182. PMID 15356786.
- Falagas, M.E.; Thomaidis, P.C.; Kotsantis, I.K.; Sgouros, K.; Samonis, G.; Karageorgopoulos, D.E. (July 2011). "Airborne hydrogen peroxide for disinfection of the hospital environment and infection control: a systematic review". Journal of Hospital Infection. 78 (3): 171–177. doi:10.1016/j.jhin.2010.12.006. PMID 21392848.
- Block, Seymour S., ed. (2000). "Chapter 9: Peroxygen compounds". Disinfection, sterilization, and preservation (5th ed.). Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger. pp. 185–204. ISBN 978-0-683-30740-5.
- "Chemical Disinfectants | Disinfection & Sterilization Guidelines | Guidelines Library | Infection Control | CDC". www.cdc.gov. 4 April 2019. Retrieved 12 April 2020.
- McDonnell, G; Russell, AD (January 1999). "Antiseptics and disinfectants: activity, action, and resistance". Clinical Microbiology Reviews. 12 (1): 147–79. doi:10.1128/cmr.12.1.147. PMC 88911. PMID 9880479.
- Block, Seymour S., ed. (2000). "Chapter 27: Chemical Sporicidal and Sporostatic Agents". Disinfection, sterilization, and preservation (5th ed.). Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger. pp. 529–543. ISBN 978-0-683-30740-5.
- "Sec. 184.1366 Hydrogen peroxide". U.S. Government Printing Office via GPO Access. 1 April 2001. Archived from the original on 3 July 2007. Retrieved 7 July 2007.
- Capizzi, R.; Landi, F.; Milani, M.; Amerio, P. (2004). "Skin tolerability and efficacy of combination therapy with hydrogen peroxide stabilized cream and adapalene gel in comparison with benzoyl peroxide cream and adapalene gel in common acne. A randomized, investigator-masked, controlled trial". British Journal of Dermatology. 151 (2): 481–484. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2004.06067.x. PMID 15327558.
- Lane, Nick (2003). Oxygen : the molecule that made the world (First issued in paperback, repr. ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. p. 117. ISBN 978-0-19-860783-0.
- Shepherd, Steven. "Brushing Up on Gum Disease". FDA Consumer. Archived from the original on 14 May 2007. Retrieved 7 July 2007.
- Wernimont, Eric J (9–12 July 2006). System Trade Parameter Comparison of Monopropellants: Hydrogen Peroxide vs Hydrazine and Others (PDF). 42nd AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference & Exhibit. Sacramento, CA. Archived (PDF) from the original on 10 December 2014.
- "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 10 December 2014. Retrieved 10 December 2014.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Peroxide Accident – Walter Web Site". Histarmar.com.ar. Archived from the original on 10 December 2014. Retrieved 14 February 2015.
- Scott, Richard (November 1997). "Homing Instincts". Jane's Navy Steam Generated by Catalytic Decomposition of 80–90% Hydrogen Peroxide Was Used for Driving the Turbopump Turbines of the V-2 Rockets, the X-15 Rocketplanes, the Early Centaur RL-10 Engines and is Still Used on Soyuz for That Purpose Today. International. Archived from the original on 17 July 2011. Retrieved 12 May 2007.
- Soyuz using hydrogen peroxide propellant Archived 5 August 2013 at the Wayback Machine (NASA website)
- "Ways to use Hydrogen Peroxide in the Garden". Using Hydrogen Peroxide. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 3 March 2016.
- Bhattarai SP, Su N, Midmore DJ (2005). Oxygation Unlocks Yield Potentials of Crops in Oxygen-Limited Soil Environments. Advances in Agronomy. 88. pp. 313–377. doi:10.1016/S0065-2113(05)88008-3. ISBN 978-0-12-000786-8.
- "FDA Approves Additional Indications for 35% PEROX-AID (hydrogen peroxide) for Use in Certain Finfish". FDA. 26 July 2019. Retrieved 19 December 2019.
- Greene, Ben; Baker, David; Frazier, Wayne. "Hydrogen Peroxide Accidents and Incidents: What we can learn from history" (PDF). NASA. Archived (PDF) from the original on 6 April 2019. Retrieved 6 April 2019.
- "Material Compatibility with Hydrogen Peroxide". Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 3 March 2016.
- "Hydrogen Peroxide Mouthwash is it Safe?". Archived from the original on 20 December 2013. Retrieved 30 October 2013.
- "Occupational Safety and Health Guideline for Hydrogen Peroxide". Archived from the original on 13 May 2013.
- For example, see an MSDS for a 3% peroxide solution Archived 15 April 2012 at the Wayback Machine.
- H2O2 toxicity and dangers Archived 5 June 2012 at the Wayback Machine Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry website
- CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 76th Ed, 1995–1996
- "CDC – Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH): Chemical Listing and Documentation of Revised IDLH Values – NIOSH Publications and Products". 25 October 2017. Archived from the original on 17 November 2012. Retrieved 20 October 2018.
- "Threshold Limit Values for Chemical Substances and Physical Agents & Biological Exposure Indices, ACGIH" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 June 2013.
- "ATSDR – Redirect – MMG: Hydrogen Peroxide". Archived from the original on 3 March 2016. Retrieved 3 March 2016.
- Wilgus TA, Bergdall VK, Dipietro LA, Oberyszyn TM (2005). "Hydrogen peroxide disrupts scarless fetal wound repair". Wound Repair Regen. 13 (5): 513–9. doi:10.1111/j.1067-1927.2005.00072.x. PMID 16176460.
- Loo, Alvin Eng Kiat; Wong, Yee Ting; Ho, Rongjian; Wasser, Martin; Du, Tiehua; Ng, Wee Thong; Halliwell, Barry; Sastre, Juan (13 November 2012). "Effects of Hydrogen Peroxide on Wound Healing in Mice in Relation to Oxidative Damage". PLOS ONE. 7 (11): e49215. Bibcode:2012PLoSO...749215L. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0049215. PMC 3496701. PMID 23152875.
- Shaw, A; Cooperman, A; Fusco, J (1967). "Gas embolism produced by hydrogen peroxide". N Engl J Med. 277 (5): 238–41. doi:10.1056/nejm196708032770504. PMID 6029311.
- "Hydrogen peroxide: reminder of risk of gas embolism when used in surgery – GOV.UK". www.gov.uk. Archived from the original on 18 September 2016. Retrieved 31 July 2016.
- Rahman, GA; Adigun, IA; Yusuf, IF; Ofoegbu, CKP (28 May 2010). "Wound dressing where there is limitation of choice". Nigerian Journal of Surgical Research. 8 (3–4). doi:10.4314/njsr.v8i3-4.54882.
- Velding, K.; Klis, S.-A.; Abass, K. M.; Tuah, W.; Stienstra, Y.; van der Werf, T. (9 June 2014). "Wound Care in Buruli Ulcer Disease in Ghana and Benin". American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene. 91 (2): 313–318. doi:10.4269/ajtmh.13-0255. PMC 4125255. PMID 24914002.
- "Hydrogen peroxide: health effects, incident management and toxicology". Archived from the original on 25 January 2014. Retrieved 3 March 2016.
- Douglass, William Campbell (1995). Hydrogen peroxide : medical miracle. [Atlanta, GA]: Second Opinion Pub. ISBN 978-1-885236-07-4.
- Hydrogen Peroxide, 3%. 3. Hazards Identification Southeast Fisheries Science Center, daughter agency of NOAA.
- "Questionable methods of cancer management: hydrogen peroxide and other 'hyperoxygenation' therapies". CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians. 43 (1): 47–56. 1993. doi:10.3322/canjclin.43.1.47. PMID 8422605.
- Cooper, Anderson (12 January 2005). "A Prescription for Death?". CBS News. Archived from the original on 17 July 2007. Retrieved 7 July 2007.
- Mikkelson, Barbara (30 April 2006). "Hydrogen Peroxide". Snopes.com. Retrieved 7 July 2007.
- "Naturopath Sentenced For Injecting Teen With Hydrogen Peroxide – 7NEWS Denver". Thedenverchannel.com. 27 March 2006. Archived from the original on 20 March 2014. Retrieved 14 February 2015.
- Halliwell, Barry (1 January 2007). "Oxidative stress and cancer: have we moved forward?". Biochemical Journal. 401 (1): 1–11. doi:10.1042/BJ20061131. PMID 17150040.
- "Heeresversuchsstelle Kummersdorf | UrbEx | Forgotten & Abandoned". UrbEx | Forgotten & Abandoned. 23 March 2008. Archived from the original on 29 June 2018. Retrieved 1 June 2018.
- "The Nazi Doctors: Medical Killing and the Psychology of Genocide". Robert Jay Lifton. Archived from the original on 27 June 2018. Retrieved 26 June 2018.
- "Explosion and fire in a hydrogen peroxide plant". ARIA. November 2007.
- "Accident No: DCA-99-MZ-001" (PDF). U.S National Transportation Safety Board. Archived (PDF) from the original on 3 November 2015. Retrieved 30 October 2015.
- Wheaton, Sarah (16 August 2010). "Bleach Spill Shuts Part of Times Square". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 1 December 2017. Retrieved 24 February 2017.
Bibliography
- J. Drabowicz; et al. (1994). G. Capozzi; et al. (eds.). The Syntheses of Sulphones, Sulphoxides and Cyclic Sulphides. Chichester UK: John Wiley & Sons. pp. 112–6. ISBN 978-0-471-93970-2.
- N.N. Greenwood; A. Earnshaw (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Oxford UK: Butterworth-Heinemann. A great description of properties & chemistry of H
2O
2. - J. March (1992). Advanced Organic Chemistry (4th ed.). New York: Wiley. p. 723.
- W.T. Hess (1995). "Hydrogen Peroxide". Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology. 13 (4th ed.). New York: Wiley. pp. 961–995.
External links
| Wikiversity has learning resources about Observing the Effects of Concentration on Enzyme Activity |
- Hydrogen Peroxide at The Periodic Table of Videos (University of Nottingham)
- Material Safety Data Sheet
- ATSDR Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry FAQ
- International Chemical Safety Card 0164
- NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards
- Process flow sheet of Hydrogen Peroxide Production by anthrahydroquinone autoxidation
- Hydrogen Peroxide Handbook by Rocketdyne
- IR spectroscopic study J. Phys. Chem.