Potassium superoxide
Potassium superoxide is the inorganic compound with the formula KO2.[2] It is a yellow paramagnetic solid that decomposes in moist air. It is a rare example of a stable salt of the superoxide anion. Potassium superoxide is used as a CO
2 scrubber, H
2O dehumidifier and O
2 generator in rebreathers, spacecraft, submarines and spacesuit life support systems.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Potassium dioxide | |
| Other names
Potassium superoxide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.031.574 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| KO2 | |
| Molar mass | 71.096 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | yellow solid |
| Density | 2.14 g/cm3, solid |
| Melting point | 560 °C (1,040 °F; 833 K) (decomposes) |
| Hydrolysis | |
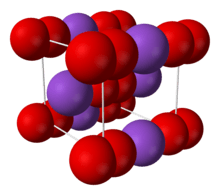
| Structure | |
| Body-centered cubic (O− 2) | |
| Thermochemistry | |
Std molar entropy (S |
117 J·mol−1·K−1[1] |
Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−283 kJ·mol−1[1] |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | corrosive, oxidant |
| R-phrases (outdated) | 8-14-34 |
| S-phrases (outdated) | 17-27-36/37/39 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions |
Potassium oxide Potassium peroxide |
Other cations |
Sodium superoxide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Production and reactions
Potassium superoxide is produced by burning molten potassium in an atmosphere of oxygen.[3]
- K + O
2 → KO
2
The salt consists of K+
and O−
2 ions, linked by ionic bonding. The O−O distance is 1.28 Å.[4]
Reactivity
Potassium superoxide is a strong oxidant, able to convert oxides into peroxides or molecular oxygen. Hydrolysis gives oxygen gas, hydrogen peroxide and potassium hydroxide:
- 2 KO
2 + 2 H
2O → 2 KOH + H
2O
2 + O
2[5]
Potassium hydroxide (KOH) absorbing carbon dioxide produces carbonates:
- 2 KOH + CO
2 → K2CO3 + H2O - KOH + CO
2 → KHCO3
Combining these two reactions produces:
- 4 KO
2 + 2 CO
2 → 2 K2CO3 + 3 O
2 - 4 KO
2 + 4 CO
2 + 2 H2O → 4 KHCO3 + 3 O
2
Potassium superoxide finds only niche uses as a laboratory reagent. Because it reacts with water, KO
2 is often studied in organic solvents. Since the salt is poorly soluble in nonpolar solvents, crown ethers are typically used. The tetraethylammonium salt is also known. Representative reactions of these salts involve using superoxide as a nucleophile, e.g., in converting alkyl bromides to alcohols and acyl chlorides to diacyl peroxides.[6]
Applications
The Russian Space Agency has had success using potassium superoxide in chemical oxygen generators for its spacesuits and Soyuz spacecraft. KO
2 has also been used in canisters for rebreathers for fire fighting and mine rescue work, but had limited use in scuba rebreathers because of its dangerously explosive reaction with water.
Theoretically, 1 kg of KO
2 absorbs 0.310 kg of CO
2 while releasing 0.338 kg of O
2. One mole of KO
2 absorbs 0.5 moles of CO
2 but only releases 0.75 moles of oxygen gas (O2) molecules. The human body will produce fewer CO
2 molecules than oxygen molecules needed because oxidation of food also needs oxygen to produce water and urea.
Hazards
Potassium superoxide is a potent oxidizer, and can produce explosive reactions when combined with a variety of substances and compounds, including water, acids, organics, or powdered graphite. Even dry superoxide can produce an impact-sensitive explosive compound when combined with organic oils such as kerosene.[7] In 1999 at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, cleanup of potassium oxides from a NaK metal leak produced an impact-sensitive explosion while saturated with mineral oil.[8]
References
- Zumdahl, Steven S. (2009). Chemical Principles (6th ed.). Houghton Mifflin. p. A22. ISBN 0-618-94690-X.
- Hayyan M.; Hashim M. A.; AlNashef I. M. (2016). "Superoxide Ion: Generation and Chemical Implications". Chem. Rev. 116: 3029–3085. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00407. PMID 26875845.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
- Jakob, Harald; Leininger, Stefan; Lehmann, Thomas; Jacobi, Sylvia; Gutewort, Sven (2007). "Peroxo Compounds, Inorganic". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a19_177.pub2.
- Abrahams, S. C.; Kalnajs, J. (1955). "The Crystal Structure of α-Potassium Superoxide". Acta Crystallographica. 8: 503–6. doi:10.1107/S0365110X55001540.
- Kumar De, Anil (2007). A Text Book of Inorganic Chemistry. New Age International. p. 247. ISBN 978-8122413847.
- Johnson, Roy A.; Adrio, Javier; Ribagorda, María (2001). "Potassium Superoxide". e-EROS Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. Wiley. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rp250.pub2.
- Aerojet Nuclear Company (1975). "An Explosives Hazards Analysis of the Eutectic Solution of NaK and KO
2". Idaho National Engineering Laboratory. - "Y-12 NaK Accident Investigation". U.S. Department of Energy. February 2000. Archived from the original on 2010-05-28.
