Cantonese
Cantonese is a language within the Chinese language family originating from the city of Guangzhou (also known as Canton) and its surrounding area in Southeastern China. It is the traditional prestige variety of the Yue Chinese dialect group, which has over 80 million native speakers.[2] While the term Cantonese specifically refers to the prestige variety, it is often used to refer to the entire Yue subgroup of Chinese, including related but largely mutually unintelligible languages and dialects such as Taishanese.
| Cantonese | |
|---|---|
| 廣東話 Gwóngdūng wá | |
 Gwóngdūng wá written in traditional Chinese (left) and simplified Chinese (right) characters | |
| Native to | China, Hong Kong, Macau and overseas communities |
| Region | Pearl River Delta of Guangdong, eastern Guangxi |
| Dialects | |
| Written Cantonese Cantonese Braille Written Chinese | |
| Official status | |
Official language in | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | yue (superset for all Yue dialects) |
| Glottolog | cant1236[1] |
| Linguasphere | 79-AAA-ma |
| Cantonese | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Chinese | 廣東話 | ||||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 广东话 | ||||||||||||
| Cantonese Yale | Gwóngdūng wá | ||||||||||||
| Literal meaning | 'Guangdong speech' | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| 'Guangzhou speech' or 'Canton speech' | |||||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 廣州話 | ||||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 广州话 | ||||||||||||
| Cantonese Yale | Gwóngjāu wá | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| 'Guangfu speech' | |||||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 廣府話 | ||||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 广府话 | ||||||||||||
| Cantonese Yale | Gwóngfú wá | ||||||||||||
| Literal meaning | Guang[dong] capital speech | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| This article is part of the series on the |
| Cantonese language |
|---|
 |
| Yue Chinese |
| Grammar |
| Orthography |
| Phonology |
|
| This article is part of the series on |
| Cantonese culture |
|---|
 |
|
|
Language
|
|
Visual arts
|
|
Performing arts
|
|
Philosophy |
|
Customs and Traditions
|
|
Taoist deities |
|
Cultural symbols
|
Cantonese is viewed as a vital and inseparable part of the cultural identity for its native speakers across large swaths of Southeastern China, Hong Kong and Macau, as well as in overseas communities. In mainland China, it is the lingua franca of the province of Guangdong (being the majority language of the Pearl River Delta) and neighbouring areas such as Guangxi. It is the dominant and official language of Hong Kong and Macau. Cantonese is also widely spoken amongst Overseas Chinese in Southeast Asia (most notably in Vietnam and Malaysia, as well as in Singapore and Cambodia to a lesser extent) and throughout the Western world.
Although Cantonese shares much vocabulary with Mandarin, the two Sinitic languages are mutually unintelligible, largely because of lexical differences, but also due to differences in grammar and pronunciation. Sentence structure, in particular the placement of verbs, sometimes differs between the two varieties. A notable difference between Cantonese and Mandarin is how the spoken word is written; both can be recorded verbatim, but very few Cantonese speakers are knowledgeable in the full Cantonese written vocabulary, so a non-verbatim formalized written form is adopted, which is more akin to the Mandarin written form.[3][4] This results in the situation in which a Cantonese and a Mandarin text may look similar but are pronounced differently.
Names
In English, the term "Cantonese" can be ambiguous. Cantonese proper is the variety native to the city of Canton, which is the traditional English name of Guangzhou. This narrow sense may be specified as "Canton language" or "Guangzhou language".[5]
However, "Cantonese" may also refer to the primary branch of Chinese that contains Cantonese proper as well as Taishanese and Gaoyang; this broader usage may be specified as "Yue speech" (粵語; 粤语; Yuhtyúh). In this article, "Cantonese" is used for Cantonese proper.
Historically, speakers called this variety "Canton speech" or "Guangzhou speech" (廣州話; 广州话; Gwóngjāu wá), although this term is now seldom used outside Guangzhou. In Guangdong and Guangxi, people also call it "provincial capital speech" (省城話; 省城话; Sáangsìng wá) or "plain speech" (白話; 白话; Baahkwá). Also, academically called "Canton prefecture speech" (廣府話; 广府话; Gwóngfú wá).
In Hong Kong and Macau, as well as among overseas Chinese communities, the language is referred to as "Guangdong speech" or "Canton Province speech" (廣東話; 广东话; Gwóngdūng wá), or simply as "Chinese" (中文; Jūngmán).[6][7] In mainland China, the term "Guangdong speech" is also increasingly being used amongst both native and non-native speakers. Given the history of the development of the Yue languages and dialects during the Tang dynasty migrations to the region, in overseas Chinese communities, it is also referred to as "Tang speech" (唐話; Tòhng wá), given that the Cantonese people refer to themselves as "people of Tang" (唐人; Tòhng yàhn).
Due to its status as a prestige dialect among all the dialects of the Yue branch of Chinese varieties, it is often called "Standard Cantonese" (標準粵語; 标准粤语; Bīujéun Yuhtyúh).
Geographic distribution
Hong Kong and Macau
The official languages of Hong Kong are Chinese and English, as defined in the Hong Kong Basic Law.[8] The Chinese language has many different varieties, of which Cantonese is one. Given the traditional predominance of Cantonese within Hong Kong, it is the de facto official spoken form of the Chinese language used in the Hong Kong Government and all courts and tribunals. It is also used as the medium of instruction in schools, alongside English.
A similar situation also exists in neighboring Macau, where Chinese is an official language alongside Portuguese. As in Hong Kong, Cantonese is the predominant spoken variety of Chinese used in everyday life and is thus the official form of Chinese used in the government. The Cantonese spoken in Hong Kong and Macau is mutually intelligible with the Cantonese spoken in the mainland city of Guangzhou, although there exist some minor differences in accent, pronunciation, and vocabulary.
Mainland China
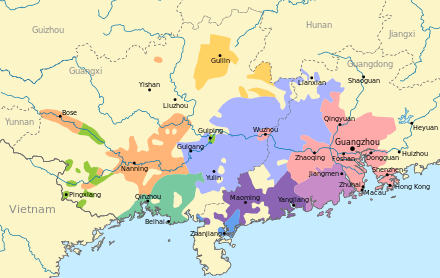
Cantonese first developed around the port city of Guangzhou in the Pearl River Delta region of southeastern China. Due to the city's long standing as an important cultural center, Cantonese emerged as the prestige dialect of the Yue varieties of Chinese in the Southern Song dynasty and its usage spread around most of what is now the provinces of Guangdong and Guangxi.[9]
Despite the cession of Macau to Portugal in 1557 and Hong Kong to Britain in 1842, the ethnic Chinese population of the two territories largely originated from the 19th and 20th century immigration from Guangzhou and surrounding areas, making Cantonese the predominant Chinese language in the territories. On the mainland, Cantonese continued to serve as the lingua franca of Guangdong and Guangxi provinces even after Mandarin was made the official language of the government by the Qing dynasty in the early 1900s.[10] Cantonese remained a dominant and influential language in southeastern China until the establishment of the People's Republic of China in 1949 and its promotion of Standard Mandarin Chinese as the sole official language of the nation throughout the last half of the 20th century, although its influence still remains strong within the region.[11]
While the Chinese government vehemently discourages the official use of all forms of Chinese except Standard Chinese, Cantonese enjoys a relatively higher standing than other Chinese languages, with its own media and usage in public transportation in Guangdong province.[12] Furthermore, it is also a medium of instruction in select academic curricula, including some university elective courses and Chinese as a foreign language programs.[13][14] The permitted usage of Cantonese in mainland China is largely a countermeasure against Hong Kong's influence, as the autonomous territory has the right to freedom of the press and speech and its Cantonese-language media have a substantial exposure and following in Guangdong.[15]
Nevertheless, the place of local Cantonese language and culture remains contentious. A 2010 proposal to switch some programming on Guangzhou television from Cantonese to Mandarin was abandoned following massive public protests, the largest since the Tiananmen Square protests of 1989. As a major economic center of China, there have been recent concerns that the use of Cantonese in Guangzhou is diminishing in favour of Mandarin, both through the continual influx of Mandarin-speaking migrants from impoverished areas and strict government policies. As a result, Cantonese is being given a more important status by the natives than ever before as a common identity of the local people.[16]
Southeast Asia
Cantonese has historically served as a lingua franca among overseas Chinese in Southeast Asia, who speak a variety of other forms of Chinese including Hokkien, Teochew, and Hakka.[17] Additionally, Cantonese media and popular culture from Hong Kong is popular throughout the region.
Vietnam
In Vietnam, Cantonese is the dominant language of the ethnic Chinese community, usually referred to as Hoa, which numbers about one million people and constitutes one of the largest minority groups in the country.[18] Over half of the ethnic Chinese population in Vietnam speaks Cantonese as a native language and the variety also serves as a lingua franca between the different Chinese dialect groups. Many speakers reflect their exposure to Vietnamese with a Vietnamese accent or a tendency to code-switch between Cantonese and Vietnamese.[19]
Malaysia
In Malaysia, Cantonese is widely spoken amongst the Malaysian Chinese community in the capital city of Kuala Lumpur[20] and the surrounding areas in the Klang Valley (Petaling Jaya, Ampang, Cheras, Selayang, Sungai Buloh, Puchong, Shah Alam, Kajang, Bangi, and Subang Jaya). The dialect is also widely spoken as well in the town of Sekinchan in the district of Sabak Bernam located in the northern part of Selangor state and also in the state of Perak, especially in the state capital city of Ipoh and its surrounding towns of Gopeng, Batu Gajah, and Kampar of the Kinta Valley region plus the towns of Tapah and Bidor in the southern part of the Perak state, and also widely spoken in the eastern Sabahan town of Sandakan as well as the towns of Kuantan, Raub, Bentong, and Mentakab in Pahang state, and they are also found in other areas such as Sarikei, Sarawak, and Mersing, Johor.
Although Hokkien is the most spoken variety of Chinese, and Mandarin is the medium of education at Chinese-language schools, Cantonese is largely influential in the local Chinese-language media and is used in commerce by Chinese Malaysians.[21]
Due to the popularity of Hong Kong popular culture, especially through drama series and popular music, Cantonese is widely understood by the Chinese in all parts of Malaysia, even though a large proportion of the Chinese Malaysian population is non-Cantonese. Television networks in Malaysia regularly broadcast Hong Kong television programmes in their original Cantonese audio and soundtrack. Cantonese radio is also available in the nation and Cantonese is prevalent in locally produced Chinese television.[22][23]
Cantonese spoken in Malaysia often exhibits influences from Malay and other Chinese varieties spoken in the country, such as Hokkien and Teochew.[24]
Singapore
In Singapore, Mandarin is the official variety of the Chinese language used by the government, which has a Speak Mandarin Campaign (SMC) seeking to actively promote the use of Mandarin at the expense of other Chinese varieties. Cantonese is spoken by a little over 15% of Chinese households in Singapore. Despite the government's active promotion of SMC, the Cantonese-speaking Chinese community has been relatively successful in preserving its language from Mandarin compared to other dialect groups.[25]
Notably, all nationally produced non-Mandarin Chinese TV and radio programs were stopped after 1979.[26] The prime minister, Lee Kuan Yew, then, also stopped giving speeches in Hokkien to prevent giving conflicting signals to the people.[26] Hong Kong (Cantonese) and Taiwanese dramas are unavailable in their untranslated form on free-to-air television, though drama series in non-Chinese languages are available in their original languages. Cantonese drama series on terrestrial TV channels are instead dubbed in Mandarin and broadcast without the original Cantonese audio and soundtrack. However, originals may be available through other sources such as cable television and online videos.
Furthermore, an offshoot of SMC is the translation to Hanyu Pinyin of certain terms which originated from southern Chinese varieties. For instance, dim sum is often known as diǎn xīn in Singapore's English-language media, though this is largely a matter of style, and most Singaporeans will still refer to it as dim sum when speaking English.[27]
Nevertheless, since the government restriction on media in non-Mandarin varieties was relaxed in the mid-1990s and 2000s, the presence of Cantonese in Singapore has grown substantially. Forms of popular culture from Hong Kong, such as television series, cinema and pop music have become popular in Singaporean society, and non-dubbed original versions of the media became widely available. Consequently, there is a growing number of non-Cantonese Chinese Singaporeans being able to understand or speak Cantonese to some varying extent, with a number of educational institutes offering Cantonese as an elective language course.[28]
Cambodia
Cantonese is widely used as the inter-communal language among Chinese Cambodians, especially in Phnom Penh and other urban areas. While Teochew speakers form the majority of the Chinese population in Cambodia, Cantonese is often used as a vernacular in commerce and with other Chinese variant groups in the nation.[29] Chinese-language schools in Cambodia are conducted in both Cantonese and Mandarin, but schools may be conducted exclusively in one Chinese variant or the other.[30]
Thailand
Thailand is home to the largest overseas Chinese community in the world, numbering over 9 million individuals. However, the vast majority of ethnic Chinese in Thailand speak Thai exclusively.[31] Among Chinese-speaking Thai households, Cantonese is the fourth most-spoken variety of Chinese after Teochew, Hakka and Hainanese.[32] Nevertheless, within the Thai Chinese commercial sector, it serves as a common language alongside Teochew or Thai. Chinese-language schools in Thailand have also traditionally been conducted in Cantonese. Furthermore, Cantonese serves as the lingua franca with other Chinese communities in the region.[33]
Indonesia
In Indonesia, Cantonese is locally known as Konghu and is one of the variants spoken by the Chinese Indonesian community, with speakers largely concentrated in major cities such as Jakarta, Surabaya and Batam. However, it has a relatively minor presence compared to other Southeast Asian nations, being the fourth most spoken Chinese variety after Hokkien, Hakka and Teochew. [34]
North America
United States

Over a period of 150 years, Guangdong has been the place-of-origin for most Chinese emigrants to Western nations; one coastal county, Taishan (or Tóisàn, where the Sìyì or sei yap variety of Yue is spoken), alone may be the origin of the vast majority of Chinese immigrants to the U.S. before 1965.[35] As a result, Yue languages such as Cantonese and the closely related variety of Taishanese have been the major Chinese varieties traditionally spoken in the United States.
The Zhongshan variant of Cantonese, with origins in the western Pearl River Delta, is spoken by many Chinese immigrants in Hawaii, and some in San Francisco and the Sacramento River Delta (see Locke, California); it is a Yuehai variety much like Guangzhou Cantonese, but has "flatter" tones. Chinese is the third most widely spoken non-English language in the United States when both Cantonese and Mandarin are combined, behind Spanish and French.[36] Many institutes of higher education have traditionally had Chinese programs based on Cantonese, with some continuing to offer these programs despite the rise of Mandarin. The most popular romanization for learning Cantonese in the United States is Yale Romanization.
The majority of Chinese emigrants have traditionally originated from Guangdong and Guangxi, as well as Hong Kong and Macao (beginning in the latter half of the 20th century and before the Handover) and Southeast Asia, with Cantonese as their native language. However, more recent immigrants are arriving from the rest of mainland China and Taiwan and most often speak Standard Mandarin (Putonghua) as their native language,[37][38] although some may also speak their native local variety, such as Shanghainese, Hokkien, Fuzhounese, Hakka, etc. As a result, Mandarin is becoming more common among the Chinese American community.
The increase of Mandarin-speaking communities has resulted in the rise of separate neighborhoods or enclaves segregated by the primary Chinese variety spoken. Socioeconomic statuses are also a factor as well.[39] For example, in New York City, Cantonese still predominates in the city's older, traditional western portion of Chinatown in Manhattan and in Brooklyn's small new Chinatowns in sections of Bensonhurst and in Homecrest. The newly emerged Little Fuzhou eastern portion of Manhattan's Chinatown and Brooklyn's main large Chinatown in and around Sunset Park are mostly populated by Fuzhounese speakers, who often speak Mandarin as well. The Cantonese and Fuzhounese enclaves in New York City are more working class. However, due to the rapid gentrification of Manhattan's Chinatown and with NYC's Cantonese and Fuzhou populations now increasingly shifting to other Chinese enclaves in the Outer Boroughs of NYC such as Brooklyn and Queens, but most mainly in Brooklyn's newer Chinatowns, the Cantonese speaking population in NYC are now increasingly becoming more mainly concentrated into Brooklyn's neighborhoods of Bensonhurst and Homecrest, also known as Bensonhurst's Little Hong Kong/Guangdong and Homecrest's Little Hong Kong/Guangdong while the Fuzhou population of NYC are increasingly becoming more mainly concentrated into Brooklyn's neighborhood of Sunset Park, also known as Little Fuzhou, Brooklyn, which is now increasingly resulting in NYC's growing Cantonese and Fuzhou enclaves to become more increasingly distanced and isolated away from each other including much more isolated away from other Chinese enclaves in the NYC borough of Queens that have more Mandarin and other various diverse Chinese dialect speakers. Flushing's large Chinatown, which now holds the crown as the largest Chinatown of the city, and Elmhurst's smaller Chinatown in Queens are very mixed, with large numbers of Mandarin speakers from many various different regions of China and Taiwan. The Chinatowns of Queens comprise the primary cultural center for New York City's Chinese population and are more middle class.[40][41][42][43][44][45][46][47]
In Northern California, especially in the San Francisco Bay Area, Cantonese has historically and continues to dominate in the Chinatowns of San Francisco and Oakland, as well as the surrounding suburbs and metropolitan area, although Mandarin is now also found in Silicon Valley. In contrast, Southern California hosts a much larger Mandarin-speaking population, with Cantonese found in more historical Chinese communities such as that of Chinatown, Los Angeles, and older Chinese ethnoburbs such as San Gabriel, Rosemead, and Temple City.[48] Mandarin predominates in the emergent Chinese enclave lying 15 miles to the east at the intersection of Los Angeles, San Bernardino, and Riverside counties, in the cities of Diamond Bar, Chino Hills, Chino, Ontario, and Eastvale; Mandarin also dominates in the new Chinese enclave in Southern Orange County centered on Irvine.
While a number of more-established Taiwanese immigrants have learned Cantonese to foster relations with the traditional Cantonese-speaking Chinese American population, more recent arrivals and the larger number of mainland Chinese immigrants have largely continued to use Mandarin as the exclusive variety of Chinese. This has led to a linguistic discrimination that has also contributed to social conflicts between the two sides, with a growing number of Chinese Americans (including American-born Chinese) of Cantonese background defending the historic Chinese-American culture against the impacts of increasing Mandarin-speaking new arrivals.[39][49]
Canada
Cantonese is the most common Chinese variety spoken among Chinese Canadians. According to the Canada 2016 Census, there were 565,275 Canadian residents who reported Cantonese as their native language.
As in the United States, the Chinese Canadian community traces its roots to early immigrants from Guangdong during the latter half of the 19th century.[50] Later Chinese immigrants came from Hong Kong in two waves, first in the late 1960s to mid 1970s, and again in the 1980s to late 1990s on fears arising from the impending handover to the People's Republic of China. Chinese-speaking immigrants from conflict zones in Southeast Asia, especially Vietnam, arrived as well, beginning in the mid-1970s and were also largely Cantonese-speaking. Unlike the United States, recent immigration from mainland China and Taiwan to Canada has been small, and Cantonese still remains the predominant Chinese variety in the country.[51]
Western Europe
United Kingdom
The overwhelming majority of Chinese speakers in the United Kingdom use Cantonese, with about 300,000 British people claiming it as their first language.[52] This is largely due to the presence of British Hong Kongers and the fact that many British Chinese also have origins in the former British colonies in Southeast Asia of Singapore and Malaysia.
France
Among the Chinese community in France, Cantonese is spoken by immigrants who fled the former French Indochina (Vietnam, Cambodia and Laos) following the conflicts and communist takeovers in the region during the 1970s. While a slight majority of ethnic Chinese from Indochina speak Teochew at home, knowledge of Cantonese is prevalent due to its historic prestige status in the region and is used for commercial and community purposes between the different Chinese variety groups. As in the United States, there is a divide between Cantonese-speakers and those speaking other mainland Chinese varieties.[53]
Portugal
Cantonese is spoken by ethnic Chinese in Portugal who originate from Macau, the most established Chinese community in the nation with a presence dating back to the 16th century and Portuguese colonialism. Since the late-20th century, however, Mandarin- and Wu-speaking migrants from mainland China have outnumbered those from Macau, although Cantonese is still retained among mainstream Chinese community associations.[54]
Australia
Cantonese has traditionally been the dominant Chinese language of the Chinese Australian community since the first ethnic Chinese settlers arrived in the 1850s. It maintained this status until the mid-2000s, when a heavy increase in immigration from Mandarin-speakers largely from Mainland China led to Mandarin surpassing Cantonese as the dominant Chinese dialect spoken. Cantonese is the third most-spoken language in Australia. In the 2011 census, the Australian Bureau of Statistics listed 336,410 and 263,673 speakers of Mandarin and Cantonese, respectively.
History
During the Southern Song period, Guangzhou became the cultural center of the region.[9] Cantonese emerged as the prestige variety of Yue Chinese when the port city of Guangzhou on the Pearl River Delta became the largest port in China, with a trade network stretching as far as Arabia.[55] Cantonese was also used in the popular Yuè'ōu, Mùyú and Nányīn folksong genres, as well as Cantonese opera.[56][57] Additionally, a distinct classical literature was developed in Cantonese, with Middle Chinese texts sounding more similar to modern Cantonese than other present-day Chinese varieties, including Mandarin.[58]
As Guangzhou became China's key commercial center for foreign trade and exchange in the 1700s, Cantonese became the variety of Chinese interacting most with the Western World.[55] Around this period and continuing into the 1900s, the ancestors of most of the population of Hong Kong and Macau arrived from Guangzhou and surrounding areas after they were ceded to Britain and Portugal, respectively.[59] After the Xinhai Revolution of 1912, Cantonese almost became the official language of the Republic of China but lost by a small margin.[60]
In Mainland China, Standard Chinese (based on Mandarin) has been heavily promoted as the medium of instruction in schools and as the official language, especially after the communist takeover in 1949. Meanwhile, Cantonese has remained the official variety of Chinese in Hong Kong and Macau, both during and after the colonial period.[61]
Cultural role

Spoken Chinese has numerous regional and local varieties, many of which are mutually unintelligible. Most of these are rare outside their native areas, though they may be spoken outside of China. Many varieties also have Literary and colloquial readings of Chinese characters for newer standard reading sounds. Since a 1909 Qing dynasty decree, China has promoted Mandarin for use in education, the media, and official communications.[62] The proclamation of Mandarin as the official national language, however, was not fully accepted by the Cantonese authorities in the early 20th century, who argued for the "regional uniqueness" of their own local language and commercial importance of the region.[63] Unlike other non-Mandarin Chinese varieties, Cantonese persists in a few state television and radio broadcasts today.
Nevertheless, there have been recent attempts to minimize the use of Cantonese in China. The most notable has been the 2010 proposal that Guangzhou Television increase its broadcast in Mandarin at the expense of Cantonese programs. This however led to protests in Guangzhou, which eventually dissuaded authorities from going forward with the proposal.[64] Additionally, there are reports of students being punished for speaking other Chinese languages at school, resulting in a reluctance of younger children to communicate in their native languages, including Cantonese.[65] Such actions have further provoked Cantonese speakers to cherish their linguistic identity in contrast to migrants who have generally arrived from poorer areas of China and largely speak Mandarin or other Chinese languages.[66]
Due to the linguistic history of Hong Kong and Macau, and the use of Cantonese in many established overseas Chinese communities, the use of Cantonese is quite widespread compared to the presence of its speakers residing in China. Cantonese is the predominant Chinese variety spoken in Hong Kong and Macau. In these areas, public discourse takes place almost exclusively in Cantonese, making it the only variety of Chinese other than Mandarin to be used as an official language in the world. Because of their dominance in Chinese diaspora overseas, standard Cantonese and its dialect Taishanese are among the most common Chinese languages that one may encounter in the West.
Increasingly since the 1997 Handover, Cantonese has been used as a symbol of local identity in Hong Kong, largely through the development of democracy in the territory and desinicization practices to emphasise a separate Hong Kong identity.[67]
A similar identity issue exists in the United States, where conflicts have arisen among Chinese-speakers due to a large recent influx of Mandarin-speakers. While older Taiwanese immigrants have learned Cantonese to foster integration within the traditional Chinese American populations, more recent arrivals from the Mainland continue to use Mandarin exclusively. This has contributed to a segregation of communities based on linguistic cleavage. In particular, some Chinese Americans (including American-born Chinese) of Cantonese background emphasise their non-Mainland origins (e.g. Hong Kong, Macau, Vietnam, etc.) to assert their identity in the face of new waves of immigration.[39][49]
Along with Mandarin and Hokkien, Cantonese has its own popular music, Cantopop, which is the predominant genre in Hong Kong. Many artists from the Mainland and Taiwan have learned Cantonese to break into the market.[68] Popular native Mandarin-speaking singers, including Faye Wong, Eric Moo, and singers from Taiwan, have been trained in Cantonese to add "Hong Kong-ness" to their performances.[68]
Cantonese films date to the early days of Chinese cinema, and the first Cantonese talkie, White Gold Dragon (白金龍), was made in 1932 by the Tianyi Film Company.[69] Despite a ban on Cantonese films by the Nanjing authority in the 1930s, Cantonese film production continued in Hong Kong which was then under British colonial rule.[63][70] From the mid-1970s to the 1990s, Cantonese films made in Hong Kong were very popular in the Chinese speaking world.
Phonology
Initials and finals
The de facto standard pronunciation of Cantonese is that of Canton (Guangzhou), which is described in the Cantonese phonology article. Hong Kong Cantonese has some minor variations in phonology, but is largely identical to standard Guangzhou Cantonese.
In Hong Kong and Macau, certain phoneme pairs have merged. Although termed as "lazy sound" (懶音) and considered substandard to Guangzhou pronunciation, the phenomenon has been widespread in the territories since the early 20th century. The most notable difference between Hong Kong and Guangzhou pronunciation is the substitution of the liquid nasal (/l/) for the nasal initial (/n/) in many words.[71] An example of this is manifested in the word for you (你), pronounced as néih in Guangzhou and as léih in Hong Kong.
Another key feature of Hong Kong Cantonese is the merging of the two syllabic nasals /ŋ̩/ and /m̩/. This can be exemplified in the elimination of the contrast of sounds between 吳 (Ng, a surname) (ng4/ǹgh in Guangzhou pronunciation) and 唔 (not) (m4/m̀h in Guangzhou pronunciation). In Hong Kong, both words are pronounced as the latter.[72]
Lastly, the initials /kʷ/ and /kʷʰ/ can be merged into /k/ and /kʰ/ when followed by /ɔː/. An example is in the word for country (國), pronounced in standard Guangzhou as gwok but as gok with the merge. Unlike the above two differences, this merge is found alongside the standard pronunciation in Hong Kong rather than being replaced. Educated speakers often stick to the standard pronunciation but can exemplify the merged pronunciation in casual speech. In contrast, less educated speakers pronounce the merge more frequently.[72]
Less prevalent, but still notable differences found among a number of Hong Kong speakers include:
- Merging of /ŋ/ initial into null initial.
- Merging of /ŋ/ and /k/ codas into /n/ and /t/ codas respectively, eliminating contrast between these pairs of finals (except after /e/ and /o/): /aːn/-/aːŋ/, /aːt/-/aːk/, /ɐn/-/ɐŋ/, /ɐt/-/ɐk/, /ɔːn/-/ɔːŋ/ and /ɔːt/-/ɔːk/.
- Merging of the rising tones (陰上 2nd and 陽上 5th).[73]
Cantonese vowels tend to be traced further back to Middle Chinese than their Mandarin analogues, such as M. /aɪ/ vs. C. /ɔːi/; M. /i/ vs. C. /ɐi/; M. /ɤ/ vs. C. /ɔː/; M. /ɑʊ/ vs. C. /ou/ etc. For consonants, some differences include M. /ɕ, tɕ, tɕʰ/ vs. C. /h, k, kʰ/; M. /ʐ/ vs. C. /j/; and a greater syllable coda diversity in Cantonese (such as syllables ending in -t, -p, or -k).
Tones
Generally speaking, Cantonese is a tonal language with six phonetic tones.
Historically, finals that end in a stop consonant were considered as "checked tones" and treated separately by diachronic convention, identifying Cantonese with nine tones (九声六调). However, these are seldom counted as phonemic tones in modern linguistics, which prefer to analyse them as conditioned by the following consonant.[74]
| Syllable type | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tone name | dark flat (陰平) | dark rising (陰上) | dark departing (陰去) |
light flat (陽平) | light rising (陽上) | light departing (陽去) |
| Description | high level, high falling | medium rising | medium level | low falling, very low level | low rising | low level |
| Yale or Jyutping tone number |
1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| Example | 詩 | 史 | 試 | 時 | 市 | 是 |
| Tone letter | siː˥, siː˥˧ | siː˧˥ | siː˧ | siː˨˩, siː˩ | siː˩˧ | siː˨ |
| IPA diacritic | síː, sîː | sǐː | sīː | si̖ː, sı̏ː | si̗ː | sìː |
| Yale diacritic | sī, sì | sí | si | sìh | síh | sih |
Written Cantonese
As Cantonese is used primarily in Hong Kong, Macau, and other overseas Chinese communities, it is usually written with traditional Chinese characters. However, it includes extra characters as well as characters with different meanings from written vernacular Chinese due to the presence of words that either do not exist in standard Chinese or correspond with spoken Cantonese. This system of written Cantonese is often found in colloquial contexts such as entertainment magazines and social media, as well as on advertisements.
In contrast, standard written Chinese continues to be used in formal literature, professional and government documents, television and movie subtitles, and news media. Nevertheless, colloquial characters may be present in formal written communications such as legal testimonies and newspapers when an individual is being quoted, rather than paraphrasing spoken Cantonese into standard written Chinese.
Romanization
Cantonese romanization systems are based on the accent of Canton and Hong Kong, and have helped define the concept of Standard Cantonese. The major systems are: Jyutping, Yale, the Chinese government's Guangdong Romanization, and Meyer–Wempe. While they do not differ greatly, Jyutping and Yale are the two most used and taught systems today in the West.[75] Additionally, Hong Kong linguist Sidney Lau modified the Yale system for his popular Cantonese-as-a-second-language course and is still in use today.
While the governments of Hong Kong and Macau utilize a romanization system for proper names and geographic locations, they are inconsistent in the transcription of some sounds and the systems are not taught in schools. Furthermore, the system of Macau differs slightly from Hong Kong's in that the spellings are influenced by the Portuguese language due to colonial history. However, some words under Macau's romanization system are same as Hong Kong's (e.g. Lam 林, Chan 陳). Instances of the letter ⟨u⟩ under Hong Kong's romanization systems are often replaced by ⟨o⟩ under Macao's romanization systems (e.g. Chau vs Chao 周, Leung vs Leong 梁). Both the spellings of Hong Kong and Macau Cantonese romanization systems do not look similar to the mainland China's pinyin system. Generally, plain stops are written with voiced consonants (/p/, /t/, /ts/, and /k/ as b, d, z/j, and g respectively), and aspirated stops with unvoiced ones, as in pinyin.
Early Western effort
Systematic efforts to develop an alphabetic representation of Cantonese began with the arrival of Protestant missionaries in China early in the nineteenth century. Romanization was considered both a tool to help new missionaries learn the variety more easily and a quick route for the unlettered to achieve gospel literacy. Earlier Catholic missionaries, mostly Portuguese, had developed romanization schemes for the pronunciation current in the court and capital city of China but made few efforts to romanize other varieties.
Robert Morrison, the first Protestant missionary in China published a "Vocabulary of the Canton Dialect" (1828) with a rather unsystematic romanized pronunciation. Elijah Coleman Bridgman and Samuel Wells Williams in their "Chinese Chrestomathy in the Canton Dialect" (1841) were the progenitors of a long-lived lineage of related romanizations with minor variations embodied in the works of James Dyer Ball, Ernst Johann Eitel, and Immanuel Gottlieb Genăhr (1910). Bridgman and Williams based their system on the phonetic alphabet and diacritics proposed by Sir William Jones for South Asian languages.
Their romanization system embodied the phonological system in a local dialect rhyme dictionary, the Fenyun cuoyao, which was widely used and easily available at the time and is still available today. Samuel Wells Willams' Tonic Dictionary of the Chinese Language in the Canton Dialect (Yinghua fenyun cuoyao 1856), is an alphabetic rearrangement, translation and annotation of the Fenyun. To adapt the system to the needs of users at a time when there were only local variants and no standard—although the speech of the western suburbs, Xiguan, of Guangzhou was the prestige variety at the time—Williams suggested that users learn and follow their teacher's pronunciation of his chart of Cantonese syllables. It was apparently Bridgman's innovation to mark the tones with an open circle (upper register tones) or an underlined open circle (lower register tones) at the four corners of the romanized word in analogy with the traditional Chinese system of marking the tone of a character with a circle (lower left for "even," upper left for "rising," upper right for "going," and lower right for "entering" tones).
John Chalmers, in his "English and Cantonese pocket-dictionary" (1859) simplified the marking of tones using the acute accent to mark "rising" tones and the grave to mark "going" tones and no diacritic for "even" tones and marking upper register tones by italics (or underlining in handwritten work). "Entering" tones could be distinguished by their consonantal ending. Nicholas Belfeld Dennys used Chalmers romanization in his primer. This method of marking tones was adopted in the Yale romanization (with low register tones marked with an 'h'). A new romanization was developed in the first decade of the twentieth century which eliminated the diacritics on vowels by distinguishing vowel quality by spelling differences (e.g. a/aa, o/oh). Diacritics were used only for marking tones.
The name of Tipson is associated with this new romanization which still embodied the phonology of the Fenyun to some extent. It is the system used in Meyer-Wempe and Cowles' dictionaries and O'Melia's textbook and many other works in the first half of the twentieth century. It was the standard romanization until the Yale system supplanted it. The distinguished linguist Y. R. Chao developed a Cantonese adaptation of his Gwoyeu Romatzyh system. The Barnett-Chao romanization system was first used in Chao's Cantonese Primer, published in 1947 by Harvard University Press (The Cantonese Primer was adapted for Mandarin teaching and published by Harvard University Press in 1948 as Mandarin Primer). The BC system was also used in textbooks published by the Hong Kong government.
Cantonese romanization in Hong Kong
An influential work on Cantonese, A Chinese Syllabary Pronounced According to the Dialect of Canton, written by Wong Shik Ling, was published in 1941. He derived an IPA-based transcription system, the S. L. Wong system, used by many Chinese dictionaries later published in Hong Kong. Although Wong also derived a romanization scheme, also known as the S. L. Wong system, it is not widely used as his transcription scheme. This system was preceded by the Barnett–Chao system used by the Hong Government Language School.
The romanization advocated by the Linguistic Society of Hong Kong (LSHK) is called Jyutping. The phonetic values of some consonants are closer to the approximate equivalents in IPA than in other systems. Some effort has been undertaken to promote Jyutping, but the success of its proliferation within the region has yet to be examined.
Another popular scheme is Cantonese Pinyin, which is the only romanization system accepted by Hong Kong Education and Manpower Bureau and Hong Kong Examinations and Assessment Authority. Books and studies for teachers and students in primary and secondary schools usually use this scheme. But there are teachers and students who use the transcription system of S.L. Wong.
Despite the efforts to standardize Cantonese romanization, those learning the language may feel frustrated that most native Cantonese speakers, regardless of their level of education, are unfamiliar with any romanization system. Because Cantonese is primarily a spoken language and does not carry its own writing system (written Cantonese, despite having some Chinese characters unique to it, primarily follows modern standard Chinese, which is closely tied to Mandarin), it is not taught in schools. As a result, locals do not learn any of these systems. In contrast with Mandarin-speaking areas of China, Cantonese romanization systems are excluded in the education systems of both Hong Kong and the Guangdong province. In practice, Hong Kong follows a loose, unnamed romanization scheme used by the Government of Hong Kong.
Google Cantonese input uses Yale, Jyutping or Cantonese Pinyin, Yale being the first standard.[76][77]
Comparison
Differences between the three main standards are in bold.
Initials
| Romanization system | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yale | b | p | m | f | d | t | n | l | g | k | ng | h | j | ch | s | gw | kw | y | w | |
| Cantonese Pinyin | b | p | m | f | d | t | n | l | g | k | ng | h | dz | ts | s | gw | kw | j | w | |
| Jyutping | b | p | m | f | d | t | n | l | g | k | ng | h | z | c | s | gw | kw | j | w | |
| IPA | p | pʰ | m | f | t | tʰ | n | l | k | kʰ | ŋ | h | ts | tsʰ | s | kw | kʰw | j | w | |
Finals
| Romanization system | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yale | aa | aai | aau | aam | aan | aang | aap | aat | aak | ai | au | am | an | ang | ap | at | ak | e | ei | eng | ek | i | iu | im | in | ing | ip | it | ik |
| Cantonese Pinyin | aa | aai | aau | aam | aan | aang | aap | aat | aak | ai | au | am | an | ang | ap | at | ak | e | ei | eng | ek | i | iu | im | in | ing | ip | it | ik |
| Jyutping | aa | aai | aau | aam | aan | aang | aap | aat | aak | ai | au | am | an | ang | ap | at | ak | e | ei | eng | ek | i | iu | im | in | ing | ip | it | ik |
| IPA | aː | aːi | aːu | aːm | aːn | aːŋ | aːp | aːt | aːk | ɐi | ɐu | ɐm | ɐn | ɐŋ | ɐp | ɐt | ɐk | ɛː | ei | ɛːŋ | ɛːk | iː | iːu | iːm | iːn | eŋ | iːp | iːt | ek |
| Romanization system | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yale | o | oi | ou | on | ong | ot | ok | u | ui | un | ung | ut | uk | eu | eung | euk | eui | eun | eut | yu | yun | yut | m | ng | |||||
| Cantonese Pinyin | o | oi | ou | on | ong | ot | ok | u | ui | un | ung | ut | uk | oeu | oeng | oek | oey | oen | oet | y | yn | yt | m | ng | |||||
| Jyutping | o | oi | ou | on | ong | ot | ok | u | ui | un | ung | ut | uk | oe | oeng | oek | eoi | eon | eot | yu | yun | yut | m | ng | |||||
| IPA | ɔː | ɔːy | ou | ɔːn | ɔːŋ | ɔːt | ɔːk | uː | uːy | uːn | oŋ | uːt | ok | œː | œːŋ | œːk | ɵy | ɵn | ɵt | yː | yːn | yːt | m̩ | ŋ̩ | |||||
Tones
| Yale | ā,à | á | a | àh | áh | āh | āk | ak | ahk |
| Cantonese Pinyin | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
| Jyutping | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 1 | 3 | 6 |
| IPA | 55, 53 | 35 | 33 | 21, 11 | 24, 13 | 22 | 5 | 3 | 2 |
| Tone Contour[78] | ˥, ˥˧ | ˧˥ | ˧ | ˨˩, ˩ | ˨˦, ˩˧ | ˨ | ˥ | ˧ | ˨ |
Loanwords
Cantonese has some substrate influence from Kra–Dai languages due to the historic proximity of speakers from both linguistic groups.[79]
Life in Hong Kong is characterized by the blending of Asian (mainly south Chinese), British and other Western influences, as well as the status of the city as a major international business centre. Influences from this territory are widespread in foreign cultures. As a result, many loanwords are created and exported to China, Taiwan, and Singapore. Some of the loanwords are even more popular than their Chinese counterparts. At the same time, some new words created are vividly borrowed by other languages as well.
See also
- Cantonese culture
- Cantonese people
- Cantonese slang
- Cantonese grammar
- Cantonese phonology
- Cantonese profanity
- Languages of China
- Yue Chinese
- List of varieties of Chinese
- List of English words of Cantonese origin
- Protection of the Varieties of Chinese
References
Citations
- Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds. (2017). "Cantonese". Glottolog 3.0. Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.
- Cantonese at Ethnologue (23nd ed., 2020)
- Matthews, Stephen; Yip, Virginia (1994). Cantonese: A Comprehensive Grammar. Routledge. p. 5. ISBN 9780203420843. Archived from the original on 2016-05-02. Retrieved 2015-11-09.
- Snow, Donald B. (2004). Cantonese as Written Language: The Growth of a Written Chinese Vernacular. Hong Kong University Press. p. 48. ISBN 9789622097094. Archived from the original on 2016-04-24. Retrieved 2015-11-09.
- Ramsey and Ethnologue, respectively
- "The Hong Kong Observatory is one of the examples of the Hong Kong Government officially adopting the name "廣東話"". Hong Kong Observatory – Audio Web Page. Archived from the original on 23 January 2018. Retrieved 29 January 2018.
- Cantonese program at Chinese University of Hong Kong, designating standard Cantonese as 廣東話 (PDF), Yale-China Chinese Language Centre, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, retrieved 29 January 2018
- "Basic Law, Chapter I : General Principles". Basiclaw.gov.hk. Archived from the original on 29 January 2018. Retrieved 29 January 2018.
- Yue-Hashimoto (1972), p. 4.
- Coblin (2000), pp. 549–550.
- Ramsey (1987), pp. 3–15.
- 中国广播电视播音员主持人职业道德准则 [Code of Professional Ethics of Radio and Television Hosts of China] (in Chinese). State Administration of Radio, Film, and Television (SARFT). 2005-02-07. Archived from the original on 2011-07-18. Retrieved 2010-07-26.
- "Chinese Language Programes". South China University of Technology. Archived from the original on 2016-02-29.
- "Chinese Language non-degree program". South China Normal University. Archived from the original on 2016-03-04.
- Zhang & Yang (2004), p. 154.
- Wong, Edward (2010-07-26). "Move to Limit Cantonese on Chinese TV Is Assailed". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 2018-09-24. Retrieved 2018-09-24.
- West (2010), pp. 289–90
- Kết quả toàn bộ Tổng điều tra Dân số và Nhà ở Việt Nam năm 2009–Phần I: Biểu Tổng hợp [Results of the 2009 Vietnam Population and Housing Census – Part I: Summary Table] (in Vietnamese), General Statistics Office of Vietnam, p. 134/882, archived from the original on 14 November 2012, retrieved 13 December 2012
- Khanh (1993), p. 31
- Sin, Ka Lin (2009). 《马来西亚的三个汉语方言》中之 吉隆坡广东话阅谭 [A review on Kuala Lumpur’s Cantonese in part of "The Three Chinese Dialects in Malaysia"] (PDF). New Era College Academic Journal (in Chinese). New Era University College. 6: 83–131. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2013-05-11. Retrieved 29 January 2018.
- Sim, Tze Wei (2012). "Why are the Native Languages of the Chinese Malaysians in Decline". Journal of Taiwanese Vernacular. 4 (1): 75.
- "Malaysian Cantonese". 2014-05-27. Archived from the original on 2014-05-27. Retrieved 2019-08-01.
- Sim, Tze Wei (2012). "Why are the Native Languages of the Chinese Malaysians in Decline". Journal of Taiwanese Vernacular. 4 (1): 74.
- Wee Kek Koon (2018-11-01). "Why Cantonese spoken in Malaysia sounds different to Hong Kong Cantonese, and no it's not 'wrong'". South China Morning Post. Archived from the original on 2018-11-15. Retrieved 2018-11-15.
- Lee, Edmond Eu Fah, "Profile of the Singapore Chinese dialect groups" (PDF), Statistics Singapore Newsletter, archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-02-05
- "Use of dialects interfere with learning of Mandarin & English". Channelnewsasia.com. 2009-03-06. Archived from the original on 2009-03-07. Retrieved 2012-01-20.CS1 maint: BOT: original-url status unknown (link)
- "Speak Mandarin Campaign". Singapore Promote Mandarin Council. Archived from the original on 2012-04-07. Retrieved 2010-10-07.
- Chua, Beng Huat (2003). Life is Not Complete Without Shopping: Consumption Culture in Singapore. Singapore University Press. pp. 89–90.
- "Cambodia – The Chinese". Countrystudies.us. Archived from the original on 2011-06-29. Retrieved 2016-04-22.
- Chan, Sambath (2005). The Chinese Minority in Cambodia: Identity Construction and Contestation (PDF) (Master's thesis). Concordia University. p. 34. Archived (PDF) from the original on 11 October 2017. Retrieved 29 January 2018.
- Luangthongkum, Theraphan (2007). "The Position of Non-Thai Languages in Thailand". In Guan, Lee Hock; Suryadinata, Leo Suryadinata (eds.). Language, Nation and Development in Southeast Asia. ISEAS Publishing. p. 191. ISBN 9789812304827 – via Google Books.
- Knodel, John; Ofstedal, Mary Beth; Hermalin, Albert I (2002). "2 The Demographic, Socioeconomic, and Cultural Context of the Four Study Countries". The Well-Being of the Elderly in Asia: A Four-Country Comparative Study. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Press. pp. 38–39. hdl:2027/mdp.39015060636282. ISBN 0-472-11280-5.
- Tong, Chee Kiong; Chan, Kwok B., eds. (2001). Alternate Identities: The Chinese of Contemporary Thailand. Brill. pp. 21–25.
- Lewis 2005, p. 391.
- Bryson, Bill. Made in America.
- Lai, H. Mark (2004). Becoming Chinese American: A History of Communities and Institutions. AltaMira Press. ISBN 978-0-7591-0458-7. need page number(s)
- "Mandarin Use Up in Chinese American Communities". Associated Press. December 29, 2003. Archived from the original on 16 March 2018. Retrieved 29 January 2018 – via HSK Tests Online.
- "As Mandarin language becomes standard, Chinatown explores new identity". News.medill.northwestern.edu. Archived from the original on 2012-01-20. Retrieved 2012-01-20.
- Tan, Chee-Beng, ed. (2007). Chinese Transnational Networks. Taylor & Francis. p. 115.
- Semple, Kirk (October 21, 2009). "In Chinatown, Sound of the Future Is Mandarin". The New York Times. p. 2. Archived from the original on 2017-10-19. Retrieved March 22, 2014.
- "Asian boom in Brooklyn".
- Wu, Elizabeth (2014-06-30). "Bensonhurst becomes Brooklyn's second Chinatown". China Daily USA.
- Robbins, Liz (April 15, 2015). "With an Influx of Newcomers, Little Chinatowns Dot a Changing Brooklyn". The New York Times.
- Chinese Population by Census Tract – New York City, 2010 (PDF), New York City Department of City Planning
- "Mapping America: Every City, Every Block". The New York Times. 2010-12-13. Retrieved 2020-05-14.
- https://www1.nyc.gov/assets/planning/download/pdf/data-maps/nyc-population/nny2013/chapter3.pdf
- Beekman, Daniel (August 5, 2011). "The changing Chinatowns: Move over Manhattan, Sunset Park now home to most Chinese in NYC". New York Daily News.
- Pierson, David (2006-03-31). "Dragon Roars in San Gabriel". Los Angeles Times. Archived from the original on 2012-05-03. Retrieved 2014-11-21.
- Him Mark Lai; Hsu, Madeline Y. (2010). Chinese American Transnational Politics. University of Illinois Press. pp. 49–51.
- Berton, Pierre (1989). The Last Spike. Penguin. pp. 249–250. ISBN 0-14-011763-6.
- Post, National (2012-03-03). "Why is Canada keeping out China's rich?". Canada.com. Archived from the original on 2014-04-11. Retrieved 2012-05-02.
- "Cantonese speakers in the UK". Ethnologue.com. Archived from the original on 2012-01-19. Retrieved 2012-01-20.
- Laurent, Annabelle (28 June 2010). ""Chinois de France" ne veut rien dire" ["Chinese from France" means nothing]. Slate.fr (in French). Archived from the original on 15 February 2018. Retrieved 29 January 2018.
- de Oliveira, Catarina Reis (July 2003), "Immigrant's Entrepreneurial Opportunities: The Case of the Chinese in Portugal" (PDF), FEEM Working Papers (75), doi:10.2139/ssrn.464682, SSRN 464682
- Li (2006), p. 126.
- Yue-Hashimoto (1972), pp. 5–6.
- Ramsey (1987), p. 99.
- Yue-Hashimoto (1972), p. 5.
- Yue-Hashimoto (1972), p. 70.
- "Cantonese almost became the official language". South China Morning Post. October 6, 2009. Archived from the original on June 17, 2016. Retrieved April 30, 2016.
- Zhang & YangDang (2004), p. 154.
- Minglang Zhou, Hongkai Sun (2004). Language Policy in the People's Republic of China: Theory and Practice Since 1949. Springer. ISBN 978-1402080388. Archived from the original on 2016-05-18. Retrieved 2015-11-09.
- Yingjin Zhang, ed. (1999). Cinema and Urban Culture in Shanghai, 1922–1943. Stanford University Press. p. 184. ISBN 978-0804735728. Archived from the original on 2016-05-10. Retrieved 2015-11-09.
- Chu, Yiu-Wai (2013). Lost in Transition: Hong Kong Culture in the Age of China. State University of New York Press. pp. 147–148. ISBN 978-1438446455.
- 学校要求学生讲普通话 祖孙俩竟变"鸡同鸭讲" [Grandma and granddaughter can't communicate each other due to school rules] (in Chinese). Yangcheng Evening News. 2010-07-09. Archived from the original on 2010-07-12. Retrieved 2010-07-27.
- "Archived copy" 粵語播音須報准 民轟「弱智」. Apple Daily. 2011-12-19. Archived from the original on 2012-01-11. Retrieved 2012-01-06 – via Tw.nextmedia.com.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- McLean-Dreyfus, Marie-Alice (2014-11-06). "Say It Loud: Language and Identity in Taiwan and Hong Kong". Thinking Taiwan. Archived from the original on 2018-09-24. Retrieved 2018-09-24.
- Donald, Stephanie; Keane, Michael; Hong, Yin (2002). Media in China: Consumption, Content and Crisis. RoutledgeCurzon. p. 113. ISBN 978-0-7007-1614-2.
- Meaghan Morris, Siu Leung Li, Stephen Ching-kiu Chan (2006). Hong Kong Connections: Transnational Imagination in Action Cinema. Duke University Press Books. p. 193. ISBN 978-1932643015.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
- Lisa Odham Stokes (2007). Historical Dictionary of Hong Kong Cinema. Scarecrow Press. p. 427. ISBN 978-0810855205.
- Matthews, Steven; Yip, Virginia (2011). Cantonese: A Comprehensive Grammar (2nd ed.). p. 4.
- Matthews, Steven; Yip, Virginia (2011). Cantonese: A Comprehensive Grammar (2nd ed.). p. 37.
- Bauer, Robert S.; Cheung, Kwan-hin; Cheung, Pak-man (2003). "Variation and merger of the rising tones in Hong Kong Cantonese" (PDF). Language Variation and Change. 15 (2): 211–225. doi:10.1017/S0954394503152039. hdl:10397/7632.
- Bauer & Benedict (1997:119–120)
- Kataoka, Shin; Lee, Cream (2008). "A System without a System: Cantonese Romanization Used in Hong Kong Place and Personal Names". Hong Kong Journal of Applied Linguistics. 11: 83–84.
- LLC, Google (28 August 2017). "Google Cantonese Input". Play.google.com. Archived from the original on 16 March 2018. Retrieved 29 January 2018 – via Google Play.
- 廣東話拼音 – Google 搜尋建議. Google Hong Kong. Archived from the original on 18 January 2018. Retrieved 29 January 2018.
- Matthews, S.; Yip, V. (1994). Cantonese: A Comprehensive Grammar. London: Routledge.
- Bauer (1996), pp. 1835–1836.
Works cited
- Bauer, Robert S.; Benedict, Paul K. (1997), Modern Cantonese Phonology, Walter de Gruyter, ISBN 978-3-11-014893-0.
- Bauer, Robert S. (1996), "Identifying the Tai substratum in Cantonese" (PDF), Proceedings of the Fourth International Symposium on Languages and Linguistics, Pan-Asiatic Linguistics V: 1 806- 1 844, Bangkok: Institute of Language and Culture for Rural Development, Mahidol University at Salaya.
- Coblin, W. South (2000), "A brief history of Mandarin", Journal of the American Oriental Society, 120 (4): 537–552, doi:10.2307/606615, JSTOR 606615.
- Li, Qingxin (2006), Maritime Silk Road, trans. William W. Wang, China Intercontinental Press, ISBN 978-7-5085-0932-7.
- Ramsey, S. Robert (1987), The Languages of China, Princeton, New Jersey: Princeton University Press, ISBN 978-0-691-01468-5.
- Yue-Hashimoto, Anne Oi-Kan (1972), Studies in Yue Dialects 1: Phonology of Cantonese, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-08442-0.
- Zhang, Bennan; Yang, Robin R. (2004), "Putonghua education and language policy in postcolonial Hong Kong", in Zhou, Minglang (ed.), Language policy in the People's Republic of China: theory and practice since 1949, Kluwer Academic Publishers, pp. 143–161, ISBN 978-1-4020-8038-8.
Further reading
- Benoni, Lanctot (1867). Chinese and English phrase book : with the Chinese pronunciation indicated in English. San Francisco: A. Roman & Company. OCLC 41220764. OL 13999723M.
- Bridgman, Elijah Coleman (1841). A Chinese Chrestomathy in the Canton Dialect. Macao: S. Wells Williams. OCLC 4614795. OL 6542029M.
- Matthew, W. (1880). The book of a thousand words: translated, annotated and arranged so as to indicate the radical number and pronunciation (in Mandarin and Cantonese) of each character in the text. Stawell: Thomas Stubbs. OL 13996959M.
- Morrison, Robert (1828). Vocabulary of the Canton Dialect: Chinese words and phrases. Macao: Steyn. hdl:2027/uc1.b4496041. OCLC 17203540.
- Williams, Samuel Wells (1856). Tonic dictionary of the Chinese language in the Canton dialect. Canton: Chinese Repository. OCLC 6512080. OL 14002589M.
External links
| Cantonese edition of Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia |
- 粵語審音配詞字庫. The Chinese University of Hong Kong.
- Hong Kong Government site on the HK Supplementary Character Set (HKSCS)
- Online Cantonese Editor
- Cantonese Tools
- 粵語/廣東話參考資料 Yue References by wordshk – GitHub Pages. Github.