Old Xiang
Old Xiang, also known as Lou-Shao (娄邵片 / 婁邵片), is a conservative Xiang Chinese language. It is spoken in the central areas of Hunan where it has been to some extent isolated from the neighboring Chinese languages, Southwestern Mandarin and Gan languages, and it retains the voiced plosives of Middle Chinese, which are otherwise only preserved in Wu languages like Shanghainese. See Shuangfeng dialect for details.
| Old Xiang | |
|---|---|
| Lou-Shao | |
| Native to | People's Republic of China |
| Region | Hunan |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | None (mis) |
| ISO 639-6 | louo |
| Glottolog | luos1238[1] |
| Linguasphere | 79-AAA-eab |
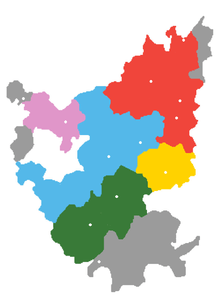 Old Xiang is in blue. It is in contact with New Xiang (red), Ji-Xu Xiang (pink), Southwestern Mandarin, Gan, and Yong-Quan Xiang (dark green, south). | |
Dialects and regions
The Shuangfeng dialect is representative.
| Subdialect | Main Counties | |
|---|---|---|
| Xiang-Shuang | Xiangtan, Shuangfeng, Shaoshan, Urban Loudi, Anhua*, Hengshan* | |
| Lian-Mei | Lianyuan, Lengshuijiang*, Anhua, Ningxiang* | |
| Xinhua | Xinhua, Lengshuijiang | |
| Shao-Wu | Urban Shaoyang, Wugang, Shaodong, Shaoyang County, Xinshao, Longhui, Xinning, Chengbu, Dongkou* | |
| Sui-Hui | Suining, Huitong | |
| *Small part of this territory is Hunanese-speaking. | ||
gollark: Sure.
gollark: https://discord.com/channels/198130613759246337/530071845181849630/968620277045010483
gollark: The anomalous bracket thing is due to quirks of `lua.lua`.
gollark: It's just lacking all else.
gollark: It has multiterminal support.
References
- Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds. (2017). "Luoshao". Glottolog 3.0. Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.