Uzbek language
Uzbek is a Turkic language that is the first official and only declared national language of Uzbekistan. The language of Uzbeks, it is spoken by some 27 million native speakers in Uzbekistan and elsewhere in Central Asia (2015), making it the second-most widely spoken Turkic language after Turkish.
| Uzbek | |
|---|---|
| O‘zbekcha, o‘zbek tili, Ўзбекча, ўзбек тили, اۉزبېکچه, اۉزبېک تیلی | |
| Native to | Uzbekistan, Afghanistan, Tajikistan, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Turkmenistan, Russia, China |
| Ethnicity | Uzbeks |
Native speakers | 27 million (2015)[1] |
Early form | |
| Official status | |
Official language in | |
Recognised minority language in | |
| Regulated by | Tashkent State University of Uzbek language and literature |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | uz |
| ISO 639-2 | uzb |
| ISO 639-3 | uzb – inclusive codeIndividual codes: uzn – Northernuzs – Southern |
| Glottolog | uzbe1247[4] |
| Linguasphere | 44-AAB-da, db |
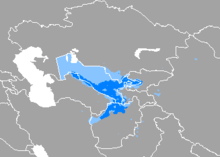 Dark blue = majority; light blue = minority | |
Uzbek belongs to the Eastern Turkic or Karluk branch of the Turkic language family. External influences include Arabic, Persian and Russian. One of the most noticeable distinctions of Uzbek from other Turkic languages is the rounding of the vowel /ɑ/ to /ɒ/, a feature that was influenced by Persian. As with its sister Karluk language Uyghur, vowel harmony is somewhat less strictly observed compared to other Turkic languages.
Name
In the language itself, Uzbek is oʻzbek tili or oʻzbekcha. In Cyrillic, it is ўзбек тили or ўзбекча. In Arabic script, اۉزبېک تیلی and اۉزبېکچه.
History
Turkic speakers probably settled the Amu Darya, Syr Darya and Zarafshan river basins from at least 600–700 CE, gradually ousting or assimilating the speakers of Eastern Iranian languages who previously inhabited Sogdia, Bactria and Khwarezm. The first Turkic dynasty in the region was that of the Kara-Khanid Khanate in the 9th–12th centuries,[5] who were a confederation of Karluks, Chigils, Yaghma and other tribes.[6]
Uzbek can be considered the direct descendant or a later form of Chagatai, the language of great Turkic Central Asian literary development in the realm of Chagatai Khan, Timur (Tamerlane), and the Timurid dynasty[7] (including the early Mughal rulers of India). The language was championed by Ali-Shir Nava'i in the 15th and 16th centuries. Nava'i was the greatest representative of Chagatai language literature.[8][9] He significantly contributed to the development of the Chagatai language and its direct descendant Uzbek and is widely considered to be the founder of Uzbek literature.[10][11][12][13][14][15][16] Ultimately based on the Karluk variant of the Turkic languages, Chagatai contained large numbers of Persian and Arabic loanwords. By the 19th century it was rarely used for literary composition, but disappeared only in the early 20th century.
The term Uzbek as applied to language has meant different things at different times. Prior to 1921 "Uzbek" and "Sart" were considered to be different dialects:
- "Uzbek" was a vowel-harmonised Kipchak variety spoken by descendants of those who arrived in Transoxiana with Muhammad Shaybani in the 16th century, who lived mainly around Bukhara and Samarkand, although the Turkic spoken in Tashkent was also vowel-harmonised. It can be called old Uzbek and it's considered to be related to that specific group of people.
- "Sart" was a Karluk dialect spoken by the older settled Turkic populations of the region in the Fergana Valley and the Qashqadaryo Region, and in some parts of what is now the Samarqand Region; it contained a heavier admixture of Persian and Arabic, and did not have vowel harmony. It became the standard Uzbek language and the official dialect of Uzbekistan.
In Khanate of Khiva, Sarts spoke a highly Oghuz Turkified form of Karluk Turkic. After 1921 the Soviet regime abolished the term Sart as derogatory, and decreed that henceforth the entire settled Turkic population of Turkestan would be known as Uzbeks, even though many had no Uzbek tribal heritage.
However, the standard written language that was chosen for the new republic in 1924, despite the protests of Uzbek Bolsheviks such as Fayzulla Khodzhayev, was not pre-revolutionary "Uzbek" but the "Sart" language of the Samarkand region. Edward A. Allworth argued that this "badly distorted the literary history of the region" and was used to give authors such as the 15th-century author Ali-Shir Nava'i an Uzbek identity.[17] All three dialects continue to exist within modern spoken Uzbek.
Writing systems

Uzbek has been written in a variety of scripts throughout history:
- Pre-1928: the Arabic-based Yaña imlâ alphabet by literates, approximately 3.7% of Uzbeks at the time.[18]
- 1880s: Russian missionaries attempted to use Cyrillic for Uzbek.[18]
- 1928–1940: the Latin-based Yañalif used officially.
- 1940–1992: the Cyrillic script used officially.
- Since 1992: a Yañalif-based Latin script is official in Uzbekistan.
Despite the official status of the Latin script in Uzbekistan, the use of Cyrillic is still widespread, especially in advertisements and signs. In newspapers, scripts may be mixed, with headlines in Latin and articles in Cyrillic.[19] The Arabic script is no longer used in Uzbekistan except symbolically in limited texts[19] or for the academic studies of Chagatai (Old Uzbek).[18]
In the western Chinese region of Xinjiang, where there is an Uzbek minority, Arabic is still used.
In Afghanistan, the traditional Arabic orthography is still used.
Grammar
Phonology
Vowels
Standard Uzbek has six vowel phonemes:[20]
| Front | Central | Back | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Close | i | u | |
| Mid | e | o | |
| Open | æ ~ ɑ | ɒ | |
- /i/ and /u/ can have short allophones of [ɪ] and [ʊ], and central allophones [ɨ̞] and [ʉ]. /ɒ/ can have an mid open back allophone [ɔ].
Consonants
| Labial | Dental | Alveolar | Palatal | Velar | Uvular | Glottal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m | n | ŋ | |||||
| Plosive/ Affricate |
voiceless | p | t̪ | (t͡s) | t͡ʃ | k | q | (ʔ) |
| voiced | b | d̪ | d͡ʒ | ɡ | ||||
| Fricative | voiceless | ɸ | s | ʃ | χ | h | ||
| voiced | w~v | z | (ʒ) | ʁ | ||||
| Approximant | l | j | ||||||
| Rhotic | ɾ | |||||||
Morphology and syntax
As a Turkic language, Uzbek is null subject, agglutinative and has no articles and no noun classes (gender or otherwise). The word order is subject–object–verb (SOV). Words are usually oxytones (i.e. the last syllable is stressed), but certain endings and suffixal particles are not stressed.
In Uzbek, there are two main categories of words:
- nominals (equivalent to nouns, pronouns, adjectives and some adverbs)
- verbals (equivalent to verbs and some adverbs)
- Verbs
Uzbek uses the following verbal suffixes:
| Suffix | Function | Example | Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| -moq | infinitive | kelmoq | to come |
| -di | past tense | keldi | came |
| -ing | imperative | keling! | come! |
| -sa | conditional | kelsa | would come |
The present and future tenses are both expressed with the -a and -y suffixes.
- Articles
Nouns take the -ni suffix as an indefinite article. Unsuffixed nouns are understood as definite.
- Pronouns
| Pronoun | Translation |
|---|---|
| men | I |
| biz | we |
| sen | you (informal singular) |
| siz | you (formal singular and plural) |
| u | he/she/it |
| ular | they |
Word order
The word order in the Uzbek language is subject–object–verb (SOV), like all other Turkic languages. Unlike in English, the object comes before the verb and the verb is the last element of the sentence.
| I see the book | ||
|---|---|---|
| Men | kitobni | ko’rdim |
| subject | direct object | transitive verb |
| 1.SG. | book | see-PRES.IND. |
Number of speakers
Estimates of the number of speakers of Uzbek vary widely, from 25 up to 30 million. Ethnologue estimates put the number of native speakers at 27 million across all the recognized dialects. The Swedish national encyclopedia, Nationalencyklopedin, estimates the number of native speakers to be 30 million,[21] and the CIA World Factbook estimates 25 million. Other sources estimate the number of speakers of Uzbek to be 21 million in Uzbekistan,[22] 3.4 million in Afghanistan,[23] 900,000 in Tajikistan,[24] 800,000 in Kyrgyzstan,[25] 500,000 in Kazakhstan,[26] 300,000 in Turkmenistan,[27] and 300,000 in Russia.[28]
Influences
The influence of Islam, and by extension, Arabic, is evident in Uzbek loanwords. There is also a residual influence of Russian, from the time when Uzbeks were under the rule of the Russian Empire and the Soviet Union. Most importantly, Uzbek vocabulary, phraseology and pronunciation has been heavily influenced by Persian through its historic roots. Uzbek has been significantly influenced by Persian and it also influenced Tajik (a variety of Persian).[29][30] Of the Turkic languages, Uzbek is perhaps the one most strongly influenced by Persian.[31]
Dialects
Uzbek can be roughly divided into three dialect groups. The Karluk dialects, centered on Tashkent, Samarkand, Bukhara, and the Ferghana Valley, are the basis for the standard Uzbek language. This dialect group shows the most influence of Persian vocabulary, particularly in the historically Persian cities of Bukhara and Samarkand. The Kipchak dialect, spoken from the Surxondaryo region through north-central Uzbekistan into Karakalpakstan, show significant influence from the Kipchak Turkic languages, particularly in the mutation of [j] to [ʑ] as in Kazakh and Kyrgyz. The Oghuz dialect, spoken mainly in Khorezm along the Turkmenistan border, is notable for the mutation of word-initial [k] to [g].
By country
Turkmenistan
In Turkmenistan since the 2000s the government conducted a forced "Turkmenization" of ethnic Uzbeks living in the country.[32][33][34] In the Soviet years and in the 1990s, the Uzbek language was used freely in Turkmenistan. There were several hundred schools in the Uzbek language, many newspapers were published in this language. Now there are only a few Uzbek schools in the country, as well as a few newspapers in Uzbek. Despite this, the Uzbek language is still considered to be one of the recognized languages of national minorities in this country. From 300 to 600 thousand Uzbeks live in Turkmenistan. Most of the Uzbek speakers live in Dashoghuz Velayat, as well as in Lebap Velayat and partly in Ashghabad.[35]
Russia
Uzbek is one of the many recognized languages of national minorities in Russia. More than 400 thousand Uzbeks are citizens of the Russian Federation and live in this country. Also in Russia there are 2 to 6 million Uzbeks from the Central Asian republics (mainly Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan) who are immigrants and migrants. Large diasporas of Uzbeks live in such large cities of Russia as Moscow, Saint Petersburg, Yekaterinburg, Novosibirsk, Kazan, Volgograd, Samara, Rostov-on-Don, Perm, Nizhny Novgorod, Chelyabinsk, Vladivostok, Ufa, Krasnoyarsk, Omsk, Krasnodar, Voronezh, Saratov and Tyumen. Signs in Uzbek are often found in these cities. Signs refer mainly to various restaurants and eateries, barbershops, shops selling fruits, vegetables and textile products. There is a small clinic, where signs and labels in the Uzbek language. There are also illegal signs in Uzbek on the streets of these cities with underground sex services ("Call girls"). Uzbeks in Russia prefer to use the Cyrillic Uzbek alphabet, but in recent years Uzbek youth in Russia are also actively using the Latin Uzbek alphabet. Small newspapers in Uzbek are published in large cities of Russia.[36][37][38] Some instructions for immigrants and migrants are duplicated, including in Uzbek. Uzbek language is studied by Russian students in the faculties of Turkology throughout Russia.[39] The largest Uzbek language learning centers in Russia are located in the universities of Moscow and Saint Petersburg. There are also many Russians who are interested in and love the Uzbek language and culture and who study this language for themselves. Uzbek is one of the most studied languages among the many languages of the former USSR in Russia. Native speakers of Uzbek in Russia usually use in their vocabulary a lot of words from Russian.[40]
Notes
- Used in Afghanistan and China
- Third official language in areas where Uzbeks are majority[3]
References
- Uzbek at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015)
Northern at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015)
Southern at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) - Scott Newton (20 November 2014). Law and the Making of the Soviet World: The Red Demiurge. Routledge. pp. 232–. ISBN 978-1-317-92978-9.
- From amongst Pashto, Dari, Uzbeki, Turkmani, Baluchi, Pachaie, Nuristani, Pamiri and other current languages in the country, Pashto and Dari shall be the official languages of the state. In areas where the majority of the people speak in any one of Uzbeki, Turkmani, Pachaie, Nuristani, Baluchi or Pamiri languages, any of the aforementioned language, in addition to Pashto and Dari, shall be the third official language, the usage of which shall be regulated by law.
- Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds. (2017). "Uzbek". Glottolog 3.0. Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.
- "The Origins of the Uzbek Language" (in Russian). Archived from the original on 2 September 2013. Retrieved 5 January 2013.
- Golden, Peter. B. (1990), "Chapter 13 – The Karakhanids and Early Islam", in Sinor, Denis (ed.), The Cambridge History of Early Inner Asia, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0-521-24304-1
- Allworth, Edward (1994). Central Asia: 130 Years of Russian Dominance, a Historical Overview. Duke University Press. p. 72. ISBN 0-8223-1521-1.
- Robert McHenry, ed. (1993). "Navā'ī, (Mir) 'Alī Shīr". Encyclopædia Britannica. 8 (15th ed.). Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. p. 563.
- Subtelny, M. E. (1993). "Mīr 'Alī Shīr Nawā'ī". In C. E. Bosworth; E. Van Donzel; W. P. Heinrichs; Ch. Pellat (eds.). Encyclopaedia of Islam. VII. Leiden—New York: Brill Publishers. pp. 90–93.
- Valitova, A. A. (1974). "Alisher Navoi". In A. M. Prokhorov (ed.). Great Soviet Encyclopedia (in Russian). 17 (3rd ed.). Moscow: Soviet Encyclopedia. pp. 194–195.
- A. M. Prokhorov, ed. (1997). "Navoi, Nizamiddin Mir Alisher". Great Encyclopedic Dictionary (in Russian) (2nd ed.). Saint Petersburg: Great Russian Encyclopedia. p. 777.
- "Alisher Navoi". Writers History. Archived from the original on 16 October 2013. Retrieved 26 January 2012.
- Maxim Isaev (7 July 2009). "Uzbekistan – The monuments of classical writers of oriental literature are removed in Samarqand". Ferghana News. Archived from the original on 11 September 2011. Retrieved 26 January 2012.
- Kamola Akilova. "Alisher Navoi and his epoch in the context of Uzbekistan art culture development [sic]". San'at Magazine. Retrieved 28 January 2012.
- "Uzbek Culture". UzHotels. Archived from the original on 9 May 2012. Retrieved 27 January 2012.
- "Alisher Navoi – The Crown of Literature". Kitob.uz Children's Digital Library (in Uzbek). Retrieved 8 February 2012.
- Allworth, Edward A. (1990). The Modern Uzbeks: From the Fourteenth Century to the Present: A Cultural History. Hoover Institution Press. pp. 229–230. ISBN 978-0-8179-8732-9.
- Batalden, Stephen K. (1997). The Newly Independent States of Eurasia: Handbook of Former Soviet Republics. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 194. ISBN 978-0-89774-940-4.
- European Society for Central Asian Studies. International Conference (2005). Central Asia on Display. LIT Verlag Münster. p. 221. ISBN 978-3-8258-8309-6.
- Sjoberg, Andrée F. (1963). Uzbek Structural Grammar. Uralic and Altaic Series. 18. Bloomington: Indiana University. pp. 16–18.
- "Världens 100 största språk 2007" ("The World's 100 Largest Languages in 2007"), Nationalencyklopedin
- "Uzbekistan". CIA. Retrieved 7 December 2012.
- "Languages of Afghanistan". Ethnologue. Retrieved 7 December 2012.
- "Languages of Tajikistan". Ethnologue. Retrieved 7 December 2012.
- "Ethnic Makeup of the Population" (PDF). National Statistics Committee of the Kyrgyz Republic (in Russian). Retrieved 7 December 2012.
- "National Census 2009" (PDF). Statistics Agency of Kazakhstan (in Russian). Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 December 2010. Retrieved 7 December 2010.
- "Languages of Turkmenistan". Ethnologue. Retrieved 7 December 2012.
- "National Census 2010". Federal State Statistics Service (in Russian). Retrieved 7 December 2012.
- Ido, Shinji (21 March 2014). "Bukharan Tajik" (PDF). Journal of the International Phonetic Association. 44 (1): 87–102. doi:10.1017/S002510031300011X.
- Hickey, Raymond 2010. The Handbook of Language Contact. Malden, MA: Wiley- Blackwel page 655
- "AZERBAIJAN ix. Iranian Elements in Azeri Turki – Encyclopaedia Iranica". www.iranicaonline.org.
- memohrc.org — "Туркменизация" руководящих кадров в Дашогузе
- iamik.ru — Туркменизация узбеков
- vb.kg — В Туркмении завершается принудительная туркменизация
- 365info.kz — Туркменские узбеки тихо ликуют и следят за Мирзиёевым
- fergananews.com — В Москве начинает выходить газета на узбекском языке
- vesti.kg — В Москве начинает выходить газета на узбекском языке
- caravan.kz — В Москве начинает выходить газета на узбекском языке
- uz.sputniknews.ru — На языке Навои: кто и зачем учит узбекский в России
- the-village.ru — Москвичи, изучающие узбекский, таджикский и молдавский языки
- [ ]
Sources
- Mamatov, Jahangir; Kadirova, Karamat (2008). Comprehensive Uzbek-English Dictionary. Hyattsville, Maryland: Dunwoody Press. ISBN 978-1-931546-83-6. OCLC 300453555.
- Csató, Éva Ágnes; Johanson, Lars (1936). The Turkic Languages. London: Routledge. ISBN 0-415-41261-7. OCLC 40980286.
- Bregel, Yu (1978). "The Sarts in The Khanate of Khiva". Journal of Asian History. 12 (2): 120–151. JSTOR 41930294.
- Bodrogligeti, András J. E. (2002). Modern Literary Uzbek: A Manual for Intensive Elementary, Intermediate, and Advanced Courses. München: Lincom Europa. ISBN 3-89586-695-4. OCLC 51061526.
- Fierman, William (1991). Language Planning and National Development: The Uzbek Experience. Berlin: Mouton de Gruyter. ISBN 3-11-085338-8. OCLC 815507595.
- Ismatullaev, Khaĭrulla (1995). Modern literary Uzbek I. Bloomington, Indiana: Indiana University, Research Institute for Inner Asian Studies. ISBN 0-933070-36-5. OCLC 34576336.
- Karl, A. Krippes (1996). Uzbek-English Dictionary (Rev ed.). Kensington: Dunwoody Press. ISBN 1-881265-45-5. OCLC 35822650.
- Sjoberg, Andrée Frances (1997). Uzbek Structural Grammar. Richmond: Curzon Press. ISBN 0-7007-0818-9. OCLC 468438031.
- Waterson, Natalie (1980). Uzbek-English Dictionary. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-713597-8. OCLC 5100980.
- Republic of Uzbekistan, Ministry of Higher and Middle Eductation. Lotin yozuviga asoslangan oʻzbek alifbosi va imlosi (Latin writing based Uzbek alphabet and orthography), Tashkent Finance Institute: Tashkent, 2004.
- A. Shermatov. "A New Stage in the Development of Uzbek Dialectology" in Essays on Uzbek History, Culture and Language. Ed. Bakhtiyar A. Nazarov & Denis Sinor. Bloomington, Indiana, 1993, pp. 101–9.
External links
| Uzbek edition of Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia |
| Wikibooks has more on the topic of: Uzbek language |
| Wikivoyage has a phrasebook for Uzbek. |
- Converters
- Uzbek Cyrillic–Latin converter
- Uzbek Cyrillic-Latin text and website converter
- Uzbek Latin-Cyrillic text and website converter
- Dictionaries
- Dictionary of the Uzbek Language Volume I (А—Р) (Tashkent, 1981)
- Dictionary of the Uzbek Language, Volume II (С—Ҳ) (Tashkent, 1981)
- English-Uzbek and Uzbek-English online dictionary
- English-Uzbek and Uzbek-English online dictionary
- Russian-Uzbek and Uzbek-Russian online dictionary
- Uzbek<>Turkish dictionary (Pamukkale University)
- Ole Olufsen: "A Vocabulary of the Dialect of Bokhara" (København 1905)
- Grammar and orthography
- Introduction to the Uzbek Language, Mark Dickens
- Principal Orthographic Rules For The Uzbek Language, translation of Uzbekistan Cabinet of Minister's Resolution No. 339, of August 24, 1995
- Uzbek alphabet, Omniglot
- Learning/teaching materials
- Ona tili uz, a website about Uzbek
- Uzbek language materials, Uz-Translations