Tausug language
Tausug (Tausug: Bahasa Sūg, Malay: Bahasa Suluk) is an Austronesian language spoken in the province of Sulu in the Philippines, and in the eastern area of the state of Sabah, Malaysia by the Tausug people.
| Tausug | |
|---|---|
| Bahasa Sūg بَهَسَ سُوگ | |
| Native to | Philippines, Malaysia |
| Region | — Spoken throughout the Sulu Archipelago and eastern Sabah — Also spoken in Zamboanga City |
| Ethnicity | Tausug |
Native speakers | 1.1 million (2000)[1] |
Austronesian
| |
| Latin (Malay alphabet) Arabic (Jawi) | |
| Official status | |
Official language in | Regional language in the Philippines |
| Regulated by | Komisyon sa Wikang Filipino |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | tsg |
| Glottolog | taus1251[2] |
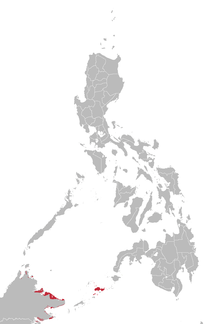 Areas where Tausug is the majority language | |
It is widely spoken in the Sulu Archipelago (Tawi-Tawi), Zamboanga Peninsula (Zamboanga del Norte, Zamboanga Sibugay, Zamboanga del Sur, and Zamboanga City), Southern Palawan and Malaysia (eastern Sabah). Tausug and Chavacano are the only Philippine languages spoken on the island of Borneo.
The Tausug language is very closely related to the Surigaonon language of the provinces Surigao del Norte, Surigao del Sur and Agusan del Sur, and to the Butuanon language of Agusan del Norte.
Etymology
The name of the language in Tausug is bahasa Sūg ("language of Sulu"). Tausug (Tausug: tau Sūg, "people of Sulu") is derived from two words: tau ("person") and sūg ("current"), presumably referring to their economic livelihood that depends on the strong currents of the Sulu Sea, where they used to trans-navigate as fishermen, pearl divers and traders.
Even today, the Sulu Sea is still the strategic trade route of the southern Philippines and the nearby ASEAN nations. As early as the 10th century, the trade route between Sulu and China and North Borneo is believed to have been already flourishing. The people in the area were known as the "people of the current", the literal translation of "Tausūg".
Phonology
Vowels
Tausug has three vowel phonemes: /a/, /i/, /u/, with phonemic length (e.g. īpun "shrimp" vs. ipun "tooth"). Stress is not phonemic and usually occurs on the final syllable.[3]
The vowel phonemes have a broad range of allophones:[4]
- /a/: [a,ɐ,ɑ]
- /i/: [i,ɪ]
- /u/: [u,ʊ,ɤ,ʌ,ə]
Consonants
The consonant phonemes are:[5]
| Labial Labiodental |
Alveolar | Palatal | Velar | Glottal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m | n | ŋ | |||
| Plosive Affricate |
voiceless | p | t | k | ʔ | |
| voiced | b | d | d͡ʒ <j> | ɡ | ||
| Fricative | f | s | h | |||
| Approximant | l | j <y> | w | |||
| Trill | r | |||||
Allophones:[4]
- /b/: per default [b], but [β] between vowels
- /g/: per default [ɡ], but [ɣ] between vowels
- /h/: per default [h], but [ɦ] between vowels
- /r/: per default [r], but [ɹ] before /m,n,g,k/
Medial gemination (of all non-glottal consonants) is phonemic.[4]
Grammar
Pronouns
Personal pronouns
Tausug has three pronouns sets:[6]
| nominative | genitive | oblique | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1st person singular | aku | ku | kaku' |
| 1st person dual | kita | ta | katu' |
| 2nd person singular | ikaw, kaw | mu | kaymu |
| 3rd person singular | siya | niya | kaniya |
| 1st person plural inclusive | kitaniyu | taniyu | katu'niyu, katu'natu' |
| 1st person plural exclusive | kami | namu | kamu' |
| 2nd person plural | kamu | niyu | kaniyu |
| 3rd person plural | sila | nila | kanila |
Demonstratives
Case markers
The case markers of Tausug are:[7]
| nominative | genitive | oblique | |
|---|---|---|---|
| common | in | sin | ha |
| proper singular | hi | kay | |
| proper plural | hinda' | kanda' | |
Non-subject undergoers take the oblique marker when definite or a proper noun, but indefinite common nouns take the genitive marker sin.
- Hi Nasul in kimaun ha mampallam. "It was Nasul who ate the mango."
- Nagdakdak sin baju' in manga bujang. "The maidens washed clothes."
Existentials
The positive existential ("there is") is aun, the negative existential ("there is none") is way.[8]
Interrogative words
| English | Tausug |
|---|---|
| Who? | Hisiyu?[9] |
| What? | Unu? |
| Where? | Diin? or Hain? |
| Why? | Mayta'? |
| When? (future) | Ku'nu? |
| When? (past) | Ka'nu? |
| How? (manner) | Biya'diin? |
| How many? | Pila? |
Verbs
Verbs in Tausug are inflected for focus and aspect.[10]
| completed | progressive | contemplative | imperative | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Actor focus | ⟨im⟩ nag- naN- | C⟨im⟩V- nag-CV- naN-CV- | ‹um› mag- maN- | ∅ ∅ paN- |
| Patient focus | ⟨i⟩ | C⟨i⟩V- | -un | -a |
| Locative focus | ⟨i⟩ -an | C⟨i⟩V- -an | -an | -i |
| Instrument focus | ⟨i⟩ | C⟨i⟩V- | hi- | -an |
Affixes expressing ability:
| completed | progressive | contemplative | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Actor focus | naka- | nakaka- | maka- |
| Patient focus | na- | na-CV- | ma- |
| Locative focus | kia- -an | kia-CV- -an | ka- -an |
| Instrument focus | kia- | kia-CV- | hika- |
Writing system
The Tausūg language was previously written with the Arabic alphabet. The script used was inspired by the use of Jawi in writing the Malay language.
An example of the Arabic alphabet in writing the Tausūg language:
- Latin script – Wayruun tuhan malaingkan Allāh, hi Muhammad ing rasūl sin Allāh
- Arabic script – وَيْـرُٷنْ تُـهَـنْ مَـلَـيِـڠْـكَـن هَالله، هِـمُـحَـمَّـدْ ئِـڠ رَسُـولْ سِـڠ الله
- English translation – There is no god but Allah, Muhammad is the Messenger of Allah
The Arabic script used to write the Tausug language differs in some aspects to the script used for the Arabic language and in the Jawi script used for Malay languages. One of the main differences is in the way that word-initial vowels are written.
In Arabic, /in/ is (إن); in Jawi (Malay), it is (ان). In Tausug, it is (ئِن). The Tausug Arabic script utilises the letter yā' with a hamza (ئ) to represent a short vowel. If a kasra (ئِ) is added, it becomes an 'i' sound. If a fatha (ئَ) is added, it becomes an 'a' sound. If a damma (ئُ) is added, it becomes a 'u' sound.
Latin
| Letter | A | B | D | G | H | I | J | K | L | M |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Alip | bā' | dāl | gā' | hā' | ī | jīm | kāp | lām | mīm |
| IPA | /a/ | /b/, /β/ | /d/ | /ɡ/, /ɣ/ | /h/, /ɦ/ | /i/ | /dʒ/ | /k/ | /l/ | /m/ |
| Letter | N | Ng | P | R | S | T | U | W | Y | ' |
| Name | nūn | ngā' | pā' | rā' | sīn | tā' | ū | wāw | yā' | hamja |
| IPA | /n/ | /ŋ/ | /p/ | /r/, /ɹ/ | /s/ | /t/ | /u/ | /w/ | /j/ | /ʔ/ |
Arabic
| Character | Isolated | Initial | Medial | Final | Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ا | ﺍ | ﺎ | alip | ||
| ب | ﺏ | ﺑ | ـﺒ | ـﺐ | bā' |
| ت | ﺕ | ﺗ | ـﺘ | ـﺖ | tā' |
| ج | ﺝ | ﺟ | ـﺠ | ـﺞ | jīm |
| د | د | ـد | dāl | ||
| ر | ﺭ | ـر | rā' | ||
| س | ﺱ | ﺳ | ـﺴ | ـﺲ | sīn |
| غ | ﻍ | ﻏ | ـﻐـ | ـﻎ | gayn |
| ڠ | ڠ | ڠـ | ـڠـ | ـڠ | ngā' |
| ف | ﻑ | ﻓ | ـﻔ | ـﻒ | pā' |
| ک | ک | ﻛ | ـﻜ | ـک | kāp |
| گ | گ | ﮔ | ـﮕـ | ـﮓ | gāp |
| ل | ﻝ | ﻟ | ـﻠ | ـﻞ | lām |
| م | ﻡ | ﻣ | ـﻤ | ـﻢ | mīm |
| ن | ﻥ | ﻧ | ـﻨ | ﻦ | nūn |
| و | ﻭ | ـو | wāw | ||
| ه | ﻩ | ﻫ | ـﻬ | ﻪ | hā' |
| ي | ﻱ | ﻳ | ـﻴـ | ﻲ | yā' |
| ء | ء | ء | hamja | ||
| أ | أ | ـأ | alip with hamja above | ||
| ﺅ | ﺅ | ـﺆ | wāw with hamja above | ||
| ئ | ئ | ئـ | ــئـ | ـئ | yā' with hamja above |
| لا | لا | لا | ــلا | ــلا | lām alip |
Examples
| English | Tausug Latin Script | Tausug Arabic Script |
|---|---|---|
| What is your name? | Unu in ngān mu? | اُنُ ئِـن ڠَـان مُ؟ |
| My name is Muhammad | In ngān ku Muhammad | ئِـن ڠَـان كُ مُـحَـمَّـد |
| How are you? | Maunu-unu nakaw? | مَـؤُنُعاُنُ نَـكَـو؟ |
| I am good | Marayaw da isab | مَـرَيَـو دَ ئِـسَـب |
| Where is Ahmad? | Hawnu hi Ahmad? | هَـونُ هِ أحـمَـد؟ |
| He is in the house | Ha bāy siya | هَ بَـاي سِـيَ |
| Thank you | Magsukul | مَـگـسُـكُـل |
Loanwords
Many Tausug words derive from the Arabic language.
Some examples of Arabic words in Tausug are
| Tausug Word | Meaning (Tausug) | Arabic Word | Pronunciation | Meaning (Arabic) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adab | manners | أدب | adab | manners |
| Ahirat | Hereafter | آخرة | ākhirah | hereafter |
| Ajayb | amazing | عجيب | 'ajīb | amazing |
| Akkal | intelligence | عقل | 'Aql | intellect |
| Alam | universe | عالم | 'ālam | world |
| Allāh | God | الله | Allāh | God |
| Amānat | message | أمانة | amānah | trust |
| Ammal | use | عمل | 'amal | to make |
| Awal | origin | أوّل | awwal | first |
| Awliya | ascetic | أولياء | awliyā' | ascetics |
| Ayat | verse | آية | āyah | verse |
| Ayb | shame | عيب | 'ayb | shame |
| Barawi | Desert robber | بدوي | badawī | bedouin |
| Batāl | unclean | باطل | bātil | void |
| Bilāl | Muezzin/caller to prayer | بلال | Bilāl | Bilal ibn Rabah |
| Daawa | excuse/alibi | دعوة | da'wah | invitation |
| Duhul | extremity | دخول | dukhūl | entrance |
| Daira | city | دائرة | dā'irah | area |
| Dayyus | cuckold | ديّوث | dayyūth | cuckold |
| Dunya | earth | دنيا | dunyā | world |
| Duwaa | prayer | دعاء | du'ā | prayer/supplication |
| Habal | news | خبر | khabar | news |
| Hadas | impurity | حدث | hadath | impurity |
| Hakīka | birth ritual | عقيقة | aqīqah | birth ritual |
| Hakīkat | truth | حقيقة | haqīqah | truth |
| Hatīb | speaker | خطيب | khatīb | speaker |
| Hawa | Eve | حواء | Hawā' | Eve |
| Hidāyat | announcement | هداية | hidāyah | guidance |
| Hikmat | wisdom | حكمة | hikmah | wisdom |
| Hukum | judge | حكم | hukm | ruling |
| Humus | alms | خمس | khums | fifth |
| Hutba' | sermon | خطبة | khutbah | sermon |
| Hurup | sound of a letter | حروف | hurūf | letters |
| Ibilīs | demon | إبليس | Iblīs | devil |
| Ihilās | sincerity | إخلاص | ikhlās | sincerity |
| Ijin | blessing | إذن | idhn | permission |
| Ilmu' | knowledge | علم | 'ilm | knowledge |
| Imān | forbearingness | إيمان | īmān | faith |
| Intiha' | end | إنتهى | intihā | end |
| Irādat | determination | إرادة | irādah | determination |
| Islām | Islam | إسلام | Islām | Islam |
| Istigapar | to beg pardon | إستغفار | istighfār | to beg pardon |
| Instinja | pure | إستنجاء | istinjā' | to clean one's self |
| Jabūr | Psalms | زبور | zabūr | Psalms |
| Jāhil | foolish | جاهل | jāhil | ignorant |
| Jakāt | tithe | زكاة | zakāh | tithe |
| Jamāa | congregation | جماعة | jamā'ah | congregation |
| Jamān | clock | زمان | zamān | time |
| Janāja | bier | جنازة | janāzah | funeral |
| Jāt | appearance | ذات | dhāt | self |
| Jaytūn | olive | زيتون | zaytūn | olive |
| Jin | spirit | جنّ | jinn | demon |
| Jinā | adultery | زنا | zinā | adultery |
| Juba | garment | جبّة | jubbah | garment |
| Jubul | anus | دبر | dubr | anus |
| Junub | pollution | جنوب | junūb | dirty |
| Jurriyat | lineage | ذرية | dhurriyyah | offspring |
| Kahawa | coffee | قهوة | qahwah | coffee |
| Kāpil | disbeliever | كافر | kāfir | disbeliever |
| Karāmat | miracle | كرامة | karāmah | miracle |
| Kawwāt | power | قوّة | quwwah | force |
| Kubul | grave | قبور | qubūr | graves |
| Kudarat | Power of God | قدرة | qudrah | ability |
| Kulbān | sacrifice | قربان | qurbān | sacrifice |
| Kuppiya' | male head covering | كوفيّة | kūffiyah | kefiyyeh |
| Kupul | disbelief | كفز | kufr | disbelief |
| Lidjiki' | blessing | رزق | rizq | sustenance |
| Maana | meaning | معنة | ma'nah | meaning |
| Magrib | sunset | مغرب | maghrib | sunset |
| Magsukul | Thanks | شكر | shukr | thanks |
| Mahluk | human | مخلوق | maklūq | created |
| Maksud | purpose | مقصود | maqsūd | intended |
| Makbul | fulfilled | مقبول | maqbūl | accepted |
| Malak | Beautiful | ملك | malak | Angel |
| Maruhum | deceased | مرحوم | marhūm | deceased |
| Masrik | east | مشرق | mashriq | east |
| Matakaddam | parable | متقدّم | mutaqaddam | preceding |
| Mayat | corpse | ميت | mayt | dead |
| Mujijat | mystery | معجزة | mu'jizah | miracle |
| Mulid | pupil | مريد | murīd | pupil |
| Munapik | hypocrite | منافق | munāfiq | hypocrite |
| Murtad | apostate | مرتد | murtad | apostate |
| Muskil | uncommon | مشكل | mushkil | problem |
| Mustahak | lawful owner | مستحقّ | mustahaqq | deserving |
| Mustajab | occurred | مستجاب | mustajāb | answered |
| Muwallam | scholar | معلّم | mu'allim | teacher |
| Nabī | prophet | نبي | nabī | prophet |
| Najal | promise | نذر | nadhar | vow/promise |
| Najjis | filth | ناجس | nājis | filthy |
| Napas | breath | نفس | nafas | breathe |
| Napsu | desire | نفس | nafs | ego/desire |
| Nasihat | advice | نصيحة | nasīhah | advice |
| Paham | familiarity | فهم | fahm | understanding |
| Pardu' | legislation | فرض | fard | compulsory |
| Piil | action | فعل | fi'l | action |
| Pikil | think | فكر | fikr | thought |
| Pir'awn | Pharaoh | فرعون | fir'awn | Pharaoh |
| Rahmat | blessing | رحمة | rahmah | mercy |
| Rasūl | messenger | رسول | rasūl | messenger |
| Ruku' | bow | ركوع | rukū' | bowing |
| Rukun | precept | ركن | rukn | pillar |
| Sabab | because | سبب | sabab | reason/cause |
| Sahabat | follower | صحابة | sahābah | companions |
| Saytān | Satan | شيطان | shaytān | Satan |
| Sual | discussion | سؤال | su'āl | question |
| Subu | dawn | صبح | subh | dawn |
| Sunnat | female circumcision | سنّة | sunnah | tradition/sunnah |
| Takabbul | arrogant | تكبّر | takabbur | arrogance |
| Takwīm | calendar | تقويم | taqwīm | calendar |
| Tallak | divorce | طلاق | talāq | divorce |
| Tarasul | Tausug poem | تراسل | tarāsul | correspondence |
| Tasbi | prayer beads | تسبيح | tasbīh | praise |
| Ummul | age | عمر | 'amr | age |
| Wajib | compulsory | واجب | wājib | compulsory |
| Wakap | pause | وقف | waqf | pause |
| Waktu | time | وقت | waqt | time |
Tausug words derived from Sanskrit
| Tausug Word | Meaning (Tausug) | Sanskrit Word | Pronunciation | Meaning (Sanskrit) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guru | teacher | गुरु | guru | teacher |
| Naga | dragon | नाग | nāga | serpent |
| Āgama | religion | आगम | āgama | religion |
| Lahu' | eclipse | राहु | rāhu | eclipse |
| Lupa | appearance | रूप | rūpa | appearance |
| Dukka | grieve | दुःख | duḥkha | suffering |
| Sutla' | silk | सूत्र | sūtra | to sew/thread |
See also
References
- Tausug at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015)
- Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds. (2017). "Tausug". Glottolog 3.0. Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.
- Peneyra (1992), pp. 1–2.
- Tan, Evangeline K. (1967). "The phonology of Tausug: a descriptive analysis". open.library.ubc.ca. M.A.Thesis, University of British Columbia. p. 16.
- Peneyra (1992), p. 1.
- Peneyra (1992), pp. 4–5.
- Peneyra (1992), pp. 7; 14–15.
- Peneyra (1992), p. 32.
- Zorc, David Paul (1977). The Bisayan Dialects of the Philippines: Subgrouping and Reconstruction. Canberra, Australia: Dept. of Linguistics, Research School of Pacific Studies, Australian National University. doi:10.15144/PL-C44. ISBN 0858831570.
- Peneyra (1992), pp. 35–47.
Bibliography
- Peneyra, Irma V. (1992). A grammatical sketch of the Tausug language. The Archive, Publication 6. Diliman: University of the Philippines.
Further reading
- Sundita, Christopher Allen (2002). In Bahasa Sug: An Introduction to Tausug. Lobel & Tria Partnership, Co. ISBN 971-92226-6-2.
- Cameron, C. R. (1917). Sulu Writing, an Explanation of the Sulu-Arabic Script as Employed in Writing the Sulu Language of the Southern Philippines. Zamboanga: The Sulu Press.
External links
| Tausug language test of Wikipedia at Wikimedia Incubator |
- Publications in Tausūg and other Philippine languages
- Tausug-English Dictionary of SIL International. online version accessible from Webonary.org.
- Tausug Language by Dr. Carl G. Rubino
- Bansa.org Tausug Dictionary
- Tausug English Glossary Search for common Tausug Words
- Tausug 101 by Anak Iluh