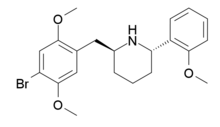
DMBMPP
DMBMPP, or 2-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromobenzyl)-6-(2-methoxyphenyl)piperidine, is a 2-benzylpiperidine analog of the hallucinogenic N-benzylphenethylamine 25B-NBOMe and was discovered in 2011 by Jose Juncosa in the group of David E. Nichols at Purdue University.[1][2] DMBPP differs from 25B-NBOMe by having a piperidine ring conformed to the amine, making for a more rigid molecular structure than that of the open-chain 25B-NBOMe. The presence of the piperidine ring introduces two stereocenters, thus, four stereoisomers of this compound can be made.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Juncosamine |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C21H26BrNO3 |
| Molar mass | 420.347 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Pharmacology
The (S,S)-isomer (2S,6S-DMBMPP) is the most interesting scientifically as it is the most selective agonist for the human 5-HT2A receptor yet discovered, with a Ki of 2.5 nM at the human 5-HT2A receptor and with 124-fold selectivity for 5-HT2A over the structurally similar 5-HT2C-receptor.[3] Together with 25CN-NBOH,[4] 2S,6S-DMBMPP is the only known 5-HT2A agonist to exhibit this level of selectivity.
| Ligand | Ki ± SEM (nM) | Ki ± SEM (nM) | Ki ± SEM (nM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| [3H] ketanserin | [3H] mesulergine | fold selectivity | |
| h5-HT2A | h5-HT2C | h5-HT2C/h5-HT2A | |
| 2C-B | 6.0 ± 0.3 | 23.8 ± 2.6 | 9.5 |
| 25B-NBOMe | 0.19 ± 0.01 | 4.0 ± 0.4 | 21 |
| (±)-DMBMPP | 5.3 ± 0.3 | 520 ± 22 | 98 |
| (S,S)-(−)-DMBMPP | 2.5 ± 0.1 | 310 ± 42 | 124 |
| (R,R)-(+)-DMBMPP | 2,100 ± 171 | 28,600 ± 4700 | 27 |
References
- Juncosa JI (2011-05-07). Organic synthesis combined with molecular modeling: A powerful approach to map the functional topography of dopamine and serotonin receptors (Ph.D. thesis). Purdue University.
- Juncosa JI, Hansen M, Bonner LA, Cueva JP, Maglathlin R, McCorvy JD, Marona-Lewicka D, Lill MA, Nichols DE (January 2013). "Extensive rigid analogue design maps the binding conformation of potent N-benzylphenethylamine 5-HT2A serotonin receptor agonist ligands". ACS Chemical Neuroscience. 4 (1): 96–109. doi:10.1021/cn3000668. PMC 3547484. PMID 23336049.
- Juncosa JI, Hansen M, Bonner LA, Cueva JP, Maglathlin R, McCorvy JD, Marona-Lewicka D, Lill MA, Nichols DE (January 2013). "Extensive rigid analogue design maps the binding conformation of potent N-benzylphenethylamine 5-HT2A serotonin receptor agonist ligands". ACS Chemical Neuroscience. 4 (1): 96–109. doi:10.1021/cn3000668. PMC 3547484. PMID 23336049.
- Hansen M, Phonekeo K, Paine JS, Leth-Petersen S, Begtrup M, Bräuner-Osborne H, Kristensen JL (March 2014). "Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of N-benzyl phenethylamines as 5-HT2A/2C agonists". ACS Chemical Neuroscience. 5 (3): 243–9. doi:10.1021/cn400216u. PMC 3963123. PMID 24397362.
| 5-HT1 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-HT2 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-HT3–7 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||