Foreign relations of Serbia
Foreign relations of Serbia are accomplished by efforts of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Serbia has inherited the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, along with all of its holdings, after the dissolution of the previous state union with Montenegro. Serbian foreign ministries continue to serve citizens of Montenegro in countries that do not have Montenegrin diplomatic presence. The governments of Serbia and Montenegro expressed an interest in pursuing a common foreign policy. Former President of Serbia Boris Tadić referred to relations with the European Union (EU), Russia, United States and China as the four pillars of foreign policy.[1] Serbia joined the United Nations on 1 November 2000.
 |
|---|
| This article is part of a series on the politics and government of Serbia |
|
|
Legislature
|
|
Judiciary
|
|
|
History
Serbian Revolution and Autonomous Principality (1804–1878)
Serbia gained its partial independence from the Ottoman Empire in two uprisings in 1804 (led by Đorđe Petrović – Karađorđe) and 1815 (led by Miloš Obrenović), although Turkish troops continued to garrison the capital, Belgrade, until 1867. In 1817 the Principality of Serbia was granted de facto independence from the Ottoman Empire. [2] High officials in the Austro-Hungarian Empire lobbied for Ottoman approval of the liberal 1869 constitution for Serbia, which depended on the Porte for final approval. Vienna's strategy was that a liberal political system in Serbia would divert its impulse to foment nationalist unrest within the its neighbors, and also delay its efforts to gain territory at the expense of the Ottoman Empire.[3]
Principality/Kingdom of Serbia (1878–1918)
The Autonomous Principality became an internationally recognized independent country following the Russo-Turkish War in 1878. Serbia remained a principality or kneževina (knjaževina), until 1882 when it became a Kingdom, during which the internal politics revolved largely around dynastic rivalry between the Obrenović and Karađorđević families.
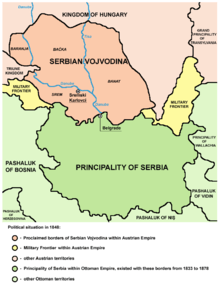
In 1885, Serbia protested against the unification of Bulgaria and Eastern Rumelia. The Serbian king, Milan Obrenovic´ (1854–1901), who needed to divert attention away from his domestic problems, demanded that Bulgaria cede some of its territory to Serbia. The Great Powers discouraged him, but he declared war on Bulgaria on November 13, 1885. The Serbo-Bulgarian War ended on March 3, 1886. The Serbian army crossed the lightly defended northwest border of Bulgaria aiming to seize Sofia, the Bulgarian capital. The Bulgarian defenders defeated the invaders and then invaded Serbia. Vienna brokered a peace that restored the old status quo. Serbian casualties totaled 6,800, about triple the 2,300 Bulgarian total. The defeat forced Obrenovic to abdicate in March 1889, and the Serbian crown passed to a regency in the name of his son Alexander (1876–1903).[4]
Serbian strategic goals
Serbia had multiple national goals.[5][6][7] Serbian intellectuals dreamed of a South Slavic state--which in the 1920s became Yugoslavia. The large number of Serbs living in Bosnia looked to Serbia as the focus of their nationalism, but they were ruled by the Germans of the Austrian Empire. Austria's annexation of Bosnia in 1908 deeply alienated the Serbian peoples. Plotters swore revenge, which they achieved in 1914 by assassination of the Austrian heir.[8] Serbia was landlocked, and strongly felt the need for access to the Mediterranean, preferably through the Adriatic Sea. Austria worked hard to block Serbian access to the sea, for example by helping with the creation of Albania in 1912. Montenegro, Serbia's main ally, did have a small port, but Austrian territory intervened, blocking access until Serbia acquired Novi Pazar and part of Macedonia from the Ottoman Empire in 1913. To the south, Bulgaria blocked Serbian access to the Aegean Sea.[9] Serbia, Greece, Montenegro and Bulgaria formed the Balkan League and went to war with the Ottomans in 1912–1913. They won decisively and expelled that Empire from almost all of the Balkans.[10] The main remaining foe was Austria, which strongly rejected Pan-Slavism and Serbian nationalism and was ready to make war to end those threats.[11] Ethnic nationalism would doom the multicultural Austro-Hungarian Empire. Expansion of Serbia would block Austrian and German aspirations for direct rail connections to Constantinople and the Middle East. Serbia relied primarily on Russia for Great Power support but Russia was very hesitant at first to support Pan-Slavism, and counselled caution. However, in 1914 it reversed positions and promised military support to Serbia.[12]
World War I
The 28 June 1914 assassination of Austrian Crown Prince Franz Ferdinand in Sarajevo, by Gavrilo Princip, a pro-Serbian member of Young Bosnia served as the basis for the Austrian declaration of war on Serbia on 28 July 1914. Vienna acted despite Serbia's acceptance three days earlier of nearly all of Vienna's demands. Vienna was convinced that Serbia was behind the plot in an effort to destabilize the multi-nation empire.[13] The Austro-Hungarian army invaded Serbia capturing Belgrade on 2 December 1914, however the Serbian Army successfully defended the country, won several victories, and on 15 December 1914 recaptured Belgrade.[14]
On 28 July 1914, Austria-Hungary declared war on Serbia. Within days, long-standing mobilization plans went into effect to initiate invasions or guard against them and Russia, France and Britain stood arrayed against Austria and Germany in what at the time was called the "Great War", and was later named "World War I" or "First World War." Austria thought in terms of one small limited war involving just the two countries. It did not plan a wider war such as exploded in a matter of days.
British historian John Zametica argued that Austria-Hungary was primarily responsible for starting the war, as its leaders believed that a successful war against Serbia was the only way it could remain a Great Power, solve deep internal disputes caused by Hungarian demands, and regain influence in the Balkan states.[15] Others, most notably Prof. Christopher Clark, have argued that Austria-Hungary, confronted with a Serbia that seemed determined to incite continual unrest and ultimately acquire all of the "Serb" inhabited lands of the Monarchy (which, according to the Pan-Serb point of view included all of Croatia, Dalmatia, Bosnia, Hercegovina and some of the southern counties of the Hungary(roughly corresponding to today's Vojvodina), and whose military and government was intertwined with the irredentist terrorist group known as "The Black Hand," saw no practical alternative to the use of force in ending what amounted to subversion from Serbia directed at a large chunk of its territories. In this perspective, Austria had little choice but to credibly threaten war and force Serbian submission if it wished to remain a Great Power.[16]
Bilateral relations
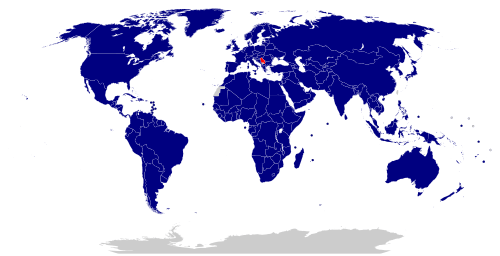
Serbia has established diplomatic relations with 191 UN member states,[17] the Holy See and Palestine,[17] the Sovereign Military Order of Malta,[17] and the European Union.[17]
Serbia has not established diplomatic relations with:[18]
- Marshall Islands,[19] Micronesia.[19]
- All of the states with limited recognition
Africa
Ever since the times of Josip Broz Tito and the Non-Aligned Movement, Serbia has enjoyed excellent relations with African nations. Angola, Ethiopia, Nigeria, Zimbabwe and South Africa are Serbia's closest allies in Sub-Saharan Africa. South Africa and Serbia have had excellent relations since the signing of diplomatic relations in 1992 following the end of the Apartheid system. Many ANC and Umkhonto we Sizwe resistance fighters received training in Serbia during Apartheid. South Africa is also home to around 20,000 Serbs, mainly living in the Johannesburg area.[20] South Africa is also voicing support for Serbia over the Kosovo issue.[21] Nelson Mandela was also made an honorary citizen of Belgrade.[22] Serbia is also actively involved in many investments in Angola with whom it has excellent political and economic relations.
| Country | Formal relations began | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1962 | See Algeria-Serbia relations | |
| 1975 |
| |
| 1962 |
Diplomatic relations between Benin and Serbia were established in 1962.[25] | |
| 1970 |
Diplomatic relations between Botswana and Serbia were established in 1970.[26] | |
| 1968 |
Diplomatic relations between Burkina Faso and Serbia were established in 1968.[27] | |
| 1962 |
Both countries established diplomatic relations in 1962.[28] | |
| 1976 | ||
| 1960 |
Diplomatic relations between Cameroon and Serbia were established in 1960.[29] | |
| 1960 |
Diplomatic relations between Central African Republic and Serbia were established in 1960.[30] | |
| 1966 |
Diplomatic relations between Chad and Serbia were established in 1966.[31] | |
| 1976 |
Diplomatic relations between Comoros and Serbia were established in 1976.[32] | |
| 1961 |
| |
| 1964 |
Diplomatic relations between Republic of the Congo and Serbia were established in 1964.[33] | |
| 1968 |
Diplomatic relations between Côte d'Ivoire and Serbia were established in 1968.[34] | |
| 1978 |
Diplomatic relations between Djibouti and Serbia were established in 1978.[35] | |
See Egypt-Serbia relations
| ||
| 2012 |
Diplomatic relations between Eritrea and Serbia were established in 2012.[37] | |
| 1952[38] | See Ethiopia–Serbia relations | |
| 1970 |
Diplomatic relations between Equatorial Guinea and Serbia were established in 1978.[39] | |
| 1960 | ||
| 1965 |
Both countries established diplomatic relations in 1965.[40] | |
| 1957 | ||
| ||
| 1975 |
Diplomatic relations between Guinea-Bissau and Serbia were established in 1975.[41] Guinea-Bissau supports Serbia's position regarding Kosovo, and prime minister Umaro Sissoco Embaló visited Belgrade in November 2017 to expand trade relations and affirm his nation's position on Kosovo.[42] | |
| 1963 |
| |
| 1972 |
Both countries have established diplomatic relations in 1972.[43] | |
| 1959 |
Diplomatic relations between Liberia and Serbia were established in 1959.[44] | |
| 1955 | See Libya–Serbia relations
| |
| 1968 | ||
| 1998 |
Both countries established diplomatic relations in 1998.[49] | |
| 1961 | ||
|
Serbia is represented in Mauritania by its embassy in Rabat.[50] | ||
| 1969 |
Both countries have established diplomatic relations in 1969.[51] | |
| 1978 |
Diplomatic relations between Mozambique and Serbia were established in 1975.[52] | |
| 1990 | Diplomatic relations between Namibia and Serbia were established in 1990.[53]
See Namibia–Serbia relations | |
| 1960 | ||
| 1971 |
Diplomatic relations between Rwanda and Serbia were established in 1971.[54] | |
| 1977 |
Diplomatic relations between São Tomé and Príncipe and Serbia were established in 1977.[55] | |
| 1961 |
Both countries have established diplomatic relations in 1961.[56] | |
| 1977 | ||
| 1961 |
Diplomatic relations between Sierra Leone and Serbia were established in 1961.[59] | |
| 1960 |
See Somalia–Serbia relations | |
| 2 April 1992 |
See South Africa–Serbia relations
| |
| 1956 |
Diplomatic relations between Sudan and Serbia were established in 1956.[61] | |
| 4 January 2012[62] | ||
| 1968 | ||
| 1961 |
Diplomatic relations between Tanzania and Serbia were established in 1961.[63] | |
| 1960 |
Diplomatic relations between Togo and Serbia were established in 1960.[64] | |
| 1957 |
| |
| 1963 |
Diplomatic relations between Uganda and Serbia were established in 1963.[65] | |
| 1964 |
| |
| 1980 |
See Zimbabwe–Serbia relations
|
America
Serbia has strong but strained relations with the United States and a bit more relaxed relations with Canada, because of their hostile recognition of Kosovo's independence and NATO bombing from 1999, which aimed to help this secession. On 25 February 2008, Serbian Prime Minister Vojislav Koštunica demanded that the United States rescind its recognition of Kosovo, warning that "there will be no stability until the fake state" is annulled.[68]
Serbia has very good relations with Latin America, except Colombia and Panama, which did recognize Kosovo's independence. Brazil, the largest country in the region, decided not to recognize Kosovo's independence until an agreement with Serbia is reached.[69]
| Country | Formal relations began | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1928 | See Argentina–Serbia relations
| |
| 1988 | ||
| November 1977 |
| |
| 1952 |
| |
| 1946 | See Brazil–Serbia relations | |
| 30 May 1941[77] | See Canada–Serbia relations
| |
| 1935 |
| |
| 1966 | ||
| 1952 | ||
| 1951 | See Cuba–Serbia relations
Cuba and Serbia have a long history of diplomatic relations from the period of Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia when both countries were members of Non-Aligned Movement. Cuba supports Serbia in its stance towards Kosovo considering Kosovo's independence an illegitimate act and a violation of international law and principles of the United Nations Charter.[85] Serbia supports Cuba at the United Nations in condemning the United States embargo.[86] | |
| 2010[87] | ||
| 1983 |
| |
| 1956 |
| |
| 1956 |
| |
| July 1978 |
| |
| 1987 |
| |
| 5 November 1968 | ||
| 1984 |
| |
| 1953 |
| |
| 1968 |
| |
| 24 May 1946 | See Mexico–Serbia relations
| |
| 1979 |
| |
| 1956 | ||
| 1950 |
Both countries have established diplomatic relations in 1950.[101] | |
| ||
| 2011[102] | ||
| 1976 |
| |
| 1974 | ||
| 14 October 1881[106] | See Serbia–United States relations
Prior to World War I and creation of Yugoslavia, Serbia and the US enjoyed excellent relations. Bilateral relations between Serbia and the United States were established in 1881. At the outset of hostilities between NATO and the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia in the spring of 1999, the United States and Yugoslavia severed diplomatic relations. After the overthrow of the Milosevic government in October 2000, the following month the United States reestablished a diplomatic presence. The U.S. Embassy formally reopened in May 2001. The Serbian Embassy in Washington and the U.S. Embassy in Belgrade have reestablished bilateral relations and provide a full range of consular services. In February 2008 Serbia recalled its ambassador from the United States, following the U.S. recognition of the unilaterally declared independence of Kosovo. The US established full diplomatic relations at Ambassador level with the Republic of Kosovo, which broke away from Serbia in February 2008.[107] | |
| 1950 | ||
| 1951 | See Serbia-Venezuela relations
|
Asia
Serbia has excellent relations with countries such as China, Indonesia, India, Iran, Iraq, Israel, Japan, Kazakhstan, Lebanon, South Korea, Vietnam, and the United Arab Emirates. These countries are important economic partners for Serbia in Asia.
| Country | Formal relations began | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1954 |
| |
| 1994 | See Armenia–Serbia relations
| |
| 1997 | See Azerbaijan–Serbia relations
| |
| 1989 | ||
| 1971 |
Both countries have established diplomatic relations in 1971.[112] | |
| 9 December 2011 | ||
| 5 December 2011 |
| |
| 1956 | ||
| 2 January 1955 | See China–Serbia relations
China has always traditionally had very warm and close relations with Belgrade since the establishing of diplomatic relations in 1955.[113] | |
|
Serbia is represented in Timor by its embassy in Jakarta.[114] | ||
| 26 June 1995 | [115] | |
| 1948 | See India–Serbia relations
| |
| 1954 | See Indonesia–Serbia relations
Indonesia has very close relations with Serbia, especially within the fields of trade, culture and tourism. Indonesia has also voiced support for Serbia's territorial integrity over the Kosovo issue.[120] | |
| 1945 |
| |
| 1958 | ||
| 1992[123] |
| |
| 1952[126] | See Japan–Serbia relations | |
| 1996 |
See Kazakhstan–Serbia relations
| |
| 1963 |
| |
| 1998 | ||
| 1962 |
Both countries have established diplomatic relations in 1962.[135] | |
| 1967/2003 |
| |
| 1974 | ||
| 20 November 1956[137][138] | ||
| 1950 | See Myanmar-Serbia relations | |
| 1959 | ||
| 30 October 1948 | See North Korea–Serbia relations
Serbia maintains friendly relations with North Korea. Relations between the two countries started in 1948 under the Yugoslav President Josip Broz Tito. Relations between the two countries are still strong in both political and military terms. The North Korean embassy to Serbia is accredited to Sofia, Bulgaria. | |
| 1974 |
| |
| 1948 | See Pakistan–Serbia relations
Pakistan considers Serbia to be a very important country and that the relations between the two states are warm and friendly.[143] | |
| 1988 | See Palestine–Serbia relations
Relations between Serbia and the Palestinian Authority have been very close and friendly. The Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia was one of the first countries to recognize Palestinian Authority in November 1988 and its successor Serbia maintained close relations, favoring a Two-State solution. The Palestinian Authority for its part, has refused to recognize the independence of Kosovo.[144][145] | |
| 1972 | ||
| 1989 |
| |
| 17 April 2013[149] |
| |
| 1967 |
Both countries have established diplomatic relations in 1967.[150] | |
| 27 December 1989[151] | See Serbia–South Korea relations
The establishment of diplomatic relations between Република Србија Serbia and the Republic of Korea began on 27 December 1989. | |
| 1956 | ||
| 1946 |
| |
| 1995 | ||
| 1954 |
| |
| 1879[159] | See Serbia–Turkey relations
| |
| 1996 | ||
| 21 March 2007 |
See Serbia–United Arab Emirates relations
| |
| 18 January 1995 |
Both countries have established diplomatic relations in 1995.[161] | |
| 1957 |
| |
| 1957 | Formal relations started in 1957[162] |
Europe
_location_map.svg.png)
Serbia has signed the Stabilisation and Association Agreement (SAA) with the European Union on 29 April 2008 and is in the process of the Republic of being admitted into the framework of the European Union as a full-fledged member state. Serbia officially applied for European Union membership on 22 December 2009,[163] and the European Commission recommended making it an official candidate on 12 October 2011. After the vote of the 27 EU foreign ministers on 28 February 2012, where with 26 votes for and 1 vote against, a candidate status recommendation was issued, and Serbia received full candidate status on 1 March. On 28 June 2013 the European Council endorsed the Council of Ministers conclusions and recommendations to open accession negotiations with Serbia.[164][165] In December 2013 the Council of the European Union approved opening negotiations on Serbia's accession in January 2014,[166] and the first Intergovernmental Conference was held on 21 January at the European Council in Brussels.[167]
Former Yugoslav Republics and Provinces
| Country | Formal relations began | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| See Bosnia and Herzegovina–Serbia relations
Bosnia and Herzegovina has an embassy in Belgrade. Serbia has an embassy in Sarajevo and a consulate-general in Banja Luka. Both countries are full members of the Council of Europe, the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE) and the Central European Free Trade Agreement (CEFTA). Serbia is an official candidate and Bosnia-Herzegovina is recognized as potential candidate country by the European Union. | ||
| See Croatia–Serbia relations
The two countries established diplomatic relations on 9 September 1996. Croatia has an embassy in Belgrade and a general consulate in Subotica. Serbia has an embassy in Zagreb and two general consulates (in Rijeka and Vukovar). There are around 200,000 people of Serbian descent living in Croatia and around 70,000 people of Croatian descent living in Serbia. | ||
|
On 17 February 2008, the former province of Kosovo unilaterally declared independence from Serbia, forming the Republic of Kosovo in the process. Serbia, Russia, China, India Algeria, Morocco, Greece, Mexico, Romania, Ukraine, Spain, Brazil, Nigeria, South Africa, Argentina, Belarus, Palestine, Bolivia, and many others do not recognize Kosovo as an independent state. Serbia has vowed to fight Kosovo's admission to international organizations. The Republic of Kosovo does not have and has not yet applied for United Nations membership. As of 2 March 2020, 112 United Nations member states and the Republic of China, Sovereign Military Order of Malta, Niue and the Cook Islands recognized Kosovo as an independent state. But still, with the strong and firm opposition of both Russia and China and their allies, Kosovo has no current prospects of becoming a member of the United Nations.[168] Serbia, in response to nations which have recognized Kosovo as an independent nation, has consistently recalled its ambassadors to these nations in an act of protest.[169] These countries include the United States, Albania, Bulgaria, Republic of North Macedonia, Colombia, Croatia, France, Germany, Hungary, Turkey, Slovenia and the United Kingdom. States which recognize the Province of Kosovo-Metohija as an integral part of the Republic of Serbia and states which recognize Kosovo as an independent nation Serbia States which recognize the Province of Kosovo as an integral part of Serbia States which recognize Kosovo as an independent country | ||
| See North Macedonia–Serbia relations
The Federal Republic of Yugoslavia that was formed in 1992 by the remaining Yugoslav republics Montenegro and Serbia established diplomatic relations with the Republic of North Macedonia on 8 April 1996.[170] The establishment of bilateral relations has been done under North Macedonia's former constitutional name – Republic of Macedonia.[171] Serbia therefore was one of 125 countries in the world recognizing Macedonia under the former constitutional name.[172]North Macedonia has an embassy in Belgrade, while Serbia's embassy is located in Skopje. | ||
| See Montenegro–Serbia relations
Montenegro has an embassy in Belgrade. Serbia has an embassy in Podgorica and a Consulate-General in Herceg Novi. | ||
See Serbia–Slovenia relations
|
Other European countries
| Country | Formal relations began | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 25 April 1914 | See Albania–Serbia relations | |
| 1874 | See Austria–Serbia relations
| |
| 2005 |
Both countries have established diplomatic relations in 2005.[181] | |
| 15 November 1994 | See Belarus–Serbia relations
| |
| 1886 |
| |
| 18 January 1879 | See Bulgaria–Serbia relations | |
| 1960 | See Cyprus–Serbia relations
| |
| 1918 | See Czech Republic–Serbia relations
| |
| 1917 | See Denmark–Serbia relations
| |
| 9 February 2001 |
| |
| 1928 | See Finland–Serbia relations
| |
| 18 January 1879 | See France–Serbia relations
| |
| 18 January 1879 | See Germany–Serbia relations
| |
| 18 January 1879 | See Greece–Serbia relations
Friendly relations have played an important role in bilateral relations between the two nations, especially during the wars of the 1990s and the Balkans Campaign[191] in World War I. Due to the strong historical friendship and the deep cultural and religious ties between the two nations, Greece and Serbia enjoy historically, religiously and culturally close ties which are confirmed by a regular political dialogue. Greece is the top investor in Serbian economy[192] and during the NATO bombing of Yugoslavia, Greece openly expressed its disapproval and polls revealed that 94% of the Greek population were completely opposed to the bombing.[193] The more dramatic event was a People's Tribunal of over a 10.000 people in Athens, Greece, where the Greek Supreme Court declared president Clinton and NATO leaders guilty of war crimes.[194] | |
| See Holy See–Serbia relations | ||
See Hungary–Serbia relations
| ||
| 2000 | ||
| 18 January 1879 | See Italy–Serbia relations and Italy-Yugoslavia relations
| |
| December 2000 | ||
| 14 December 2000 |
| |
| 6 January 1969 | See Malta–Serbia relations
| |
| March 1995 |
| |
| 2007 |
Both countries have established diplomatic relations in November 2007.[205] | |
| 1899 |
| |
| 1942 | See Norway–Serbia relations
| |
| 1919 | See Poland–Serbia relations
| |
| October 1917 | See Portugal–Serbia relations
| |
| April 1879 | See Romania–Serbia relations | |
| 1838/1940 | See Russia–Serbia relations
Diplomatic relations between the Kingdom of Yugoslavia and the Soviet Union were established on 24 June 1940, and Serbia and the Russian Federation recognize the continuity of all inter-State documents signed between the two countries. There are about 70 bilateral treaties, agreements and protocols signed in the past. Serbia and the Russian Federation have signed and ratified 43 bilateral agreements and treaties in diverse areas of mutual cooperation so far.[211] | |
| 14 February 2002 | See San Marino–Serbia relations
| |
| 1993 | See Serbia–Slovakia relations
| |
| October 1916 | See Serbia–Spain relations
| |
| 1917 | See Serbia–Sweden relations
| |
| 1916 | See Serbia–Switzerland relations
| |
| 15 April 1994 | See Serbia–Ukraine relations
| |
| 1837 | See Serbia–United Kingdom relations
|
Oceania
| Country | Formal relations began | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1966 | See Australia–Serbia relations
| |
| 1976 | ||
| 1951 |
| |
| 1976 |
Both countries have established diplomatic relations in 1976.[226] | |
| 13 September 2012 |
Both countries have established diplomatic relations on 13 September 2012.[227] | |
| 1 March 2013 |
See also
References
- "B92 – Info – Tadi on Serbia's "four pillars of diplomacy"". B92. Archived from the original on 19 February 2015. Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- Lawrence P. Meriage, "The First Serbian Uprising (1804-13) and the Nineteenth-Century Origins of the Eastern Question." Slavic Review (1978) 37#3 pp 421-439.
- Ian D. Armour, "Killing Nationalism with Liberalism? Austria–Hungary and the Serbian Constitution of 1869." Diplomacy & Statecraft 21.3 (2010): 343-367.
- Ferdinand Schevill, History of the Balkans (1922) pp. 411–413.
- Martin Gilbert, First World War Atlas (1970) p 8.
- Richard C. Hall, "Serbia," in Richard F. Hamilton, and Holger H. Herwig, eds. The Origins of World War I (Cambridge UP, 2003) pp 92–111.
- Christopher Clark, The Sleepwalkers: How Europe Went to War in 1914 (2012) pp 3–64 online.
- Bernadotte E. Schmitt (1937). The Annexation of Bosnia, 1908–1909. Cambridge UP. p. vii.
- Gunnar Hering, "Serbian-Bulgarian relations on the eve of and during the Balkan Wars." Balkan Studies (1962) 4#2 pp 297-326.
- Richard C. Hall, "Balkan Wars," History Today (2012) 62#11 pp 36-42,
- Béla K. Király, and Gunther Erich Rothenberg, War and Society in East Central Europe: Planning for war against Russia and Serbia: Austro-Hungarian and German military strategies, 1871–1914 (1993).
- Gale Stokes, "The Serbian Documents from 1914: A Preview" Journal of Modern History 48#3 (1976), pp. 69-84 online
- Richard C. Hall, "Serbia," in Richard F. Hamilton, and Holger H. Herwig, eds. The Origins of World War I (Cambridge UP, 2003) pp 92–111.
- James B. Lyon, Serbia and the Balkan Front, 1914: The Outbreak of the Great War (2015).
- John Zametica, In Folly and Malice (2017)
- Christopher Clark, "The Sleepwalkers: How Europe Went to War in 1914" 2012: Allen Lane, U.S. ed. 2013
- "Serbia Diplomatic List 2012" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 3 October 2013. Retrieved 20 October 2012.
- "Serbia Bilateral Relations".
- Recognizes the Republic of Kosovo.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Serbia".
- Thomson Reuters Foundation. "Thomson Reuters Foundation". Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- "Nelson Mandela named Belgrade's honorary citizen". Archived from the original on 27 September 2007. Retrieved 16 May 2007.
- "Serbian Ministry of Foreign Affairs: direction of the Algerian embassy in Belgrade".
- "Ambasada Republike Srbije - Alžir". www.ambserbie-alger.com. Retrieved 26 October 2017.
- "Benin". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Botswana". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Burkina Faso". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Burundi". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Cameroon". www.mfa.gov.rs. Retrieved 26 October 2017.
- "Central African Republic". www.mfa.gov.rs. Retrieved 26 October 2017.
- "Chad". www.mfa.gov.rs. Retrieved 26 October 2017.
- "Union of the Comoros". www.mfa.gov.rs. Retrieved 26 October 2017.
- "Congo, Republic". www.mfa.gov.rs. Retrieved 26 October 2017.
- "Côte D'Ivoire". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Djibouti". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- Serbian embassy in Cairo Archived 1 March 2009 at the Wayback Machine
- "Eritrea". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Ethiopia". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Equatorial Guinea". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Gambia". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Guinea Bissau". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- Guinea-Bissau Officially Revokes Recognition of Kosovo, InSerbia, 2017-11-22
- "Lesotho". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Liberia". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Serbian Ministry of Foreign Affairs: direction of the Libya embassy in Belgrade".
- "Serbian Ministry of Foreign Affairs: direction of the Serbian embassy in Tripoli".
- "Swaziland". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Malawi". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Other Countries RS- Mauritania". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Mauritius". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Mozambique". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Namibia". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Rwanda". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Sao Tome and Principe". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Senegal". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Seychelles". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Sierra Leone". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Serbian embassy in Pretoria". Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- "Sudan". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- Ariath, Ater Garang (4 January 2012). "South Sudan: Govt, Serbia Establish Bilateral Ties" – via AllAfrica.
- "Tanzania". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Togo". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Uganda". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- Editorial Staff. "Interview With President Mugabe by Serbian Broadcasting." African Globe Net. African Globe, 4 February 2014. Web. 12 May 2016.
- "Zimbabwe". www.upi.com.
- Kirka, Danica (26 February 2008). "Putin's Likely Successor, Pledging Support for Serbia, Signs Pipeline Deal". The Washington Post. Associated Press. p. A11.
- "Brasil não reconhece Kosovo sem acordo com Sérvia". Diário Catarinense. Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- Political relations with Argentina Archived 14 August 2009 at the Wayback Machine, Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Serbia
- "Bahamas". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Barbados". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Bolivia". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Colombia". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Canada". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Canadian embassy in Belgrade". International.gc.ca. Retrieved 3 June 2011.
- "Serbian embassy in Ottawa". Serbianembassy.ca. Archived from the original on 6 July 2011. Retrieved 3 June 2011.
- "Serbian general consulate in Toronto". Gktoronto.com. Retrieved 3 June 2011.
- "Chile". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Costa Rica". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Spoljna politika". Mfa.gov.rs. Archived from the original on 17 June 2012. Retrieved 2012-07-26.
- Beta (20 March 2012). "Dobri odnosi Kube i Srbije | Aktuelno". Novosti.rs. Retrieved 26 July 2012.
- "Dominica and Serbia strengthen diplomatic ties". Dominica News Online. Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- "Dominican Republic". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Ecuador". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "El Salvador". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Grenada". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Guatemala". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Guyana". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Other Countries RS- Guyana". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Haiti". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Honduras". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Jamaica". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Nicaragua". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Panama". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Paraguay". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "i-witness-news.com". Archived from the original on 29 June 2013. Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- "Suriname". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Trinidad and Tobago". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "USA". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "US Embassy Pristina". Retrieved 17 April 2008.
- "Uruguay". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Venezuela's Chavez won't recognize independent Kosovo". International Herald Tribune. 21 February 2008. Archived from the original on 20 February 2009.
- "Chavez: U.S. encouraging Tibet violence - USATODAY.com". Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- "Bangladesh". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- Foreign Relations of the People's Republic of China
- "Other Countries RS- East Timor". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Relations Between Georgia and the Republic of Serbia". Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Georgia). Archived from the original on 16 November 2011. Retrieved 11 July 2011.
- "Georgia will not recognize Kosovo" Archived 16 September 2009 at the Wayback Machine, B92, 2008-05-09
- Tanjug. “Serbia Supports Territorial Integrity of Georgia.” B92.Net, 3 June 2015
- Indian embassy in Belgrade Archived 10 April 2009 at the Wayback Machine. Embassyofindiabelgrade.org. Retrieved 12 November 2011.
- Serbian embassy in New Delhi. Embassyofserbiadelhi.net.in. Retrieved 12 November 2011.
- "People's Daily Online – Indonesia voices support for Serbia in Kosovo spat". Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- "Embassy of Iraq in Belgrade, Serbia". Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- "Embassy of Serbia in Baghdad, Iraq". Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- "Israel and Serbia mark 20 years since renewal of diplomatic ties". GxMSDev. Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- "Error-2010-f3". Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- "embassyserbia.co.il". Archived from the original on 25 February 2012. Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- "Japan". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "在セルビア日本国大使館". Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- "Welcome to the home page of the Embassy of the Republic of Serbia in Japan". Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- "Untitled Document". Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- "在セルビア日本国大使館". www.yu.emb-japan.go.jp (in Japanese). Retrieved 30 July 2018.
- "Japan-Serbia Relations". Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Japan. Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- Urazova, DinaraU. "Kazakh Embassy Opens in Belgrade." Tengri News. Tengri News, 6 June 2015. Web. 4 April 2016.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 17 April 2013. Retrieved 18 April 2013.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Kyrgyzstan". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Laos". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Malaysia". Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- "Mongolia". Retrieved 2 May 2016.
- http://www.mfa.gov.mn/en/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=70%3A2009-12-21-02-02-12&catid=39%3A2009-12-20-21-53-08&Itemid=170&lang=en%5B%5D
- "Myanmar". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 31 December 2016. Retrieved 30 December 2016.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Nepal". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Pakistan, Serbia to strengthen bilateral ties". Associated Press of Pakistan. 15 July 2009. Archived from the original on 9 August 2009.
- Tadić, Abbas discuss Kosovo, Middle East Archived 9 July 2009 at the Wayback Machine, B92, 2009-07-07
- PM meets with Palestinian leader Archived 8 September 2009 at the Wayback Machine, B92, 2009-08-07
- "Philippines". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Blic Online – Srbija i Saudijska Arabija uspostavili diplomatske odnose". Blic Online. Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- "Singapore". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea. "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Europe". Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea. Archived from the original on 24 December 2013. Retrieved 2 May 2016.
- http://www.seoul.mfa.gov.rs/cir/
- http://overseas.mofa.go.kr/rs-ko/index.do
- "Sri Lanka". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Official presentation of the Republic of Serbia in Damascus – Syria". Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- "Tajikistan". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Thai Consulate – Počasni Konzulat Kraljevine Tajland u Republici Srbiji". www.thaiconsulate.rs.
- "Turkey". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Uzbekistan". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Yemen". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Serbia applies for EU membership". Swedish Presidency of the European Union. Archived from the original on 27 January 2010. Retrieved 25 December 2009.
- http://www.consilium.europa.eu/uedocs/cms_data/docs/pressdata/en/ec/137634.pdf
- "EU set for Serbia membership talks". BBC News. 28 June 2013. Retrieved 28 June 2013.
- "Council conclusions on Enlargement and Stabilisation and Association Process" (PDF). Council of the European Union. 17 December 2013. Retrieved 17 December 2013.
- "Serbia starts negotiations to join EU". B92. 21 January 2014. Retrieved 21 January 2014.
- "Rift Emerges at the United Nations Over Kosovo". New York Sun. 19 February 2008.
- PROTEST CONVEYED TO FRANCE, BRITAIN, COSTA RICA, AUSTRALIA, ALBANIA at the Wayback Machine (archive index)
- Ministry of Foreign Affairs – Republic of Macedonia Archived 30 September 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- "Republic of Serbia – Ministry of Foreign Affairs".
- "FM Milososki: Name row a result of Greece's desire to protect its myth of pure nation". Archived from the original on 3 August 2009.
the fact that 125 countries in the world have recognised Macedonia's constitutional name is a clear signal that the country has international support
- Serbian embassy in Ljubljana (in Serbian and Slovenian only) Archived 8 April 2009 at the Wayback Machine
- "Embassy of the Republic of Slovenia Belgrade". Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- "Vandals damage Albanian embassy in Belgrade". BBC. 29 March 1999.
- "Serbian charge d'affaires prepares to quit Albania". BBC. 20 February 2008.
- Austrian embassy in Belgrade (in German and Serbian only)
- "Serbian embassy in Vienna (in German and Serbian only)".
- "Consulate General of The Republic of Serbia in Salzburg". Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- 20 Minuten Online: Serben-Demo eskaliert in Wien
- "Andorra". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Belgian embassy in Belgrade". Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- Serbian Ministry of Foreign Affairs about relations with Cyprus
- The Cypriot Minister voiced his full support to Serbia's territorial integrity and EU integration, which should lead to full EU membership.
- Serbian embassy in Nicosia Archived 1 June 2013 at the Wayback Machine
- "Czech embassy in Belgrade (in Czech and Serbian only)". Mzv.cz. 30 April 2010. Retrieved 14 April 2011.
- "Suomen suurlähetystö, Belgrad". Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- "Embassy of the Republic of Serbia in the Republic of Finland". Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- "French embassy in Belgrade (in French and Serbian only)". Ambafrance-srb.org. Retrieved 10 June 2011.
- "Serbian embassy in Paris(in French and Serbian only)". Amb-serbie.fr. Archived from the original on 29 June 2007. Retrieved 10 June 2011.
- "Serbian embassy in Berlin (in German and Serbian only)". Embassy of Serbia, Berlin. Retrieved 31 December 2010.
- "Serbian general consulates in Germany (in German and Serbian only)". Konzulati-rs.de. Retrieved 31 December 2010.
- "World War I". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- "Grci spremni da ulože 3 mlrd. evra". B92. Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- "NATO and Greece, Clinton's visit". Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- Censored 2000. Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- "Hungarian embassy in Belgrade".
- "Hungarian general consulate in Subotica(in Hungarian and Serbian only)".
- "Embassy of the Republic of Serbia in Hungary". Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- "Iceland". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Ambasciata d'Italia – Belgrado". Retrieved 2 May 2016.
- "Latvia". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Bilateral Agreements - MFA of Latvia". www.mfa.gov.lv.
- Dizaino Kryptis. "Lietuvos Respublikos užsienio reikalų ministerija – Lietuvos Respublikos užsienio reikalų ministerija". Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- "Sorry. The page you are looking for does not exist" (PDF). Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- "Monaco". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Netherlands Embassy in Belgrade, Serbia". Archived from the original on 22 July 2010. Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- "Index of /~yuambanl". Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- "Norway – The official site in Serbia". Retrieved 15 January 2016.
- "Embassy of Serbia in Oslo". Archived from the original on 12 August 2007. Retrieved 24 July 2009.
- "B92 – Info – Serbia, Norway boost military ties". B92. Archived from the original on 19 February 2015. Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- Bilateral Political Relations with Russia, Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Serbia
- "Embassy of the Republic of Serbia in the Slovak Republic". Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- "Veľvyslanectvo Slovenskej republiky v Belehrade". Archived from the original on 19 February 2015. Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- "Home". Archived from the original on 19 November 2014. Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- Spanish embassy in Belgrade (in Serbian and Spanish only) Archived 22 December 2007 at the Wayback Machine
- "Belgrade – SwedenAbroad". Archived from the original on 15 April 2012. Retrieved 2 May 2016.
- "Embassy of Switzerland in Serbia". Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- "Serbian embassy in Bern". Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- "Generalni konzulat Republike Srbije u Cirihu". Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- "Erstmals über eine Million EU- und EFTA Angehörige in der Schweiz". Neue Zürcher Zeitung. 14 October 2008.
- "UK and Serbia". Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- "Embassy of the Republic of Serbia in Great Britain". Retrieved 2 May 2016.
- "Home". Retrieved 2 May 2016.
- "Serbian Ministry of Foreign Affairs about relations with New Zealand".
- Ethnic group (total responses) for the census usually resident population count, 2006 Archived 27 November 2007 at the Wayback Machine (Excel 97 format), Classification counts, 2006 Census, Statistics New Zealand.
- "Papua New Guinea". www.mfa.gov.rs.
- "Solomon Islands". www.mfa.gov.rs.
Further reading
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to International relations of Serbia. |
.svg.png)