Member states of the League of Nations
Between 1920 and 1939, a total of 63 countries became member states of the League of Nations. The Covenant forming the League of Nations was included in the Treaty of Versailles and came into force on 10 January 1920, with the League of Nations being dissolved on 18 April 1946; its assets and responsibilities were transferred to the United Nations.
The League's greatest extent was from 28 September 1934 (when Ecuador joined) to 23 February 1935 (when Paraguay withdrew) with 58 members. At this time, only Costa Rica (22 January 1925), Brazil (14 June 1926), Japan (27 March 1933) and Germany (19 October 1933) had withdrawn, and only Egypt was left to join (on 26 May 1937).
The members (listed from earliest joining and alphabetically if they joined on the same day) at this time were Argentina, Australia, Belgium, Bolivia, the British Empire, Canada, Chile, China, Colombia, Cuba, Czechoslovakia, Denmark, El Salvador, France, Greece, Guatemala, Haiti, Honduras, India, Italy, Liberia, the Netherlands, New Zealand, Nicaragua, Norway, Panama, Paraguay, Persia/Iran, Peru, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Siam, South Africa, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Uruguay, Venezuela, Yugoslavia, Austria, Bulgaria, Finland, Luxembourg, Albania, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Hungary, the Irish Free State, Ethiopia, the Dominican Republic, Mexico, Turkey, Iraq, the Soviet Union, Afghanistan, and Ecuador.
Of the 42 founding members, 23 (or 24, counting Free France) were members when the League of Nations was dissolved in 1946. A further 21 countries joined between 1920 and 1937, but seven withdrew, left, or were expelled before 1946.
Countries are listed under the year in which they joined. The word "withdrew" indicates that a country left of its own choice. The word "left" indicates a country that ceased to exist after annexation by Germany, Italy or the Soviet Union. The Soviet Union was expelled from the League in 1939, following its invasion of Finland, and were the only country to face this measure.
Despite formulating the concept and signing the Covenant, the United States never joined the League of Nations, and some relatively isolated sovereign states in Asia also did not join, including Saudi Arabia, Yemen, Mongolia, Nepal, and Bhutan.
Likewise, none of the European microstates of Andorra, Liechtenstein, Monaco, San Marino, and Vatican City ever sought membership in the organization.
Map
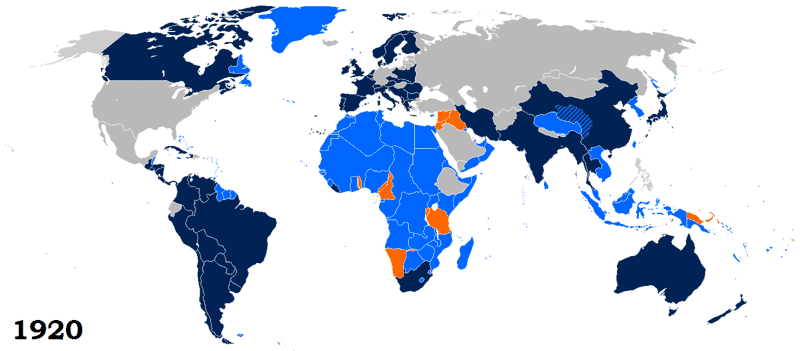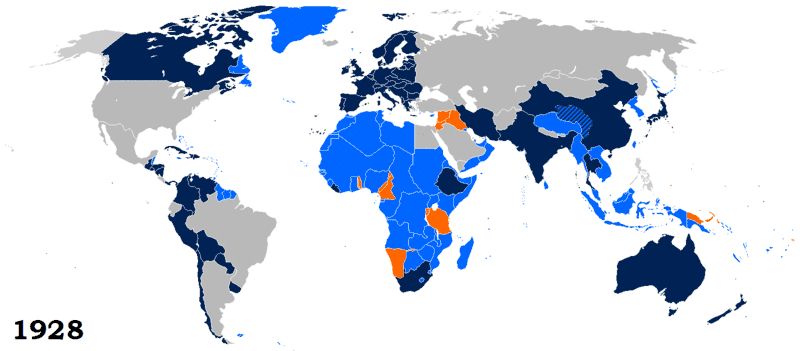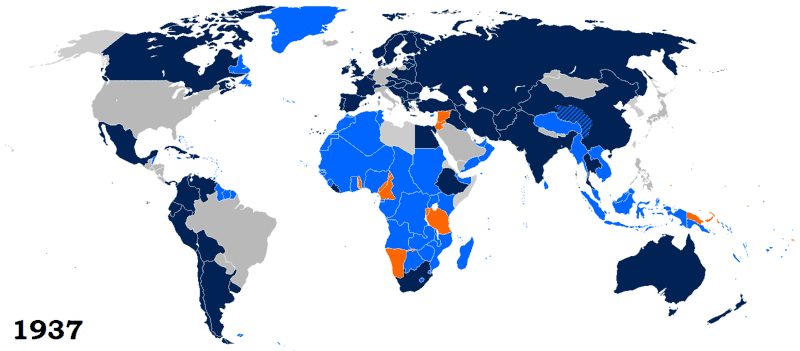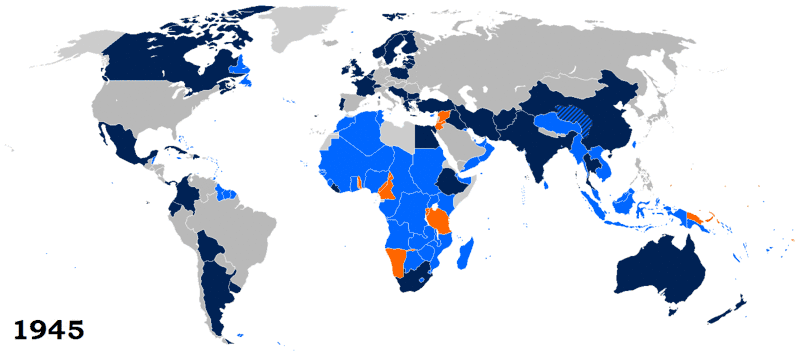
10 January 1920: founding members

.svg.png)

.svg.png)


.svg.png)

.svg.png)

.svg.png)
.svg.png)

.svg.png)
.gif)
_crowned.svg.png)
.svg.png)



.svg.png)
.svg.png)

.svg.png)



.svg.png)



.svg.png)
.svg.png)
1920


.svg.png)


.svg.png)
1921


.svg.png)
1922
.svg.png)
1923

.svg.png)
1924

1926
.svg.png)
1934
.svg.png)
.svg.png)

1937
.svg.png)
See also
References
- South America Archived 10 May 2008 at the Wayback Machine, Encyclopedia of World History
- League of Nations chronology, United Nations
- Members of the 1st Assembly, League of Nations, Geneva, 15 November – 18 December 1920.
- Czechoslovakia never formally left the League and was present at the last meeting of the Assembly in 1946
- Left upon German takeover in 1943
- Hannsjoachim Wolfgang Koch, Macmillan International Higher Education, 1985, Aspects Of The Third Reich, p. 297
- Hell, Stephan (8 January 2020). "A seat at the table". Bangkok Post. Retrieved 8 January 2020.
- Occupied by Axis Powers 1941–1945
- Withdrew from active participation in the League after its defeat by the Soviet Union in 1944.
- Forced to withdraw by German occupation in May 1940 and incorporation into the German Reich.
- Forced to withdraw by Italian invasion of 1939.
- Toledo-García, Itzel; University of Essex, UK: ‘’"La cuestión de la dignidad nacional en el ingreso de México a la Sociedad de Naciones, 1919-1931"’’ Retrieved 4 September 2016. (Translated from Spanish: "On September 7th, 1931, the British Empire, Germany, Northern Ireland, Spain, France, Italy and Japan began the initiative; next day the proposal was adopted unanimously by the assembly, and the invitation was sent to the government of Mexico. The 10th of September the acceptance was communicated in Geneva… Two days later, Mexico was declared member of the League of Nations.")
Further reading
- Hell, Stefan (2019). Siam and The League of Nations; Modernisation, Sovereignty, and Multilateral Diplomacy, 1920-1940. Bangkok: River Books. ISBN 9789749863893. Retrieved 8 January 2020.