Central European Initiative
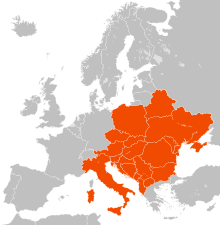
The Central European Initiative (CEI) is a forum of regional cooperation in Central and Eastern Europe, counting 18 member states. It was formed in Budapest in 1989. The CEI headquarters have been in Trieste, Italy, since 1996.
History
The Central European Initiative or CEI, is the largest and oldest forum of regional cooperation in Central, Eastern and South Eastern Europe. It now counts 17 member states, many of whom are not even part of Central Europe: Albania, Belarus, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, the Czech Republic, Hungary, Italy, Moldova, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Poland, Romania, Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia and Ukraine. The origin of the Central European Initiative lies in the creation of the Quadragonale in Budapest on 11 November 1989 whose founding members were Italy, Austria, Hungary and the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (SFRY).
The Initiative aimed at overcoming the division in blocks by re-establishing cooperation links, among countries of different political orientations and economic structures.
At the first Summit in Venice in 1990, Czechoslovakia was admitted and the Initiative was renamed Pentagonale. In 1991, with the admission of Poland it became the Hexagonale.
The organisation was renamed Central European Initiative (CEI) in 1992. On the same occasion, Macedonia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia and Slovenia were admitted as member states.
The Czech Republic and Slovakia were admitted to the CEI in 1993 following the dissolution of Czechoslovakia. In 1996 Albania, Belarus, Bulgaria, Moldova, Romania and Ukraine joined the CEI as full-fledged members.
The current membership derives from the adhesion of the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (afterwards State Union of Serbia and Montenegro and later on Serbia) in 2000 and of Montenegro in 2006.
Structures
The CEI has a three-pilar system: It cooperates in governmental dimension, parliamentary dimension and business dimension.
It promotes connectivity and diversity through 6 main areas: Good governance, economic growth, media freedom, environmental protection, intercultural cooperation and scientific cooperation/ education & training.
The CEI implements is activities through its cooperative activities, EU-projects, Know-how exchange programme and technical cooperation with the European Bank for Reconstruction and development(EBRD).
Secretary General
In 2019, Mr. Roberto Antonione (Italy) has taken up his duties as Secretary General.
CEI Presidencies
| Year | Country |
|---|---|
| 1989 | Hungary |
| 1990 | Italy |
| 1991 | SFR Yugoslavia |
| 1992 | Austria |
| 1993 | Hungary |
| 1994 | Italy |
| 1995 | Poland |
| 1996 | Austria |
| 1997 | Bosnia and Herzegovina |
| 1998 | Croatia |
| 1999 | Czech Republic |
| 2000 | Hungary |
| 2001 | Italy |
| 2002 | Macedonia |
| 2003 | Poland |
| 2004 | Slovenia |
| 2005 | Slovakia |
| 2006 | Albania |
| 2007 | Bulgaria |
| 2008 | Moldova |
| 2009 | Romania |
| 2010 | Montenegro |
| 2011 | Serbia |
| 2012 | Ukraine |
| 2013 | Hungary |
| 2014 | Austria |
| 2015 | Macedonia |
| 2016 | Bosnia and Herzegovina |
| 2017 | Belarus |
| 2018 | Croatia |
| 2019 | Italy |
2020 Montenegro
Membership
Founding members:
Joined later:

.svg.png)



.svg.png)









%3B_Flag_of_Serbia_and_Montenegro_(2003%E2%80%932006).svg.png)


See also
- Central Europe
- Southeastern Europe
- Southeast European Cooperation Process (SEECP)
- Central European Free Trade Agreement (CEFTA)
- Southeast European Cooperative Initiative (SECI)
- Black Sea Economic Co-operation (BSEC)
- Adriatic-Ionian Initiative (AII)
- Regional Cooperation Council (RCC)
- Visegrad Group (V4)
- Three Seas Initiative (TSI)
References
- "CEI Summit successfully held in Zagreb". Central European Initiative. 2018-05-12. Retrieved 2019-05-28.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Central European Initiative. |