Warsaw
Warsaw (/ˈwɔːrsɔː/ WOR-saw; Polish: Warszawa [varˈʂava] (![]()
Warsaw Warszawa | |
|---|---|
  .jpg)      | |
| Nickname(s): Paris of the North, Phoenix City | |
| Motto(s): Semper invicta (Latin "Ever invincible") | |
 Warsaw Location within Poland  Warsaw Location within Europe | |
| Coordinates: 52°14′N 21°1′E | |
| Country | Poland |
| Voivodeship | Masovia |
| County | city county |
| Founded | 13th century |
| City rights | 1323 |
| Districts | |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Rafał Trzaskowski (PO) |
| Area | |
| • Capital city and county | 517.24 km2 (199.71 sq mi) |
| • Metro | 6,100.43 km2 (2,355.39 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 78–116 m (328 ft) |
| Population (31 December 2019) | |
| • Capital city and county | 1,790,658 (1st) |
| • Rank | 1st in Poland (8th in EU) |
| • Density | 3,448/km2 (8,930/sq mi) |
| • Metro | 3,100,844[2] |
| • Metro density | 509.1/km2 (1,319/sq mi) |
| Demonym(s) | Varsovian |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
| Postal code | 00-001 to 04–999 |
| Area code(s) | +48 22 |
| Website | um.warszawa.pl |
| Official name | Historic Centre of Warsaw |
| Type | Cultural |
| Criteria | ii, vi |
| Designated | 1980 (4th session) |
| Reference no. | |
| UNESCO region | Europe |
The city rose to prominence in the late 16th century, when Sigismund III decided to move the Polish capital and his royal court from Kraków. The elegant architecture, grandeur and extensive boulevards earned Warsaw the nickname Paris of the North prior to the Second World War. Bombed at the start of the German invasion in 1939, the city withstood a siege,[6][7][8] but was largely destroyed by the Warsaw Ghetto Uprising in 1943, the general Warsaw Uprising in 1944 and the systematic razing by the Germans in advance of the Vistula–Oder Offensive. Warsaw gained the new title of Phoenix City because of its complete reconstruction after the war, which had left over 85% of its buildings in ruins.[9][10]
In 2012, the Economist Intelligence Unit ranked Warsaw as the 32nd most liveable city in the world.[11] In 2017, the city came 4th in the "Business-friendly", 8th in "Human capital and life style" and topped the quality of life rankings in the region.[12] The city is a significant centre of research and development, business process outsourcing and information technology outsourcing. The Warsaw Stock Exchange is the largest and most important in Central and Eastern Europe.[13][14] Frontex, the European Union agency for external border security as well as ODIHR, one of the principal institutions of the Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe have their headquarters in Warsaw. Jointly with Frankfurt and Paris, Warsaw features one of the highest number of skyscrapers in the European Union.[15]
The city is the seat of the Polish Academy of Sciences, National Philharmonic Orchestra, University of Warsaw, the Warsaw University of Technology, the National Museum, Zachęta Art Gallery and the Warsaw Grand Theatre, the largest of its kind in the world.[16] The picturesque Old Town, which represents examples of nearly every European architectural style and historical period,[17] was listed as a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in 1980. Other main architectural attractions include the Royal Castle and the iconic King Sigismund's Column, the Wilanów Palace, the Palace on the Isle, St. John's Cathedral, Main Market Square as well as numerous churches and mansions along the Royal Route. Warsaw is positioning itself as Central and Eastern Europe's chic cultural capital with thriving art or club scenes and restaurants,[18] with around a quarter of the city's area occupied by parks.[19]
Toponymy and names
Warsaw's name in the Polish language is Warszawa. Other previous spellings of the name may have included Warszewa, Warszowa, Worszewa or Werszewa.[20][21] The exact origin of the name is uncertain and has not been fully determined.[22][23] Originally, Warszawa was the name of a small fishing settlement on the banks of the Vistula river. One theory states that Warszawa means "belonging to Warsz", Warsz being a shortened form of the masculine Old Polish name Warcisław, which etymologically is linked with Wrocław.[24] However the ending -awa is unusual for a large city; the names of Polish cities derived from personal names usually end in -ów/owo/ew/ewo (e.g. Piotrków, Adamów).
Folk etymology attributes the city name to a fisherman, Wars, and his wife, Sawa. According to legend, Sawa was a mermaid living in the Vistula with whom Wars fell in love.[25] In actuality, Warsz was a 12th/13th-century nobleman who owned a village located at the modern-day site of the Mariensztat neighbourhood.[26] The official city name in full is miasto stołeczne Warszawa ("The Capital City of Warsaw").[27]
Other names for Warsaw include Varsovia (Latin, Spanish) and Varsóvia (Portuguese), Varsovie (French), Varsavia (Italian), Warschau (German, Dutch), װאַרשע /Varshe (Yiddish), Варшава / Varšava (Russian), Varšuva (Lithuanian), Varsó (Hungarian), Varšava (Croatian), (Serbian), (Slovene) and (Czech).
A native or resident of Warsaw is known as a Varsovian – in Polish warszawiak, warszawianin (male), warszawianka (female), warszawiacy, and warszawianie (plural).
History
1300–1800
.jpg)
The first fortified settlements on the site of today's Warsaw were located in Bródno (9th/10th century) and Jazdów (12th/13th century).[28] After Jazdów was raided by nearby clans and dukes, a new fortified settlement was established on the site of a small fishing village called "Warszowa". The Prince of Płock, Bolesław II of Masovia, established the modern-day city in about 1300 and the first historical document attesting to the existence of a castellany dates to 1313.[29] With the completion of St John's Cathedral in 1390, Warsaw became one of the seats of the Dukes of Masovia and was granted official capital status of the Masovian Duchy in 1413.[28] The economy then predominantly rested on craftsmanship or trade, and the town housed approximately 4,500 people at the time.
During the 15th century, the population migrated and spread beyond the northern city wall into a newly-formed self-governing precinct called New Town. The existing older settlement became eventually known as the Old Town. Both possessed their own town charter and independent councils. The aim of establishing a separate district was to accommodate new incomers or undesirables who were not permitted to settle in Old Town, particularly the Jews.[30] Social and financial disparities between the classes in the two precincts led to a minor revolt in 1525.[29] Following the sudden death of Janusz III and the extinction of the local ducal line, Masovia was incorporated into the Kingdom of Poland in 1526.[28] Bona Sforza, wife of Sigismund I of Poland, was widely accused of poisoning the duke to uphold Polish rule over Warsaw.[31][32]

In 1529, Warsaw for the first time became the seat of a General Sejm, and held that privilege permanently from 1569.[28] The city's rising importance encouraged the construction of a new set of defenses, including the landmark Barbican. Renowned Italian architects were brought to Warsaw to reshape the Royal Castle, the streets and the marketplace, resulting in the Old Town's early Italianate appearance. In 1573, the city gave its name to the Warsaw Confederation which formally established religious freedom in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. Due to its central location between the Commonwealth's two major cities of Kraków and Vilnius, Warsaw became the capital of the Commonwealth and the Polish Crown when Sigismund III Vasa transferred his royal court in 1596.[28] In the subsequent years the town significantly expanded to the south and westwards. Several private independent districts (jurydyka) were the property of aristocrats and the gentry, which they ruled by their own laws. Between 1655 and 1658 the city was besieged and pillaged by the Swedish, Brandenburgian and Transylvanian forces.[28][33] The conduct of the Great Northern War (1700–1721) also forced Warsaw to pay heavy tributes to the invading armies.[34]
The reign of Augustus II and Augustus III was a time of great development for Warsaw, which turned into an early-capitalist city. The Saxon monarchs employed many German architects, sculptors and engineers, who rebuilt the city in a style similar to Dresden. The year 1727 marked the opening of the Saxon Garden in Warsaw, one of the first publicly accessible parks in the world.[35][36] The Załuski Library, the first Polish public library and the largest at the time, was founded in 1747.[37] Stanisław II Augustus, who remodelled the interior of the Royal Castle, also made Warsaw a centre of culture and the arts.[38][39] He extended the Royal Baths Park and ordered the construction or refurbishment of numerous palaces, mansions and richly-decorated tenements. This earned Warsaw the nickname Paris of the North.[40]
Warsaw remained the capital of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth until 1795, when it was annexed by the Kingdom of Prussia in the third and final partition of Poland;[41] it subsequently became the capital of the province of South Prussia.
1800–1939

Warsaw was made the capital of a newly created French client state, known as the Duchy of Warsaw, after a portion of Poland's territory was liberated from Prussia, Russia and Austria by Napoleon in 1806.[28] Following Napoleon's defeat and exile, the 1815 Congress of Vienna assigned Warsaw to Congress Poland, a constitutional monarchy within the easternmost sector (or partition) under a personal union with Imperial Russia.[28] The Royal University of Warsaw was established in 1816.
With the violation of the Polish constitution, the 1830 November uprising broke out against foreign influence. The Polish-Russian war of 1831 ended in the uprising's defeat and in the curtailment of Congress Poland's autonomy.[28] On 27 February 1861, a Warsaw crowd protesting against Russian control over Congress Poland was fired upon by Russian troops.[42][43] Five people were killed. The Underground Polish National Government resided in Warsaw during the January Uprising in 1863–64.[43]


Warsaw flourished in throughout the 19th century under Mayor Sokrates Starynkiewicz (1875–92), who was appointed by Alexander III. Under Starynkiewicz Warsaw saw its first water and sewer systems designed and built by the English engineer William Lindley and his son, William Heerlein Lindley, as well as the expansion and modernisation of trams, street lighting, and gas infrastructure.[28] Between 1850 and 1882, the population grew by 134% to 383,000 as a result of rapid urbanisation and industrialisation. Many migrated from surrounding rural Masovian towns and villages to the city for employment opportunities. The western borough of Wola was transformed from an agricultural periphery occupied mostly by small farms and windmills (mills being the namesake of Wola's central neighborhood Młynów) to an industrial and manufacturing centre.[44] Metallurgical, textile and glassware factories were commonplace, with chimneys dominating the westernmost skyline.[45]
Similarly to London, Warsaw's population was subjected to income segmentation. Gentrification of inner suburbs forced poorer residents to move across the river into Praga or Powiśle districts, alike the East End of London and London Docklands.[46] Poorer religious and ethnic minorities such as the Jews settled in the crowded parts of northern Warsaw, in Muranów.[47] The Imperial Census of 1897 recorded 626,000 people living in Warsaw, making it the third-largest city of the Empire after St. Petersburg and Moscow as well as the largest city in the region.[48] Grand architectural complexes and structures were also erected in the city centre, including the Warsaw Philharmonic, the Church of the Holiest Saviour and tenements along Marszałkowska Street.
During World War I, Warsaw was occupied by Germany from 4 August 1915 until November 1918. The Armistice of 11 November 1918 concluded that defeated Germany is to withdraw from all foreign areas, which included Warsaw.[49] Germany did so, and underground leader Józef Piłsudski returned to Warsaw on the same day which marked the beginning of the Second Polish Republic, the first truly sovereign Polish state after 1795. In the course of the Polish–Soviet War (1919–1921), the 1920 Battle of Warsaw was fought on the eastern outskirts of the city. Poland successfully defended the capital, stopped the brunt of the Bolshevik Red Army and temporarily halted the "export of the communist revolution" to other parts of Europe.[50]
The interwar period (1918–1939) was a time of major development in the city's infrastructure. New modernist housing estates were built in Mokotów to de-clutter the densely populated inner suburbs. In 1921, Warsaw's total area was estimated at only 124.7 square kilometres with 1 million inhabitants–over 8,000 people per square kilometre made Warsaw more densely populated than contemporary London.[51] The Średnicowy Bridge was constructed for railway (1921–1931), connecting both parts of the city across the Vistula. Warszawa Główna railway station (1932–1939) was not completed due to the outbreak of the Second World War.
Stefan Starzyński was the Mayor of Warsaw between 1934 and 1939.
Second World War

After the German Invasion of Poland on 1 September 1939 started the Second World War, Warsaw was defended until 27 September. Central Poland, including Warsaw, came under the rule of the General Government, a German Nazi colonial administration. All higher education institutions were immediately closed and Warsaw's entire Jewish population – several hundred thousand, some 30% of the city – were herded into the Warsaw Ghetto.[53] In July on 1942, the Jews of the Warsaw Ghetto began to be deported en masse to the Aktion Reinhard extermination camps, particularly Treblinka.[53] The city would become the centre of urban resistance to Nazi rule in occupied Europe.[54] When the order came to annihilate the ghetto as part of Hitler's "Final Solution" on 19 April 1943, Jewish fighters launched the Warsaw Ghetto uprising.[55] Despite being heavily outgunned and outnumbered, the Ghetto held out for almost a month.[55] When the fighting ended, almost all survivors were massacred, with only a few managing to escape or hide.[55][56]
By July 1944, the Red Army was deep into Polish territory and pursuing the Nazis toward Warsaw.[58] Knowing that Stalin was hostile to the idea of an independent Poland, the Polish government-in-exile in London gave orders to the underground Home Army (AK) to try to seize control of Warsaw before the Red Army arrived. Thus, on 1 August 1944, as the Red Army was nearing the city, the Warsaw uprising began.[58] The armed struggle, planned to last 48 hours, was partially successful, however it went on for 63 days. Eventually the Home Army fighters and civilians assisting them were forced to capitulate.[58] They were transported to PoW camps in Germany, while the entire civilian population was expelled.[58] Polish civilian deaths are estimated at between 150,000 and 200,000.[59]
Hitler, ignoring the agreed terms of the capitulation, ordered the entire city to be razed to the ground and the library and museum collections taken to Germany or burned.[58] Monuments and government buildings were blown up by special German troops known as Verbrennungs- und Vernichtungskommando ("Burning and Destruction Detachments").[58] About 85% of the city was destroyed, including the historic Old Town and the Royal Castle.[60]
On 17 January 1945 – after the beginning of the Vistula–Oder Offensive of the Red Army – Soviet troops and Polish troops of the First Polish Army entered the ruins of Warsaw, and liberated Warsaw's suburbs from German occupation.[61] The city was swiftly taken by the Soviet Army, which rapidly advanced towards Łódź, as German forces regrouped at a more westward position.
1945–1989

In 1945, after the bombings, revolts, fighting, and demolition had ended, most of Warsaw lay in ruins. The area of the former Warsaw Ghetto was razed to the ground, with only a sea of rubble remaining. However, the city officially resumed its role as the capital of Poland and the country's centre of political and economic life.
After World War II, the "Bricks for Warsaw" campaign was initiated and large prefabricated housing projects were erected in Warsaw to address the major housing shortage. Plattenbau apartment blocks were a solution to avoid Warsaw's former density problem and to create more green spaces. Some of the buildings from the 19th century that have survived in a reasonably reconstructible form were nonetheless demolished in the 1950s and 1960s, like the Kronenberg Palace.[62][63] The Śródmieście (central) region's urban system was completely reshaped; former cobblestone streets were asphalted and significantly widened for traffic use. Many notable streets such as Gęsia, Nalewki and Wielka disappeared as a result of these changes and some were split in half due to the construction of Plac Defilad (Parade Square), one of the largest of its kind in Europe.[64]
Much of the central district was also designated for future skyscrapers. The 237-metre Palace of Culture and Science resembling New York's Empire State Building was built as a gift from the Soviet Union.[65] Warsaw's urban landscape is one of modern and contemporary architecture.[66] Despite wartime destruction and post-war remodelling, many of the historic streets, buildings, and churches were restored to their original form. In 1980, Warsaw's historic Old Town was inscribed onto UNESCO's World Heritage list.[67]
John Paul II's visits to his native country in 1979 and 1983 brought support to the budding "Solidarity" movement and encouraged the growing anti-communist fervor there.[68] In 1979, less than a year after becoming pope, John Paul celebrated Mass in Victory Square in Warsaw and ended his sermon with a call to "renew the face" of Poland.[68] These words were meaningful for Varsovians and Poles who understood them as the incentive for liberal-democratic reforms.[68]
1989–present
In 1995, the Warsaw Metro opened with a single line. A second line was opened in March 2015.[69] With the entry of Poland into the European Union in 2004, Warsaw is experiencing the largest economic boom of its history.[70] The opening fixture of UEFA Euro 2012 took place in Warsaw[71] and the city also hosted the 2013 United Nations Climate Change Conference and the 2016 NATO Summit.
Geography
Location and topography

Warsaw lies in east-central Poland about 300 km (190 mi) from the Carpathian Mountains and about 260 km (160 mi) from the Baltic Sea, 523 km (325 mi) east of Berlin, Germany.[72] The city straddles the Vistula River. It is located in the heartland of the Masovian Plain, and its average elevation is 100 metres (330 ft) above sea level. The highest point on the left side of the city lies at a height of 115.7 metres (379.6 ft) ("Redutowa" bus depot, district of Wola), on the right side – 122.1 metres (400.6 ft) ("Groszówka" estate, district of Wesoła, by the eastern border). The lowest point lies at a height 75.6 metres (248.0 ft) (at the right bank of the Vistula, by the eastern border of Warsaw). There are some hills (mostly artificial) located within the confines of the city – e.g. Warsaw Uprising Hill (121 metres (397.0 ft)) and Szczęśliwice hill (138 metres (452.8 ft) – the highest point of Warsaw in general).

Warsaw is located on two main geomorphologic formations: the plain moraine plateau and the Vistula Valley with its asymmetrical pattern of different terraces. The Vistula River is the specific axis of Warsaw, which divides the city into two parts, left and right. The left one is situated both on the moraine plateau (10 to 25 m (32.8 to 82.0 ft) above Vistula level) and on the Vistula terraces (max. 6.5 m (21.3 ft) above Vistula level). The significant element of the relief, in this part of Warsaw, is the edge of moraine plateau called Warsaw Escarpment. It is 20 to 25 m (65.6 to 82.0 ft) high in the Old Town and Central district and about 10 m (32.8 ft) in the north and south of Warsaw. It goes through the city and plays an important role as a landmark.
The plain moraine plateau has only a few natural and artificial ponds and also groups of clay pits. The pattern of the Vistula terraces is asymmetrical. The left side consists mainly of two levels: the highest one contains former flooded terraces and the lowest one the flood plain terrace. The contemporary flooded terrace still has visible valleys and ground depressions with water systems coming from the old Vistula – riverbed. They consist of still quite natural streams and lakes as well as the pattern of drainage ditches. The right side of Warsaw has a different pattern of geomorphological forms. There are several levels of the Vistula plain terraces (flooded as well as formerly flooded), and only a small part is a not so visible moraine escarpment. Aeolian sand with a number of dunes parted by peat swamps or small ponds cover the highest terrace. These are mainly forested areas (pine forest).
Climate

Officially, Warsaw experiences an oceanic climate, denoted by Cfb by Köppen's original classification.[73][74] But the city being in the midst of Siberian air mass and far from the coast has clear continental influences (Dfb), defined as such with old data.[75][76][77][78] By the Köppen-Geiger climate classification measure, Warsaw is defined as having a humid continental climate (Köppen climate classification Dfb), with long cold winters and short warm summers, though the urban heat island effect does make Warsaw's winters slightly less severe than in the surrounding rural areas.[79][80] However, by classification of the Wincenty Okołowicz, it has a warm-temperate climate in the center of continental Europe with the "fusion" of different features.[81]
The city has cold, sometimes snowy, cloudy winters and warm, sunny, stormy summers. Spring and autumn can be unpredictable, highly prone to sudden weather changes; however, temperatures are usually mild and with low humidity, especially around May and September.[75] The average temperature ranges between −1.8 °C (29 °F) in January and 19.2 °C (66.6 °F) in July. The mean year temperature is 8.5 °C (47.3 °F). Temperatures may often reach 30 °C (86 °F) in the summer, although the effects of hot weather are usually offset by relatively low dew points and large diurnal temperature differences. Warsaw is Europe's sixth driest major city (third in Eastern Europe), with yearly rainfall averaging 529 millimetres (20.8 in), the wettest month being July.[82]
| Climate data for Warsaw (WAW), 1981–2010 normals[lower-alpha 1], extremes 1951–present | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 13.0 (55.4) |
17.2 (63.0) |
22.9 (73.2) |
30.4 (86.7) |
32.8 (91.0) |
35.1 (95.2) |
35.9 (96.6) |
37.0 (98.6) |
31.1 (88.0) |
25.9 (78.6) |
18.9 (66.0) |
15.4 (59.7) |
37.0 (98.6) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 0.6 (33.1) |
1.9 (35.4) |
6.6 (43.9) |
13.6 (56.5) |
19.5 (67.1) |
21.9 (71.4) |
24.4 (75.9) |
23.9 (75.0) |
18.4 (65.1) |
12.7 (54.9) |
5.9 (42.6) |
1.6 (34.9) |
12.6 (54.7) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −1.8 (28.8) |
−0.6 (30.9) |
2.8 (37.0) |
8.7 (47.7) |
14.2 (57.6) |
17.0 (62.6) |
19.2 (66.6) |
18.3 (64.9) |
13.5 (56.3) |
8.5 (47.3) |
3.3 (37.9) |
−0.7 (30.7) |
8.5 (47.3) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −4.2 (24.4) |
−3.6 (25.5) |
−0.6 (30.9) |
3.9 (39.0) |
8.9 (48.0) |
11.8 (53.2) |
13.9 (57.0) |
13.1 (55.6) |
9.1 (48.4) |
4.8 (40.6) |
0.6 (33.1) |
−3.0 (26.6) |
4.6 (40.3) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −31.0 (−23.8) |
−27.6 (−17.7) |
−22.6 (−8.7) |
−7.2 (19.0) |
−3.1 (26.4) |
1.6 (34.9) |
4.6 (40.3) |
3.0 (37.4) |
−2.0 (28.4) |
−9.6 (14.7) |
−17.0 (1.4) |
−24.8 (−12.6) |
−31.0 (−23.8) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 27 (1.1) |
26 (1.0) |
31 (1.2) |
34 (1.3) |
56 (2.2) |
69 (2.7) |
73 (2.9) |
64 (2.5) |
46 (1.8) |
32 (1.3) |
37 (1.5) |
34 (1.3) |
529 (20.8) |
| Average rainy days | 12 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 14 | 13 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 14 | 163 |
| Average snowy days | 14 | 14 | 9 | 2 | 0.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 7 | 14 | 61 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 87 | 85 | 78 | 71 | 70 | 72 | 73 | 74 | 81 | 84 | 89 | 89 | 79 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 42 | 67 | 108 | 155 | 218 | 230 | 235 | 219 | 143 | 102 | 41 | 29 | 1,589 |
| Average ultraviolet index | 1 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 3 |
| Source: Pogodaiklimat.ru[83], NOAA[84][85] and Weather Atlas[86] | |||||||||||||
- Sunshine data is calculated at Warsaw-Bielany weather station from 1961–1990. Rest of the climate data is recorded at Warsaw-Okecie.
| Climate data for Warsaw | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily daylight hours | 8.0 | 10.0 | 12.0 | 14.0 | 16.0 | 17.0 | 16.0 | 15.0 | 13.0 | 11.0 | 9.0 | 8.0 | 12.4 |
| Source: Weather Atlas (sunshine data) [87] | |||||||||||||
Cityscape
Urbanism and architecture
Warsaw's long and eclectic history left a noticeable mark on its architecture and urban form. Unlike most Polish cities, Warsaw's cityscape is mostly contemporary – modern glass buildings are towering above older historical edifices which is a common feature of North American metropolises. A concentric zone pattern emerged within the last decades; the majority of Warsaw's residents live outside the commercial city centre and commute by metro, bus or tram.[88] Tenements and apartments in the central neighbourhoods are often reserved for commercial activity or temporary (tourist, student) accommodation. The nearest residential zones are predominantly located on the outskirts of the inner borough, in Ochota, Mokotów and Żoliborz or along the Vistula in Powiśle.[88]
A seat of Polish monarchs since the end of the 16th century, Warsaw remained a small city with only privately-owned palaces, mansions, villas and several streets of townhouses. These displayed a richness of colour and architectonic details. The finest German, Italian and Dutch architects were employed, among them Tylman van Gameren, Andreas Schlüter, Jakub Fontana and Enrico Marconi.[89] The buildings situated in the vicinity of the Warsaw Old Town represent nearly every European architectural style and historical period. Warsaw has excellent examples of architecture from the Gothic, Renaissance, Baroque and Neoclassical periods, all of which are located within walking distance of the centre.
Gothic architecture is represented in the majestic churches but also at the burgher houses and fortifications. The most significant buildings are St John's Cathedral (1390), a typical example of the so-called Masovian Brick Gothic style; St Mary's Church (1411); the Burbach townhouse (14th century);[90] Gunpowder Tower (after 1379); and Royal Castle's Curia Maior (1407–1410). The most notable examples of Renaissance architecture in the city are the house of the Baryczko merchant family (1562), a building called "The Negro" (early 17th century), and Salwator tenement (1632), all situated on the Old Market Place. The most interesting examples of Mannerist architecture are the Royal Castle (1596–1619) and the Jesuit Church (1609–1626). Among the first structures of the early Baroque, the most important are St. Hyacinth's Church (1603–1639) and Sigismund's Column (1644), the first secular monument in the form of a column in modern history.[91]

Some of the best examples of palatial Baroque architecture are Krasiński Palace (1677–1683), Wilanów Palace (1677–1696) and St Kazimierz Church (1688–1692). The most impressive examples of rococo architecture are Czapski Palace (1712–1721), Palace of the Four Winds (1730s) and Visitationist Church (façade 1728–1761). The neoclassical architecture in Warsaw can be described by the simplicity of the geometrical forms teamed with a great inspiration from the Roman period. Some of the best examples of the neoclassical style are the Palace on the Isle (1775–1795), Królikarnia (1782–1786), Carmelite Church (façade 1761–1783) and the Holy Trinity Church (1777–1782). The neoclassical revival affected all aspects of architecture; the most notable examples are the Great Theater (1825–1833) and buildings located at Bank Square (1825–1828).
Exceptional examples of the bourgeois architecture of the later periods were not restored by the communist authorities after the war or were remodelled into a socialist realist style (like Warsaw Philharmonic edifice originally inspired by Palais Garnier in Paris). Despite that, the Warsaw University of Technology (Polytechnic) building (1899–1902)[92] is the most interesting of the late 19th-century architecture. Some 19th-century industrial and brick workhouse buildings in the Praga district were restored, though many have been poorly maintained or demolished. Some of the important landmarks lost are the Saxon Palace and the Brühl Palace, the most distinctive buildings in prewar Warsaw.[93]
Notable examples of post-war architecture include the Palace of Culture and Science (1952–1955), a soc-realist and art deco skyscraper based on the Empire State Building in New York. The Constitution Square with its monumental socialist realism architecture (MDM estate) was modelled on the grand squares of Paris, London, Moscow and Rome.[94] Italianate tuscan-styled colonnades based on those at Piazza della Repubblica in Rome were also erected on Saviour Square.[95]
Contemporary architecture in Warsaw is represented by the Metropolitan Office Building at Pilsudski Square by Norman Foster,[96] Warsaw University Library (BUW) by Marek Budzyński and Zbigniew Badowski, featuring a garden on its roof and view of the Vistula River, Rondo 1 office building by Skidmore, Owings & Merrill, Museum of the History of Polish Jews by Rainer Mahlamäki and Golden Terraces, consisting of seven overlapping domes retail and business centre. Jointly with Frankfurt, London, Paris and Rotterdam, Warsaw is one of the cities with the highest number of skyscrapers in Europe.[15][97]
Landmarks

Map of Warsaw Old Town 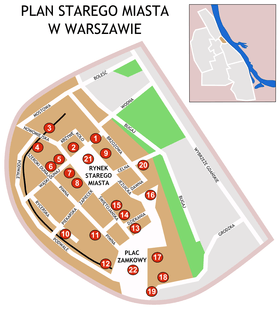
|
Although contemporary Warsaw is a fairly young city compared to other European capitals, it has numerous tourist attractions and architectural monuments dating back centuries. Apart from the Warsaw Old Town quarter, reconstructed after World War II, each borough has something to offer. Among the most notable landmarks of the Old Town are the Royal Castle, Sigismund's Column, Market Square, and the Barbican.
Further south is the so-called Royal Route, with many historical churches, Baroque and Classicist palaces, most notably the Presidential Palace, and the University of Warsaw campus. The former royal residence of King John III Sobieski at Wilanów is notable for its Baroque architecture and eloquent palatial garden.[98]
Powązki Cemetery is one of the oldest cemeteries in Europe,[99] featuring of sculptures, some of them by the most renowned Polish artists of the 19th and 20th centuries. Since it serves the religious communities of Warsaw such as Catholics, Jews, Orthodox Christians, Muslims or Protestants, it is often called a necropolis. Nearby is the Okopowa Street Jewish Cemetery, one of the largest Jewish cemeteries in Europe.

In many places in the city the Jewish culture and history resonates down through time.[100] Among them the most notable are the Jewish theater, the Nożyk Synagogue, Janusz Korczak's Orphanage and the picturesque Próżna Street.[100] The tragic pages of Warsaw's history are commemorated in places such as the Monument to the Ghetto Heroes, the Umschlagplatz, fragments of the Ghetto wall on Sienna Street and a mound in memory of the Jewish Combat Organization.[100]
There are also many places commemorating the heroic history of Warsaw.[101] Pawiak, an infamous German Gestapo prison now occupied by a Mausoleum of Memory of Martyrdom and the museum, is only the beginning of a walk in the traces of Heroic City.[101] The Warsaw Citadel, an impressive 19th-century fortification built after the defeat of the November uprising, was a place of martyrdom for the Poles.[101] Another important monument, the statue of Little Insurrectionist located at the ramparts of the Old Town, commemorates the children who served as messengers and frontline troops in the Warsaw Uprising, while the impressive Warsaw Uprising Monument by Wincenty Kućma was erected in memory of the largest insurrection of World War II.[101][102]
In Warsaw there are many places connected with the life and work of Frédéric Chopin who was born near the city in Żelazowa Wola. The heart of the Polish composer is sealed inside Warsaw's Holy Cross Church.[103] During the summer time the Chopin Statue in Łazienki Park is a place where pianists give concerts to the park audience.[104]
Also many references to Marie Curie, her work and her family can be found in Warsaw; Curie's birthplace at the Warsaw New Town, the working places where she did her first scientific works[105] and the Radium Institute at Wawelska Street for the research and the treatment of which she founded in 1925.[106]


 Carmelite Church has an original 18th-century façade
Carmelite Church has an original 18th-century façade- Wilanów Palace, once a royal residence
- Belweder Palace, official seat of the President
.jpg)
 Krasiński Palace, a branch of the National Library
Krasiński Palace, a branch of the National Library Canon Square (Kanonia) with the narrowest townhouse in Europe
Canon Square (Kanonia) with the narrowest townhouse in Europe
 Three Crosses Square marks the entry into Old Town
Three Crosses Square marks the entry into Old Town Barbican, a remaining relic of historic fortifications.
Barbican, a remaining relic of historic fortifications.
Flora and fauna
Green space covers almost a quarter of Warsaw's total area.[107] These range from small neighborhood parks and green spaces along streets or in courtyards, to tree-lined avenues, large historic parks, nature conservation areas and urban forests at the fringe of the city. There are as many as 82 parks in the city;[108] the oldest ones were once part of representative palaces and include the Saxon and Krasiński Gardens, Łazienki Park (Royal Baths Park) and Wilanów Palace Parkland.
.jpg)
The Saxon Garden, covering an area of 15.5 ha, formally served as a royal garden to the now nonexistent Saxon Palace. In 1727, it was made into one of the world's first public parks and later remodelled in the forest-like English style. The Tomb of the Unknown Soldier is situated at the east end of the park near the central fountain, on Piłsudski Square. With its benches, flower carpets and a central pond, the Krasiński Palace Garden was once a notable strolling destination for most Varsovians. The Łazienki Park covers an area of 76 ha and its unique character and history is reflected in the landscape architecture (pavilions, sculptures, bridges, water cascades) and vegetation (domestic and foreign species of trees and shrubs). The presence of peacocks, pheasants and squirrels at Łazienki attracts tourists and locals. The Wilanów Palace Parkland on the outskirts of Warsaw traces it history to the second half of the 17th century and covers an area of 43 ha. Its French-styled alleys corresponds to the ancient, Baroque forms of the palace.

The Botanical Garden and the University Library rooftop garden host an extensive collection of rare domestic and foreign plants, while a palm house in the New Orangery displays plants of subtropics from all over the world.[109] Mokotów Field (once a racetrack), Ujazdów Park and Skaryszewski Park are also located within the city borders. The oldest park in the Praga borough was established between 1865 and 1871.[110]
The flora of Warsaw may be considered very rich in species on city standards. This is mainly due to the location of Warsaw within the border region of several big floral regions comprising substantial proportions of close-to-wilderness areas (natural forests, wetlands along the Vistula) as well as arable land, meadows and forests. The nearby Kampinos Nature Reserve is the last remaining part of the Masovian Primeval Forest and is protected by law.[111] The Kabaty Woods are by the southern city border and are visited by the residents of southern boroughs such as Ursynów. There are 13 natural reserves in the vicinity and just 15 kilometres (9 miles) from Warsaw, the environment features a perfectly preserved ecosystem with a habitat of animals like the otter, beavers and hundreds of bird species.[112] There are also several lakes in Warsaw – mainly the oxbow lakes at Czerniaków and Kamionek.

The Warsaw Zoo covers an area of 40 hectares (99 acres).[113] There are about 5,000 animals representing nearly 500 species.[113] Although officially created in 1928,[113] it traces back its roots to 17th century private menageries, often open to the public.[114][115]
Demographics
Demographically, Warsaw was the most diverse city in Poland, with significant numbers of foreign-born residents.[116] In addition to the Polish majority, there was a large and thriving Jewish minority. According to the Imperial Census of 1897, out of the total population of 638,000, Jews constituted 219,000 (equivalent to 34%).[117] Prior to the Second World War, Warsaw hosted the world's second largest Jewish population after New York – approximately 30 percent of the city's total population in the late 1930s.[53] In 1933, 833,500 out of 1,178,914 people declared Polish as their mother tongue.[118] There was also a notable German community.[119] The ethnic composition of contemporary Warsaw is incomparable to the diversity that existed for nearly 300 years.[53] Most of the modern-day population growth is based on internal migration and urbanisation.
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1700 | 30,000 | — |
| 1792 | 120,000 | +300.0% |
| 1800 | 63,400 | −47.2% |
| 1830 | 139,700 | +120.3% |
| 1850 | 163,600 | +17.1% |
| 1882 | 383,000 | +134.1% |
| 1901 | 711,988 | +85.9% |
| 1909 | 764,054 | +7.3% |
| 1925 | 1,003,000 | +31.3% |
| 1933 | 1,178,914 | +17.5% |
| 1939 | 1,300,900 | +10.3% |
| 1945 | 422,000 | −67.6% |
| 1950 | 803,800 | +90.5% |
| 1960 | 1,136,000 | +41.3% |
| 1970 | 1,315,600 | +15.8% |
| 1980 | 1,596,100 | +21.3% |
| 1990 | 1,655,700 | +3.7% |
| 2000 | 1,672,400 | +1.0% |
| 2005 | 1,697,500 | +1.5% |
| 2010 | 1,710,398 | +0.8% |
| 2015 | 1,744,351 | +2.0% |
| 2019 | 1,783,321 | +2.2% |
| Note: 2010[120] 2014[121] 2018[1] | ||
| Foreign residents (2019)[122] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nationality | Population | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14,765 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3,448 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2,957 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1,882 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1,837 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1,080 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 891 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 845 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
In 1939, approximately 1,300,000 people resided in Warsaw;[123] by 1945 the population had dropped to 420,000. During the first years after the war, the population growth rate was high and the city soon began to suffer from the lack of flats and dwellings to house new incomers. The first remedial measure was the enlargement of Warsaw's total area (1951) – however the city authorities were still forced to introduce limitations; only the spouses and children of permanent residents as well as some persons of public importance (renowned specialists, artists, engineers) were permitted to stay. This negatively affected the image of an average Warsaw citizen, who was perceived as more privileged than those migrating from rural areas, towns or other cities. While all restrictions on residency registration were scrapped in 1990, the negative opinion of Varsovians in some form continues to this day.[124][125]
Immigrant population
Much like most capital cities in Europe, Warsaw boasts a foreign-born population that is significantly larger than in other cities, although not coming close to the figures representing the likes of Madrid or Rome. In 2019, it was estimated that 40,000 people living in Warsaw were born overseas, although it is suspected that the actual number could range between 60,000 and 150,000,[126] or 1.2~3.4% – 8.5% of all Varsovians. Of those, Ukrainians, Vietnamese, Belarusians, Russians and Indians were the most prominent groups.[127]
Religion
Throughout its existence, Warsaw had been a multi-cultural and multi-religious city.[128] According to the 1901 census, out of 711,988 inhabitants 56.2% were Catholics, 35.7% Jews, 5% Greek Orthodox Christians and 2.8% Protestants.[129] Eight years later, in 1909, there were 281,754 Jews (36.9%), 18,189 Protestants (2.4%) and 2,818 Mariavites (0.4%).[130] This led to construction of hundreds of places of religious worship in all parts of the town. Most of them were destroyed in the aftermath of the Warsaw Uprising in 1944. After the war, the new communist authorities of Poland discouraged church construction and only a small number were rebuilt.[131]

The Archdiocese of Warsaw and the Diocese of Warsaw-Praga are the two ecclesiastical districts active in the city which serve the large Roman Catholic population of 1.4 million.[132] The Lutheran Diocese of Warsaw is one of six in Poland; its main temple is the Holy Trinity Church from 1782, one of Warsaw's most important and historic landmarks. The Evangelical Reformed Parish (Calvinist) is leading the Polish Reformed Church. The main tserkva of the Orthodox Christians is Praga's Cathedral of St. Mary Magdalene from 1869. The Jewish Commune of Warsaw (Gmina Wyznaniowa Żydowska) is one of eight in the country; Chief Rabbi of Poland Michael Schudrich resides in the city. There are also 3 active synagogues, one of which is the pre-war Nożyk Synagogue designated for Orthodox Jews. A small mosque in Wilanów serves the Muslims.
Government and politics
As the capital of Poland, Warsaw is the political centre of the country. All state agencies are located there, including the Polish Parliament, the Presidential Office and the Supreme Court. In the Polish parliament the city and the area are represented by 31 MPs (out of 460). Additionally, Warsaw elects two MEPs (Members of the European Parliament).
The Sejm, the lower house of the Polish parliament, is situated in Warsaw on Wiejska Street. The Sejm is composed of 460 members (in Polish deputowany or poseł). It is elected by universal ballot and is presided over by a speaker called the Marshal of the Sejm (Marszałek Sejmu).
Municipal government
The municipal government existed in Warsaw until World War II and was restored in 1990 (during the communist times, the National City Council – Miejska Rada Narodowa – governed in Warsaw). Since 1990, the system of city administration has been changed several times – also as the result of the reform which restored powiats, cancelled in 1975. Finally, according to the Warsaw Act, the city is divided into 18 districts and forms one city powiat with a unified municipal government.[133]

The basic unit of territorial division in Poland is a commune (gmina).[134] A city is also a commune – but with a city charter.[134] Both cities and communes are governed by a mayor – but in the communes the mayor is vogt (wójt in Polish), however in the cities – burmistrz. Some bigger cities obtain the entitlements, i.e. tasks and privileges, which are possessed by the units of the second level of the territorial division – counties (powiaty in Polish). An example of such entitlement is a car registration: a gmina cannot register cars, this is a powiat's task (i.e. a registration number depends on what powiat a car had been registered in, not the gmina). In this case we say "city county" or powiat grodzki. Such cities are for example Lublin, Kraków, Gdańsk, and Poznań. In Warsaw, its districts additionally have some of a powiat's entitlements – like the already mentioned car registration. For example, the Wola district has its own evidence and the Ursynów district – its own (and the cars from Wola have another type of registration number than those from Ursynów). But for instance the districts in Kraków do not have the entitlements of a powiat, so the registration numbers in Kraków are of the same type for all districts.

Legislative power in Warsaw is vested in a unicameral Warsaw City Council (Rada Miasta), which comprises 60 members.[133] Council members are elected directly every five years (since 2018 election). Like most legislative bodies, the city council divides itself into committees which have the oversight of various functions of the city government.[133] Bills passed by a simple majority are sent to the mayor (the President of Warsaw), who may sign them into law. If the mayor vetoes a bill, the Council has 30 days to override the veto by a two-thirds majority vote.
Each of the 18 separate city districts has its own council (Rada dzielnicy).[133] Their duties are focused on aiding the President and the City Council, as well as supervising various municipal companies, city-owned property and schools. The head of each of the District Councils is named the Mayor (Burmistrz) and is elected by the local council from the candidates proposed by the President of Warsaw.
The mayor of Warsaw is called President. Generally, in Poland, the mayors of bigger cities are called presidents – i.e. cities with over 100,000 people or that had a president before 1990. The first Warsaw President was Jan Andrzej Menich (1695–1696).[135] Between 1975 and 1990 the Warsaw presidents simultaneously led the Warsaw Voivode. Since 1990 the President of Warsaw had been elected by the city council.[136] In the years of 1994–1999 the mayor of the district Centrum automatically was designated as the President of Warsaw: the mayor of Centrum was elected by the district council of Centrum and the council was elected only by the Centrum residents. Since 2002 the President of Warsaw is elected by all of the citizens of Warsaw.[136]
The President of Warsaw is Rafał Trzaskowski. The first president elected according these rules was Lech Kaczyński. When he was elected as the President of Polish Republic (December 2005) he resigned as mayor on the day before taking office.
- Headquarters of Polish government agencies in Warsaw


.jpg) The Presidential Palace, seat of the Polish president
The Presidential Palace, seat of the Polish president

 The seat of the administration of the Masovian Voivodeship
The seat of the administration of the Masovian Voivodeship- Mostowski Palace, the seat of Warsaw's police headquarters
 The main gate of the Ministry of Health
The main gate of the Ministry of Health
Districts
| District | Population | Area |
|---|---|---|
| Mokotów | 220,682 | 35.4 km2 (13.7 sq mi) |
| Praga Południe | 178,665 | 22.4 km2 (8.6 sq mi) |
| Ursynów | 145,938 | 48.6 km2 (18.8 sq mi) |
| Wola | 137,519 | 19.26 km2 (7.44 sq mi) |
| Bielany | 132,683 | 32.3 km2 (12.5 sq mi) |
| Targówek | 123,278 | 24.37 km2 (9.41 sq mi) |
| Śródmieście | 122,646 | 15.57 km2 (6.01 sq mi) |
| Bemowo | 115,873 | 24.95 km2 (9.63 sq mi) |
| Białołęka | 96,588 | 73.04 km2 (28.20 sq mi) |
| Ochota | 84,990 | 29.7 km2 (11.5 sq mi) |
| Wawer | 69,896 | 79.71 km2 (30.78 sq mi) |
| Praga Północ | 69,510 | 11.4 km2 (4.4 sq mi) |
| Ursus | 53,755 | 29.35 km2 (11.33 sq mi) |
| Żoliborz | 48,342 | 28.5 km2 (11.0 sq mi) |
| Włochy | 38,075 | 28.63 km2 (11.05 sq mi) |
| Wilanów | 23,960 | 36.73 km2 (14.18 sq mi) |
| Rembertów | 23,280 | 19.30 km2 (7.45 sq mi) |
| Wesoła | 22,811 | 22.6 km2 (8.7 sq mi) |
| Total | 1,708,491[137] | 521.81 km2 (201.47 sq mi) |
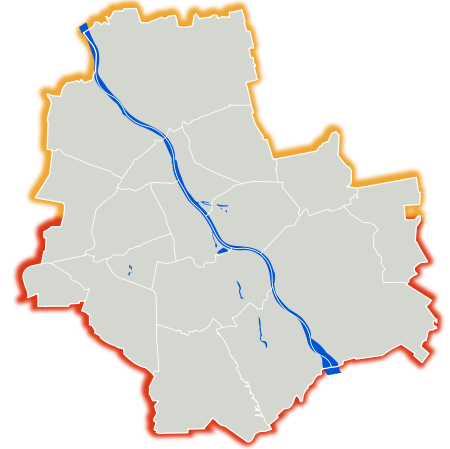
Until 1994, there were 7 districts in Warsaw: Śródmieście, Praga Północ, Praga Południe, Żoliborz, Wola, Ochota, and Mokotów. Between 1994 and 2002, there were 11 districts: Centrum, Białołęka, Targówek, Rembertów, Wawer, Wilanów, Ursynów, Włochy, Ursus, Bemowo, and Bielany. In 2002, the town Wesoła was incorporated and the territorial division of Warsaw was established as follows:
Warsaw is a county (powiat), and is further divided into 18 districts (dzielnica),[138] each one with its own administrative body.[139] Each of the districts is customarily subdivided into several neighbourhoods which have no legal or administrative status. Warsaw has two historic neighbourhoods, called Old Town (Stare Miasto) and New Town (Nowe Miasto), in the borough of Śródmieście.[140]
Economy
In 2011, Warsaw was ranked the world's 46th most expensive city to live in.[141] It was classified as an alpha world city (also known as a "major global city that links economic regions into the world economy") by the Globalization and World Cities (GaWC) Study Group and Network from Loughborough University, placing it on a par with cities such as Sydney, Istanbul, Amsterdam or Seoul.
Business and commerce

Warsaw, especially its city centre (Śródmieście), is home not only to many national institutions and government agencies, but also to many domestic and international companies. In 2006, 304,016 companies were registered in the city.[142] Warsaw's ever-growing business community has been noticed globally, regionally, and nationally. MasterCard Emerging Market Index has noted Warsaw's economic strength and commercial center. Warsaw was ranked as the seventh-greatest emerging market. Foreign investors' financial participation in the city's development was estimated in 2002 at over 650 million €.
Warsaw produces 12% of Poland's national income,[143] which in 2008 was 305.1% of the Polish average per capita (or 160% of the European Union average). The Nominal GDP per capita in Warsaw amounted to 140,000 Polish Zloty in 2017 (c. €32,500 or around $80,000 in PPP[144]).[145] Warsaw leads East-Central Europe in foreign investment and in 2006, GDP growth met expectations with a level of 6.1%.[146] It also has one of the fastest growing economies, with GDP growth at 6.5 percent in 2007 and 6.1 percent in the first quarter of 2008.[147]
At the same time the unemployment rate is one of the lowest in Poland, at around 4% in February 2015.[148] The city itself receives around 8,740,882,000 złotys in taxes and direct government grants.
Warsaw Stock Exchange

Warsaw's first stock exchange was established in 1817 and continued trading until World War II. It was re-established in April 1991, following the end of the post-war communist control of the country and the reintroduction of a free-market economy.[149] Today, the Warsaw Stock Exchange (WSE) is, according to many indicators,[147] the largest market in the region, with 374 companies listed and total capitalisation of 162,584 mln EUR as of 31 August 2009.[150] From 1991 until 2000, the stock exchange was, ironically, located in the building previously used as the headquarters of the Polish United Workers' Party (PZPR).[151]
Industry
During Warsaw's reconstruction after World War II, the communist authorities decided that the city would become a major industrial centre. As a result, numerous large factories were built in and around the city. The largest were the Huta Warszawa Steel Works, the FSO car factory and the "Ursus" tractor factory.

As the communist economy deteriorated, these factories lost significance and most went bankrupt after 1989.[152][153] Today, the Arcelor Warszawa Steel mill (formerly Huta Warszawa) is the only major factory remaining.
The FSO Car Factory was established in 1951. A number of vehicles have been assembled there over the decades, including the Warszawa, Syrena, Fiat 125p (under license from Fiat, later renamed FSO 125p when the license expired) and the Polonez. The last two models listed were also sent abroad and assembled in a number of other countries, including Egypt and Colombia. In 1995 the factory was purchased by the South Korean car manufacturer Daewoo, which assembled the Tico, Espero, Nubia, Tacuma, Leganza, Lanos and Matiz there for the European market. In 2005 the factory was sold to AvtoZAZ, a Ukrainian car manufacturer which assembled the Chevrolet Aveo there. The license for the production of the Aveo expired in February 2011 and has not been renewed since. The company is defunct.
The "Ursus" factory opened in 1893 and is still in operation. Throughout its history various machinery was assembled there, including motorcycles, military vehicles, trucks and buses; but since World War II it has produced only tractors.
The number of state-owned enterprises continues to decrease while the number of companies operating with foreign capital is on the rise, reflecting the continued shift towards a modern market-based economy.[152] The largest foreign investors are Coca-Cola Amatil and Metro AG.[152] Warsaw has the biggest concentration of electronics and high-tech industry in Poland, while the growing consumer market perfectly fosters the development of the food-processing industry.[152]
Education
Higher education in Warsaw Name and year established
|
Warsaw holds some of the finest institutions of higher education in Poland. It is home to four major universities and over 62 smaller schools of higher education.[154] The overall number of students of all grades of education in Warsaw is almost 500,000 (29.2% of the city population; 2002). The number of university students is over 280,000.[155] Most of the reputable universities are public, but in recent years there has also been an upsurge in the number of private universities.

The University of Warsaw was established in 1816, when the partitions of Poland separated Warsaw from the oldest and most influential Polish academic center, in Kraków.[156] Warsaw University of Technology is the second academic school of technology in the country, and one of the largest in East-Central Europe, employing 2,000 professors.[157] Other institutions for higher education include the Medical University of Warsaw, the largest medical school in Poland and one of the most prestigious; the National Defence University, highest military academic institution in Poland; the Fryderyk Chopin University of Music, the oldest and largest music school in Poland and one of the largest in Europe;[158] the Warsaw School of Economics, the oldest and most renowned economic university in the country;[159] the Warsaw University of Life Sciences, the largest agricultural university, founded in 1818;[160] and the University of Social Sciences and Humanities, the first private secular university in the country.

Warsaw has numerous libraries, many of which contain vast collections of historic documents. The most important library in terms of historic document collections is the National Library of Poland. The library holds 8.2 million volumes in its collection.[161] Formed in 1928,[162] it sees itself as a successor to the Załuski Library, the biggest in Poland and one of the first and biggest libraries in the world.[162][163]
Another important library – the University Library, founded in 1816,[164] is home to over two million items.[165] The building was designed by architects Marek Budzyński and Zbigniew Badowski and opened on 15 December 1999.[166] It is surrounded by green. The University Library garden, designed by Irena Bajerska, was opened on 12 June 2002. It is one of the largest and most beautiful roof gardens in Europe with an area of more than 10,000 m2 (110,000 sq ft), and plants covering 5,111 m2 (55,010 sq ft).[167] As the university garden it is open to the public every day.[167]
Transport

Warsaw is a considerable transport hub linking Western, Central and Eastern Europe. The city has a good network of buses and a continuously expanding perpendicular metro running north to south and east to west. The tram system is one of the biggest in Europe, with a total length of 132 km (82 mi).[168] As a result of increased foreign investment, economic growth and EU funding, the city has undertaken the construction of new roads, flyovers and bridges.[169] The supervising body is the City Roads Authority (ZDM – Zarząd Dróg Miejskich).
Warsaw lacks a complete ring road system and most traffic goes directly through the city centre, leading to the eleventh highest level of congestion in Europe.[170] The Warsaw ring road has been planned to consist of three express roads: S2 (south), S8 (north-west) and S17 (east). S8 and a part of S2 are open, with S2 to be finished by 2020.[171]
The A2 motorway opened in June 2012, stretches west from Warsaw and is a direct motorway connection with Łódź, Poznań and ultimately with Berlin.
The city has two international airports: Warsaw Chopin Airport, located just 10 kilometres (6.2 mi) from the city centre, and Warsaw-Modlin Airport, located 35 kilometres (22 mi) to the north, opened in July 2012. With around 100 international and domestic flights a day and with 15 500 000 passengers served in 2017, Warsaw Frédéric Chopin Airport is by far the biggest airport in Poland and in Central-Eastern Europe.[172] and it has also been called "the most important and largest airport in Central Europe".[173]
Public transport also extends to light rail Warszawska Kolej Dojazdowa line, urban railway Szybka Kolej Miejska, regional rail Koleje Mazowieckie (Mazovian Railways),[174] and bicycle sharing systems (Veturilo). The buses, trams, urban railway and Metro are managed by Warszawski transport Publiczny (WTP, Warsaw Public Transpoert).
The regional rail and light rail is operated by Polish State Railways (PKP). There are also some suburban bus lines run by private operators.[175] Bus service covers the entire city, with approximately 170 routes totalling about 2,603 kilometres (1,617 mi), and with some 1,600 vehicles.
The first section of the Warsaw Metro was opened in 1995 initially with a total of 11 stations.[176] As of 2020, it has 34 stations running a distance of approximately 32 km (20 mi).[177]
The main railway station is Warszawa Centralna serving both domestic traffic to almost every major city in Poland, and international connections. There are also five other major railway stations and a number of smaller suburban stations.
- Public transport in Warsaw



 Pendolino high-speed trains at Warszawa Centralna
Pendolino high-speed trains at Warszawa Centralna
Culture
Music and theatre

Thanks to numerous musical venues, including the Teatr Wielki, the Polish National Opera, the Chamber Opera, the National Philharmonic Hall and the National Theatre, as well as the Roma and Buffo music theatres and the Congress Hall in the Palace of Culture and Science, Warsaw hosts many events and festivals. Among the events worth particular attention are: the International Frédéric Chopin Piano Competition, the International Contemporary Music Festival Warsaw Autumn, the Jazz Jamboree, Warsaw Summer Jazz Days, the International Stanisław Moniuszko Vocal Competition, the Mozart Festival, and the Festival of Old Music.[178]
Warsaw is also considered as one of the European hubs of underground electronic music with a very attractive house and techno music scene.[179]
Warsaw is home to over 30 major theatres spread throughout the city, including the National Theatre (founded in 1765) and the Grand Theatre (established 1778).[180]

Warsaw also attracts many young and off-stream directors and performers who add to the city's theatrical culture. Their productions may be viewed mostly in smaller theatres and Houses of Culture (Domy Kultury), mostly outside Śródmieście (Central Warsaw). Warsaw hosts the International Theatrical Meetings.
From 1833 to the outbreak of World War II, Plac Teatralny (Theatre Square) was the country's cultural hub and home to the various theatres.[181] Plac Teatralny and its environs was the venue for numerous parades, celebrations of state holidays, carnival balls and concerts.
The main building housed the Great Theatre from 1833 to 1834, the Rozmaitości Theatre from 1836 to 1924 and then the National Theatre, the Reduta Theatre from 1919 to 1924, and from 1928 to 1939 – the Nowy Theatre, which staged productions of contemporary poetical drama, including those directed by Leon Schiller.[181]
Nearby, in Ogród Saski (the Saxon Garden), the Summer Theatre was in operation from 1870 to 1939,[182] and in the inter-war period, the theatre complex also included Momus, Warsaw's first literary cabaret, and Leon Schiller's musical theatre Melodram. The Wojciech Bogusławski Theatre (1922–26) was the best example of "Polish monumental theatre". From the mid-1930s, the Great Theatre building housed the Upati Institute of Dramatic Arts – the first state-run academy of dramatic art, with an acting department and a stage directing department.[181]
Events
Several commemorative events take place every year. Gatherings of thousands of people on the banks of the Vistula on Midsummer's Night for a festival called Wianki (Polish for Wreaths) have become a tradition and a yearly event in the programme of cultural events in Warsaw.[183][184] The festival traces its roots to a peaceful pagan ritual where maidens would float their wreaths of herbs on the water to predict when they would be married, and to whom.[183] By the 19th century this tradition had become a festive event, and it continues today.[183] The city council organize concerts and other events.[184] Each Midsummer's Eve, apart from the official floating of wreaths, jumping over fires, and looking for the fern flower, there are musical performances, dignitaries' speeches, fairs and fireworks by the river bank.[184]
Warsaw Multimedia Fountain Park is located in an enchanting place, near the Old Town and the Vistula. The ‘Water – Light – Sound’ multimedia shows take place each Friday and Saturday from May till September at 9.30 pm (May and – 9 October pm). On other weekdays, the shows do not include lasers and sound.
The Warsaw Film festival, an annual festival that takes place every October.[185] Films are usually screened in their original language with Polish subtitles and participating cinemas include Kinoteka (Palace of Science and Culture), Multikino at Golden Terraces and Kultura. Over 100 films are shown throughout the festival, and awards are given to the best and most popular films.[185]
Museums and art galleries
Museums in Warsaw
|
The levelling of Warsaw during the war has left gaping holes in the city's historic collections.[186] Although a considerable number of treasures were spirited away to safety in 1939, a great number of collections from palaces and museums in the countryside were brought to Warsaw at that time as the capital was considered a safer place than some remote castle in the borderlands.[186] Thus losses were heavy.[186]
As interesting examples of expositions the most notable are: the world's first Museum of Posters boasting one of the largest collections of art posters in the world,[187] the Museum of Hunting and Riding and the Railway Museum. From among Warsaw's 60 museums, the most prestigious ones are the National Museum with a collection of works whose origin ranges in time from antiquity till the present epoch as well as one of the best collections of paintings in the country including some paintings from Adolf Hitler's private collection,[188] and the Museum of the Polish Army whose set portrays the history of arms.
The collections of Łazienki and Wilanów palaces focus on the paintings of the "old masters", as do those of the Royal Castle which displays the Lanckoroński Collection including two paintings by Rembrandt.[189] The Palace in Natolin, a former rural residence of Duke Czartoryski, is another venue with its interiors and park accessible to tourists.

Holding Poland's largest private collection of art, the Carroll Porczyński Collection Museum[190] displays works from such varied artists as Paris Bordone, Cornelis van Haarlem, José de Ribera, William-Adolphe Bouguereau, Pierre-Auguste Renoir and Vincent van Gogh[191] along with some copies of masterpieces of European painting.
A fine tribute to the fall of Warsaw and history of Poland can be found in the Warsaw Uprising Museum and in the Katyń Museum which preserves the memory of that crime.[192] The Warsaw Uprising Museum also operates a rare preserved and operating historic stereoscopic theatre, the Warsaw Fotoplastikon. The Museum of Independence preserves patriotic and political objects connected with Poland's struggles for independence. Dating back to 1936 the Warsaw Historical Museum contains 60 rooms which host a permanent exhibition of the history of Warsaw from its origins until today.
The 17th century Royal Ujazdów Castle houses the Centre for Contemporary Art, with some permanent and temporary exhibitions, concerts, shows and creative workshops. The Centre realizes about 500 projects a year. The Zachęta National Gallery of Art, the oldest exhibition site in Warsaw, with a tradition stretching back to the mid-19th century organises exhibitions of modern art by Polish and International Artists and promotes art in many other ways. Since 2011, Warsaw Gallery Weekend is held on the last weekend of September.
The city also possesses some oddities such as the Neon Museum, the Museum of Caricature,[193] the Museum of John Paul II and Primate Wyszyński, the Legia Warsaw Museum, and a Motorisation Museum in Otrębusy.[194]
Media and film

Warsaw is the media centre of Poland, and the location of the main headquarters of TVP and other numerous local and national TV and radio stations, such as Polskie Radio (Polish Radio), TVN, Polsat, TV4, TV Puls, Canal+ Poland, Cyfra+ and MTV Poland.[195]
Since May 1661 the first Polish newspaper, the Polish Ordinary Mercury, was printed in Warsaw. The city is also the printing capital of Poland with a wide variety of domestic and foreign periodicals expressing diverse views, and domestic newspapers are extremely competitive. Rzeczpospolita, Gazeta Wyborcza and Dziennik Polska-Europa-Świat, Poland's large nationwide daily newspapers,[196] have their headquarters in Warsaw.
Warsaw also has a sizable movie and television industry. The city houses several movie companies and studios. Among the movie companies are TOR, Czołówka, Zebra and Kadr which is behind several international movie productions.[197]
Over the next few years the new Film City in Nowe Miasto, located a mere 80 km (50 mi) from Warsaw, will become the centre of Polish film production and international co-production.[197] It is to be the largest high-tech film studio in Europe.[197] The first projects filmed in the new Film City will be two films about the Warsaw uprising.[197] Two backlots will be constructed for these projects – a lot of pre-World War II Warsaw and city ruins.[197]
Since World War II, Warsaw has been the most important centre of film production in Poland. It has also been featured in numerous movies, both Polish and foreign, for example: Kanał and Korczak by Andrzej Wajda and The Decalogue by Krzysztof Kieślowski, also including Oscar winner The Pianist by Roman Polański.[198]
It is also home to the National Film Archive, which, since 1955, has been collecting and preserving Polish film culture.[199]
Sports
On 9 April 2008 the President of Warsaw, Hanna Gronkiewicz-Waltz, obtained from the mayor of Stuttgart Wolfgang Schuster a challenge award – a commemorative plaque awarded to Warsaw as the European capital of Sport in 2008.[200]
.jpg)
The National Stadium, a 58,580-seat-capacity football (soccer) stadium, replaced Warsaw's recently demolished 10th-Anniversary Stadium.[201] The national stadium hosted the opening match, 2 group matches, a quarterfinal, and a semi-final of the UEFA Euro 2012 hosted jointly by Poland and Ukraine.[202]
There are many sports centres in the city as well. Most of these facilities are swimming pools and sports halls, many of them built by the municipality in the past several years. The main indoor venue is Hala Torwar, used for all kinds of indoor sports (it was a venue for the 2009 EuroBasket[203] but it is also used as an indoor skating rink). There is also an open-air skating rink (Stegny) and a horse racetrack (Służewiec).
The best of the city's swimming centres is at Wodny Park Warszawianka, 4 km (2 mi) south of the centre at Merliniego Street, where there's an Olympic-sized pool as well as water slides and children's areas.[204]
From the Warsovian football teams, the most famous is Legia Warsaw – the army club with a nationwide following play at Polish Army Stadium, just southeast of the centre at Łazienkowska Street. Established in 1916, they have won the country's championship 13 times (most recently in 2018) and won the Polish Cup 19 times. In the Champions League season 1995/96 they reached the quarter-finals, where they lost to Panathinaikos Athens.
Their local rivals, Polonia Warsaw, have significantly fewer supporters, yet they managed to win the country's championship two times (in 1946 and 2000) and won the cup twice as well. Polonia's home venue is located at Konwiktorska Street, a ten-minute walk north from the Old Town. Polonia was relegated from the country's top flight in 2013 because of their disastrous financial situation. They are now playing in the second league (3rd tier in Poland).
Legia Warsaw's basketball team was one of the country's best teams in 50s and 60s. They are now participating in PLK, the highest-tier level of the Polish basketball.
Warsaw Mermaid
The mermaid (syrenka) is Warsaw's symbol[205] and can be found on statues throughout the city and on the city's coat of arms. This imagery has been in use since at least the mid-14th century.[206] The oldest existing armed seal of Warsaw is from the year 1390, consisting of a round seal bordered with the Latin inscription Sigilium Civitatis Varsoviensis (Seal of the city of Warsaw).[207] City records as far back as 1609 document the use of a crude form of a sea monster with a female upper body and holding a sword in its claws.[208] In 1653 the poet Zygmunt Laukowski asks the question:
Warsaw of strong walls; why was the emblem Mermaid with sharp sword, given you by the kings?
— Zygmunt Laukowski[209]

The Mermaid Statue stands in the very centre of Old Town Square, surrounded by a fountain. Due to vandalism, the original statue had been moved to the grounds of the Museum of Warsaw – the statue in the square is a copy. This is not the only mermaid in Warsaw. Another is located on the bank of the Vistula River near Świętokrzyski Bridge and another on Karowa Street.
The origin of the legendary figure is not fully known. The best-known legend, by Artur Oppman, is that long ago two of Triton's daughters set out on a journey through the depths of the oceans and seas. One of them decided to stay on the coast of Denmark and can be seen sitting at the entrance to the port of Copenhagen. The second mermaid reached the mouth of the Vistula River and plunged into its waters. She stopped to rest on a sandy beach by the village of Warszowa, where fishermen came to admire her beauty and listen to her beautiful voice. A greedy merchant also heard her songs; he followed the fishermen and captured the mermaid.[210]
Another legend says that a mermaid once swam to Warsaw from the Baltic Sea for the love of the Griffin, the ancient defender of the city, who was killed in a struggle against the Swedish invasions of the 17th century. The mermaid, wishing to avenge his death, took the position of defender of Warsaw, becoming the symbol of the city.[210]
Every member of the Queen's Royal Hussars of the UK's light cavalry wears the Maid of Warsaw, the crest of the City of Warsaw, on the left sleeve of his No. 2 (Service) Dress.[211] Members of 651 Squadron Army Air Corps of the United Kingdom also wear the Maid of Warsaw on the left sleeve of their No. 2 (Service) Dress.[212]
Famous people
One of the most famous people born in Warsaw was Maria Skłodowska-Curie, who achieved international recognition for her research on radioactivity and was the first female recipient of the Nobel Prize.[213] Famous musicians include Władysław Szpilman and Frédéric Chopin. Though Chopin was born in the village of Żelazowa Wola, about 60 km (37 mi) from Warsaw, he moved to the city with his family when he was seven months old.[214] Casimir Pulaski, a Polish general and hero of the American Revolutionary War, was born here in 1745.[215]
Tamara de Lempicka was a famous artist born in Warsaw.[216] She was born Maria Górska in Warsaw to wealthy parents and in 1916 married a Polish lawyer Tadeusz Łempicki.[217] Better than anyone else she represented the art deco style in painting and art.[216] Nathan Alterman, the Israeli poet, was born in Warsaw, as was Moshe Vilenski, the Israeli composer, lyricist, and pianist, who studied music at the Warsaw Conservatory.[218] Russian Jewish poet and essayist Osip Mandelstam, one of the foremost members of the Acmeist school of poetry was born in Warsaw while it was part of the Russian Empire. Other notables include Samuel Goldwyn, the founder of Goldwyn Pictures, mathematician Benoit Mandelbrot, physicist Joseph Rotblat, biochemist Casimir Funk, and Moshe Prywes, an Israeli physician who was the first President of Ben-Gurion University of the Negev. Warsaw was the beloved city of Isaac Bashevis Singer, which he described in many of his novels:[219] "Warsaw has just now been destroyed. No one will ever see the Warsaw I knew. Let me just write about it. Let this Warsaw not disappear forever", he wrote.[220]
Rankings
- Largest capital cities of the European Union: ranked 7th (2020).
- Most expensive cities: ranked 113th of 144.
- Livability index: ranked 32nd (2012)[11] Spies of Warsaw was partly filmed in Warsaw.
International relations
Twin towns – sister cities













Partnership and friendship
Warsaw also cooperates with:[221]










.svg.png)


Locations named after Warsaw
- Warsaw, Ontario
- Warsaw (town), New York
- Warsaw (village), New York, within the town of Warsaw
- Warsaw, California
- Warsaw, Illinois
- Warsaw, Indiana
- Warsaw, Kentucky
- Warsaw, Missouri
- Warsaw, North Carolina
- Warsaw, North Dakota
- Warsaw, Ohio
- Warsaw, Pennsylvania
- Warsaw, Texas
- Warsaw, Virginia
See also
- Battle of Warsaw
- Destruction of Warsaw
- List of tallest buildings in Warsaw
- List of honorary citizens of Warsaw
- Street names of Warsaw
- Tourism in Poland
- Treaty of Warsaw (disambiguation)
- Warsaw concentration camp
- Warsaw dialect
- Warsaw Fire Guard
Notes
- "Local Data Bank". Statistics Poland. Retrieved 1 June 2019. Data for territorial unit 1465000.
- http://appsso.eurostat.ec.europa.eu/nui/show.do?dataset=urb_lpop1&lang=en
- "Population on 1 January by age groups and sex – functional urban areas". Eurostat. Retrieved 6 February 2017.
- "Warsaw". goeuro2012.com. Archived from the original on 3 June 2008. Retrieved 15 July 2008.
- "The World According to GaWC 2018". GaWC. Retrieved 28 December 2018.
- "Coat of Arms and Colours of the Capital City of Warsaw". bip.warszawa.pl. Retrieved 14 January 2009.
- Czerkawski, Andrzej; Jurga, Tadeusz (1969). Dla ciebie ojczyzno. Sport i Turystyka. p. 435.
ORDER OF VALOUR "VIRTUTI MILITARI", FIFTH CLASS Capital City of Warsaw 1940 To the inhabitants of the Capital City of Warsaw – in recognition of their heroism and unshakable bravery in the struggle with the Nazi aggressor.
- "Warsaw – Phoenix City Rebuilt From the Ashes". youramazingplaces.com. 26 December 2014.
- "The SETAC Europe 18th Annual Meeting". setac.eu. Archived from the original on 28 May 2008. Retrieved 22 January 2009.
- "The city of phoenix – War*saw everything" (in Polish). Archived from the original on 27 January 2009. Retrieved 22 January 2009.
- Best cities ranking and report (PDF). A special report from the Economist Intelligence Unit, 2012.
- "Warsaw City". msz.gov.pl. Retrieved 7 May 2017.
- "Warsaw Stock Exchange, Poland, stocks, investing online – Fio bank". Retrieved 9 April 2017.
- "Warsaw: The Region's Key Market". Warsaw Capital Market Summit 2015. Archived from the original on 8 December 2015. Retrieved 29 October 2015.
- James Newman, ed. (2015). "Europes Top Skyscraper Cities". The Top 500. SkyscraperNews.com. Retrieved 20 October 2015.
- "The Grand Theater in Warsaw: one of the largest theatres in Europe and one of the biggest stages in the world –". communications-unlimited.nl. Retrieved 14 November 2017.
- WorldlyTraveller (10 May 2016). "Warsaw, City of Classical Music and Varied Architecture in Poland – Worldly Resort". Retrieved 9 April 2017.
- Charly Wilder (23 December 2015). "36 Hours in Warsaw, Poland". The New York Times. Retrieved 29 December 2015.
- Skoczeń, Paulina. "Warsaw is a green city". Retrieved 9 April 2017.
- Samuel Bogumił Linde, Slownik jẹzyka polskiego (1808)
- Julian Weinberg, Polacy w Rodzinie Sławian (1878)
- "Online Etymology Dictionary". etymonline.com.
- Babik, Zbigniew (31 December 2015). "Pre-Slavic toponomastic layer of Northern Mazovia: corrections and addenda (the Narew drainage)". Linguistica. 55 (1): 29–46. doi:10.4312/linguistica.55.1.29-46 – via revije.ff.uni-lj.si.
- Kazimierz Rymut (1987). Nazwy miast Polski (in Polish). Zakład Narodowy im. Ossolińskich. ISBN 83-04-02436-5.
- "The Warsaw Mermaid". Retrieved 11 February 2008.
- "Historia Warszawy" (in Polish). Archived from the original on 13 May 2010. Retrieved 11 February 2008.
- "Ustawa o ustroju miasta stołecznego Warszawy". prawo.lex.pl (in Polish). Archived from the original on 1 January 2007. Retrieved 15 July 2008.
- "Warsaw's history". e-warsaw.pl. Retrieved 24 July 2008.
- Dobrosław Kobielski (1984). Widoki dawnej Warszawy (Views of Old Warsaw) (in Polish). Warsaw: Krajowa Agencja Wydawnicza. ISBN 83-03-00702-5.
- Davies, Norman (2005). God's Playground (2 ed.). Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-925339-0.
- "Fragment of a robe of the dukes of Masovia".
- "Mało czarujący koniec Piastów mazowieckich - Kwartalnik Przekrój". przekroj.pl.
- Neal Ascheron. "The Struggles for Poland". halat.pl. Retrieved 24 July 2008.
- Marian Marek Drozdowski; Andrzej Zahorski (2004). Historia Warszawy [History of Warsaw] (in Polish). Warsaw. ISBN 83-89632-04-7.
- (english) nathansvilla.com Archived 2008-01-01 at the Wayback Machine accessed 19 February 2008
- "The Bygone Warsaw". 14 March 2008. Archived from the original on 14 March 2008. Retrieved 18 November 2017.
- Michał Rożek; Doris Ronowicz (1988). Cracow: a treasury of Polish culture and art. Interpress Publishers. p. 74. ISBN 83-223-2245-3.
- John Stanley (March–June 2004). "Literary Activities and Attitudes in the Stanislavian Age in Poland (1764–1795): A Social System?". Archived from the original on 14 May 2011. Retrieved 23 April 2009 – via Find Articles.
- Cornelia Golna (2004). City of man's desire: a novel of Constantinople. Go-Bos Press. p. 318. ISBN 90-804114-4-2.
- Crowley, David (2003). Warsaw. London: Reaktion Books. p. 10.
- (in French) Zbigniew Naliwajek. Romain Rolland et la littérature polonaise. Revue de littérature comparée 3/2003 (n°307), p. 325-338.
- Augustin P. O'Brien (1864). Petersburg and Warsaw: Scenes Witnessed During a Residence in Poland and Russia in 1863–64. R. Bentley. Retrieved 28 January 2009.
- "Wyborcza.pl". warszawa.wyborcza.pl.
- https://sarp.warszawa.pl/wordpress/wp-content/uploads/2015/10/H.Radziejowska_Wola_przemys%C5%82.pdf
- "Wyborcza.pl". warszawa.wyborcza.pl.
- "Żydowska Warszawa. Współcześnie". 12 April 2018.
- "Visualizing the 1897 Census in Pie Charts - Russian History Blog". russianhistoryblog.org. Retrieved 27 September 2018.
- Piotr S. Wandycz (1962). France and Her Eastern Allies, 1919–1925: French-Czechoslovak-Polish Relations from the Paris Peace Conference to Locarno. U of Minnesota Press. p. 18. ISBN 9780816658862.
- Adam Zamoyski, Warsaw 1920: Lenin's Failed Conquest of Europe (2008)
- http://datablog.pl/wykres-powierzchnia-warszawy-w-latach-1921-2008/#:~:text=Historyczne%20dane%20G%C5%82%C3%B3wnego%20Urz%C4%99du%20Statystycznego,ona%20oko%C5%82o%20517%20km%20kwadratowych.
- M.M. (2 August 2006). "Warsaw: A Last Glimpse". warsawvoice.pl. Archived from the original on 26 September 2006. Retrieved 29 July 2008.
- "Warsaw". United States Holocaust Memorial Museum. Retrieved 29 July 2008.
- Snyder, Timothy (2010). Bloodlands. London: The Bodley Head. p. 280.
- "The Warsaw Ghetto Uprising". United States Holocaust Memorial Museum. Archived from the original on 17 May 2008. Retrieved 29 July 2008.
- "The Warsaw Ghetto Uprising". aish.com. Archived from the original on 23 June 2008. Retrieved 29 July 2008.
- "Warsaw Uprising". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 5 February 2009. Hoping to gain control of Warsaw before the Red Army could "liberate" it, the Home Army followed the Soviet suggestion to revolt.
- "Warsaw Uprising of 1944". warsawuprising.com. Retrieved 14 July 2008.
- Borkiewicz, Adam (1957). Powstanie warszawskie 1944: zarys działań natury wojskowej. Warsaw: PAX.
- "Warsaw Uprising of 1944". warsawuprising.com. Retrieved 14 July 2008.
- Wesley Adamczyk (2004). When God looked the other way: an odyssey of war, exile, and redemption. University of Chicago Press. p. 170. ISBN 0-226-00443-0.
The Soviet troops, ordered by Stalin to wait until the Germans had destroyed the remnants of Polish resistance, then moved into what was left of Warsaw, flushed out the remaining Germans, and proclaimed themselves liberators of the city.
- "Warsaw's lost architecture portrayed in miniature". Retrieved 11 June 2017.
- "Pałac Leopolda Kronenberga". warszawa1939.pl (in Polish). Retrieved 29 July 2008.
- https://www.google.com.au/books/edition/200_lat_muzealnictwa_warszawskiego/FsAhAQAAIAAJ?hl=en&gbpv=1&bsq=plac+defilad+warszawa+jednym+z+najwiekszym+plac%C3%B3w+w+europie&dq=plac+defilad+warszawa+jednym+z+najwiekszym+plac%C3%B3w+w+europie&printsec=frontcover
- Ziemichód, Przemysław (2 June 2017). "Pałac Kultury i Nauki - najmniej lubiany symbol Warszawy". Warszawa Nasze Miasto.
- David Crowley (2003). Warsaw. Reaktion Books. p. 156. ISBN 18-61891-79-2.
- "Historic Centre of Warsaw". UNESCO. Retrieved 24 July 2008.
- "Pope in Warsaw". destinationwarsaw.com. Archived from the original on 2 February 2009. Retrieved 5 February 2009.
- UK, DVV Media. "Warszawa opens second metro line". railwaygazette.com.
- "Attracting foreign investments". polandtrade.com.hk. Archived from the original on 8 November 2007. Retrieved 24 July 2008.
- "The National Stadium in Warsaw". poland2012.net. Retrieved 24 July 2008.
- "Geography of Warsaw". geography.howstuffworks.com. Archived from the original on 12 July 2011. Retrieved 27 February 2009.
- "City: Introduction and characteristics" (PDF). Infrastuktura - Miasto Stołeczne Warszawa.
- "Warsaw, Poland Köppen Climate Classification (Weatherbase)". Weatherbase. Retrieved 10 March 2019.
- "Average Temperatures in Warsaw, Poland Temperature". warsaw.climatemps.com. Archived from the original on 30 August 2017. Retrieved 20 October 2017.
- Zawidzki, Machi (15 September 2016). Discrete Optimization in Architecture: Building Envelope. Springer. ISBN 9789811013911.
- Lindner-Cendrowska, Katarzyna; Błażejczyk, Krzysztof (2018). "Impact of selected personal factors on seasonal variability of recreationist weather perceptions and preferences in Warsaw (Poland)". International Journal of Biometeorology. 62 (1): 113–125. doi:10.1007/s00484-016-1220-1. ISSN 0020-7128. PMC 5752755. PMID 27498882.
- "Warsaw (12375) - WMO Weather Station". NOAA. Archived from the original on 27 December 2018. Retrieved 29 December 2018.
- Peel, M. C.; Finlayson, B. L.; McMahon, T. A. (2007). "Updated world map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification" (PDF). Hydrology and Earth System Sciences. 11 (5): 1633–1644. doi:10.5194/hess-11-1633-2007. ISSN 1607-7938.
- Błażejczyk, Krzysztof; Baranowski, Jarosław; Jendritzky, Gerd; Błażejczyk, Anna; Bröde, Peter; Fiala, Dusan (2015). "Regional features of the bioclimate of Central and Southern Europe against the background of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification" (PDF). Geographia Polonica. 88 (3): 439–453. doi:10.7163/GPol.0027. ISSN 0016-7282. DOI is here
- Alex (10 May 2015). "Climates classification by Wincenty Okołowicz". Vivid Maps. Retrieved 10 March 2019.
- "European Cities With Driest Weather - Current Results". www.currentresults.com. Retrieved 12 March 2019.
- "Climate Warsaw". Pogoda.ru.net. Retrieved 18 May 2019.
- "WARSZAWA-OKECIE 1961–1990". NOAA. Retrieved 18 May 2019.
- "WARSAW–BIELANY 1961–1990". NOAA. Retrieved 18 May 2019.
- d.o.o, Yu Media Group. "Warsaw, Poland - Detailed climate information and monthly weather forecast". Weather Atlas. Retrieved 2 July 2019.
- "Warsaw, Poland - Monthly weather forecast and Climate data". Weather Atlas. Retrieved 10 February 2019.
- Stępniak, Marcin (25 March 2015). "PRZEKSZTAŁCENIA PRZESTRZENNEGO ROZMIESZCZENIA ZASOBÓW MIESZKANIOWYCH W WARSZAWIE W LATACH 1945-2008". IGiPZ PAN – via Google Books.
- https://www.google.com.au/books/edition/Cztery_wieki_Mazowsza/Az48AAAAMAAJ?hl=en&gbpv=1&bsq=warszawa+architekt+z+w%C5%82och,+niemiec+niderland%C3%B3w&dq=warszawa+architekt+z+w%C5%82och,+niemiec+niderland%C3%B3w&printsec=frontcover
- "A town house of the Burbach family". eGuide / Treasures of Warsaw on-line. Archived from the original on 28 May 2007. Retrieved 23 February 2009.
- Redakcja, przez (21 January 2020). "Wyremontują kolumnę Zygmunta III Wazy za ponad 230 tys. złotych!".
- "Politechnika Warszawska". warszawa1939.pl (in Polish). Retrieved 27 February 2009.
- "As good as new". The official website of the City of Warsaw. 1 March 2006. Archived from the original on 20 May 2008.
- Sampo Ruoppila (2004). Processes of Residential Differentiation in Socialist Cities (PDF). European Journal of Spatial Development. pp. 9–10. Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 August 2010. Retrieved 10 October 2010.
- "Warszawa: Modny Plac Zbawiciela, orientalne restauracje i wielkie zakupy". podroze.se.pl.
- "Metropolitan Life". warsawvoice.pl. 4 February 2004. Archived from the original on 25 May 2006. Retrieved 23 February 2009.
- "Warsaw – The Skyscraper Center".
- "Palace". wilanow-palac.art.pl. Retrieved 21 February 2008.
- "Short and long history of the Powiązki Cemetery" (in Polish). Retrieved 11 February 2008.
- "Warsaw Judaica". um.warszawa.pl. Archived from the original on 5 August 2007. Retrieved 26 January 2010.
- "Heroic City". um.warszawa.pl. Archived from the original on 4 July 2013. Retrieved 26 January 2010.
- James Ramsay Montagu Butler; Norman Henry Gibbs; J. M. A. Gwyer; John Patrick William Ehrman; Michael Eliot Howard (1976). "History of the Second World War; United Kingdom military series 5". In James Ramsay Montagu Butler (ed.). Grand strategy. H. M. Stationery Office. p. 369.
- "Church of the Holy Cross". eGuide / Treasures of Warsaw on-line. Archived from the original on 18 February 2006. Retrieved 23 February 2009.
- "Frédéric Chopin Monument". eGuide / Treasures of Warsaw on-line. Archived from the original on 28 May 2007. Retrieved 23 February 2009.
- "Polish Girlhood (1867–1891)". aip.org. American Institute of Physics. Retrieved 25 February 2009.
- "The Radium Institute (1919–1934)". aip.org. American Institute of Physics. Retrieved 25 February 2009.
- Warsaw Tourist Office. "Parks & Gardens". warsawtour.pl. Archived from the original on 12 January 2010. Retrieved 23 February 2009. "Warsaw is a green city. Almost a quarter of its area is comprised of fields, parks, green squares and lush gardens, making Warsaw a European metropolis that truly offers its visitors a breath of fresh air."
- "Parki i lasy Warszawy". um.warszawa.pl (in Polish). Archived from the original on 16 May 2016. Retrieved 25 February 2009.
- "Nowa Pomarańczarnia". ePrzewodnik / Perełki Warszawy on-line (in Polish). Archived from the original on 8 February 2006. Retrieved 24 February 2009.
- "Park Praski". zielona.um.warszawa.pl (in Polish). Archived from the original on 13 March 2010. Retrieved 19 April 2011. Powstał w latach 1865–1871, według projektu Jana Dobrowolskiego, na prawym brzegu Wisły.
- "Nature reserves as a refuge of Grifola frondosa (DICKS.: FR.) GRAY in central Poland". bpn.com.pl. Retrieved 24 February 2009.
- "Kayaking on the Vistula". warsawvoice.pl. 30 August 2006. Archived from the original on 26 September 2006. Retrieved 24 February 2009.
- "Warsaw Zoo". zoo.waw.pl. Retrieved 24 February 2009.
- Warsaw Zoo opened 11 March 1928, on Ratuszowa Street. It was not the first zoological garden in Warsaw; King Jan Sobieski III kept a court menagerie in Wilanów. Several private zoos were also established in Warsaw in the 19th century. "New Zoo Revue". warsawvoice.pl. 24 April 2003. Archived from the original on 18 January 2005. Retrieved 9 May 2009.
- Vernon N. Kisling, ed. (2000). Zoo and aquarium history: ancient animal collections to zoological gardens. CRC Press. pp. 118–119. ISBN 0-8493-2100-X.
- "Migrations Map: Where are migrants coming from? Where have migrants left?". MigrationsMap.net. Archived from the original on 11 February 2016. Retrieved 12 February 2016.
- Joshua D. Zimmerman (2004). Poles, Jews and the politics of nationality. University of Wisconsin Press. p. 16. ISBN 0-299-19464-7.
- F.A. Brockhaus Verlag Leipzig (1935). Der Grosse Brockhaus: Handbuch des Wissens (in German). 20 (15th ed.). Brockhaus. p. 25.
- "Narodowości w II RP na przedwojennych wykresach. Gdzie było najmniej Polaków, a gdzie najwięcej?". WielkaHistoria. 27 October 2019.
- "Ludność w gminach. Stan w dniu 31 marca 2011 r. – wyniki spisu ludności i mieszkań 2011 r." Główny Urząd Statystyczny. Archived from the original on 27 November 2011. Retrieved 20 August 2012.
- "Population in Poland. Size and structure by territorial division as of December 31, 2015" (in Polish). Retrieved 26 May 2016.
- "Cudzoziemcy w Warszawie. Jak im się żyje w stolicy? Obcokrajowcy oceniają otwartość warszawiaków, wskazują wady i zalety miasta". warszawa.naszemiasto.pl. 12 August 2019.
- Dānishgāh-i Tihrān. Faculty of Fine Arts (1990). International Conference on Reconstruction of War-Damaged Areas: 6–16 March 1986 : Faculty of Fine Arts, University of Tehran, Iran. University of Tehran Press. p. 148.
- Michał Kopiński (28 November 2008). "Warszawa da się lubić? Nie w Poznaniu". poznan.gazeta.pl/poznan (in Polish). Retrieved 29 September 2010.
- Joanna Blewąska (28 November 2008). "Warszawa da się lubić?". Gazeta Wyborcza (in Polish). Retrieved 29 September 2010.
- "Czy boimy się cudzoziemców w Warszawie?". oknonawarszawe.pl.
- "Warszawa lubiana przez cudzoziemców. Ilu ich mieszka w stolicy?". gazeta.pl. Retrieved 22 October 2016.
- Geert Mak (2008). In Europe: travels through the twentieth century. New York: Pantheon Books. p. 427. ISBN 0-307-28057-8.
Today Warsaw is a monocultural city, which is some people's ideal. But before 1939 it was a typically multicultural society. Those were the city's most productive years. We lost that multicultural character during the war.
- Hermann Julius Meyer (1909). Meyers Konversations-Lexikon (in German). 20 (6th ed.). Leipzig and Vienna. p. 388.
- Erich Zechlin (1916). Die Bevölkerungs- und Grundbesitzverteilung im Zartum Polen [The distribution of population and property in tsaristic Poland] (in German). Berlin: Reimer. pp. 82–83.
- Marian S. Mazgaj (2010). Church and State in Communist Poland: A History, 1944–1989. McFarland. p. 67. ISBN 0-7864-5904-2.
- Konferencja Episkopatu Polski, Informator 2017, Biblos 2017, ISBN 978-83-7793-478-4
- "Administration". e-warsaw.pl. Archived from the original on 18 December 2008. Retrieved 31 January 2009.
- Uwe Altrock (2006). Spatial planning and urban development in the new EU member states: from adjustment to reinvention. Ashgate Publishing, Ltd. p. 262. ISBN 0-7546-4684-X.
- Barbara Petrozolin-Skowrońska (1994). "Encyklopedia Warszawy". Warsaw Encyclopedia (in Polish). Polish Scientific Publishers PWN. p. 94. ISBN 83-01-08836-2.
- Masa Djordjevic (2006). Politics of Urban Development Planning: Building Urban Governance in Post-Socialist Warsaw?. Ashgate Publishing, Ltd. p. 8. Retrieved 10 October 2010.
- "Ludność w gminach według stanu w dniu 31.12.2011 r. bilans opracowany w oparciu o wyniki NSP'2011" (in Polish). Glówny Urząd Statystyczny. Archived from the original on 17 August 2012. Retrieved 21 August 2012.
- Turystyki, Stołeczne Biuro. "WarsawTour – Official Tourist Portal of Warsaw". Retrieved 6 February 2017.
- "Dzielnice". um.warszawa.pl (in Polish). Archived from the original on 1 July 2008. Retrieved 11 July 2008.
- Mark Baker; Kit F. Chung (2011). Frommer's Poland. John Wiley & Sons. p. 80. ISBN 04-70964-24-3.
- "The most expensive and richest cities in the world". UBS. 18 August 2011. Retrieved 1 April 2012.
- "Podmioty gospodarki narodowej" (PDF). stat.gov.pl (in Polish). 15 February 2007. Archived from the original (PDF) on 10 September 2008. Retrieved 28 July 2008.
- "Warsaw City Report – March 2007" (PDF). pbwfund.com. Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 November 2018. Retrieved 28 July 2008.
- "Conversion rates - Purchasing power parities (PPP) - OECD Data". theOECD.
- "Database - Eurostat". ec.europa.eu.
- "Agriculture and industry". pmrconsulting.com. Archived from the original on 7 February 2009. Retrieved 29 April 2009.
- "Big Chance for the Capital". Warsaw – CEE Financial Hub Conference. warsawvoice.pl. 11 June 2008. Archived from the original on 6 December 2008. Retrieved 28 July 2008.
- www.ideo.pl, ideo -. "Statistical Office in Warszawa / Warsaw". stat.gov.pl. Archived from the original on 6 September 2015.
- "History". gpw.pl. Retrieved 24 May 2012.
- "Giełda Papierów Wartościowych w Warszawie". Gpw.pl. Archived from the original on 26 July 2011. Retrieved 22 January 2010.
- "Tourism". poland.gov.pl. Retrieved 28 July 2008.
- "Industry". e-warsaw.pl. Retrieved 28 July 2008.
- Jerzy J. Parysek. "The socio-economic and spatial transformation of Polish cities after 1989" (PDF). ff.uni-lj.si. Archived from the original (PDF) on 10 September 2008. Retrieved 28 July 2008.
- "Statistical Yearbook of the Republic of Poland 2008" (PDF). stat.gov.pl. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 February 2009. Retrieved 30 January 2009.
- "Studia w liczbach: Warszawa bije Kraków". miasta.gazeta.pl (in Polish). 10 March 2008. Retrieved 30 January 2009.
- "University of Warsaw". uw.edu.pl. Archived from the original on 18 January 2009. Retrieved 30 January 2009.
- "Warsaw University of Technology (WUT)". onelab.eu. Archived from the original on 20 July 2011. Retrieved 30 January 2009. With over 30,000 students served by over 2,000 professors and instructors, WUT is the largest and the highest-ranking engineering university in Poland.
- "The Fryderyk Chopin University of Music". infochopin.pl. Archived from the original on 24 May 2008. Retrieved 30 January 2009.
- "Warsaw School of Economics – Overview". sgh.waw.pl. Retrieved 30 January 2009.
- "Warsaw University of Life Sciences". sggw.pl. Archived from the original on 27 November 2012. Retrieved 30 January 2009. Warsaw University of Life Sciences – SGGW (WULS – SGGW) is the oldest agricultural academic school in Poland, its history dates back to 1816.
- "Historia zbiorów". bn.org.pl (in Polish). Retrieved 30 January 2009.
- Maria Witt (15 September – 15 October 2005). "The Zaluski Collection in Warsaw". The Strange Life of One of the Greatest European Libraries of the Eighteenth Century. FYI France. Retrieved 17 February 2008.
- S.D. Chrostowska. "Polish Literary Criticism Circa 1772: A Genre Perspective". utoronto.ca. Archived from the original on 3 February 2008. Retrieved 17 February 2008.
- "Historia". buw.uw.edu.pl (in Polish). Retrieved 30 January 2009.
- "Zbiory główne". buw.uw.edu.pl (in Polish). Retrieved 30 January 2009.
- "Library building". buw.uw.edu.pl. Retrieved 30 January 2009.
- "Garden". buw.uw.edu.pl. Retrieved 30 January 2009.
- https://www.um.warszawa.pl/budzetwpigulce/2017-wykonanie-budzetu-transport-i-komunikacja
- Michal Jeziorski (7 March 2007). "Improving Infrastructure". warsawvoice.pl. Archived from the original on 27 June 2009. Retrieved 28 May 2009.
- "TomTom Traffic Index". TomTom. 2018. Retrieved 6 August 2018.
- "Map of motorways and express roads in Poland". SISKOM. Retrieved 1 August 2018.
- "Frédéric Chopin International Airport". airport-technology.com. Retrieved 24 July 2008.
- "Pole position: Developing "the most important and largest airport in Central Europe"". airport-business.com. Retrieved 30 December 2015.
- "Public transport". e-warsaw.pl. Retrieved 22 August 2008.
- "From monopoly towards market" (PDF). World Bank. Retrieved 22 August 2008.
- "A History of Subway Construction". metro.waw.pl. Archived from the original on 10 December 2006. Retrieved 30 January 2009.
- "Technical and Operating Data of the Existing Subway Section". metro.waw.pl. Archived from the original on 17 January 2007. Retrieved 30 January 2009.
- Mark Salter; Jonathan Bousfield (2002). Poland. Rough Guides. ISBN 1-85828-849-5.
- "New Europe: Poles dancing". The Guardian. Retrieved 12 February 2016.
- "Teatr Wielki-Polish National Opera". Archived from the original on 8 February 2008. Retrieved 11 February 2008.
- "The Theatre's history". teatrwielki.pl. 1998. Archived from the original on 18 April 2008. Retrieved 21 February 2008.
- "Teatr Letni". warszawa1939.pl (in Polish). Retrieved 14 February 2008.
- Staś Kmieć. "Midsummer's Eve". polamjournal.com. Retrieved 2 February 2009.
- Staś Kmieć. "Wianki 2008". aktivist.pl (in Polish). Archived from the original on 17 April 2009. Retrieved 2 February 2009.
- "Warsaw Film Festival". wff.pl. Retrieved 16 February 2009.
- Włodzimierz Kalicki. "Sztuka zagrabiona" (in Polish). Polish American Congress of Southern California. Archived from the original on 11 June 2010. Retrieved 30 January 2009.
- "The Poster Museum at Wilanów". postermuseum.pl. Archived from the original on 25 May 2011. Retrieved 10 February 2009.
- Schwarz, Birgit (2009). Geniewahn: Hitler und die Kunst. Böhlau Verlag Wien. p. 312. ISBN 32-05783-07-7.
Mehrere Gemälde aus dem Berghof befinden sich heute im Nationalmuseum in Warschau. Bordones Venus und Amor etwa (Abb. 100) ebenso wie der Madonnen-Tondo Bugiardinis (Abb. 62) oder ein großes Ruinenbild von Pannini, das in der verglasten Veranda gehangen hatte (Abb. 113).
- Wetering, van de, Ernst (2005). A Corpus of Rembrandt Paintings IV: Self-Portraits. Springer. p. 245. ISBN 14-02032-80-3.
- Official name: Museum of John Paul II Collection
- "Museum of John Paul II Collection". muzeummalarstwa.pl. Archived from the original on 29 December 2008. Retrieved 24 February 2009.
- Mark Baker; Kit F. Chung (2009). Frommer's Poland. Frommer's. p. 79. ISBN 0-470-15819-0.
- "Exhibitions". warsaw.com. Retrieved 30 January 2009.
- "Museum history". muzeum-motoryzacji.com.pl. Archived from the original on 29 January 2009. Retrieved 30 January 2009.
- Chris Dziadul. "A decade of progress". broadbandtvnews.com. Retrieved 14 February 2009.
- "Press release" (PDF). instytut.com.pl. 6 October 2008. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 February 2009. Retrieved 14 February 2009.
- "Poland film production guide 2008" (PDF). pisf.pl. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 February 2009. Retrieved 14 February 2009.
- "The Pianist". thepianistmovie.com. Archived from the original on 22 August 2008. Retrieved 14 February 2009.
- "About the National Film Archive". fn.org.pl. National Film Archive. Retrieved 27 September 2017.
- "European Capitals of Sport". aces-europa.eu. Archived from the original on 20 July 2011. Retrieved 30 January 2009.
- Ryan Lucas. "UEFA turns attention to Euro 2012". Sports Illustrated. Archived from the original on 8 July 2011. Retrieved 31 January 2009.
- "Warsaw". e2012.org. Archived from the original on 3 August 2008. Retrieved 31 January 2009.
- 2009 EuroBasket, ARCHIVE.FIBA.com. Retrieved 5 June 2016.
- "Wodny Park". wodnypark.com.pl. Retrieved 31 January 2009.
- "The Mermaid". Archived from the original on 10 March 2008. Retrieved 11 February 2008.
- "Warsaw Mermaid's Statue". Archived from the original on 7 December 2008. Retrieved 10 July 2008.
- "History of Warsaw's Coat of Arms". e.warsaw.pl. Retrieved 10 July 2008.
- Ewa Bratosiewicz. "Other symbols of Warsaw". warsaw-guide.invito.pl. Retrieved 10 July 2008.
- "Warsaw Mermaid – Syrena". Retrieved 10 July 2008.
- "History of Warsaw's Coat of Arms". e-warsaw.pl. Retrieved 10 July 2008.
- "The Maid of Warsaw". The Queen's Own Hussars Museum. Archived from the original on 12 October 2008. Retrieved 10 July 2008.
- "RAF Odiham" (PDF). army.mod.uk. p. 16. Archived from the original (PDF) on 10 September 2008. Retrieved 10 July 2008.
- "Marie Curie – The Nobel Prize in Physics 1903". Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 10 July 2008.
- Joanna Ławrynowicz. "Frederick Francois Chopin, the most eminent Polish composer". infochopin.pl. Archived from the original on 16 May 2008. Retrieved 10 July 2008.
- "Kazimierz Pulaski – Polish patriot and United States army officer". Encyclopædia Britannica.
- Uta Grosenick; Ilka Becker (2001). Women artists in the 20th and 21st century. Taschen. p. 576. ISBN 3-8228-5854-4.
- "Tamara Łempicka". marchand.pl (in Polish). Retrieved 22 January 2009.
- "Moshe Vilensky". Jewishvirtuallibrary.org. Retrieved 31 July 2011.
- "The 5th Festival of Jewish Culture 'Singer's Warsaw'". jewish-theatre.com (in Polish). Archived from the original on 5 November 2010. Retrieved 4 March 2009.
- Richard Burgin; Issac Bashevis Singer (1978). Issac bashevis Singer Talks... About Everything. The New York Times Magazine. p. 46. in: David Neal Miller; Isaac Bashevis Singer (1986). Recovering the canon: essays on Isaac Bashevis Singer. BRILL. p. 40. ISBN 90-04-07681-6.
- "Miasta partnerskie Warszawy". um.warszawa.pl (in Polish). Warsaw. Retrieved 2 August 2020.
- "Convenios Internacionales". buenosaires.gob.ar (in Spanish). Buenos Aires. Retrieved 2 August 2020.
- "Warsaw, Poland". coventry.gov.uk. Coventry City Council. Retrieved 2 August 2020.
- "Agreements with cities". madrid.es. Madrid. Retrieved 2 August 2020.
- "Friendship and cooperation agreements". Paris: Marie de Paris. Archived from the original on 3 April 2016. Retrieved 10 September 2016.
- "Partner cities". yerevan.am. Yerevan. Retrieved 2 August 2020.
References
- Crowley, David (2003). Warsaw. Reaktion Books. ISBN 1-86189-179-2. Retrieved 28 August 2011.
- Olchowik-Adamowska, Liliana; Ławecki, Tomasz (1 April 2006). Travellers Warsaw (First ed.). Peterborough, United Kingdom: Thomas Cook Publishing. ISBN 978-1-84157-492-9. Retrieved 11 March 2010.
- Official webpage of Warsaw includes 360° panoramas of the UNESCO listed area.
- District Police Headquarters – Warsaw II (part of Warsaw Metropolitan Police)
- Warsaw Guide. Online City Guide for Warsaw in Poland. Retrieved 17 May 2015.
- What to do and see in Warsaw
Further reading
External links
- Official website (in English)