Delhi
Delhi (English: /ˈdɛli/; Hindi: [ˈdɪlːi] Dillī; Punjabi: [ˈdɪlːi] Dillī; Urdu: [ˈdeːɦli] Dēhlī), officially known as the National Capital Territory of Delhi (NCT), is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India.[14][15] It is bordered by the state of Haryana on three sides and by Uttar Pradesh to the east. The NCT covers an area of 1,484 square kilometres (573 sq mi). According to the 2011 census, Delhi's city proper population was over 11 million,[5] the second-highest in India after Mumbai,[16] while the whole NCT's population was about 16.8 million.[6] Delhi's urban area is now considered to extend beyond the NCT boundaries, and include the neighbouring satellite cities of Ghaziabad, Faridabad, Gurgaon and Noida in an area called the National Capital Region (NCR) and had an estimated 2016 population of over 26 million people, making it the world's second-largest urban area according to the United Nations.[7] Recent estimates of the metro economy of its urban area have ranked Delhi either the most or second-most productive metro area of India.[10][17] Delhi is the second-wealthiest city in India after Mumbai and is home to 18 billionaires and 23,000 millionaires.[18] Delhi ranks fifth among the Indian states and union territories in human development index.[12] Delhi has the second-highest GDP per capita in India.[9] Delhi is of great historical significance as an important commercial, transport, and cultural hub, as well as the political centre of India.[19]
Delhi | |
|---|---|
| National Capital Territory of Delhi | |
 | |
 Emblem | |
 Location of Delhi in India | |
| Coordinates: 28°36′36″N 77°13′48″E | |
| Country | |
| Settled | 6th century B.C. |
| Capital formation | 1911 |
| Formation of Union Territory[1][2] | 1956 |
| Formation of National Capital Territory[3] | 1 February 1992 |
| Capital | New Delhi |
| Districts | 11 |
| Government | |
| • Body | Government of Delhi |
| • Lt. Governor | Anil Baijal, IAS[4] |
| • Chief Minister | Arvind Kejriwal (AAP) |
| • Deputy Chief Minister | Manish Sisodia (AAP) |
| • Legislature | Unicameral (70 seats) |
| • Parliamentary constituencies |
|
| Area | |
| • Union territory | 1,484.0 km2 (573.0 sq mi) |
| • Water | 18 km2 (6.9 sq mi) |
| Area rank | 31st |
| Elevation | 200–250 m (650–820 ft) |
| Population (2011)[5] | |
| • Union territory | 16,787,941 |
| • Density | 11,312/km2 (29,298/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 16,349,831 (2nd) |
| • Megacity | 11,034,555 (2nd) |
| • Metro (2016) | 26,454,000 (1st) |
| Demonym(s) | Delhiite |
| Languages | |
| • Official | |
| • Additional official | |
| GDP (2018–19) | |
| • Nominal | ₹7.80 lakh crore (US$110 billion) |
| • Nominal Per Capita | ₹365,529 (US$5,100) |
| • Metro GDP/PPP | $370 billion[10] |
| Time zone | UTC+5.30 (IST) |
| PINs[11] | 110000–110099 |
| Area code(s) | +91 11 |
| ISO 3166 code | IN-DL |
| Vehicle registration | DL |
| HDI (2018) | |
| Literacy (2011) | 86.21%[13] |
| Sex ratio (2011) | 868 ♀/1000 ♂[13] |
| Website | delhi |
Delhi has been continuously inhabited since the 6th century BCE.[20] Through most of its history, Delhi has served as a capital of various kingdoms and empires, most notably the Pandavas, the Delhi Sultanate and the Mughal Empire. The city has been captured, ransacked and rebuilt several times, particularly during the medieval period, and modern Delhi is a cluster of a number of cities spread across the metropolitan region. For many centuries Delhi has been a dominant trading and commercial centre in northern India, and after 1990s it has emerged as an important node in the international corporate and financial network.[21]
A union territory, the political administration of the NCT of Delhi today more closely resembles that of a state of India, with its own legislature, high court and an executive council of ministers headed by a Chief Minister. New Delhi is jointly administered by the federal government of India and the local government of Delhi, and serves as the capital of the nation as well as the NCT of Delhi. Delhi hosted the inaugural 1951 Asian Games, 1982 Asian Games, 1983 NAM Summit, 2010 Men's Hockey World Cup, 2010 Commonwealth Games, 2012 BRICS Summit and was one of the major host cities of the 2011 Cricket World Cup.
Delhi is also the centre of the National Capital Region (NCR), which is a unique 'interstate regional planning' area created by the National Capital Region Planning Board Act of 1985.[22][23]
Toponym
There are a number of myths and legends associated with the origin of the name Delhi. One of them is derived from Dhillu or Dilu, a king who built a city at this location in 50 BCE and named it after himself.[24][25][26] Another legend holds that the name of the city is based on the Hindi/Prakrit word dhili (loose) and that it was used by the Tomaras to refer to the city because the iron pillar of Delhi had a weak foundation and had to be moved.[26] According to Panjab Notes and Queries, the name of the city at the time of King Prithviraj was dilpat, and that dilpat and dilli are probably derived from the old Hindi word dil meaning eminence. The former director of the Archaeological Survey of India, Alexander Cunningham, mentioned that dilli later became dihli/dehli.[27] Some suggest the coins in circulation in the region under the Tomaras were called dehliwal.[28] According to the Bhavishya Purana, King Prithiviraja of Indraprastha built a new fort in the modern-day Purana Qila area for the convenience of all four castes in his kingdom. He ordered the construction of a gateway to the fort and later named the fort dehali.[29] Some historians believe that Dhilli or Dhillika is the original name for the city while others believe the name could be a corruption of the Hindustani words dehleez or dehali—both terms meaning "threshold" or "gateway"—and symbolic of the city as a gateway to the Gangetic Plain.[30][31][32]
The people of Delhi are referred to as Delhiites or Dilliwalas.[33] The city is referenced in various idioms of the Northern Indo-Aryan languages. Examples include:
- Abhi Dilli door hai (अभी दिल्ली दूर है) or its Persian version, Hanuz Dehli dur ast (هنوز دهلی دور است), literally meaning "Delhi is still far away", which is generically said about a task or journey still far from completion.[34][35]
- Dilli dilwalon ka shehr (दिल्ली दिलवालों का शहर) or Dilli dilwalon ki (दिल्ली दिलवालों की), meaning "Delhi belongs to the large-hearted/daring".[36]
- Aas-paas barse, Dilli pani tarse (आस-पास बरसे, दिल्ली पानी तरसे), literally meaning "It pours all around, while Delhi lies parched". An allusion to the sometimes semi-arid climate of Delhi, it idiomatically refers to situations of deprivation when one is surrounded by plenty.[35]
History
Ancient and Early Medieval Periods
The area around Delhi was probably inhabited before the second millennium BCE and there is evidence of continuous inhabitation since at least the 6th century BCE.[20] The city is believed to be the site of Indraprastha, the legendary capital of the Pandavas in the Indian epic Mahabharata.[24] According to the Mahabharata, this land was initially a huge mass of forests called 'Khandavaprastha' which was burnt down to build the city of Indraprastha. The earliest architectural relics date back to the Maurya period (c. 300 BCE); in 1966, an inscription of the Mauryan Emperor Ashoka (273–235 BCE) was discovered near Srinivaspuri. Remains of several major cities can be found in Delhi. The first of these were in the southern part of present-day Delhi. King Anang Pal of the Tomara dynasty founded the city of Lal Kot in 736 CE. Prithviraj Chauhan conquered Lal Kot in 1178 and renamed it Qila Rai Pithora.
- The ancient Yogmaya Temple, claimed to be one of the five temples from the era of Mahabharata in Indraprastha.[37]
- The iron pillar of Delhi is said to have been fashioned at the time of Chandragupta Vikramaditya (375–413 CE) of the Gupta Empire.[38]
_-New_Delhi_-_N-DL-52_c(1).jpg)
 The bastion of Lal Kot fort in Delhi's Mehrauli attributed to the Tomara ruler, Anangpal in c. 736 CE.[40]
The bastion of Lal Kot fort in Delhi's Mehrauli attributed to the Tomara ruler, Anangpal in c. 736 CE.[40] Sculpture of ancient temple in Qutb Minar complex
Sculpture of ancient temple in Qutb Minar complex
Late Medieval Period

The king Prithviraj Chauhan was defeated in 1192 by Muhammad Ghori in the second battle of Tarain, a Muslim invader from Afghanistan, who made a concerted effort to conquer northern India.[24] By 1200, native Hindu resistance had begun to crumble, and the Muslim invaders were victorious. The newfound dominance of foreign Turkic Muslim dynasties in north India would last for the next five centuries. The slave general of Ghori, Qutb-ud-din Aibak, was given the responsibility of governing the conquered territories of India until Ghori returned to his capital, Ghor. When Ghori died without an heir in 1206 CE, his territories fractured, with various generals claiming sovereignty over different areas. Qutb-ud-din assumed control of Ghori's Indian possessions, and laid the foundation of the Delhi Sultanate and the Mamluk dynasty. He began construction of the Qutb Minar and Quwwat-al-Islam (Might of Islam) mosque, the earliest extant mosque in India. It was his successor, Iltutmish (1211–1236), who consolidated the Turkic conquest of northern India.[24][41] Razia Sultan, daughter of Iltutmish, succeeded him as the Sultan of Delhi. She was the first and only woman to rule over Delhi.
.jpg)
For the next three hundred years, Delhi was ruled by a succession of Turkic and an Afghan, Lodi dynasty. They built several forts and townships that are part of the seven cities of Delhi.[43] Delhi was a major centre of Sufism during this period.[44] The Mamluk Sultanate (Delhi) was overthrown in 1290 by Jalal ud din Firuz Khalji (1290–1320). Under the second Khalji ruler, Ala-ud-din Khalji, the Delhi sultanate extended its control south of the Narmada River in the Deccan. The Delhi sultanate reached its greatest extent during the reign of Muhammad bin Tughluq (1325–1351). In an attempt to bring the whole of the Deccan under control, he moved his capital to Daulatabad, Maharashtra in central India. However, by moving away from Delhi he lost control of the north and was forced to return to Delhi to restore order. The southern provinces then broke away. In the years following the reign of Firoz Shah Tughlaq (1351–1388), the Delhi Sultanate rapidly began to lose its hold over its northern provinces. Delhi was captured and sacked by Timur in 1398,[45] who massacred 100,000 captives.[46] Delhi's decline continued under the Sayyid dynasty (1414–1451), until the sultanate was reduced to Delhi and its hinterland. Under the Afghan Lodi dynasty (1451–1526), the Delhi sultanate recovered control of the Punjab and the Gangetic plain to once again achieve domination over Northern India. However, the recovery was short-lived and the sultanate was destroyed in 1526 by Babur, founder of the Mughal dynasty.
Early Modern Period
Babur was a descendant of Genghis Khan and Timur, from the Fergana Valley in modern-day Uzbekistan. In 1526, he invaded India, defeated the last Lodhi sultan in the First Battle of Panipat and founded the Mughal Empire that ruled from Delhi and Agra.[24] The Mughal dynasty ruled Delhi for more than three centuries, with a sixteen-year hiatus during the reigns of Sher Shah Suri and Hemu from 1540 to 1556.[47] In 1553, the Hindu king Hemu acceded to the throne of Delhi by defeating forces of Mughal Emperor Humayun at Agra and Delhi. However, the Mughals re-established their rule after Akbar's army defeated Hemu during the Second Battle of Panipat in 1556.[48][49][50] Shah Jahan built the seventh city of Delhi that bears his name Shahjahanabad, which served as the capital of the Mughal Empire from 1638 and is today known as the Old City or Old Delhi.[51]


After the death of Aurangzeb in 1707, the Mughal Empire's influence declined rapidly as the Hindu Maratha Empire from Deccan Plateau rose to prominence.[52] In 1737, Maratha forces led by Baji Rao I sacked Delhi following their victory against the Mughals in the First Battle of Delhi. In 1739, the Mughal Empire lost the huge Battle of Karnal in less than three hours against the numerically outnumbered but militarily superior Persian army led by Nader Shah of Persia. After his invasion, he completely sacked and looted Delhi, carrying away immense wealth including the Peacock Throne, the Daria-i-Noor, and Koh-i-Noor. The Mughals, severely further weakened, could never overcome this crushing defeat and humiliation which also left the way open for more invaders to come, including eventually the British.[53][54][55] Nader eventually agreed to leave the city and India after forcing the Mughal emperor Muhammad Shah I to beg him for mercy and granting him the keys of the city and the royal treasury.[56] A treaty signed in 1752 made Marathas the protectors of the Mughal throne in Delhi.[57]

In 1757, the Afghan ruler, Ahmad Shah Durrani, sacked Delhi. He returned to Afghanistan leaving a Mughal ruler named Alamgir II in nominal control. The Marathas again occupied Delhi in 1758, and were in control until their defeat in 1761 at the Third Battle of Panipat when the city was captured again by Ahmad Shah Durrani.[58] However, in 1771, the Marathas established a protectorate over Delhi when the Maratha ruler, Mahadji Shinde, recaptured Delhi and the Mughal Emperor Shah Alam II was installed as a client of the Maratha Confederacy in 1772.[59] In 1783, Sikhs under Baghel Singh captured Delhi and Red Fort but due to the treaty signed, Sikhs withdrew from Red Fort and agreed to restore Shah Alam II as the emperor.
Colonial Period
In 1803, during the Second Anglo-Maratha War, the forces of British East India Company defeated the Maratha forces in the Battle of Delhi.[60]
During the Indian Rebellion of 1857, Delhi fell to the forces of East India Company after a bloody fight known as the Siege of Delhi. The city came under the direct control of the British Government in 1858. It was made a district province of the Punjab.[24] In 1911, it was announced that the capital of British-held territories in India was to be transferred from Calcutta to Delhi.[61] The name "New Delhi" was given in 1927, and the new capital was inaugurated on 13 February 1931. New Delhi, also known as Lutyens' Delhi,[62] was officially declared as the capital of the Union of India after the country gained independence on 15 August 1947.[63] During the partition of India, thousands of Hindu and Sikh refugees, mainly from West Punjab fled to Delhi, while many Muslim residents of the city migrated to Pakistan. Migration to Delhi from the rest of India continues (as of 2013), contributing more to the rise of Delhi's population than the birth rate, which is declining.[64]
Post-Independence
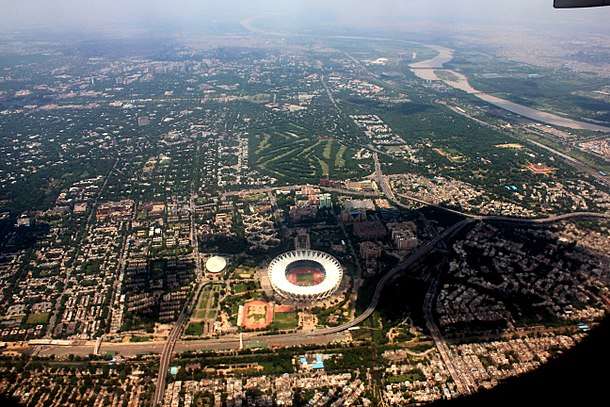

The States Reorganisation Act, 1956 created the Union Territory of Delhi from its predecessor, the Chief Commissioner's Province of Delhi.[1][2] The Constitution (Sixty-ninth Amendment) Act, 1991 declared the Union Territory of Delhi to be formally known as the National Capital Territory of Delhi.[3] The Act gave Delhi its own legislative assembly along Civil lines, though with limited powers.[3]
In 2001, the Parliament of India building in New Delhi was attacked by armed militants, killing six security personnel.[65] India suspected Pakistan-based militant groups were behind the attack, which caused a major diplomatic crisis between the two countries.[66] There were further terrorist attacks in Delhi in 2005 and 2008, resulting in a total of 103 deaths.[67]
Ecology
| Animal | Nilgai[68] | |
|---|---|---|
| Bird | House sparrow[69][70] | |
| Tree | Not designated[71] | |
| Flower | Alfalfa[68] |
Delhi is located in Northern India, at 28.61°N 77.23°E. The city is bordered on its northern, western, and southern sides by the state of Haryana and to the east by that of Uttar Pradesh (UP). Two prominent features of the geography of Delhi are the Yamuna flood plains and the Delhi ridge. The Yamuna river was the historical boundary between Punjab and UP, and its flood plains provide fertile alluvial soil suitable for agriculture but are prone to recurrent floods. The Yamuna, a sacred river in Hinduism, is the only major river flowing through Delhi. The Hindon River separates Ghaziabad from the eastern part of Delhi. The Delhi ridge originates from the Aravalli Range in the south and encircles the west, north-east and north-west parts of the city. It reaches a height of 318 m (1,043 ft) and is a dominant feature of the region.[72]
The National Capital Territory of Delhi covers an area of 1,484 km2 (573 sq mi), of which 783 km2 (302 sq mi) is designated rural, and 700 km2 (270 sq mi) urban therefore making it the largest city in terms of area in the country. It has a length of 51.9 km (32 mi) and a width of 48.48 km (30 mi).
Delhi is included in India's seismic zone-IV, indicating its vulnerability to major earthquakes.[73]
Climate
Delhi features a dry-winter humid subtropical climate (Köppen Cwa) bordering a hot semi-arid climate (Köppen BSh). The warm season lasts from 21 March to 15 June with an average daily high temperature above 39 °C (102 °F). The hottest day of the year is 22 May, with an average high of 40 °C (104 °F) and low of 28 °C (82 °F).[74] The cold season lasts from 26 November to 9 February with an average daily high temperature below 20 °C (68 °F). The coldest day of the year is 4 January, with an average low of 2 °C (36 °F) and high of 14 °C (57 °F).[74] In early March, the wind direction changes from north-westerly to south-westerly. From April to October the weather is hot. The monsoon arrives at the end of June, along with an increase in humidity.[75] The brief, mild winter starts in late November, peaks in January and heavy fog often occurs.[76]
Temperatures in Delhi usually range from 2 to 47 °C (35.6 to 116.6 °F), with the lowest and highest temperatures ever recorded being −2.2 and 48.4 °C (28.0 and 119.1 °F), respectively.[77] The annual mean temperature is 25 °C (77 °F); monthly mean temperatures range from 13 to 32 °C (55 to 90 °F). The highest temperature recorded in July was 45 °C (113 °F) in 1931.[78][79] The average annual rainfall is approximately 886 mm (34.9 in), most of which falls during the monsoon in July and August.[24] The average date of the advent of monsoon winds in Delhi is 29 June.[80]
Climate data for New Delhi (Safdarjung) 1981–2010, extremes 1901–present | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 30.0 (86.0) |
34.1 (93.4) |
40.6 (105.1) |
45.6 (114.1) |
47.2 (117.0) |
46.7 (116.1) |
45.0 (113.0) |
42.0 (107.6) |
40.6 (105.1) |
39.4 (102.9) |
36.1 (97.0) |
29.3 (84.7) |
47.2 (117.0) |
| Mean maximum °C (°F) | 25.5 (77.9) |
29.1 (84.4) |
35.3 (95.5) |
41.3 (106.3) |
43.7 (110.7) |
43.8 (110.8) |
39.7 (103.5) |
37.4 (99.3) |
37.1 (98.8) |
36.0 (96.8) |
32.2 (90.0) |
27.0 (80.6) |
44.5 (112.1) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 20.5 (68.9) |
23.9 (75.0) |
29.6 (85.3) |
36.3 (97.3) |
39.5 (103.1) |
39.2 (102.6) |
35.4 (95.7) |
34.1 (93.4) |
34.1 (93.4) |
32.8 (91.0) |
28.2 (82.8) |
23.1 (73.6) |
31.4 (88.5) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 14.1 (57.4) |
17.4 (63.3) |
22.7 (72.9) |
28.9 (84.0) |
32.7 (90.9) |
33.2 (91.8) |
31.4 (88.5) |
30.3 (86.5) |
29.6 (85.3) |
26.0 (78.8) |
20.5 (68.9) |
15.5 (59.9) |
25.2 (77.4) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 7.6 (45.7) |
10.4 (50.7) |
15.6 (60.1) |
21.3 (70.3) |
25.8 (78.4) |
27.9 (82.2) |
27.4 (81.3) |
26.6 (79.9) |
25.0 (77.0) |
19.1 (66.4) |
12.9 (55.2) |
8.3 (46.9) |
19.0 (66.2) |
| Mean minimum °C (°F) | 4.1 (39.4) |
6.1 (43.0) |
10.7 (51.3) |
16.0 (60.8) |
20.8 (69.4) |
22.3 (72.1) |
24.0 (75.2) |
23.6 (74.5) |
21.7 (71.1) |
14.7 (58.5) |
8.6 (47.5) |
4.6 (40.3) |
3.6 (38.5) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −0.6 (30.9) |
1.6 (34.9) |
4.4 (39.9) |
10.7 (51.3) |
15.2 (59.4) |
18.9 (66.0) |
20.3 (68.5) |
20.7 (69.3) |
17.3 (63.1) |
9.4 (48.9) |
3.9 (39.0) |
1.1 (34.0) |
−0.6 (30.9) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 19.3 (0.76) |
22.1 (0.87) |
15.9 (0.63) |
13.0 (0.51) |
31.5 (1.24) |
82.2 (3.24) |
187.3 (7.37) |
232.5 (9.15) |
129.8 (5.11) |
14.3 (0.56) |
4.9 (0.19) |
9.4 (0.37) |
762.3 (30.01) |
| Average rainy days | 1.3 | 1.8 | 1.6 | 1.2 | 2.5 | 4.6 | 9.4 | 9.8 | 5.5 | 1.0 | 0.5 | 0.9 | 40.1 |
| Average relative humidity (%) (at 17:30 IST) | 52 | 42 | 35 | 23 | 26 | 39 | 62 | 66 | 58 | 44 | 48 | 54 | 45 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 220.1 | 223.2 | 248.0 | 276.0 | 285.2 | 219.0 | 179.8 | 176.7 | 219.0 | 260.4 | 246.0 | 220.1 | 2,773.5 |
| Mean daily sunshine hours | 7.1 | 7.9 | 8.0 | 9.2 | 9.2 | 7.3 | 5.8 | 5.7 | 7.3 | 8.4 | 8.2 | 7.1 | 7.6 |
| Source 1: India Meteorological Department (sun 1971–2000)[81][82][83][84] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Tokyo Climate Center (mean temperatures 1981–2010)[85] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Delhi (Indira Gandhi International Airport) 1981–2010, extremes 1956–present | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 31.0 (87.8) |
35.7 (96.3) |
41.3 (106.3) |
45.3 (113.5) |
48.4 (119.1) |
47.8 (118.0) |
44.6 (112.3) |
43.2 (109.8) |
40.8 (105.4) |
40.7 (105.3) |
36.4 (97.5) |
30.4 (86.7) |
48.4 (119.1) |
| Mean maximum °C (°F) | 25.8 (78.4) |
29.4 (84.9) |
36.0 (96.8) |
42.5 (108.5) |
45.0 (113.0) |
44.9 (112.8) |
40.8 (105.4) |
38.3 (100.9) |
38.2 (100.8) |
36.7 (98.1) |
32.7 (90.9) |
27.0 (80.6) |
45.8 (114.4) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 20.4 (68.7) |
24.1 (75.4) |
29.9 (85.8) |
37.1 (98.8) |
40.3 (104.5) |
39.9 (103.8) |
35.9 (96.6) |
34.4 (93.9) |
34.7 (94.5) |
33.4 (92.1) |
28.5 (83.3) |
22.8 (73.0) |
31.8 (89.2) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 7.3 (45.1) |
10.2 (50.4) |
15.1 (59.2) |
21.4 (70.5) |
26.0 (78.8) |
27.7 (81.9) |
27.0 (80.6) |
26.2 (79.2) |
24.7 (76.5) |
19.5 (67.1) |
13.6 (56.5) |
8.8 (47.8) |
19.0 (66.2) |
| Mean minimum °C (°F) | 3.6 (38.5) |
5.7 (42.3) |
9.3 (48.7) |
15.1 (59.2) |
20.4 (68.7) |
22.1 (71.8) |
23.5 (74.3) |
23.2 (73.8) |
21.3 (70.3) |
14.9 (58.8) |
8.8 (47.8) |
4.6 (40.3) |
3.3 (37.9) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −2.2 (28.0) |
−1.6 (29.1) |
3.4 (38.1) |
8.6 (47.5) |
14.6 (58.3) |
19.8 (67.6) |
17.8 (64.0) |
20.2 (68.4) |
13.6 (56.5) |
9.9 (49.8) |
2.1 (35.8) |
−1.3 (29.7) |
−2.2 (28.0) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 18.4 (0.72) |
20.0 (0.79) |
13.2 (0.52) |
9.1 (0.36) |
37.7 (1.48) |
82.1 (3.23) |
174.4 (6.87) |
188.7 (7.43) |
105.3 (4.15) |
13.7 (0.54) |
5.1 (0.20) |
6.9 (0.27) |
674.5 (26.56) |
| Average rainy days | 1.4 | 1.7 | 1.4 | 1.0 | 2.6 | 4.0 | 8.6 | 8.3 | 4.6 | 0.9 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 35.7 |
| Average relative humidity (%) (at 17:30 IST) | 53 | 44 | 34 | 23 | 26 | 40 | 61 | 66 | 56 | 41 | 42 | 52 | 45 |
| Source: India Meteorological Department[86][87][88] | |||||||||||||
Air pollution

According to the World Health Organization (WHO) Delhi was the most polluted[90] city in the world in 2014. In 2016 WHO downgraded Delhi to eleventh-worst in the urban air quality database.[91] According to one estimate, air pollution causes the death of about 10,500 people in Delhi every year.[92][93][94] Air quality index of Delhi is generally Moderate (101–200) level between January to September, and then it drastically deteriorates to Very Poor (301–400), Severe (401–500) or Hazardous (500+) levels in three months between October to December, due to various factors including stubble burning, fire crackers burning during Diwali and cold weather.[95][96][97] During 2013–14, peak levels of fine particulate matter (PM) in Delhi increased by about 44%, primarily due to high vehicular and industrial emissions, construction work and crop burning in adjoining states.[92][98][99][100] It has the highest level of the airborne particulate matter, PM2.5 considered most harmful to health, with 153 micrograms.[101] Rising air pollution level has significantly increased lung-related ailments (especially asthma and lung cancer) among Delhi's children and women.[102][103] The dense smog and haze in Delhi during winter season results in major air and rail traffic disruptions every year.[104] According to Indian meteorologists, the average maximum temperature in Delhi during winters has declined notably since 1998 due to rising air pollution.[105]

India's Ministry of Earth Sciences published a research paper in October 2018 attributing almost 41% of PM2.5 air pollution in Delhi to vehicular emissions, 21.5% to dust/fire and 18% to industries.[106] The director of Centre for Science and Environment (CSE) alleged that the Society of Indian Automobile Manufacturers (SIAM) is lobbying "against the report" because it is "inconvenient" to the automobile industry.[107] Environmentalists have also criticised the Delhi government for not doing enough to curb air pollution and to inform people about air quality issues.[93] In 2014, an environmental panel appealed to India's Supreme Court to impose a 30% cess on diesel cars, but till date no action has been taken to penalise the automobile industry.[108]
Most of Delhi's residents are unaware of alarming levels of air pollution in the city and the health risks associated with it;[99][100] however, as of 2015, awareness, particularly among the foreign diplomatic community and high-income Indians, was noticeably increasing.[109] Since the mid-1990s, Delhi has undertaken some measures to curb air pollution—Delhi has the third-highest quantity of trees among Indian cities[110] and the Delhi Transport Corporation operates the world's largest fleet of environmentally friendly compressed natural gas (CNG) buses.[111] In 1996, the CSE started a public interest litigation in the Supreme Court of India that ordered the conversion of Delhi's fleet of buses and taxis to run on CNG and banned the use of leaded petrol in 1998. In 2003, Delhi won the United States Department of Energy's first 'Clean Cities International Partner of the Year' award for its "bold efforts to curb air pollution and support alternative fuel initiatives".[111] The Delhi Metro has also been credited for significantly reducing air pollutants in the city.[112]
However, according to several authors, most of these gains have been lost, especially due to stubble burning, a rise in the market share of diesel cars and a considerable decline in bus ridership.[113][114] According to CSE and System of Air Quality Weather Forecasting and Research (SAFAR), burning of agricultural waste in nearby Punjab, Haryana and Uttar Pradesh regions results in severe intensification of smog over Delhi.[115][116]
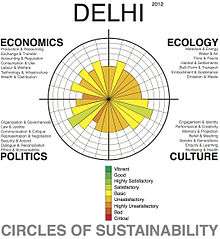
The Circles of Sustainability assessment of Delhi gives a marginally more favourable impression of the ecological sustainability of the city only because it is based on a more comprehensive series of measures than only air pollution. Part of the reason that the city remains assessed at basic sustainability is because of the low resource-use and carbon emissions of its poorer neighbourhoods.[117] In December 2019, IIT Bombay, in partnership with the McKelvey School of Engineering of Washington University in St. Louis, launched the Aerosol and Air Quality Research Facility to study air pollution in Delhi, among other Indian cities.[118] On 3 January 2020, Delhi got its first smog tower to tackle air pollution.[119][120]
Civic administration
Currently, the National Capital Territory of Delhi is made up of one division, 11 districts, 33 subdivisions, 59 census towns, and 300 villages.[121] Local civic administration has, since the trifurcation of the former Municipal Corporation of Delhi (MCD) in January 2012,[122] been in the hands of five bodies:
- the East Delhi Municipal Corporation;
- the North Delhi Municipal Corporation;
- the South Delhi Municipal Corporation;
- the New Delhi Municipal Council; and
- the Delhi Cantonment Board.
It was in July 2012, shortly after the MCD trifurcation, that the Government of Delhi increased the number of districts in the capital territory from nine to eleven.[123]
In terms of good governance and best administrative practices, Delhi was ranked fifth out of 21 Indian cities in 2014. It scored 3.6 out of 10 compared to the national average of 3.3.[124]
Delhi is home to the Supreme Court of India and the regional Delhi High Court. A Small Causes Court deals with civil cases, while a Magistrates' Court and the Sessions Court handle criminal cases in the city. For policing purposes Delhi is divided into eleven police districts which are further subdivided into 95 local police station zones.[125]
Government and politics
As a first-level administrative division, the National Capital Territory of Delhi has its own Legislative Assembly, Lieutenant Governor, council of ministers and Chief Minister. Members of the legislative assembly are directly elected from territorial constituencies in the NCT. The legislative assembly was abolished in 1956, after which direct federal control was implemented until it was re-established in 1993. The Municipal corporation handles civic administration for the city as part of the Panchayati Raj Act. The Government of India and the Government of National Capital Territory of Delhi jointly administer New Delhi, where both bodies are located. The Parliament of India, the Rashtrapati Bhavan (Presidential Palace), Cabinet Secretariat and the Supreme Court of India are located in the municipal district of New Delhi. There are 70 assembly constituencies and seven Lok Sabha (Indian parliament's lower house) constituencies in Delhi.[126][127] The Indian National Congress (Congress) formed all the governments in Delhi until the 1990s, when the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP), led by Madan Lal Khurana, came to power.[128] In 1998, the Congress returned to power under the leadership of Sheila Dikshit, who was subsequently re-elected for 3 consecutive terms. But in 2013, the Congress was ousted from power by the newly formed Aam Aadmi Party (AAP) led by Arvind Kejriwal forming the government with outside support from the Congress.[129] However, that government was short-lived, collapsing only after 49 days.[130] Delhi was then under President's rule until February 2015.[131] On 10 February 2015, the Aam Aadmi Party returned to power after a landslide victory, winning 67 out of the 70 seats in the Delhi Legislative Assembly.[132]
Since 2011 Delhi has had three municipal corporations:[133]
- SDMC having jurisdiction over South and West Delhi areas including Mahipalpur, Rajouri Garden, Janakpuri, Hari Nagar, Tilak Nagar, Dwarka, Jungpura, Greater Kailash, R K Puram, Malvya Nagar, Kalkaji, Ambedkar Nagar and Badarpur.
- NDMC has jurisdiction over areas such as Badli, Rithala, Bawana, Kirari, Mangolpuri, Tri Nagar, Model Town, Sadar Bazar, Chandni Chowk, Matia Mahal, Karol Bagh, Moti Nagar
- EDMC has jurisdiction over areas such as Patparganj, Kondli, Laxmi Nagar, Seemapuri, Gonda, Karawal Nagar, Babarpur and Shahadra
In 2017 the BJP emerged the victors in elections to all three corporations.[134]
Economy
Delhi is the largest commercial centre in northern India. As of 2016 recent estimates of the economy of the Delhi urban area have ranged from $167 to $370 billion (PPP metro GDP) ranking it either the most or second-most productive metro area of India.[17] The nominal GSDP of the NCT of Delhi for 2016–17 was estimated at ₹6,224 billion (US$87 billion), 13% higher than in 2015–16.[135][10] As per the Economic survey of Delhi (2005–2006), the tertiary sector contributes 70.95% of Delhi's gross SDP followed by secondary and primary sectors with 25.20% and 3.85% contributions, respectively.[136] Delhi's workforce constitutes 32.82% of the population, and increased by 52.52% between 1991 and 2001.[137] Delhi's unemployment rate decreased from 12.57% in 1999–2000 to 4.63% in 2003.[137] In December 2004, 636,000 people were registered with various employment exchange programmes in Delhi.[137]
In 2001 the total workforce in national and state governments and the quasi-government sector was 620,000, and the private sector employed 219,000.[137] Key service industries are information technology, telecommunications, hotels, banking, media and tourism.[138] Construction, power, health and community services and real estate are also important to the city's economy. Delhi has one of India's largest and fastest growing retail industries.[139] Manufacturing also grew considerably as consumer goods companies established manufacturing units and headquarters in the city. Delhi's large consumer market and the availability of skilled labour has also attracted foreign investment. In 2001, the manufacturing sector employed 1,440,000 workers and the city had 129,000 industrial units.[140]
Utility services
Delhi's municipal water supply is managed by the Delhi Jal Board (DJB). As of June 2005, it supplied 650 million gallons per day (MGD), whereas the estimated consumption requirement is 963 MGD.[141] The shortfall is met by private and public tube wells and hand pumps. At 240 MGD, the Bhakra storage is DJB's largest water source, followed by the Yamuna and Ganges rivers. Delhi's groundwater level is falling and its population density is increasing, so residents often encounter acute water shortage.[141] Research on Delhi suggests that up to half of the city's water use is unofficial groundwater.[142]
In Delhi, daily domestic solid waste production is 8000 tonnes which is dumped at three landfill locations by MCD.[143] The daily domestic waste water production is 470 MGD and industrial waste water is 70 MGD.[144] A large portion of the sewage flows untreated into the Yamuna river.[144]
The city's electricity consumption is about 1,265 kWh per capita but the actual demand is higher.[145] In Delhi power distribution is managed by Tata Power Distribution and BSES Yamuna & Rajdhani since 2002. The Delhi Fire Service runs 43 fire stations that attend about 15,000 fire and rescue calls per year.[146] The state-owned Mahanagar Telephone Nigam Limited (MTNL) and private enterprises such as Vodafone, Airtel, Idea Cellular, Reliance Infocomm, Aircel, Reliance Jio and Tata Docomo provide telephone and cell phone services to the city. Cellular coverage is available in GSM, CDMA, 3G and 4G.
Transport







Air
Indira Gandhi International Airport, situated to the south-west of Delhi, is the main gateway for the city's domestic and international civilian air traffic. In 2015–16, the airport handled more than 48 million passengers,[148] making it the busiest airport in India and South Asia. Terminal 3, which cost ₹96.8 billion (US$1.4 billion) to construct between 2007 and 2010, handles an additional 37 million passengers annually.[149] In 2010, IGIA was conferred the 4th best airport award in the world in the 15–25 million category, by Airports Council International. The airport was rated as the Best airport in the world in the 25–40 million passengers category in 2015, by Airports Council International. Delhi Airport was awarded The Best Airport in Central Asia and Best Airport Staff in Central Asia at the Skytrax World Airport Awards 2015.[150][151]
The Delhi Flying Club, established in 1928 with two de Havilland Moth aircraft named Delhi and Roshanara, was based at Safdarjung Airport which started operations in 1929, when it was the Delhi's only airport and the second in India.[152] The airport functioned until 2001; however, in January 2002 the government closed the airport for flying activities because of security concerns following the New York attacks in September 2001. Since then, the club only carries out aircraft maintenance courses and is used for helicopter rides to Indira Gandhi International Airport for VIP including the president and the prime minister.[152][153]
Hindon Domestic Airport in Ghaziabad was inaugurated by Prime Minister Narendra Modi as the second airport for the Delhi-NCR Region on 8 March 2019.[154]
A second international airport open for commercial flights has been suggested either by expansion of Meerut Airport or construction of a new airport in Greater Noida.[155] The Taj International Airport project in Jewar has been approved by the Uttar Pradesh government.[156]
Road
Delhi has the highest road density of 2103 km/100 km2 in India.[157] It is connected to other parts of India by five National Highways: NH 1, NH 2, NH 8, NH 10 and NH 24. The city's road network is maintained by MCD, NDMC, Delhi Cantonment Board, Public Works Department (PWD) and Delhi Development Authority.[158]
Buses are the most popular means of road transport catering to about 60% of Delhi's total demand.[159] Delhi has one of India's largest bus transport systems. In 1998, the Supreme Court of India ruled that all public transport vehicles in Delhi must be fuelled by compressed natural gas (CNG) to tackle increasing vehicular pollution.[160] The state-owned Delhi Transport Corporation (DTC) is a major bus service provider which operates the world's largest fleet of CNG-fuelled buses.[161][162] In addition, cluster scheme buses are operated by Delhi Integrated Multi-Modal Transit System (DIMTS) with the participation of private concessionaires and DTC.[163][164] In December 2017, the DTC and cluster buses carried over 4.19 million passengers per day.[165] Kashmiri Gate ISBT, Anand Vihar ISBT and Sarai Kale Khan ISBT are the main bus terminals for outstation buses plying to neighbouring states. Delhi's rapid rate of economic development and population growth has resulted in an increasing demand for transport, creating excessive pressure on the city's transport infrastructure. To meet the transport demand, the State and Union government constructed a mass rapid transit system, including the Delhi Metro.[166] Delhi Bus Rapid Transit System runs between Ambedkar Nagar and Delhi Gate.
Personal vehicles especially cars also form a major chunk of vehicles plying on Delhi roads. As of 2007, private vehicles account for 30% of the total demand for transport.[166] Delhi has the highest number of registered cars compared to any other metropolitan city in India.[167] Taxis, auto rickshaws, and cycle rickshaws also ply on Delhi roads in large numbers. As of 2008, the number of vehicles in the metropolitan region, Delhi NCR, was 11.2 million (11.2 million).[168] In 2008, there were 85 cars in Delhi for every 1,000 of its residents.[169] In 2017, the number of vehicles in Delhi city alone crossed the ten million mark with the transport department of Delhi Government putting the total number of registered vehicles at 10,567,712 until 25 May of the year.[170]
Important Roads in Delhi
Some roads and expressways serve as important pillars of Delhi's road infrastructure:
- The Inner Ring Road is one of the most important "state highways" in Delhi. It is a 51 km long circular road which connects important areas in Delhi. Owing to more than 2 dozen grade-separators/flyovers, the road is almost signal-free.
- The Outer Ring Road is another major artery in Delhi that links far-flung areas of Delhi.
- The Delhi Noida Direct Flyway or DND Flyway is an eight-laned access controlled tolled expressway which connects Delhi to Noida (an important satellite city of Uttar Pradesh).[171][172]
- The Delhi Gurgaon Expressway is a 28 km (17 mi) expressway connecting Delhi to Gurgaon, an important satellite city of Haryana.
- The Delhi Faridabad Skyway is controlled tolled expressway which connects Delhi to Faridabad, an important satellite city of Haryana.
National Highways Passing Through Delhi
Delhi is connected by road to various parts of the country through several National Highways: It is connected to other parts of India by five National Highways:
- NH 1 connects Amritsar in Punjab to New Delhi.
- NH 2 commonly referred as Delhi-Kolkata Road that runs through the states of Delhi, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Jharkhand and West Bengal.
- NH 8, now known as National Highway 48 connects the Indian capital city of New Delhi with the Indian Financial capital city of Mumbai via Jaipur and terminates at Chennai.
- NH 10, connects Fazilka in Punjab, India to Delhi.
- NH 24 connects the National capital Delhi to Uttar Pradesh state capital Lucknow running 438 kilometres (272 miles) in length.
Railway
Delhi is a major junction in the Indian railway network and is the headquarters of the Northern Railway. The main railway stations are New Delhi, Old Delhi, Hazrat Nizamuddin, Anand Vihar, Delhi Sarai Rohilla and Delhi Cantt.[166] The Delhi Metro, a mass rapid transit system built and operated by Delhi Metro Rail Corporation (DMRC), serves many parts of Delhi and the neighbouring cities Ghaziabad, Faridabad, Gurgaon and Noida.[173] As of August 2018, the metro consists of eight operational lines with a total length of 296 km (184 mi) and 214 stations, and several other lines are under construction.[174] The Phase-I was built at a cost of US$2.3 billion and the Phase-II was expected to cost an additional ₹216 billion (US$3.0 billion).[175] Phase-II has a total length of 128 km and was completed by 2010.[176] Delhi Metro completed 10 years of operation on 25 December 2012. It carries millions of passengers every day.[177] In addition to the Delhi Metro, a suburban railway, the Delhi Suburban Railway exists.[178]
Metro

The Delhi Metro is a rapid transit system serving Delhi, Ghaziabad, Faridabad, Gurgaon and Noida in the National Capital Region of India. Delhi Metro is the world's tenth-largest metro system in terms of length. Delhi Metro was India's second modern public transportation system, which has revolutionised travel by providing a fast, reliable, safe, and comfortable means of transport. The network consists of eleven lines with a total length of 311 kilometres (193 miles) with 214 stations, which are a mix of underground, at-grade and elevated stations. All stations have escalators, lifts, and tactile tiles to guide the visually impaired from station entrances to trains. There are 18 designated parking sites at Metro stations to further encourage the use of the system. In March 2010, DMRC partnered with Google India (through Google Transit) to provide train schedule and route information to mobile devices with Google Maps. It has a combination of elevated, at-grade, and underground lines, and uses both broad gauge and standard gauge rolling stock. Four types of rolling stock are used: Mitsubishi–ROTEM Broad gauge, Bombardier MOVIA, Mitsubishi–ROTEM Standard gauge, and CAF Beasain Standard gauge. The Phase-I of Delhi Metro was built at a cost of US$2.3 billion and the Phase-II was expected to cost an additional ₹216 billion (US$3.0 billion).[175] Phase-II has a total length of 128 km and was completed by 2010.[176] Delhi Metro completed 10 years of operation on 25 December 2012. It carries millions of passengers every day.[177]
Delhi Metro is being built and operated by the Delhi Metro Rail Corporation Limited (DMRC), a state-owned company with equal equity participation from Government of India and Government of National Capital Territory of Delhi. However, the organisation is under the administrative control of Ministry of Urban Development, Government of India. Besides construction and operation of Delhi Metro, DMRC is also involved in the planning and implementation of metro rail, monorail, and high-speed rail projects in India and providing consultancy services to other metro projects in the country as well as abroad. The Delhi Metro project was spearheaded by Padma Vibhushan E. Sreedharan, the managing director of DMRC and popularly known as the "Metro Man" of India. He famously resigned from DMRC taking moral responsibility for a metro bridge collapse, which took five lives. Sreedharan was awarded the prestigious Legion of Honour by the French Government for his contribution to Delhi Metro.[179]
Regional Rapid Transit System (RRTS)
The 08 RRTS Corridors have been proposed by National Capital Region Planning Board (NCRPB) to facilitate the people travelling from nearby cities in NCR to Delhi.[180] The three main corridors in the first phase are as follows:[181]
- Delhi – Alwar via Gurugram – 180.50 km
- Delhi – Panipat via Sonipat – 111 km
- Delhi – Meerut via Ghaziabad – 92.05 km
Remaining five corridors are also approved by National Capital Region Planning Board but are planned in the second phase.[181]
Demographics
| Population Growth of Delhi | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Population | %± | |
| 1901 | 405,819 | — | |
| 1911 | 413,851 | 2.0% | |
| 1921 | 488,452 | 18.0% | |
| 1931 | 636,246 | 30.3% | |
| 1941 | 917,939 | 44.3% | |
| 1951 | 1,744,072 | 90.0% | |
| 1961 | 2,658,612 | 52.4% | |
| 1971 | 4,065,698 | 52.9% | |
| 1981 | 6,220,406 | 53.0% | |
| 1991 | 9,420,644 | 51.4% | |
| 2001 | 13,782,976 | 46.3% | |
| 2011 | 16,753,235 | 21.6% | |
| source:[182] † Huge population rise in 1951 due to large scale migration after Partition of India in 1947. | |||
According to the 2011 census of India, the population of NCT of Delhi is 16,753,235.[182] The corresponding population density was 11,297 persons per km2 with a sex ratio of 866 women per 1000 men, and a literacy rate of 86.34%. In 2004, the birth rate, death rate and infant mortality rate per 1000 population were 20.03, 5.59 and 13.08, respectively.[183] In 2001, the population of Delhi increased by 285,000 as a result of migration and by 215,000 as a result of natural population growth,[183] which made Delhi one of the fastest growing cities in the world. Dwarka Sub City, Asia's largest planned residential area, is located within the National Capital Territory of Delhi.[184] Urban expansion has resulted in Delhi's urban area now being considered as extending beyond the NCT boundaries to incorporate the towns and cities of neighbouring states including Faridabad and Gurgaon of Haryana, and Ghaziabad and Noida of Uttar Pradesh, the total population of which is estimated by the United Nations at over 26 million. According to the UN this makes Delhi urban area the world's second-largest, after Tokyo,[7] although Demographia declares the Jakarta urban area to be the second-largest.[185] The 2011 census provided two figures for urban area population: 16,314,838 within the NCT boundary,[186] and 21,753,486 for the Extended Urban Area.[187] The 2021 regional plan released by the Government of India renamed the Extended Urban Area from Delhi Metropolitan Area (DMA) as defined by the 2001 plan[188] to Central National Capital Region (CNCR).[188][189]
Major social groups of Delhi include Brahmins, Jats, Punjabis, Purvanchalis, Vaishyas, Gujjars, Sikhs, Muslims, Uttarakhandis, Bengalis, etc.[190][191][192][193][182]
Religion


 Gurudwara Bangla Sahib is one of the most prominent Sikh Gurdwara in Delhi, and known for its association with the eighth Sikh Guru, Guru Har Krishan.
Gurudwara Bangla Sahib is one of the most prominent Sikh Gurdwara in Delhi, and known for its association with the eighth Sikh Guru, Guru Har Krishan.
- Cathedral Church of the Redemption, belonging to the Church of North India.
Hinduism is Delhi's predominant religious faith, with 81.68% of Delhi's population, followed by Islam (12.86%), Sikhism (3.40%), Jainism (0.99%), Christianity (0.87%), and Buddhism (0.11%).[196] Other minority religions include Zoroastrianism, Baha'ism and Judaism.[197]
Languages
According to the 50th report of the commissioner for linguistic minorities in India, which was submitted in 2014, Hindi is Delhi's most spoken language, with 80.94% speakers, followed by Punjabi (7.14%), Urdu (6.31%) and Bengali (1.50%). 4.11% of the Delhites speak other languages.[199] Hindi is also the official language of Delhi while Urdu and Punjabi have been declared as additional official languages.[199]
According to the Directorate of Education, GNCTD the following languages are taught in schools in Delhi under the three-language formula:[200]
- First Language
- Hindi
- Urdu
- English
- Second Language
- English
- Third language
- Urdu
- Punjabi
- Bengali
- Sindhi
- Tamil
- Telugu
- Malayalam
- Kannada
- Gujarati
- Marathi
- Arabic
- Persian
- Sanskrit
Culture

Delhi's culture has been influenced by its lengthy history and historic association as the capital of India, Although a strong Punjabi Influence can be seen in language, Dress and Cuisine brought by the large number of refugees who came following the partition in 1947 the recent migration from other parts of India has made it a melting pot. This is exemplified by many significant monuments in the city. Delhi is also identified as the location of Indraprastha, the ancient capital of the Pandavas. The Archaeological Survey of India recognises 1,200 heritage buildings[203] and 175 monuments as national heritage sites.[204]
In the Old City, the Mughals and the Turkic rulers constructed several architecturally significant buildings, such as the Jama Masjid—India's largest mosque[205] built in 1656[206] and the Red Fort. Three World Heritage Sites—the Red Fort, Qutub Minar and Humayun's Tomb—are located in Delhi.[207] Other monuments include the India Gate, the Jantar Mantar—an 18th-century astronomical observatory—and the Purana Qila—a 16th-century fortress. The Laxminarayan Temple, Akshardham temple, Gurudwara Bangla Sahib, the Bahá'í Lotus Temple and the ISKCON temple are examples of modern architecture. Raj Ghat and associated memorials houses memorials of Mahatma Gandhi and other notable personalities. New Delhi houses several government buildings and official residences reminiscent of British colonial architecture, including the Rashtrapati Bhavan, the Secretariat, Rajpath, the Parliament of India and Vijay Chowk. Safdarjung's Tomb is an example of the Mughal gardens style. Some regal havelis (palatial residences) are in the Old City.[208]
Lotus Temple is a Bahá'í House of Worship completed in 1986. Notable for its flowerlike shape, it serves as the Mother Temple of the Indian subcontinent and has become a prominent attraction in the city. The Lotus Temple has won numerous architectural awards and been featured in hundreds of newspaper and magazine articles. Like all other Bahá'í Houses of Worship, is open to all regardless of religion, or any other distinction, as emphasised in Bahá'í texts. The Bahá'í laws emphasise that the spirit of the House of Worship be that it is a gathering place where people of all religions may worship God without denominational restrictions.[209] The Bahá'í laws also stipulate that only the holy scriptures of the Bahá'í Faith and other religions can be read or chanted inside in any language; while readings and prayers can be set to music by choirs, no musical instruments can be played inside. Furthermore, no sermons can be delivered, and there can be no ritualistic ceremonies practised.[209]
The National Museum and National Gallery of Modern Art are some of the largest museums in the country. Other museums in Delhi include the National Museum of Natural History, National Rail Museum and National Philatelic Museum.
Chandni Chowk, a 17th-century market, is one of the most popular shopping areas in Delhi for jewellery and Zari saris.[210] Delhi's arts and crafts include, Zardozi[211]—an embroidery done with gold thread—[212] and Meenakari[213]—the art of enamelling.
Festivals

Delhi's association and geographic proximity to the capital, New Delhi, has amplified the importance of national events and holidays like Republic Day, Independence Day (15 August) and Gandhi Jayanti. On Independence Day, the Prime Minister addresses the nation from the Red Fort. Most Delhiites celebrate the day by flying kites, which are considered a symbol of freedom.[214] The Republic Day Parade is a large cultural and military parade showcasing India's cultural diversity and military strength.[215][216] Over the centuries, Delhi has become known for its composite culture, and a festival that symbolises this is the Phool Walon Ki Sair, which takes place in September. Flowers and pankhe—fans embroidered with flowers—are offered to the shrine of the 13th-century Sufi saint Khwaja Bakhtiyar Kaki and the Yogmaya Temple, both situated in Mehrauli.[217]
Religious festivals include Diwali (the festival of lights), Mahavir Jayanti, Guru Nanak's Birthday, Raksha Bandhan, Durga Puja, Holi, Lohri, Chauth, Krishna Janmastami, Maha Shivratri, Eid ul-Fitr, Moharram and Buddha Jayanti.[216] The Qutub Festival is a cultural event during which performances of musicians and dancers from all over India are showcased at night, with the Qutub Minar as a backdrop.[218] Other events such as Kite Flying Festival, International Mango Festival and Vasant Panchami (the Spring Festival) are held every year in Delhi. The Auto Expo, Asia's largest auto show,[219] is held in Delhi biennially. The New Delhi World Book Fair, held biennially at the Pragati Maidan, is the second-largest exhibition of books in the world.[220] Delhi is often regarded as the "Book Capital" of India because of high readership.[221] India International Trade Fair (IITF), organised by ITPO is the biggest cultural and shopping fair of Delhi which takes place in November each year and is visited by more than 1.5 million people.[222]
Cuisine
As India's national capital and centuries old Mughal capital, Delhi influenced the food habits of its residents and is where Mughlai cuisine originated. Along with Indian cuisine, a variety of international cuisines are popular among the residents.[224] The dearth of food habits among the city's residents created a unique style of cooking which became popular throughout the world, with dishes such as Kebab, biryani, tandoori. The city's classic dishes include butter chicken, dal makhani, shahi paneer, aloo chaat, chaat, dahi bhalla, kachori, gol gappe, samosa, chole bhature, chole kulche, gulab jamun, jalebi and lassi.[224][225]:40–50, 189–196
The fast living habits of Delhi's people has motivated the growth of street food outlets.[225]:41 A trend of dining at local dhabas is popular among the residents. High-profile restaurants have gained popularity in recent years, among the popular restaurants are the Karim Hotel, the Punjab Grill and Bukhara.[226] The Gali Paranthe Wali (the street of fried bread) is a street in Chandni Chowk particularly for food eateries since the 1870s. Almost the entire street is occupied by fast food stalls or street vendors. It has nearly become a tradition that almost every prime minister of India has visited the street to eat paratha at least once. Other Indian cuisines are also available in this area even though the street specialises in north Indian food.[225]:40–50[227]
Tourism

According to Euromonitor International, Delhi ranked as 28th-most visited city in the world and first in India by foreign visitors in 2015.[228] There are numerous tourist attractions in Delhi, both historic and modern. The three UNESCO World Heritage Sites in Delhi, Qutb Complex, Red Fort and Humayun's Tomb are among the finest examples of Indo-Islamic architecture.[229] Another prominent landmark of Delhi is India Gate, a 1931 built war memorial to soldiers of British Indian Army who died during First World War.[230] Delhi has several famous places of worship of various religions. One of the largest Hindu temple complexes in the world,[231] Akshardham is a major tourist attraction in the city. Other famous religious sites include Lal Mandir, Laxminarayan Temple, Gurudwara Bangla Sahib, Lotus Temple, Jama Masjid and ISKCON Temple.
Delhi is also a hub for shopping of all kinds. Connaught Place, Chandni Chowk, Sarojini Nagar, Khan Market and Dilli Haat are some of the major retail markets in Delhi.[232] Major shopping malls include Select Citywalk, Pacific Mall, DLF Promenade, DLF Emporio, Metro Walk and Ansal Plaza.[233]
Education
Private schools in Delhi—which use either English or Hindi as the language of instruction—are affiliated to one of three administering bodies, the Council for the Indian School Certificate Examinations (CISCE), the Central Board for Secondary Education (CBSE)[234] or the National Institute of Open Schooling (NIOS). In 2004–05, approximately 1,529,000 students were enrolled in primary schools, 822,000 in middle schools and 669,000 in secondary schools across Delhi.[235] Female students represented 49% of the total enrolment. The same year, the Delhi government spent between 1.58% and 1.95% of its gross state domestic product on education.[235]
Schools and higher educational institutions in Delhi are administered either by the Directorate of Education, the NCT government or private organisations. In 2006, Delhi had 165 colleges, five medical colleges and eight engineering colleges,[235] seven major universities and nine deemed universities.[235]
The premier management colleges of Delhi such as Faculty of Management Studies (Delhi) and Indian Institute of Foreign Trade rank the best in India. All India Institute of Medical Sciences Delhi is a premier medical school for treatment and research. National Law University, Delhi is a prominent law school and is affiliated to the Bar Council of India. The Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi situated in Hauz Khas is a premier engineering college of India and ranks as one of the top institutes in South Asia.
Delhi Technological University (formerly Delhi College of Engineering), Indraprastha Institute of Information Technology, Netaji Subhas Institute of Technology, Guru Gobind Singh Indraprastha University and National Law University, Delhi are the only state universities.[236] University of Delhi, Jawaharlal Nehru University and Jamia Millia Islamia are the central universities, and Indira Gandhi National Open University is for distance education.[237] As of 2008, about 16% of all Delhi residents possessed at least a college graduate degree.[238]
Media

As the capital of India, Delhi is the focus of political reportage, including regular television broadcasts of Parliament sessions. Many national media agencies, including the state-owned Press Trust of India, Media Trust of India and Doordarshan, is based in the city. Television programming includes two free terrestrial television channels offered by Doordarshan, and several Hindi, English, and regional-language cable channels offered by multi system operators. Satellite television has yet to gain a large quantity of subscribers in the city.[239]
Print journalism remains a popular news medium in Delhi. The city's Hindi newspapers include Navbharat Times, Hindustan Dainik, Punjab Kesari, Pavitra Bharat, Dainik Jagran, Dainik Bhaskar, Dainik Prayukti, Amar Ujala and Dainik Desbandhu. Amongst the English language newspapers, The Hindustan Times, with a daily circulation of over a million copies, is the single largest daily.[240] Other major English newspapers include The Times of India, The Hindu, Indian Express, Business Standard, The Pioneer, The Statesman, and The Asian Age. Regional language newspapers include the Malayalam daily Malayala Manorama and the Tamil dailies Dinamalar and Dinakaran.
Radio is a less popular mass medium in Delhi, although FM radio has gained popularity[241] since the inauguration of several new stations in 2006.[242] A number of state-owned and private radio stations broadcast from Delhi.[243][244]
Sports
Delhi has hosted many major international sporting events, including the inaugural 1951 Asian Games, 1982 Asian Games, 1989 Asian Athletic Championships, 2010 Hockey World Cup, 2010 Commonwealth Games and 2011 Cricket World Cup.
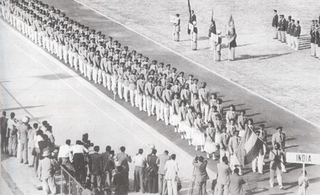
1951 Asian Games
Delhi hosted the first Asian Games in 1951 from 4 to 11 March. A total of 489 athletes representing 11 Asian National Olympic Committees participated in 57 events from eight sports and discipline. The Games was the successor of the Far Eastern Games and the revival of the Western Asiatic Games. On 13 February 1949, the Asian Games Federation was formally established in Delhi, with Delhi unanimously announced as the first host city of the Asian Games. National Stadium was the venue for all events.[245] Over 40,000 spectators watched the opening ceremony of the Games in National Stadium.[246]
1982 Asian Games
Delhi hosted the ninth Asian Games for the second time in 1982 from 19 November to 4 December. This was the second time the city has hosted the Asian Games and was also the first Asian Games to be held under the aegis of the Olympic Council of Asia. A total of 3,411 athletes from 33 National Olympic Committees participated in these games, competing in 196 events in 21 sports and 23 disciplines. The Jawaharlal Nehru Stadium, which was built purposely for the event, hosted its opening ceremony.[247]

2010 Commonwealth Games
Delhi hosted the nineteenth Commonwealth Games in 2010, which ran from 3 to 14 October and was the largest sporting event held in India.[248][249] The opening ceremony of the 2010 Commonwealth Games was held at the Jawaharlal Nehru Stadium, the main stadium of the event, in New Delhi at 7:00 pm Indian Standard Time on 3 October 2010.[250] The ceremony featured over 8,000 performers and lasted for two and a half hours.[251] It is estimated that ₹3.5 billion (US$49 million) were spent to produce the ceremony.[252] Events took place at 12 competition venues. 20 training venues were used in the Games, including seven venues within Delhi University.[253] The rugby stadium in Delhi University North Campus hosted rugby games for Commonwealth Games.[253]
Other sports

Cricket and football are the most popular sports in Delhi.[254] There are several cricket grounds, or maidans, located across the city. The Arun Jaitley Stadium (known commonly as the Kotla) is one of the oldest cricket grounds in India and is a venue for international cricket matches. It is the home ground of the Delhi cricket team, which represents the city in the Ranji Trophy, the premier Indian domestic first-class cricket championship.[255] The Delhi cricket team has produced several world-class international cricketers such as Virender Sehwag, Virat Kohli,[256] Gautam Gambhir, Madan Lal, Chetan Chauhan, Shikhar Dhawan, Ishant Sharma, Manoj Prabhakar and Bishan Singh Bedi to name a few. The Railways and Services cricket teams in the Ranji Trophy also play their home matches in Delhi, in the Karnail Singh Stadium and the Harbax Singh Stadium, respectively. The city is also home to the Indian Premier League team Delhi Capitals, who play their home matches at the Kotla.
Ambedkar Stadium, a football stadium in Delhi which holds 21,000 people, was the venue for the Indian football team's World Cup qualifier against UAE on 28 July 2012.[257] Delhi hosted the Nehru Cup in 2007[258] and 2009, in both of which India defeated Syria 1–0.[259] In the Elite Football League of India, Delhi's first professional American football franchise, the Delhi Defenders played its first season in Pune.[260] Buddh International Circuit in Greater Noida, a suburb of Delhi, formerly hosted the Formula 1 Indian Grand Prix.[261] The Indira Gandhi Arena is also in Delhi.
Delhi is a member of the Asian Network of Major Cities 21.
Current Regional and Professional Sports Teams from Delhi
| Team/Club | Tournament/League | Sport | Venue | Established |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Delhi cricket team | Ranji Trophy | Cricket | Arun Jaitley Stadium | 1934 |
| Delhi football team | Santosh Trophy | Football | Jawaharlal Nehru Stadium | 1941 |
| Delhi Capitals | Indian Premier League | Cricket | Arun Jaitley Stadium | 2008 |
| Delhi Waveriders | Hockey India League | Field hockey | Shivaji Stadium | 2012 |
| Dabang Delhi | Pro Kabaddi League | Kabaddi | Thyagaraj Sports Complex | 2014 |
| Delhi Dreams | Champions Tennis League | Tennis | R.K. Khanna Tennis Complex | 2014 |
| Indian Aces | International Premier Tennis League | Tennis | Indira Gandhi Indoor Stadium | 2014 |
| Delhi Hurricanes RFC | All India & South Asia Rugby Tournament | Rugby union | B-7 Vasant Kunj 110070 Delhi | 2004 |
| Delhi Defenders | Elite Football League of India | American football | – | 2012 |
| Delhi Wizards | World Series Hockey | Field hockey | Dhyan Chand National Stadium | 2011 |
| Delhi Capitals | UBA Pro Basketball League | Basketball | – | 2015 |
Former Regional and Professional Sports Teams from Delhi
| Team/Club | Tournament/League | Sport | Venue | Established | Ceased |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Delhi Giants | Indian Cricket League | Cricket | N/A | 2007 | 2009 |
| Delhi Dynamos | Indian Super League | Football | Kalinga Stadium | 2014 | 2019 |
Notable people
International relations
- Sister cities[262]



- Partnerships[262]
.svg.png)




See also
- Chennai district
- Delhi metropolitan area
- Kolkata district
- List of twin towns and sister cities in India
- Mumbai City district
References
- "The Constitution (Seventh Amendment) Act, 1956". Ministry of Law and Justice (India). 1956. Archived from the original on 1 May 2017. Retrieved 16 March 2017.
- "The States Reorganisation Act, 1956" (PDF). Ministry of Law and Justice (India). 1956. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 March 2017. Retrieved 16 March 2017.
- "The Constitution (Sixty-Ninth Amendment) Act, 1991". Government of India. National Informatics Centre, Ministry of Communications and Information Technology, Government of India. Archived from the original on 21 August 2016. Retrieved 8 January 2007.
- "Anil Baijal takes over as new Lt Governor of Delhi". The Times of India. Delhi. 31 December 2016. Archived from the original on 3 January 2017. Retrieved 31 December 2016.
- Delhi Metropolitan/City Population section of "Delhi Population Sex Ratio in Delhi Literacy rate Delhi NCR". 2011 Census of India. Archived from the original on 26 January 2017.
- "Delhi (India): Union Territory, Major Agglomerations & Towns – Population Statistics in Maps and Charts". City Population. Archived from the original on 2 March 2017. Retrieved 28 February 2017.
- "The World's Cities in 2016" (PDF). United Nations. October 2016. p. 4. Archived (PDF) from the original on 12 January 2017. Retrieved 4 March 2017.
- "Official Language Act 2000" (PDF). Government of Delhi. 2 July 2003. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 17 July 2015.
- "Gross State Domestic Product of Delhi" (PDF). Planning Department, Government of Delhi. p. 16. Archived (PDF) from the original on 1 July 2020. Retrieved 9 June 2019.
- "Mumbai is no more the financial capital of India". Business Insider India. 28 November 2016. Retrieved 13 August 2020.
- "Find Pin Code". Department of Posts. Archived from the original on 3 June 2019. Retrieved 5 June 2019.
- "Sub-national HDI – Area Database". Global Data Lab. Institute for Management Research, Radboud University. Archived from the original on 23 September 2018. Retrieved 25 September 2018.
- "Census 2011 (Final Data) – Demographic details, Literate Population (Total, Rural & Urban)" (PDF). planningcommission.gov.in. Planning Commission, Government of India. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 January 2018. Retrieved 3 October 2018.
- "The Constitution (Sixty-Ninth Amendment) Act, 1991". Ministry of Law and Justice, Government of India. Archived from the original on 21 August 2016. Retrieved 23 November 2014.
- Habib, Irfan (1999). The agrarian system of Mughal India, 1556–1707. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-562329-1.
... The current Survey of India spellings are followed for place names except where they vary rather noticeably from the spellings in our sources: thus I read "Dehli" not "Delhi ...
- Royal Asiatic Society (1834). "Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society of Great Britain & Ireland". Cambridge University Press.
... also Dehli or Dilli, not Delhi...
Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - Karamchandani, L.T (1968). "India, the beautiful". Sita Publication.
... According to available evidence the present Delhi, spelt in Hindustani as Dehli or Dilli, derived its name from King ...
Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - "The National geographical journal of India, Volume 40". National Geographical Society of India. 1994.
... The name which remained the most popular is "Dilli" with variation in its pronunciation as Dilli, Dehli, or Delhi ...
Cite journal requires|journal=(help)
- Royal Asiatic Society (1834). "Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society of Great Britain & Ireland". Cambridge University Press.
- "This study settles the Delhi versus Mumbai debate: The Capital's economy is streets ahead". Archived from the original on 21 December 2018. Retrieved 21 December 2018.
-
- "Global city GDP 2014". Brookings Institution. 22 January 2015. Archived from the original on 25 May 2017. Retrieved 4 March 2017.
- "Global city GDP rankings 2008–2025". PwC. Archived from the original on 4 May 2011. Retrieved 16 December 2009.
- "The Most Dynamic Cities of 2025". Foreign Policy. Archived from the original on 28 August 2012. Retrieved 24 August 2012.
- "Mumbai richest Indian city with total wealth of $820 billion, Delhi comes second: Report". The Indian Express. 27 February 2017. Archived from the original on 27 February 2017. Retrieved 28 February 2017.
- —Pletcher, Kenneth (1 April 2010). The Geography of India: Sacred and Historic Places Understanding India. Britannica Educational Publishing. p. 114. ISBN 978-1-615-30202-4. Archived from the original on 12 July 2020. Retrieved 11 July 2020.
—Prakasa Rao, Vaddiparti Lova Surya; Sundaram, K.V.; Ram, Vernon, "Delhi", Encyclopaedia Britannica, archived from the original on 25 July 2020, retrieved 5 July 2020,Delhi is of great historical significance as an important commercial, transport, and cultural hub, as well as the political centre of India.
—Seth, Himanshu; Sorathia, Keyur (21 March 2013). "ZOR SE BOLO: Interactive installations for Airport, providing a linguistic tour of New Delhi". Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers. Kharagpur: 1–7. doi:10.1109/IHCI.2012.6481861. ISBN 978-1-4673-4369-5. S2CID 16024675. Archived from the original on 13 July 2020. Retrieved 11 July 2020. - Asher, Catherine B (2000) [2000]. "Chapter 9:Delhi walled: Changing Boundaries". In James D. Tracy (ed.). City Walls. Cambridge University Press. pp. 247–281. ISBN 978-0-521-65221-6. Retrieved 1 November 2008.
- —Pletcher, Kenneth (1 April 2010). The Geography of India: Sacred and Historic Places Understanding India. Britannica Educational Publishing. p. 119. ISBN 978-1-615-30202-4. Archived from the original on 12 July 2020. Retrieved 11 July 2020.
—Prakasa Rao, Vaddiparti Lova Surya; Sundaram, K.V.; Ram, Vernon, "Delhi – Economy", Encyclopaedia Britannica, archived from the original on 29 July 2020, retrieved 5 July 2020,For many centuries Old Delhi has been a dominant trading and commercial centre in northern India. Since the 1990s New Delhi has emerged as an important node in the international corporate and financial network.
—Encyclopaedia Britannica, Inc. (1 March 2009). Britannica Guide to India. Encyclopaedia Britannica, Inc. pp. 379–380. ISBN 978-1-593-39847-7. Archived from the original on 29 July 2020. Retrieved 30 July 2020. - "Rationale". ncrpb.nic.in. NCR Planning Board. Archived from the original on 16 December 2012. Retrieved 5 March 2017.
The National Capital Region (NCR) in India was constituted under the NCRPB Act, 1985
- "Census 2011" (PDF). National Capital Region Planning Board. National Informatics Centre. p. 3. Archived (PDF) from the original on 6 April 2016. Retrieved 26 March 2016.
- "Chapter 1: Introduction" (PDF). Economic Survey of Delhi, 2005–2006. Planning Department, Government of National Capital Territory of Delhi. pp. 1–7. Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 November 2016. Retrieved 21 December 2011.
- Bakshi, S.R. (1995) [2002]. Delhi Through Ages. Whispering Eye Bangdat. p. 2. ISBN 978-81-7488-138-0.
- Smith, George (1882). The Geography of British India, Political & Physical. J. Murray. pp. 216–217. Retrieved 1 November 2008.
raja delhi BC.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 1 July 2020. Retrieved 30 July 2020.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Our Pasts II, History Textbook for Class VII". NCERT. Archived from the original on 23 June 2007. Retrieved 6 July 2007.
- Delhi City Archived 3 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine The Imperial Gazetteer of India, 1909, v. 11, p. 236..
- "A Dictionary of Urdu, Classical Hindi, and English". Dsal.uchicago.edu. 1884. Archived from the original on 16 October 2011. Retrieved 24 October 2011.
- Cohen, Richard J. (October–December 1989). "An Early Attestation of the Toponym Dhilli". Journal of the American Oriental Society. 109 (4): 513–519. doi:10.2307/604073. JSTOR 604073.
- Austin, Ian; Thhakur Nahar Singh Jasol. "Chauhans (Cahamanas, Cauhans)". The Mewar Encyclopedia. mewarindia.com. Archived from the original on 14 November 2006. Retrieved 22 December 2006.
- "Why developers charge a premium for upper storeys in Delhi/NCR region". The Economic Times. 5 August 2011. Archived from the original on 27 January 2013. Retrieved 30 May 2012.
- John Murray (1924). "A handbook for travellers in India, Burma and Ceylon". J. Murray, 1924.
... "Dilli hanoz dur ast" ("Delhi is still far off") – has passed into the currency of a proverb ...
Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - S.W. Fallon; Dihlavi Fakir Chand (1886). "A dictionary of Hindustani proverbs". Printed at the Medical hall press, 1886.
... Abhi Dilli dur hai ...
Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - "India today, Volume 31, Issues 13–25". Thomson Living Media India Ltd., 2006. 2006. Archived from the original on 13 June 2013.
... As the saying in Hindustani goes: "Dilli dilwalon ki (Delhi belongs to those with a heart)". So shed your inhibitions and try out your hand ...
Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - Prabha Chopra (1976). Delhi Gazetteer. The Unit. p. 1078.
- Finbarr Barry Flood, 2003, "Pillar, palimpsets, and princely practices" Archived 30 September 2016 at the Wayback Machine, Res, Xliii, New York University, p. 97.
- Mittal, J.P. (2006), History of Ancient India (4250 BCE to 637 CE) p. 675, ISBN 978-81-269-0616-1 (This author considers King Agrasen an actual historical figure)
- Mukherji, Anisha Shekhar (2002). The red fort of Shahjahanabad. Delhi: Oxford University Press. p. 46. ISBN 978-0-19-565775-3.
- "India: Qutb Minar and its Monuments, Delhi" (PDF). State of Conservation of the World Heritage Properties in the Asia-Pacific Region: : Summaries of Periodic Reports 2003 by property, Section II. UNESCO World Heritage Centre. pp. 71–72. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 May 2006. Retrieved 22 December 2006.
- "Under threat: The Magnificent Minaret of Jam". The New Courier No 1. UNESCO. October 2002. Archived from the original on 22 May 2006. Retrieved 3 May 2006.
- "Battuta's Travels: Delhi, capital of Muslim India". Sfusd.k12.ca.us. Archived from the original on 23 April 2008. Retrieved 7 September 2009.
- Mobilereference (2007). Travel Delhi, India. History section. p. 10. ISBN 9781605010519 – via Google books.
- "The Islamic World to 1600: The Mongol Invasions (The Timurid Empire)". Ucalgary.ca. Archived from the original on 16 August 2009. Retrieved 7 September 2009.
- Genocide: a history. W.D. Rubinstein (2004). p. 28. ISBN 978-0-582-50601-5
- "Sher Shah – The Lion King". India's History: Medieval India. indhistory.com. Archived from the original on 12 December 2006. Retrieved 22 December 2006.
- Akbar the Great, Srivastva, A.L. Vol. 1, pp. 24–26
- Himu-a forgotten Hindu Hero," Bhartiya Vidya Bhawan, p100
- Kar, L. Colonel H.C. Military History of India Calcutta 1980, p. 283
- Mobilereference (2007). Travel Delhi, India. p. 12. ISBN 9781605010519 – via Google Books.
- Thomas, Amelia (2008). Rajasthan, Delhi and Agra. Lonely Planet. ISBN 978-1-74104-690-8.
- Later Mughal.
- Boland-Crewe, Tara; Lea, David (2 September 2003). Territories and States of India. ISBN 9781135356255.
- "Iran in the Age of the Raj". Avalanchepress.com. Archived from the original on 13 January 2011. Retrieved 11 March 2011.
- Jagmohan (2005). Soul and Structure of Governance in India. ISBN 9788177648317.
- Gordon, Stewart (1993). The Marathas 1600–1818, Volume 2. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-26883-7.
- "In 1761, battle of Panipat cost Marathas Rs 93 lakh, say papers". The Times of India. 17 December 2011. Archived from the original on 29 October 2013. Retrieved 9 October 2013.
- Cole, Juan Ricardo; Momen, Moojan (1984). From Iran East and West. ISBN 978-0-933770-40-9. Retrieved 28 July 2015.
- Mayaram, Shail (2003). Against history, against state: counter perspective from the margins Cultures of history. Columbia University Press. ISBN 978-0-231-12731-8.
- "Shifting pain". The Times of India. 11 December 2011. Archived from the original on 27 January 2013. Retrieved 18 June 2012.
- "Lutyens' Delhi in race for UN heritage status". Hindustan Times. 11 June 2012. Archived from the original on 15 June 2012. Retrieved 18 June 2012.
- Mobilereference (1 January 2007). Travel Delhi. p. 8. ISBN 978-1-60501-051-9 – via Google books.
- "Fall in Delhi birth rate fails to arrest population rise". The Hindu. Chennai. 3 January 2005. Archived from the original on 4 June 2007. Retrieved 19 December 2006.
- "Terrorists attack Parliament; five intruders, six cops killed". Rediff.com. 13 December 2001. Archived from the original on 6 October 2013. Retrieved 2 November 2008.
- "India and Pakistan: Who will strike first?". Economist. 20 December 2001. Archived from the original on 5 December 2008. Retrieved 2 November 2008.
- Tripathi, Rahul (14 September 2008). "Serial blasts rock Delhi; 30 dead, 90 injured-India-The Times of India". The Times of India. Archived from the original on 15 September 2008. Retrieved 3 November 2008.
- "State Animals, Birds, Trees and Flowers of India". ENVIS Centre on Forestry. 2 July 2015. Archived from the original on 8 March 2016. Retrieved 8 March 2016.
- "Symbols of Delhi". knowindia.gov.in. Archived from the original on 12 November 2013. Retrieved 15 October 2013.
- "Symbols of Delhi" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 October 2013. Retrieved 15 October 2013.
- "State Trees of India". bsienvis.nic.in. Archived from the original on 19 June 2015. Retrieved 16 February 2016.
- Mohan, Madan (April 2002). "GIS-Based Spatial Information Integration, Modeling and Digital Mapping: A New Blend of Tool for Geospatial Environmental Health Analysis for Delhi Ridge" (PDF). Spatial Information for Health Monitoring and Population Management. FIG XXII International Congress. p. 5. Archived (PDF) from the original on 22 December 2015. Retrieved 3 February 2007.
- "Hazard profiles of Indian districts" (PDF). National Capacity Building Project in Disaster Management. UNDP. Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 May 2006. Retrieved 23 August 2006.
- "Average weather for New Delhi, India". Weatherspark.com. Archived from the original on 16 August 2013. Retrieved 2 July 2013.
- "Climate of Delhi". Delhitrip.in. Archived from the original on 13 July 2014. Retrieved 17 May 2012.
- "Fog continues to disrupt flights, trains". The Hindu. Chennai. 7 January 2005. Archived from the original on 4 March 2006.
- "Ever recorded Maximum and minimum temperatures up to 2010" (PDF). India Meteorological Department. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 March 2014. Retrieved 11 June 2016.
- "Mercury touches new high for July, Met predicts rain relief". 3 July 2012. Archived from the original on 17 March 2013.
- "Weatherbase entry for Delhi". Canty and Associates LLC. Archived from the original on 7 September 2011. Retrieved 16 January 2007.
- Kurian, Vinson (28 June 2005). "Monsoon reaches Delhi two days ahead of schedule". Business Line. Archived from the original on 30 September 2007. Retrieved 9 January 2007.
- "Station: New Delhi (Safdarjang) Climatological Table 1981–2010" (PDF). Climatological Normals 1981–2010. India Meteorological Department. January 2015. pp. 555–556. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 February 2020. Retrieved 6 February 2020.
- "Extremes of Temperature & Rainfall for Indian Stations (Up to 2012)" (PDF). India Meteorological Department. December 2016. p. M46. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 February 2020. Retrieved 6 February 2020.
- "New Delhi (Safdarjang) Climatological Table 1981–2010". India Meteorological Department. Retrieved 6 February 2020.
- "Table 3 Monthly mean duration of Sun Shine (hours) at different locations in India" (PDF). Daily Normals of Global & Diffuse Radiation (1971–2000). India Meteorological Department. December 2016. p. M-3. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 February 2020. Retrieved 7 February 2020.
- "Normals Data: New Delhi/Safdarjung - India Latitude: 28.58°N Longitude: 77.20°E Height: 211 (m)". Japan Meteorological Agency. Archived from the original on 29 February 2020. Retrieved 29 February 2020.
- "Station: New Delhi Palam (A) Climatological Table 1981–2010" (PDF). Climatological Normals 1981–2010. India Meteorological Department. January 2015. pp. 553–554. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 February 2020. Retrieved 5 February 2020.
- "Extremes of Temperature & Rainfall for Indian Stations (Up to 2012)" (PDF). India Meteorological Department. December 2016. p. M46. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 February 2020. Retrieved 5 February 2020.
- "New Delhi (Palam) Climatological Table 1981–2010". India Meteorological Department. Retrieved 5 February 2020.
- "Delhi, Blanketed in Toxic Haze, 'Has Become a Gas Chamber'". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 8 November 2017. Retrieved 7 November 2017.
- "Delhi is most polluted city in world, Beijing much better: WHO study". Hindustan Times. Archived from the original on 8 May 2014. Retrieved 8 May 2014.
- Kumar, Rahul (July 2016). "Fancy Schemes for a Dirty Business". Digital Development Debates. Archived from the original on 15 September 2016. Retrieved 5 September 2016.
- "Delhi's Air Has Become a Lethal Hazard and Nobody Seems to Know What to Do About It". Time. 10 February 2014. Archived from the original on 2 March 2014. Retrieved 10 February 2014.
- "India's Air Pollution Triggers Comparisons with China". Voice of America. Archived from the original on 21 February 2014. Retrieved 20 February 2014.
- "A Delhi particular". The Economist. 6 November 2012. Archived from the original on 6 November 2012. Retrieved 6 November 2012.
- "Pollution level in Delhi: Day after Diwali, Delhi's air turns 'hazardous". Archived from the original on 8 November 2018. Retrieved 8 November 2018.
- "Delhi breathed easier from January to April". Archived from the original on 9 November 2018. Retrieved 8 November 2018.
- "Air pollution: Delhi enjoys cleanest February in three years". Archived from the original on 9 November 2018. Retrieved 8 November 2018.
- "How Crop Burning Affects Delhi's Air". The Wall Street Journal. 15 February 2014. Archived from the original on 6 March 2014. Retrieved 15 February 2014.
- Harris, Gardiner (25 January 2014). "Beijing's Bad Air Would Be Step Up for Smoggy Delhi". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 3 November 2014. Retrieved 27 January 2014.
- Bearak, Max (7 February 2014). "Desperate for Clean Air, Delhi Residents Experiment with Solutions". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 22 February 2014. Retrieved 8 February 2014.
- Madison Park (8 May 2014). "Top 20 most polluted cities in the world". CNN. Archived from the original on 8 May 2016.
- "Children in Delhi have lungs of chain-smokers!". India Today. Archived from the original on 2 March 2014. Retrieved 22 February 2014.
- "Pollution increasing lung cancer in Indian women". DNA. Archived from the original on 5 March 2014. Retrieved 3 February 2014.
- "Delhi blanketed in thick smog, transport disrupted". Reuters. 18 December 2013. Archived from the original on 20 December 2013. Retrieved 18 December 2013.
- January days getting colder, tied to rise in pollution Archived 4 September 2015 at the Wayback Machine, Times of India, 27 January 2014
- "Usual suspects: Vehicles, industrial emissions behind foul play". The Times of India. Archived from the original on 28 December 2018. Retrieved 18 December 2018.
- "UA vicious nexus". Down to Earth. Archived from the original on 13 December 2018. Retrieved 18 December 2018.
- Impose 30% cess on diesel cars, panel tells Supreme Court Archived 4 March 2014 at the Wayback Machine, Times of India, 11 February 2014
- Gardiner Harris (14 February 2015). "Delhi Wakes Up to an Air Pollution Problem It Cannot Ignore". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 15 February 2015. Retrieved 15 February 2015.
- "Delhi 'third greenest' city". Ndtv.com. Archived from the original on 13 February 2011. Retrieved 11 March 2011.
- "Express India". The Indian Express. Archived from the original on 31 December 2010. Retrieved 11 March 2011.
- Delhi Metro helps reduce vehicular air pollution, indicates research Archived 1 March 2014 at the Wayback Machine, India Today, 28 April 2013
- R. Kumari; A.K. Attri; L. Int Panis; B.R. Gurjar (April 2013). "Emission estimates of Particulate Matter and Heavy Metals from Mobile sources in Delhi (India)". J. Environ. Science & Engg. 55 (2): 127–142. Archived from the original on 8 November 2014.
- "What is the status of air pollution in Delhi?". CSE, India. Archived from the original on 1 March 2014. Retrieved 2 March 2014.
- "Delhi's air quality deteriorating due to burning of agriculture waste". The Economic Times. 6 November 2014. Archived from the original on 11 November 2014. Retrieved 8 November 2014.
- "Thick blanket of smog envelopes Delhi, northern India". India Today. Archived from the original on 5 November 2014.
- "Circles of Sustainability Urban Profile Process". The Cities Programme. 27 July 2012. Archived from the original on 12 November 2013. Retrieved 13 May 2014.
- "McKelvey Engineering, IIT Bombay partner to study air pollution | The Source | Washington University in St. Louis". The Source. 4 December 2019. Archived from the original on 10 May 2020. Retrieved 1 March 2020.
- Mishra, Ashish (3 January 2020). "Delhi gets first smog tower today: 5 things about the air purifier at Lajpat Nagar". Hindustan Times. Archived from the original on 3 January 2020. Retrieved 3 January 2020.
- "Delhi Gets its First Smog Tower Today to Help Tackle Rising Levels of Air Pollution". News18. 3 January 2020. Archived from the original on 3 January 2020. Retrieved 3 January 2020.
- M.S.A. Rao (1970). Urbanization and Social Change: A Study of a Rural Community on a Metropolitan Fringe. Orient Longmans.
- "The Delhi Municipal Corporation (Amendment) Act 2011(Delhi Act 12 of 2011)". delhi.gov.in. Department of Law, Justice & Legislative Affairs. 29 December 2011. Archived from the original on 24 March 2017. Retrieved 24 March 2017.
- "From 9 to 11 districts for better governance in city". 17 July 2012. Archived from the original on 26 January 2013.
- Nair, Ajesh. "Annual Survey of India's City-Systems" (PDF). Janaagraha.org. Janaagraha Centre for Citizenship and Democracy. Archived (PDF) from the original on 19 March 2015. Retrieved 12 March 2015.
- "Poile Stations". Government of National Capital Territory of Delhi. Archived from the original on 10 January 2007. Retrieved 19 December 2006.
- "Delhi: Assembly Constituencies". Compare Infobase Limited. Archived from the original on 1 January 2007. Retrieved 19 December 2006.
- "Lok Sabha constituencies get a new profile". The Hindu. Chennai. 7 September 2006. Archived from the original on 4 January 2007. Retrieved 19 December 2006.
- "Politics of Delhi". INDFY. Archived from the original on 24 April 2012. Retrieved 17 May 2012.
- "Arvind Kejriwal to be Delhi Chief Minister, swearing-in at Ramleela Maidan". timesofindia-economictimes. 23 December 2013. Archived from the original on 11 May 2015. Retrieved 28 July 2015.
- Mohammad Ali; Vishal Kant; Sowmiya Ashok (14 February 2014). "Arvind Kejriwal quits over Jan Lokpal". The Hindu. Chennai. Archived from the original on 16 October 2015. Retrieved 28 July 2015.
- "President's rule imposed in Delhi". The Times of India. Archived from the original on 19 July 2015. Retrieved 28 July 2015.
- Niharika Mandhana (10 February 2015). "Upstart Party Wins India State Elections – WSJ". The Wall Street Journal. Archived from the original on 9 August 2015. Retrieved 28 July 2015.
- "Delhi govt decides to split MCD into three parts". Press Trust of India. 30 May 2011. Archived from the original on 28 July 2013.
- Hindustan Ties (29 May 2017). "MCD results 2017: BJP rides on Modi wave; AAP routed, Kejriwal accepts defeat". Archived from the original on 6 November 2017.
- "Delhi Budget Analysis 2017–18" (PDF). PRS Legislative Research. 8 March 2017. Archived (PDF) from the original on 12 March 2017. Retrieved 10 March 2017.
- "Chapter 2: State Income" (PDF). Economic Survey of Delhi, 2005–06. Planning Department, Government of National Capital Territory of Delhi. pp. 8–16. Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 June 2007.
- "Chapter 5: Employment and Unemployment" (PDF). Economic Survey of Delhi, 2005–06. Planning Department, Government of National Capital Territory of Delhi. pp. 59–65. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 February 2016.
- "Industries in Delhi". Mapsofindia.com. Archived from the original on 3 May 2012. Retrieved 7 September 2009.
- "Delhi hot favourite retail destination in India – Corporate Trends – News By Company -News". The Economic Times. Archived from the original on 7 October 2013. Retrieved 3 November 2008.
- "Chapter 9: Industrial Development" (PDF). Economic Survey of Delhi, 2005–06. Planning Department, Government of National Capital Territory of Delhi. pp. 94–107. Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 June 2007.
- "Chapter 13: Water Supply and Sewerage" (PDF). Economic Survey of Delhi, 2005–2006. Planning Department, Government of National Capital Territory of Delhi. pp. 147–162. Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 June 2007. Retrieved 21 December 2006.
- Birkinshaw, Matt (July 2016). "Unequal, Unreliable and Running Out". Digital Development Debates. Archived from the original on 15 September 2016. Retrieved 5 September 2016.
- Joshi, Sandeep (19 June 2006). "MCD developing new landfill site". The Hindu. Chennai. Archived from the original on 19 November 2006. Retrieved 19 December 2006.
- Gadhok, Taranjot Kaur. "Risks in Delhi: Environmental concerns". Natural Hazard Management. GISdevelopment.net. Archived from the original on 12 May 2012. Retrieved 19 December 2006.
- "Chapter 11: Energy" (PDF). Economic Survey of Delhi, 2005–06. Planning Department, Government of National Capital Territory of Delhi. pp. 117–129. Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 June 2007. Retrieved 21 December 2006.
- "About Us". Delhi Fire Service. Govt. of NCT of Delhi. Archived from the original on 22 January 2007. Retrieved 9 January 2007.
- "Delhi Indira Gandhi International Airport (IGI)". Airport-delhi.com. 2 May 1986. Archived from the original on 16 May 2012. Retrieved 7 September 2009.
- "Traffic Statistics – Domestic & International Passengers" (PDF). Airports Authority of India. p. 3. Archived from the original (jsp) on 27 May 2016. Retrieved 5 May 2016.
- "India begins $1.94b Delhi airport revamp". Daily Times. Pakistan. 18 February 2007. Archived from the original on 16 January 2009. Retrieved 3 November 2008.
- DelhiMarch 2, Mail Today New; March 2, 2016UPDATED; Ist, 2016 12:29. "Indira Gandhi International Airport is world's best airport for second time in row". India Today. Archived from the original on 26 October 2019. Retrieved 5 October 2019.CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link)
- "Airports Council International". 12 May 2012. Archived from the original on 12 May 2012. Retrieved 5 October 2019.
- "Mecca for young aviators". Hindustan Times. 23 September 2011. Archived from the original on 3 January 2013.
- "Ministries in row over Safdarjung Airport land". The Times of India. 13 April 2011. Archived from the original on 27 January 2013. Retrieved 17 May 2012.
- PTI (8 March 2019). "PM Narendra Modi inaugurates civil enclave at Hindon airport". The Economic Times. Archived from the original on 13 March 2019. Retrieved 10 March 2019.
- "Search". India News Analysis Opinions on Niti Central. Archived from the original on 2 January 2014. Retrieved 28 July 2015.
- Shah, Pankaj (23 February 2018). "Jewar airport will now be a full-fledged aviation hub". The Times of India. Archived from the original on 24 February 2018. Retrieved 3 March 2018.
- Pritha Chatterjee (6 April 2015). "The road that larger particles travel". The Indian Express. Archived from the original on 7 November 2016. Retrieved 7 November 2016.
- I.Prasada Rao; Dr. P.K. Kanchan; Dr. P.K. Nanda. "GIS Based Maintenance Management System (GMMS) For Major Roads of Delhi". Map India 2006: Transportation. GISdevelopment.net. Archived from the original on 26 April 2012. Retrieved 14 January 2007.
- Dipak K. Dash (5 February 2017). "Delhi traffic chaos costs Rs 60,000 crore annually". The Economic Times. Archived from the original on 24 March 2017. Retrieved 23 March 2017.
- Armin Rosencranz; Michael Jackson. "Introduction" (PDF). The Delhi Pollution Case: The Supreme Court of India and the Limits of Judicial Power. indlaw.com. p. 3. Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 June 2007. Retrieved 14 January 2007.
- "Citizen Charter". Delhi Transport Corporation. Archived from the original on 10 January 2007. Retrieved 21 December 2006.
- "DTC records highest single-day collection". NDTV. 12 July 2011. Archived from the original on 24 March 2017. Retrieved 23 March 2017.
- "Cluster buses to be back on road today". The Times of India. New Delhi. TNN. 18 March 2018. Archived from the original on 8 May 2018. Retrieved 7 May 2018.
- "Cabinet sets ball rolling to procure 1,000 cluster buses". The Times of India. New Delhi. TNN. 10 January 2018. Archived from the original on 7 May 2018. Retrieved 7 May 2018.
- "Upswing in DTC, Cluster buses daily ridership, 41.90 passengers carried per day: Sisodia". Moneycontrol.com. Press Trust of India. 22 March 2018. Archived from the original on 7 April 2018. Retrieved 7 May 2018.
- "Chapter 12: Transport" (PDF). Economic Survey of Delhi, 2005–2006. Planning Department, Government of National Capital Territory of Delhi. pp. 130–146. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 January 2007. Retrieved 21 December 2006.
- Aparajita Ray (16 June 2016). "Bengaluru retains second place after Delhi with most vehicles on roads". The Times of India. Bengaluru. TNN. Archived from the original on 14 June 2018. Retrieved 24 April 2018.
- "Traffic snarl snaps 42 Cr man-hour from Delhi, NCR workers at iGovernment". Igovernment.in. Archived from the original on 7 October 2008. Retrieved 3 November 2008.
- "Every 12th Delhiite owns a car- Automobiles-Auto-News By Industry-News-The Economic Times". The Economic Times. 2 January 2008. Archived from the original on 8 March 2012. Retrieved 3 November 2008.
- "Vehicle numbers cross one crore mark in Delhi". The Times of India. New Delhi. Press Trust of India. 4 June 2017. Archived from the original on 11 June 2018. Retrieved 24 April 2018.
- "Noida: An idea that has worked". The Times of India. 4 June 2003. Archived from the original on 1 January 2016.
- "DND Flyway". DND Flyway. Archived from the original on 2 October 2011. Retrieved 17 May 2012.
- "Faridabad Metro Corridor – Press Brief". Delhimetrorail.com. Archived from the original on 1 January 2016. Retrieved 24 December 2015.
- Barman, Sourav Roy (10 August 2018). "Since 2013, 99% of Delhi Metro trips have been on time". The Indian Express. New Delhi. Archived from the original on 11 August 2018. Retrieved 11 August 2018.
- "Bloomberg.com: Opinion". Bloomberg L.P. Archived from the original on 31 May 2012. Retrieved 3 November 2008.
- "Get ready for revolution on wheels- Shipping / Transport-Transportation-News By Industry-News-The Economic Times". The Economic Times. 6 August 2008. Archived from the original on 11 January 2009. Retrieved 3 November 2008.
- "10 years of Delhi Metro". delhimetrorail.com. 24 January 2013. Archived from the original on 30 August 2013.
- "Changing Delhi map makes Ring Railway redundant". The Indian Express. 22 February 2011. Archived from the original on 28 February 2011.
- "French award presented to Sreedharan". The Hindu. New Delhi. 23 November 2005. Archived from the original on 17 January 2017. Retrieved 24 April 2018.
- "Regional Rapid Transit System (RRTS)". Urban Mass Transit Company Limited. Archived from the original on 25 April 2018. Retrieved 24 April 2018.
- "Project Details". National Capital Region Transport Corporation. Archived from the original on 3 May 2018. Retrieved 24 April 2018.
- "Census of India: Provisional Population Totals for Census 2011: NCT of Delhi". Censusindia.gov.in. Archived from the original on 12 April 2011. Retrieved 2 May 2011.
- "Chapter 3: Demographic Profile" (PDF). Economic Survey of Delhi, 2005–2006. Planning Department, Government of National Capital Territory of Delhi. pp. 17–31. Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 June 2007. Retrieved 21 December 2006.
- Can't afford to fall ill in Dwarka Archived 27 October 2014 at the Wayback Machine, Hindustan Times, 16 July 2009
- Demographia (2016). Demographia World Urban Areas (PDF) (12th ed.). Archived (PDF) from the original on 5 August 2011. Retrieved 17 November 2016.
- "Urban agglomerations/cities having population 1 million and above" (PDF). Provisional population totals, census of India 2011. Registrar General & Census Commissioner, India. 2011. Archived (PDF) from the original on 15 December 2011. Retrieved 26 January 2012.
- "India Stats : Million plus cities in India as per Census 2011". pibmumbai.gov.in. Archived from the original on 30 June 2015. Retrieved 7 September 2015.
- "Evaluation Study of DMA Towns in National Capital Region" (PDF). Town and Country Planning Organisation. Ministry of Urban Development. September 2007. Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 March 2017. Retrieved 19 March 2017.
- "Regional Plan 2021, Chapter 4, Demographic Profile and Settlement Pattern" (PDF). NCR Planning Board. p. 28. Archived (PDF) from the original on 20 March 2017. Retrieved 19 March 2017.
- "Delhi polls: Caste to play crucial role". Archived from the original on 19 June 2014. Retrieved 15 February 2019.
- Pioneer, The. "Delhi's Jats: From farmers to determined political climbers". The Pioneer. Archived from the original on 13 April 2019. Retrieved 10 September 2018.
- Pioneer, The. "Fight for Brahmin votes intensifies". The Pioneer. Archived from the original on 13 April 2019. Retrieved 10 September 2018.
- Singh, Raj (6 February 2015). "Delhi Assembly elections 2015: Important facts and major stakeholders". India TV. Archived from the original on 12 April 2019. Retrieved 12 April 2019.
- Jha, Preeti (26 December 2007). "Guinness comes to east Delhi: Akshardham world's largest Hindu temple". The Indian Express. Archived from the original on 28 December 2007. Retrieved 2 January 2008.
- "Delhi Religion Census 2011". census2011.co.in. Census 2011 India. Archived from the original on 3 November 2017.
- "Religion PCA". censusindia.gov.in. Government of India. Archived from the original on 7 July 2016. Retrieved 8 July 2016.
- "Data on Religion". Census of India 2001. p. 1. Archived from the original on 12 August 2007. Retrieved 16 May 2006.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 15 August 2018. Retrieved 26 April 2019.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "50th REPORT OF THE COMMISSIONER FOR LINGUISTIC MINORITIES IN INDIA" (PDF). nclm.nic.in. Ministry of Minority Affairs. p. 9. Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 July 2016. Retrieved 8 July 2016.
- "52nd Report of the Commissioner for Linguistic Minorities in India" (PDF). nclm.nic.in. Ministry of Minority Affairs. p. 18. Archived from the original (PDF) on 25 May 2017. Retrieved 15 February 2018.
- Dhananjay Mahapatra (4 October 2012). "'Half of Delhi's population lives in slums'". The Times of India. Archived from the original on 14 April 2016. Retrieved 1 January 2016.
- Mayura Janwalkar (20 April 2015). "Delhi: Slum shame". The Indian Express. Archived from the original on 12 January 2016. Retrieved 1 January 2016.
- "Promote lesser-known monuments of Delhi'-Delhi-Cities". The Times of India. Press Trust of India. 27 February 2009. Archived from the original on 11 August 2011. Retrieved 7 September 2009.
- "Delhi Circle (NCT of Delhi)". List of Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Sites and Remains of National Importance. Archaeological Survey of India. Archived from the original on 14 May 2007. Retrieved 27 December 2006.
- "Jama Masjid, India's largest mosque". Terra Galleria. Archived from the original on 4 March 2009. Retrieved 13 March 2009.
- "Know India". India.gov. Archived from the original on 4 September 2015. Retrieved 22 January 2010.
- "Properties inscribed on the World Heritage List: India". UNESCO World Heritage Centre. Archived from the original on 2 May 2012. Retrieved 13 January 2007.
- Jacob, Satish (July 2002). "Wither, the walled city". Seminar (Web Edition) (515). Archived from the original on 12 December 2006. Retrieved 19 January 2007.
- Rafati, V.; Sahba, F. (1989). "Bahai temples". Encyclopædia Iranica.
- "Shopping in Delhi". Delhi Tours. About Palace on Wheels. Archived from the original on 26 April 2012. Retrieved 4 January 2007.
- Gale, Colin; Lahori, Lajwanti; Kaur, Jasbir (1 May 2002). The Textile Book. p. 99. ISBN 978-1-85973-512-1 – via Google Books.
- "Ancient and modern metal craft works attract visitors". The Times of India. 12 June 2012. Archived from the original on 27 January 2013. Retrieved 18 June 2012.
- "Delhi Handicrafts". Indian Handicrafts suppliars. Archived from the original on 1 June 2007. Retrieved 18 June 2012.
- "Independence Day". 123independenceday.com. Compare Infobase Limited. Archived from the original on 16 May 2012. Retrieved 4 January 2007.
- Ray Choudhury, Ray Choudhury (28 January 2002). "R-Day parade, an anachronism?". Business Line. Archived from the original on 18 January 2012. Retrieved 13 January 2007.
- "Fairs & Festivals of Delhi". Delhi Travel. India Tourism.org. Archived from the original on 19 March 2007. Retrieved 13 January 2007.
- Delhi: a portrait, by Khushwant Singh, Raghu Rai, Published by Delhi Tourism Development Corp., 1983. ISBN 978-0-19-561437-4. p. 15.
- Tankha, Madhur (15 December 2005). "It's Sufi and rock at Qutub Fest". The Hindu. Chennai. Archived from the original on 13 May 2006. Retrieved 13 January 2007.
- "The Hindu: Front Page: Asia's largest auto carnival begins in Delhi tomorrow". The Hindu. Chennai. 9 January 2008. Archived from the original on 17 January 2012. Retrieved 3 November 2008.
- "Delhi Metro records 10% rise in commuters-Delhi-Cities-The Times of India". The Times of India. 1 July 2008. Archived from the original on 8 May 2013. Retrieved 3 November 2008.
- Sunil Sethi / New Delhi 9 February 2008. "Sunil Sethi: Why Delhi is India's Book Capital". Business Standard. Archived from the original on 1 January 2009. Retrieved 3 November 2008.
- "Report of IITF 2014" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 February 2015.
- "Daulat Ki Chaat: In search of Delhi's secret delicacy". Archived from the original on 5 September 2015.
- Swamy, M.R.Narayan (2006). New Delhi. Marshall Cavendish. pp. 14–17. ISBN 978-981-232-996-7. Retrieved 23 June 2012.
- Singh, Chetananand (2010). "Commonwealth games guide to Delhi" (PDF). Delhi Tourism and Transportation Development Corporation Ltd. Archived (PDF) from the original on 10 May 2012. Retrieved 23 June 2012.
- Duncan, Fiona (6 March 2011). "Delhi, India: hotels, restaurants and transport". The Daily Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on 14 March 2012. Retrieved 23 June 2012.
- Brown, Lindsay; Thomas, Amelia (2008). Rajasthan, Delhi and Agra (second ed.). Footscray, Vic.: Lonely Planet. pp. 20–31. ISBN 978-1-74104-690-8.
- Bremner, Caroline. "Top 100 City Destinations Ranking" (PDF). Euromonitor International. Archived (PDF) from the original on 25 August 2018. Retrieved 9 August 2016.
- "Indo–Islamic Architecture". Centre for Cultural Resources and Training. Archived from the original on 9 May 2017. Retrieved 28 February 2017.
- "India Gate". Delhi Tourism. Archived from the original on 24 January 2017. Retrieved 28 February 2017.
- "Akshardham Temple". Delhi Tourism. Archived from the original on 2 April 2017. Retrieved 28 February 2017.
- "Shopping in Delhi". Delhi Tourism. Archived from the original on 8 December 2016. Retrieved 28 February 2017.
- "6 Best Shopping Malls in Delhi for Shopping". Traveljee. 11 October 2015. Archived from the original on 9 November 2016. Retrieved 28 February 2017.
- "Schools in Delhi". Archived from the original on 21 September 2012.
- "Chapter 15: Education" (PDF). Economic Survey of Delhi, 2005–06. Planning Department, Government of National Capital Territory of Delhi. pp. 173–187. Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 June 2007. Retrieved 21 December 2006.
- "List of State Universities". Archived from the original on 20 May 2013. Retrieved 11 May 2013.
- "THE INDIRA GANDHI NATIONAL OPEN UNIVERSITY ACT, 198" (PDF). Government of India. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 April 2012. Retrieved 17 May 2012.
- "outlookindia.com | wired". Outlookindia.com. Archived from the original on 4 November 2005. Retrieved 3 November 2008.
- Rediff Business Desk (5 September 2006). "What is CAS? What is DTH?". rediff news: Business. Rediff.com. Archived from the original on 31 May 2010. Retrieved 8 January 2007.
- "Biographical Data of Vir Sanghvi". Archived from the original on 13 May 2012. Retrieved 17 May 2012.
- Naqvi, Farah (14 November 2006). "Chapter4: Towards a Mass Media Campaign: Analysing the relationship between target audiences and mass media" (PDF). Images and icons: Harnessing the Power of Mass Media to Promote Gender Equality and Reduce Practices of Sex Selection. BBC World Service Trust. pp. 26–36. Archived (PDF) from the original on 15 April 2012. Retrieved 8 January 2007.
- "Delhi: Radio Stations in Delhi, India". ASIAWAVES: Radio and TV Broadcasting in South and South-East Asia. Alan G. Davies. 15 November 2006. Archived from the original on 27 April 2012. Retrieved 7 January 2007.
- "All India Radio". Indian government. Archived from the original on 5 May 2012. Retrieved 30 May 2012.
- "Radio Stations in Delhi, India". Asiawaves asiawaves.net. Archived from the original on 27 April 2012. Retrieved 30 May 2012.
- "OCA » New Delhi 1951". ocasia.org. Archived from the original on 20 June 2020. Retrieved 23 April 2020.
- "President Inaugurates First Asian Games". The India Express. Madras. p. 5. Archived from the original on 17 November 2015. Retrieved 14 May 2011.
- "OCA » New Delhi 1982". ocasia.org. Archived from the original on 2 July 2020. Retrieved 23 April 2020.
- Burke, Jason (3 October 2010). "'India has arrived': spectacular ceremony opens Commonwealth Games". London: The Guardian, UK. Archived from the original on 6 October 2010. Retrieved 5 October 2010.
- Hart, Simon (3 October 2010). "Commonwealth Games 2010: India opens doors to the world at opening ceremony". The Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on 6 October 2010. Retrieved 5 October 2010.
- "Biggest ever Commonwealth Games begins in Delhi". The Times of India. Press Trust of India. 3 October 2010. Archived from the original on 3 November 2012. Retrieved 14 October 2010.
- "CWG: 8,000 artists to show 5,000-year-old culture". One India News. 3 October 2010. Archived from the original on 4 January 2012. Retrieved 4 September 2011.
- "The CWG opening show reality: Rs 350 crore". The Times of India. 5 October 2010. Archived from the original on 19 March 2011. Retrieved 4 September 2011.
- "Non-Competition Venues". Commonwealth Games Organising Committee. Archived from the original on 27 September 2010. Retrieved 1 October 2010.
- Camenzuli, Charles. "Cricket may be included in the 2010 Games". Interview. International Sports Press Association. Archived from the original on 29 September 2007. Retrieved 7 January 2007.
- "A Brief History: The Ranji Trophy". ESPNcricinfo. 2 October 2006. Archived from the original on 21 April 2012. Retrieved 6 January 2007.
- "Virat Kohli: Delhi's golden boy since 2002". The Times of India. Archived from the original on 27 April 2016.
- "Ambedkar stadium to host India's World Cup qualifier". Times of Inia. 28 June 2011. Archived from the original on 10 July 2012. Retrieved 17 May 2012.
- "Bob Houghton's Boys made India proud with a superb victory over Syria". 17 May 2012. KolkataFootballs.com. Archived from the original on 10 November 2013.
- "India vs Syria Nehru Cup 2009 Football Final Results, Highlights". CLbuzz. Archived from the original on 8 October 2011. Retrieved 17 May 2012.
- 'They Need TV Product': Why American Football Is Coming To India – TIME NewsFeed Archived 25 November 2011 at the Wayback Machine. Newsfeed.time.com (4 August 2011). Retrieved 24 October 2011.
- "India company says on track for 2011 F1 race". Reuters. 15 April 2009. Retrieved 21 October 2009.
- "Sister City Agreements/Memorandum". delhi.gov.in. Department of Urban Development of Delhi. Archived from the original on 18 February 2020. Retrieved 18 February 2020.
Further reading
- Economic Survey of Delhi 2005–2006. Planning Department. Government of National Capital Territory of Delhi. Retrieved 12 February 2007
- Dalrymple, W (2003). City of Djinns (1 ed.). Penguin Books. ISBN 978-0-14-200100-4.
- Dalrymple, W (2003). Vidhya Society, (2009). Vidhya Society (NGO) is a leading charitable organization of Uttar Pradesh (India) established under society registration act 21-1860 on the special occasion of World Disable Year 2009. Director Mr. Pavan Upadhyay www.vidhyasociety.com (1 ed.). Penguin Books. ISBN 978-0-14-200100-4.
- Prager, D (2013). Delirious Delhi (1 ed.). Arcade Publishing. ISBN 978-1-61145-832-9.
- Brown, L (2011). Lonely Planet Rajasthan, Delhi & Agra (5 ed.). Lonely Planet Publications. ISBN 978-1-74179-460-1.
- Rowe, P; Coster, P (2004). Delhi (Great Cities of the World). World Almanac Library. ISBN 978-0-8368-5197-7.
- Four-part series on Delhi (2 June 2012). "Metrocity Journal: Delhi's Changing Landscape". The Wall Street Journal. Archived from the original on 9 July 2017. Retrieved 4 August 2017.
External links
General information
- Delhi Encyclopædia Britannica entry
- Delhi at Curlie

.jpg)