Bahadurgarh
Bahadurgarh, known as the "Gateway of Haryana" [1]" is a Subdistrict,and a municipal council located in Jhajjar, a district in the state of Haryana, India, which comprises 31 wards. Bahadurgarh is approximately 2 km from Delhi (Tikri Border). It is one of the major cities of Haryana and is surrounded by major NCR cities(Faridabad, Gurugram & Sonipat)
Bahadurgarh | |
|---|---|
City and Subdistrict | |
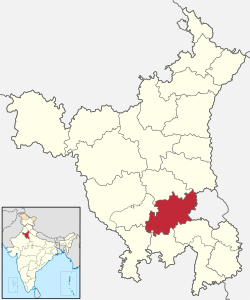
 Bahadurgarh Location in Haryana, India  Bahadurgarh Bahadurgarh (India)  Bahadurgarh Bahadurgarh (Asia) | |
| Coordinates: 28.68°N 76.92°E | |
| Country | |
| State | Haryana |
| District | Jhajjar |
| Government | |
| • Body | Municipal Council of Bahadurgarh |
| • Chairperson | Ms. Sheela Rathi |
| Area | |
| • Total | 50 km2 (20 sq mi) |
| Population (2019) | |
| • Total | 400,000 appx. |
| Languages | |
| • Official | Hindi, |
| Time zone | UTC+5:30 (IST) |
| PIN | 124507 |
| Tel Code | 01276 |
| Vehicle registration | HR 13(Private), HR 63(Commercial) |
| Sex ratio | 1.13 ♂/♀ |
| Vidhan Sabha | Bahadurgarh |
| Planning agency | Haryana Shahari Vikas Pradhikaran |
| Civic agency | Municipal corporation of Bahadurgarh |
History
The city was founded by Mughal Emperor Alamgir II, who was the Sultan of Delhi from 1754 to 1759. He gave the town in jagir to Bahadur Khan and Tej Khan, Baloch rulers of Farrukhnagar in 1754, who changed its name from Sharafabad to Bahadurgarh.[2] They also constructed a fort named Bahadurgarh Fort.
Bahadurgarh came into the hands of Sindhia in 1793. After Sindhia's defeat in 1803 at the hands of the British, Lord Lake transferred control of the town's government to the brother of the Nawab of Jhajjar.
During 1995–1998, a series of rapes and murders of young girls by the Bahadurgarh baby killer led to several dharnas and bandhs by the local population. The police prosecuted three men as the "baby killer", before the real culprit was caught in November 1998.[3][4]
Geography
Bahadurgarh is located in the Jhajjar district in the Indian state of Haryana and is situated in the eastern part of the state, and northern part of the country. The city is located on the border with New Delhi (commonly known as Tikri Border). The city has a total area of 50 km2. It is located between 76º-55'-25" East longitude and 28º-43'-50" North latitude. The city of Bahadurgarh is very well linked with New Delhi and other important towns such as Rohtak, Sonipat, Najafgarh and Nangloi by Roads and Railways.[5]
Climate
The climate of Bahadurgarh is considered to be a local steppe climate. Here, there is little rainfall throughout the year. This climate is considered to be BSh according to the Köppen-Geiger climate classification. The average temperature in the city is 25.1 °C.[6] The average annual rainfall is approximately 510 mm.[7] The city experiences all four seasons along with the monsoon season setting in towards the later half of the summer. Summers are usually long and hot extending from early April to October which includes the monsoon season. Whereas winters start in November and extend till late February. The winters are usually cold and foggy with a few sunny days.
| Climate data for Bahadurgarh | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 27 (81) |
31 (88) |
38 (100) |
43 (109) |
46 (115) |
51 (124) |
44 (111) |
40 (104) |
39 (102) |
38 (100) |
33 (91) |
29 (84) |
47 (117) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 23 (73) |
26 (79) |
32 (90) |
39 (102) |
43 (109) |
43 (109) |
38 (100) |
35 (95) |
35 (95) |
34 (93) |
30 (86) |
25 (77) |
33.5 (92.3) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 6 (43) |
8 (46) |
13 (55) |
20 (68) |
26 (79) |
29 (84) |
28 (82) |
26 (79) |
24 (75) |
19 (66) |
13 (55) |
8 (46) |
18.3 (64.9) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 0 (32) |
2 (36) |
7 (45) |
14 (57) |
21 (70) |
25 (77) |
25 (77) |
24 (75) |
21 (70) |
15 (59) |
8 (46) |
2 (36) |
0 (32) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 8 (0.3) |
18 (0.7) |
10 (0.4) |
11 (0.4) |
21 (0.8) |
49 (1.9) |
135 (5.3) |
128 (5.0) |
66 (2.6) |
18 (0.7) |
2 (0.1) |
7 (0.3) |
476 (18.7) |
| Average rainy days | 2.2 | 4.4 | 4.2 | 4 | 6.9 | 12 | 22.2 | 22.6 | 10.9 | 2.1 | 0.7 | 1.5 | 93.7 |
| Source: MeteoBlue (Based on 30-year Data)[8] | |||||||||||||
Demographics
According to the 2011 census, the population of Bahadurgarh is 170,426: 91,736 men and 78,690 women. There are 20,374 total children (0-6) --11,420 boys and 8,954 girls. The child gender ratio is 784 girls per 1000 boys. The average literacy rate in Bahadurgarh is 88.04%; the male and female literacy rates were 94.27 and 80.87 percent.
Economics
Industrial Model Township Bahadurgarh
Bahadurgarh also considered as "industrial hub".Bahadurgarh Industrial Area in NCR is a large Industrial area of Haryana on the western border of Delhi and it lies east of Rohtak along Delhi Western Peripheral Expressway.[9] It is connected to Delhi Metro on 24 Jun 2018 and located on the planned Delhi-Bhadurgarh-Rohtak Regional Rapid Transport System (RRTS), it is part of Amritsar Delhi Kolkata Industrial Corridor (ADKIC) on Eastern Dedicated Freight Corridor (EDFC), that is on track. Dr. B. Ravi Pillai, owner of RP Group and the richest Indian billionaire in Dubai and Middle East which employ over 70,000 employees, offered to CM of Haryana in December 2017 to invest in a logistics company in Integrated Multimodel Logistics Hub, Nangal Chaudhary (North India's largest logistics hub) and in Prime Minister's Housing for All (PMAY) low-cost urban housing in 3 Industrial Model Townships (IMT) along Delhi Western Peripheral Expressway in IMT Bahadurgarh, IMT Kundli, Sonipat and IMT Manesar with construction to be completed within 1 year.[9] The major industries of Bahadurgarh is Parle, Yokohoma, Relaxo, Surya Roshni, Somany Ceramics, Coim India Pvt ltd, Seaga India, Aerobok Shoe Pvt ltd and others.
Education

Bahadurgarh is considered a Knowledge Hub due to presence of a number of Govt. & Private College & Institutions including PDM University, Bls Institute of Technology and Management, Haryana Institute of Technology (HIT), DTC (Delhi Tech. Campus), AKIDO College of Engineering, MERI Engineering college, Ganga Technical Campus, Sat Kabir Institute of Technology, Vaish Kanya Mahavidyalay, Govt. PG College for Boys and Govt. PG College for Girls, Sainik Public School. There are approx. 100 schools in the city, affiliated to CBSE & State Board.[10]
Transport
Bahadurgarh is well connected with other parts of the country through Roadways, Railways ( Including National Railways as well as Delhi Metro).
Roads
The major highway that passes through the city is National Highway 9. The highway links Bahadurgarh to Delhi, Hisar, Rohtak and various other cities of Haryana. Multiple modes of public transport are available such as taxis, buses, e-rickshaws, and auto rickshaws.[11]
Delhi Metro
Bahadurgarh is connected to the Delhi Metro since 24 Jun 2018. The project has a route length of 11.182 km and cost of Rs. 1991 crore. Haryana contributed Rs. 787.96 crore.[12] From Inderlok/Kirti Nagar to Brigadier Hoshiar Singh Metro Station in Bahadurgarh, the total travel time on Delhi Metro is approx 50 minutes.
Census 2011
As per provisional reports of Census India, the population of Bahadurgarh in 2011 is 170,426; of which males and females are 91,736 and 78,690 respectively. In the education section, total literates in Bahadurgarh city are 132,108 of which 75,714 are males while 56,394 are females. The average literacy rate of Bahadurgarh city is 88.04 percent of which male and female literacy was 94.27 and 80.87 percent. The sex ratio of Bahadurgarh city is 858 per 1000 males. The child sex ratio of girls is 784 per 1000 boys. Total children (0-6) in Bahadurgarh city are 20,374 as per figure from Census India report on 2011. There were 11,420 boys while 8,954 are girls. The child forms 11.95% of the total population of Bahadurgarh City.
See also
- Rohtak
- Desalpur, Bahadurgarh
- Gurgaon
- Faridabad
- Jhajjar
- Kheri Jasaur
- Surya Roshni Limited
References
- "Bahadurgarh: Fourth city in NCR".
- "Bahadurgarh". The Imperial Gazetteer of India. 1909. p. 194, v. 6. Retrieved 3 August 2009.
- Yoginder Gupta (16 January 2007). "Nithari-like case at Bahadurgarh". The Tribune.
- Dalbir Bharti (2006). Police And People : Role And Responsibilities. APH Publishing. pp. 204–209. ISBN 978-81-313-0045-9.
- "Bahadurgarh Development Plan" (PDF). tcpharyana.gov.in/. Retrieved 26 April 2016.
- "Bahadurgarh Climate". Retrieved 26 April 2016.
- "Bahadurgarh Weather". Retrieved 26 April 2016.
- "Climate Details Bahadurgarh, Haryana". Meteoblue. Retrieved 26 April 2016.
- "Dubai-based company keen on investing in state". tribuneindia.com. 6 December 2017. Retrieved 7 December 2017.
- "List of colleges in Bahadurgarh Haryana". Retrieved 1 November 2014.
- "Transport in Bahadurgarh". Retrieved 25 April 2016.
- "Foundation stone laid for Bahadurgarh-Delhi metro". Hindustan Times. 2 February 2013. Retrieved 16 May 2013.