Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka (UK: /sri ˈlæŋkə, ʃriː -/, US: /- ˈlɑːŋkə/ (![]()
Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka | |
|---|---|
.svg.png) | |
| Capital | Sri Jayawardenepura Kotte (legislative)[1] Colombo (executive and judicial)[2] 6°56′N 79°52′E |
| Largest city | Colombo |
| Official languages | Sinhala Tamil[3] |
| Recognised languages | English |
| Ethnic groups (2012[4]) | 74.9% Sinhalese 11.2% Sri Lankan Tamils 9.2% Sri Lankan Moors 4.2% Indian Tamils 0.5% Others (incl. Burghers, Malays, Veddas, Chinese, Indians) |
| Religion | 70.2% Buddhism 12.6% Hinduism 9.7% Islam 7.4% Christianity 0.1% Other/None |
| Demonym(s) | Sri Lankan |
| Government | Unitary semi-presidential constitutional republic |
| Gotabaya Rajapaksa | |
| Mahinda Rajapaksa | |
| Vacant | |
| Jayantha Jayasuriya | |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| Independence from the United Kingdom | |
• Dominion | 4 February 1948 |
• Republic | 22 May 1972 |
| 7 September 1978 | |
| Area | |
• Total | 65,610 km2 (25,330 sq mi) (120th) |
• Water (%) | 4.4 |
| Population | |
• 2019 estimate | 21,803,000[5] (58th) |
• 2012 census | 20,277,597[6] |
• Density | 327/km2 (846.9/sq mi) (43rd) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2020 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| GDP (nominal) | 2020 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| Gini (2016) | 39.8[8] medium |
| HDI (2018) | high · 71st |
| Currency | Sri Lankan rupee (Rs) (LKR) |
| Time zone | UTC+5:30 (SLST) |
| Date format |
|
| Driving side | left |
| Calling code | +94 |
| ISO 3166 code | LK |
| Internet TLD | |
Website www | |
Sri Lanka's documented history spans 3,000 years, with evidence of prehistoric human settlements dating back at least 125,000 years.[12] It has a rich cultural heritage, and the first known Buddhist writings of Sri Lanka, the Pāli Canon, date back to the Fourth Buddhist council in 29 BC.[13][14] Its geographic location and deep harbours made it of great strategic importance from the time of the ancient Silk Road through to the modern Maritime Silk Road.[15][16][17] Its location as a major trading hub made it known to both the far East as well as the European continent from as far back as the Anuradhapura period. The country's trade in luxury goods and spices attracted traders of many nations, creating Sri Lanka's diverse population. During a period of great political crisis the Portuguese, whose arrival in Sri Lanka was largely accidental, sought to control the island's maritime regions and its lucrative external trade. The Portuguese possessions were later taken over by the Dutch. The Dutch possessions were then taken by the British, who later extended their control over the whole island, colonising it from 1815 to 1948. Resistance to the British was immediate. A national movement for political independence arose in the early 20th century; and in 1948, Ceylon became a republic, and it adopted its current name in 1972. Sri Lanka's recent history has been marred by a 26-year civil war, which ended decisively when the Sri Lanka Armed Forces defeated the Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam in 2009.[18]
Sri Lanka's current constitution stipulates it as a republic and unitary state governed by a semi-presidential system. It has had a long history of international engagement, as a founding member of the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC), and a member of the United Nations, the Commonwealth of Nations, the G77, and the Non-Aligned Movement. Sri Lanka is rated "high" on the Human Development Index (HDI), with its HDI rating and per capita income the highest among South Asian nations.[19] The Sri Lankan constitution accords Buddhism the "foremost place", although it does not identify it as a state religion. Buddhism is given special privileges in the Sri Lankan constitution.[20]
Sri Lanka is home to many cultures, languages and ethnicities. The majority of the population are from the Sinhalese ethnicity, while a large minority of Tamils have also played an influential role in the island's history. Moors, Burghers, Malays, Chinese, and the indigenous Vedda are also established groups.[21]
Toponymy
In antiquity, Sri Lanka was known to travellers by a variety of names. According to the Mahavamsa, the legendary Prince Vijaya named the land Tambapanni ('copper-red hands' or 'copper-red earth'), because his followers' hands were reddened by the red soil of the area.[22][23] In Hindu mythology, such as the Ramayana, the island was referred to as Lankā ('Island'). The Tamil term Eelam (Tamil: ஈழம், romanized: īḻam), was used to designate the whole island in Sangam literature.[24][25] The island was known under Chola rule as Mummudi Cholamandalam ('realm of the three crowned Cholas').[26]
Ancient Greek geographers called it Taprobanā (Ancient Greek: Ταπροβανᾶ) or Taprobanē (Ταπροβανῆ)[27] from the word Tambapanni. The Persians and Arabs referred to it as Sarandīb (the origin of the word "serendipity") from Sanskrit Siṃhaladvīpaḥ.[28][29] Ceilão, the name given to Sri Lanka by the Portuguese Empire when it arrived in 1505,[30] was transliterated into English as Ceylon.[31] As a British crown colony, the island was known as Ceylon; it achieved independence as Ceylon in 1948.
The country is now known in Sinhala as Śrī Laṃkā (Sinhala: ශ්රී ලංකා) and in Tamil as Ilaṅkai (Tamil: இலங்கை, IPA: [iˈlaŋɡaɪ]). In 1972, its formal name was changed to "Free, Sovereign and Independent Republic of Sri Lanka". Later, in 1978, it was changed to the "Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka".[32] As the name Ceylon still appears in the names of a number of organisations, the Sri Lankan government announced in 2011 a plan to rename all those over which it has authority.[33]
History
Prehistoric Sri Lanka
The pre-history of Sri Lanka goes back 125,000 years and possibly even as far back as 500,000 years.[34] The era spans the Palaeolithic, Mesolithic, and early Iron Ages. Among the Paleolithic human settlements discovered in Sri Lanka, Pahiyangala (named after the Chinese traveller monk Faxian), which dates back to 37,000 BP,[35] Batadombalena (28,500 BP)[36] and Belilena (12,000 BP) are the most important. In these caves, archaeologists have found the remains of anatomically modern humans which they have named Balangoda Man, and other evidence[37] suggesting that they may have engaged in agriculture and kept domestic dogs for driving game.[38]
One of the first written references to the island is found in the Indian epic Ramayana, which provides details of a kingdom named Lanka that was created by the divine sculptor Vishwakarma for Kubera, the Lord of Wealth.[39] It is said that Kubera was overthrown by his demon stepbrother Ravana, the powerful emperor who built a mythical flying machine named Dandu Monara.[40] The modern city of Wariyapola is described as Ravana's airport.[41]
Early inhabitants of Sri Lanka were probably ancestors of the Vedda people,[42] an indigenous people numbering approximately 2,500 living in modern-day Sri Lanka. The 19th-century Irish historian James Emerson Tennent theorised that Galle, a city in southern Sri Lanka, was the ancient seaport of Tarshish from which King Solomon is said to have drawn ivory, peacocks, and other valuables.
Ancient Sri Lanka
According to the Mahāvamsa, a Sinhalese chronicle written in Pāḷi, the original inhabitants of Sri Lanka are said to be the Yakshas and Nagas. Ancient cemeteries that were used before 600 BC and other signs of advanced civilisation have also been discovered in Sri Lanka.[43] Sinhalese history traditionally starts in 543 BC with the arrival of Prince Vijaya, a semi-legendary prince who sailed with 700 followers to Sri Lanka, after being expelled from Vanga Kingdom (present-day Bengal).[44] He established the Kingdom of Tambapanni, near modern-day Mannar. Vijaya (Singha) is the first of the approximately 189 monarchs of Sri Lanka described in chronicles such as the Dipavamsa, Mahāvaṃsa, Cūḷavaṃsa, and Rājāvaliya.[45]

The Anuradhapura period (377 BC–1017 AD) began with the establishment of the Anuradhapura Kingdom in 380 BC during the reign of Pandukabhaya. Thereafter, Anuradhapura served as the capital city of the country for nearly 1,400 years.[46] Ancient Sri Lankans excelled at building certain types of structures such as tanks, dagobas and palaces.[47] Society underwent a major transformation during the reign of Devanampiya Tissa, with the arrival of Buddhism from India. In 250 BC,[48] Mahinda, a bhikkhu and the son of the Mauryan Emperor Ashoka arrived in Mihintale carrying the message of Buddhism.[49] His mission won over the monarch, who embraced the faith and propagated it throughout the Sinhalese population.[50]
Succeeding kingdoms of Sri Lanka would maintain many Buddhist schools and monasteries and support the propagation of Buddhism into other countries in Southeast Asia. Sri Lankan Bhikkhus studied in India's famous ancient Buddhist University of Nalanda, which was destroyed by Bakhtiyar Khilji. It is probable that many of the scriptures from Nalanda are preserved in Sri Lanka's many monasteries and that the written form of the Tipitaka, including Sinhalese Buddhist literature, were part of the University of Nalanda.[51] In 245 BC, bhikkhuni Sangamitta arrived with the Jaya Sri Maha Bodhi tree, which is considered to be a sapling from the historical Bodhi tree under which Gautama Buddha became enlightened.[52] It is considered the oldest human-planted tree (with a continuous historical record) in the world. (Bodhivamsa)[53]
Sri Lanka experienced the first of many foreign invasions during the reign of Suratissa, who was defeated by two horse traders named Sena and Guttika from South India.[50] The next invasion came immediately in 205 BC by a Chola named Elara, who overthrew Asela and ruled the country for 44 years. Dutugemunu, the eldest son of the southern regional sub-king, Kavan Tissa, defeated Elara in the Battle of Vijithapura. During its two and a half millennia of existence, the Sinhala Kingdom was invaded at least eight times by neighbouring South Indian dynasties such as the Chola, Pandya, Chera, and Pallava. These invaders were all subsequently driven back.[54] There also were incursions by the kingdoms of Kalinga (modern Odisha) and from the Malay Peninsula as well.

The Fourth Buddhist council of Theravada Buddhism was held at the Anuradhapura Maha Viharaya in Sri Lanka under the patronage of Valagamba of Anuradhapura in 25 BC. The council was held in response to a year in which the harvests in Sri Lanka were particularly poor and many Buddhist monks subsequently died of starvation. Because the Pāli Canon was at that time oral literature maintained in several recensions by dhammabhāṇakas (dharma reciters), the surviving monks recognised the danger of not writing it down so that even if some of the monks whose duty it was to study and remember parts of the Canon for later generations died, the teachings would not be lost.[55] After the Council, palm-leaf manuscripts containing the completed Canon were taken to other countries such as Burma, Thailand, Cambodia and Laos.
Sri Lanka was the first Asian country known to have a female ruler: Anula of Anuradhapura (r. 47–42 BC).[56] Sri Lankan monarchs undertook some remarkable construction projects such as Sigiriya, the so-called "Fortress in the Sky", built during the reign of Kashyapa I of Anuradhapura, who ruled between 477 and 495. The Sigiriya rock fortress is surrounded by an extensive network of ramparts and moats. Inside this protective enclosure were gardens, ponds, pavilions, palaces and other structures.[57][58]
In AD 993, the invasion of Chola emperor Rajaraja I forced the then Sinhalese ruler Mahinda V to flee to the southern part of Sri Lanka. Taking advantage of this situation, Rajendra I, son of Rajaraja I, launched a large invasion in 1017. Mahinda V was captured and taken to India, and the Cholas sacked the city of Anuradhapura causing the fall of Anuradhapura Kingdom. Subsequently, they moved the capital to Polonnaruwa.[59]
Post-classical Sri Lanka
Following a seventeen-year-long campaign, Vijayabahu I successfully drove the Chola out of Sri Lanka in 1070, reuniting the country for the first time in over a century.[60][61] Upon his request, ordained monks were sent from Burma to Sri Lanka to re-establish Buddhism, which had almost disappeared from the country during the Chola reign.[62] During the medieval period, Sri Lanka was divided into three sub-territories, namely Ruhunu, Pihiti and Maya.[63]
.jpg)
Sri Lanka's irrigation system was extensively expanded during the reign of Parākramabāhu the Great (1153–1186).[64] This period is considered as a time when Sri Lanka was at the height of its power.[65][66] He built 1470 reservoirs – the highest number by any ruler in Sri Lanka's history – repaired 165 dams, 3910 canals, 163 major reservoirs, and 2376 mini-reservoirs.[67] His most famous construction is the Parakrama Samudra,[68] the largest irrigation project of medieval Sri Lanka. Parākramabāhu's reign is memorable for two major campaigns – in the south of India as part of a Pandyan war of succession, and a punitive strike against the kings of Ramanna (Burma) for various perceived insults to Sri Lanka.[69]
After his demise, Sri Lanka gradually decayed in power. In 1215, Kalinga Magha, an invader with uncertain origins, identified as the founder of the Jaffna kingdom, invaded and captured the Kingdom of Polonnaruwa. He sailed from Kalinga[67] 690 nautical miles on 100 large ships with a 24,000 strong army. Unlike previous invaders, he looted, ransacked, and destroyed everything in the ancient Anuradhapura and Polonnaruwa Kingdoms beyond recovery.[70] His priorities in ruling were to extract as much as possible from the land and overturn as many of the traditions of Rajarata as possible. His reign saw the massive migration of native Sinhalese people to the south and west of Sri Lanka, and into the mountainous interior, in a bid to escape his power.[71][72]
Sri Lanka never really recovered from the impact of Kalinga Magha's invasion. King Vijayabâhu III, who led the resistance, brought the kingdom to Dambadeniya. The north, in the meanwhile, eventually evolved into the Jaffna kingdom.[71][72] The Jaffna kingdom never came under the rule of any kingdom of the south except on one occasion; in 1450, following the conquest led by king Parâkramabâhu VI's adopted son, Prince Sapumal.[73] He ruled the North from AD 1450 to 1467.[74]
The next three centuries starting from 1215 were marked by kaleidoscopically shifting collections of kingdoms in south and central Sri Lanka, including Dambadeniya, Yapahuwa, Gampola, Raigama, Kotte,[75] Sitawaka, and finally, Kandy. Chinese admiral Zheng He and his naval expeditionary force landed at Galle, Sri Lanka in 1409 and got into battle with the local king Vira Alakesvara of Gampola. Zheng He captured King Vira Alakesvara and later released him.[76][77][78][79] Zheng He erected the Galle Trilingual Inscription, a stone tablet at Galle written in three languages (Chinese, Tamil, and Persian), to commemorate his visit.[80][81] The stele was discovered by S. H. Thomlin at Galle in 1911 and is now preserved in the Colombo National Museum.
Early Modern Sri Lanka

The early modern period of Sri Lanka begins with the arrival of Portuguese soldier and explorer Lourenço de Almeida, the son of Francisco de Almeida, in 1505.[82] In 1517, the Portuguese built a fort at the port city of Colombo and gradually extended their control over the coastal areas. In 1592, after decades of intermittent warfare with the Portuguese, Vimaladharmasuriya I moved his kingdom to the inland city of Kandy, a location he thought more secure from attack.[83] In 1619, succumbing to attacks by the Portuguese, the independent existence of the Jaffna kingdom came to an end.[84]
During the reign of the Rajasinghe II, Dutch explorers arrived on the island. In 1638, the king signed a treaty with the Dutch East India Company to get rid of the Portuguese who ruled most of the coastal areas.[85] The following Dutch–Portuguese War resulted in a Dutch victory, with Colombo falling into Dutch hands by 1656. The Dutch remained in the areas they had captured, thereby violating the treaty they had signed in 1638. The Burgher people, a distinct ethnic group, emerged as a result of intermingling between the Dutch and native Sri Lankans in this period.[86]
The Kingdom of Kandy was the last independent monarchy of Sri Lanka.[87] In 1595, Vimaladharmasurya brought the sacred Tooth Relic – the traditional symbol of royal and religious authority amongst the Sinhalese – to Kandy, and built the Temple of the Tooth.[87] In spite of on-going intermittent warfare with Europeans, the kingdom survived. Later, a crisis of succession emerged in Kandy upon king Vira Narendrasinha's death in 1739. He was married to a Telugu-speaking Nayakkar princess from South India (Madurai) and was childless by her.[87]
Eventually, with the support of bhikku Weliwita Sarankara, the crown passed to the brother of one of Narendrasinha's princesses, overlooking the right of "Unambuwe Bandara", Narendrasinha's own son by a Sinhalese concubine.[88] The new king was crowned Sri Vijaya Rajasinha later that year. Kings of the Nayakkar dynasty launched several attacks on Dutch controlled areas, which proved to be unsuccessful.[89]

During the Napoleonic Wars, fearing that French control of the Netherlands might deliver Sri Lanka to the French, Great Britain occupied the coastal areas of the island (which they called Ceylon) with little difficulty in 1796.[90] Two years later, in 1798, Sri Rajadhi Rajasinha, third of the four Nayakkar kings of Sri Lanka, died of a fever. Following his death, a nephew of Rajadhi Rajasinha, eighteen-year-old Kannasamy, was crowned.[91] The young king, now named Sri Vikrama Rajasinha, faced a British invasion in 1803 but successfully retaliated. The First Kandyan War ended in a stalemate.[91]
By then the entire coastal area was under the British East India Company as a result of the Treaty of Amiens. On 14 February 1815, Kandy was occupied by the British in the second Kandyan War, ending Sri Lanka's independence.[91] Sri Vikrama Rajasinha, the last native monarch of Sri Lanka, was exiled to India.[92] The Kandyan Convention formally ceded the entire country to the British Empire. Attempts by Sri Lankan noblemen to undermine British power in 1818 during the Uva Rebellion were thwarted by Governor Robert Brownrigg.[93]
The beginning of the modern period of Sri Lanka is marked by the Colebrooke-Cameron reforms of 1833.[94] They introduced a utilitarian and liberal political culture to the country based on the rule of law and amalgamated the Kandyan and maritime provinces as a single unit of government.[94] An executive council and a legislative council were established, later becoming the foundation of a representative legislature. By this time, experiments with coffee plantations were largely successful.[95]
Soon, coffee became the primary commodity export of Sri Lanka. Falling coffee prices as a result of the depression of 1847 stalled economic development and prompted the governor to introduce a series of taxes on firearms, dogs, shops, boats, etc., and to reintroduce a form of rajakariya, requiring six days free labour on roads or payment of a cash equivalent.[95] These harsh measures antagonised the locals, and another rebellion broke out in 1848.[96] A devastating leaf disease, Hemileia vastatrix, struck the coffee plantations in 1869, destroying the entire industry within fifteen years.[97] The British quickly found a replacement: abandoning coffee, they began cultivating tea instead. Tea production in Sri Lanka thrived in the following decades. Large-scale rubber plantations began in the early 20th century.
By the end of the 19th century, a new educated social class transcending race and caste arose through British attempts to staff the Ceylon Civil Service and the legal, educational, and medical professions.[98] New leaders represented the various ethnic groups of the population in the Ceylon Legislative Council on a communal basis. Buddhist and Hindu revivalism reacted against Christian missionary activities.[99][100] The first two decades in the 20th century are noted by the unique harmony among Sinhalese and Tamil political leadership, which has since been lost.[101]
In 1919, major Sinhalese and Tamil political organisations united to form the Ceylon National Congress, under the leadership of Ponnambalam Arunachalam,[102] pressing colonial masters for more constitutional reforms. But without massive popular support, and with the governor's encouragement for "communal representation" by creating a "Colombo seat" that dangled between Sinhalese and Tamils, the Congress lost momentum towards the mid-1920s.[103]
The Donoughmore reforms of 1931 repudiated the communal representation and introduced universal adult franchise (the franchise stood at 4% before the reforms). This step was strongly criticised by the Tamil political leadership, who realised that they would be reduced to a minority in the newly created State Council of Ceylon, which succeeded the legislative council.[104][105] In 1937, Tamil leader G. G. Ponnambalam demanded a 50–50 representation (50% for the Sinhalese and 50% for other ethnic groups) in the State Council. However, this demand was not met by the Soulbury reforms of 1944–45.
Contemporary Sri Lanka

The Soulbury constitution ushered in dominion status, with independence proclaimed on 4 February 1948.[106] D. S. Senanayake became the first Prime Minister of Ceylon.[107] Prominent Tamil leaders including Ponnambalam and Arunachalam Mahadeva joined his cabinet.[104][108] The British Royal Navy remained stationed at Trincomalee until 1956. A countrywide popular demonstration against withdrawal of the rice ration, known as Hartal 1953, resulted in the resignation of prime minister Dudley Senanayake.[109]
S. W. R. D. Bandaranaike was elected prime minister in 1956. His three-year rule had a profound impact through his self-proclaimed role of "defender of the besieged Sinhalese culture".[110] He introduced the controversial Sinhala Only Act, recognising Sinhala as the only official language of the government. Although partially reversed in 1958, the bill posed a grave concern for the Tamil community, which perceived in it a threat to their language and culture.[111][112][113]
The Federal Party (FP) launched a movement of non-violent resistance (satyagraha) against the bill, which prompted Bandaranaike to reach an agreement (Bandaranaike–Chelvanayakam Pact) with S. J. V. Chelvanayakam, leader of the FP, to resolve the looming ethnic conflict.[114] The pact proved ineffective in the face of ongoing protests by opposition and the Buddhist clergy. The bill, together with various government colonisation schemes, contributed much towards the political rancour between Sinhalese and Tamil political leaders.[115] Bandaranaike was assassinated by an extremist Buddhist monk in 1959.[116]
Sirimavo Bandaranaike, the widow of Bandaranaike, took office as prime minister in 1960, and withstood an attempted coup d'état in 1962. During her second term as prime minister, the government instituted socialist economic policies, strengthening ties with the Soviet Union and China, while promoting a policy of non-alignment. In 1971, Ceylon experienced a Marxist insurrection, which was quickly suppressed. In 1972, the country became a republic named Sri Lanka, repudiating its dominion status. Prolonged minority grievances and the use of communal emotionalism as an election campaign weapon by both Sinhalese and Tamil leaders abetted a fledgling Tamil militancy in the north during the 1970s.[117] The policy of standardisation by the Sirimavo government to rectify disparities created in university enrolment, which was in essence an affirmative action to assist geographically disadvantaged students to obtain tertiary education,[118] resulted in reducing the proportion of Tamil students at university level and acted as the immediate catalyst for the rise of militancy.[119][120] The assassination of Jaffna Mayor Alfred Duraiyappah in 1975 by the Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam (LTTE) marked a crisis point.[121][122]
The government of J. R. Jayawardene swept to power in 1977, defeating the largely unpopular United Front government.[123] Jayawardene introduced a new constitution, together with a free-market economy and a powerful executive presidency modelled after that of France. It made Sri Lanka the first South Asian country to liberalise its economy.[124] Beginning in 1983, ethnic tensions were manifested in an on-and-off insurgency against the government by the LTTE. An LTTE attack on 13 soldiers resulted in the anti-Tamil race riots in July 1983, allegedly backed by Sinhalese hard-line ministers, which resulted in more than 150,000 Tamil civilians fleeing the island, seeking asylum in other countries.[125][126]
Lapses in foreign policy resulted in India strengthening the Tigers by providing arms and training.[127][128][129] In 1987, the Indo-Sri Lanka Accord was signed and the Indian Peace Keeping Force (IPKF) was deployed in northern Sri Lanka to stabilise the region by neutralising the LTTE.[130] The same year, the JVP launched its second insurrection in Southern Sri Lanka,[131] necessitating redeployment of the IPKF in 1990.[132] In October 1990, the LTTE expelled Sri Lankan Moors (Muslims by religion) from northern Sri Lanka.[133] In 2002, the Sri Lankan government and LTTE signed a Norwegian-mediated ceasefire agreement.[113]
The 2004 Asian tsunami killed over 35,000 in Sri Lanka.[134] From 1985 to 2006, the Sri Lankan government and Tamil insurgents held four rounds of peace talks without success. Both LTTE and the government resumed fighting in 2006, and the government officially backed out of the ceasefire in 2008.[113] In 2009, under the Presidency of Mahinda Rajapaksa, the Sri Lanka Armed Forces defeated the LTTE and re-established control of the entire country by the Sri Lankan Government.[135] Overall, between 60,000 and 100,000 people were killed during the 26 years of conflict.[136][137]
Forty thousand Tamil civilians may have been killed in the final phases of the Sri Lankan civil war, according to an Expert Panel convened by UN Secretary General Ban Ki-moon. The exact number of Tamils killed is still a speculation that needs further study.[138] Following the LTTE's defeat, the Tamil National Alliance, the largest Tamil political party in Sri Lanka, dropped its demand for a separate state in favour of a federal solution.[139][140] The final stages of the war left some 294,000 people displaced.[141][142] The UN Human Rights Council has documented over 12,000 named individuals who have undergone disappearance after detention by security forces in Sri Lanka, the second highest figure in the world since the Working Group came into being in 1980. In March 2009, 378 people had been killed in one day and at least another 1,212 injured. The report was based only on those casualties brought to the hospital. The UN described the situation as a "bloodbath", and one that its Colombo office had been warning against for some time. Their spokesperson Gordon Weiss said that over 100 children had been killed over the weekend in the "large-scale killing of civilians".[143][144]
According to the Ministry of Resettlement, most of the displaced persons had been released or returned to their places of origin, leaving only 6,651 in the camps as of December 2011.[145] In May 2010, President Rajapaksa appointed the Lessons Learnt and Reconciliation Commission (LLRC) to assess the conflict between the time of the ceasefire agreement in 2002 and the defeat of the LTTE in 2009.[146][147] Sri Lanka has emerged from its 26-year war to become one of the fastest-growing economies of the world.[148][149]
Geography
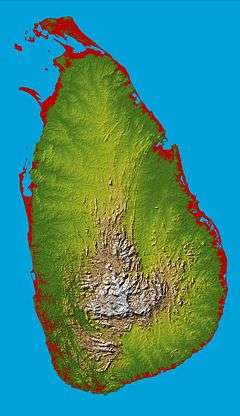
Sri Lanka lies on the Indian Plate, a major tectonic plate that was formerly part of the Indo-Australian Plate.[150] It is in the Indian Ocean southwest of the Bay of Bengal, between latitudes 5° and 10° N, and longitudes 79° and 82° E.[151] Sri Lanka is separated from the mainland portion of the Indian subcontinent by the Gulf of Mannar and Palk Strait. According to Hindu mythology, a land bridge existed between the Indian mainland and Sri Lanka. It now amounts to only a chain of limestone shoals remaining above sea level.[152] Legends claim that it was passable on foot up to 1480 AD, until cyclones deepened the channel.[153][154] Portions are still as shallow as 1 metre (3 ft), hindering navigation.[155] The island consists mostly of flat to rolling coastal plains, with mountains rising only in the south-central part. The highest point is Pidurutalagala, reaching 2,524 metres (8,281 ft) above sea level.
Sri Lanka has 103 rivers. The longest of these is the Mahaweli River, extending 335 kilometres (208 mi).[156] These waterways give rise to 51 natural waterfalls of 10 metres (33 ft) or more. The highest is Bambarakanda Falls, with a height of 263 metres (863 ft).[157] Sri Lanka's coastline is 1,585 km (985 mi) long.[158] Sri Lanka claims an Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) extending 200 nautical miles, which is approximately 6.7 times Sri Lanka's land area. The coastline and adjacent waters support highly productive marine ecosystems such as fringing coral reefs and shallow beds of coastal and estuarine seagrasses.[159]
Sri Lanka has 45 estuaries and 40 lagoons.[158] Sri Lanka's mangrove ecosystem spans over 7,000 hectares and played a vital role in buffering the force of the waves in the 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami.[160] The island is rich in minerals such as ilmenite, feldspar, graphite, silica, kaolin, mica and thorium.[161][162] Existence of petroleum and gas in the Gulf of Mannar has also been confirmed and the extraction of recoverable quantities is underway.[163]
Climate
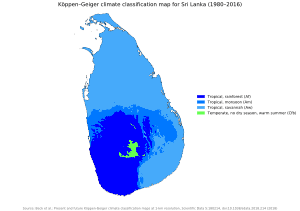
The climate is tropical and warm, due to the moderating effects of ocean winds. Mean temperatures range from 17 °C (62.6 °F) in the central highlands, where frost may occur for several days in the winter, to a maximum of 33 °C (91.4 °F) in other low-altitude areas. Average yearly temperatures range from 28 °C (82.4 °F) to nearly 31 °C (87.8 °F). Day and night temperatures may vary by 14 °C (25.2 °F) to 18 °C (32.4 °F).[164]
Rainfall pattern is influenced by monsoon winds from the Indian Ocean and Bay of Bengal. The "wet zone" and some of the windward slopes of the central highlands receive up to 2,500 millimetres (98.4 in) of rain each year, but the leeward slopes in the east and northeast receive little rain. Most of the east, southeast, and northern parts of Sri Lanka comprise the "dry zone", which receives between 1,200 and 1,900 mm (47 and 75 in) of rain annually.[165]
The arid northwest and southeast coasts receive the least amount of rain at 800 to 1,200 mm (31 to 47 in) per year. Periodic squalls occur and sometimes tropical cyclones bring overcast skies and rains to the southwest, northeast, and eastern parts of the island. Humidity is typically higher in the southwest and mountainous areas and depends on the seasonal patterns of rainfall.[166]
An increase in average rainfall coupled with heavier rainfall events has resulted in recurrent flooding and related damages to infrastructure, utility supply and the urban economy.[167]
Flora and fauna
Lying within the Indomalayan realm, Sri Lanka is one of 25 biodiversity hotspots in the world.[169] Although the country is relatively small in size, it has the highest biodiversity density in Asia.[170] A remarkably high proportion of the species among its flora and fauna, 27% of the 3,210 flowering plants and 22% of the mammals (see List), are endemic.[171] Sri Lanka has declared 24 wildlife reserves, which are home to a wide range of native species such as Asian elephants, leopards, sloth bears, the unique small loris, a variety of deer, the purple-faced langur, the endangered wild boar, porcupines and Indian pangolins.[172]
Flowering acacias flourish on the arid Jaffna Peninsula. Among the trees of the dry-land forests are valuable species such as satinwood, ebony, ironwood, mahogany and teak. The wet zone is a tropical evergreen forest with tall trees, broad foliage, and a dense undergrowth of vines and creepers. Subtropical evergreen forests resembling those of temperate climates flourish in the higher altitudes.[173]
.jpg)
Yala National Park in the southeast protects herds of elephant, deer, and peacocks. The Wilpattu National Park in the northwest, the largest national park, preserves the habitats of many water birds such as storks, pelicans, ibis, and spoonbills. The island has four biosphere reserves: Bundala, Hurulu Forest Reserve, the Kanneliya-Dediyagala-Nakiyadeniya, and Sinharaja.[174] Of these, Sinharaja forest reserve is home to 26 endemic birds and 20 rainforest species, including the elusive red-faced malkoha, the green-billed coucal and the Sri Lanka blue magpie.

The untapped genetic potential of Sinharaja flora is enormous. Of the 211 woody trees and lianas within the reserve, 139 (66%) are endemic. The total vegetation density, including trees, shrubs, herbs and seedlings, has been estimated at 240,000 individuals per hectare. The Minneriya National Park borders the Minneriya tank, which is an important source of water for numerous elephants (Elephus maximus) inhabiting the surrounding forests. Dubbed "The Gathering", the congregation of elephants can be seen on the tank-bed in the late dry season (August to October) as the surrounding water sources steadily disappear. The park also encompasses a range of micro-habitats which include classic dry zone tropical monsoonal evergreen forest, thick stands of giant bamboo, hilly pastures (patanas). and grasslands (talawas).[175]
Sri Lanka is home to over 250 types of resident birds (see List). It has declared several bird sanctuaries including Kumana.[176] During the Mahaweli Program of the 1970s and 1980s in northern Sri Lanka, the government set aside four areas of land totalling 1,900 km2 (730 sq mi) as national parks. Sri Lanka's forest cover, which was around 49% in 1920, had fallen to approximately 24% by 2009.[177][178]
Politics
Sri Lanka is the oldest democracy in Asia.[179] The Donoughmore Constitution, drafted by the Donoughmore Commission in 1931, enabled general elections with adult universal suffrage (universal adult voting) in the country.[180] The first election under the universal adult franchise, held in June 1931, was for the Ceylon State Council. Sir Don Baron Jayatilaka was elected as Leader of the House.[181]
In 1944, the Soulbury Commission was appointed to draft a new constitution. During this time, struggle for independence was fought on "constitutionalist" lines under the leadership of D. S. Senanayake.[182] The draft constitution was enacted in the same year, and Senanayake was appointed Prime Minister following the parliamentary election in 1947. The Soulbury constitution ushered in Dominion status and granted independence to Sri Lanka in 1948.[180]
Political culture
The current political culture in Sri Lanka is a contest between two rival coalitions led by the centre-leftist and progressivist United People's Freedom Alliance (UPFA), an offspring of Sri Lanka Freedom Party (SLFP), and the comparatively right-wing and pro-capitalist United National Party (UNP).[183] Sri Lanka is essentially a multi-party democracy with many smaller Buddhist, socialist and Tamil nationalist political parties. As of July 2011, the number of registered political parties in the country is 67.[184] Of these, the Lanka Sama Samaja Party (LSSP), established in 1935, is the oldest.[185]
The UNP, established by D. S. Senanayake in 1946, was until recently the largest single political party.[186] It is the only political group which had representation in all parliaments since independence.[186] SLFP was founded by S. W. R. D. Bandaranaike, who was the Cabinet minister of Local Administration before he left the UNP in July 1951.[187] SLFP registered its first victory in 1956, defeating the ruling UNP in 1956 Parliamentary election.[187] Following the parliamentary election in July 1960, Sirimavo Bandaranaike became the prime minister and the world's first elected female head of government.[188]
G. G. Ponnambalam, the Tamil nationalist counterpart of S. W. R. D. Bandaranaike,[189] founded the All Ceylon Tamil Congress (ACTC) in 1944. Objecting to Ponnambalam's cooperation with D. S. Senanayake, a dissident group led by S.J.V. Chelvanayakam broke away in 1949 and formed the Illankai Tamil Arasu Kachchi (ITAK), also known as the Federal Party, becoming the main Tamil political party in Sri Lanka for next two decades.[190] The Federal Party advocated a more aggressive stance toward the Sinhalese.[191]
With the constitutional reforms of 1972, the All Ceylon Tamil Congress (ACTC) and Illankai Tamil Arasu Kachchi (ITAK) created a common front called the Tamil United Front (later Tamil United Liberation Front). Following a period of turbulence as Tamil militants rose to power in the late 1970s, these Tamil political parties were succeeded in October 2001 by the Tamil National Alliance.[191][192] Janatha Vimukthi Peramuna, a Marxist–Leninist political party founded by Rohana Wijeweera in 1965, serves as a third force in the current political context.[193] It endorses leftist policies which are more radical than the traditionalist leftist politics of the LSSP and the Communist Party.[191] Founded in 1981, the Sri Lanka Muslim Congress is the largest Muslim political party in Sri Lanka.[194]
Government
| Flag | Lion Flag |
|---|---|
| Emblem | Gold Lion Passant |
| Anthem | "Sri Lanka Matha" |
| Butterfly | Sri Lankan birdwing |
| Animal | Grizzled giant squirrel |
| Bird | Sri Lanka junglefowl |
| Flower | Blue water lily |
| Tree | Ceylon ironwood (nā) |
| Sport | Volleyball |
| Source: [195][196] | |

Sri Lanka is a democratic republic and a unitary state which is governed by a semi-presidential system, with a mixture of a presidential system and a parliamentary system.[197] Most provisions of the constitution can be amended by a two-thirds majority in parliament. The amendment of certain basic features such as the clauses on language, religion, and reference to Sri Lanka as a unitary state require both a two-thirds majority and approval in a nationwide referendum.
In common with many democracies, the Sri Lankan government has three branches:
- Executive: The President of Sri Lanka is the head of state, the commander in chief of the armed forces; head of government, and is popularly elected for a five-year term.[198] The President heads the cabinet and appoints ministers from elected members of parliament.[199] The president is immune from legal proceedings while in office with respect to any acts done or omitted to be done by him or her in either an official or private capacity.[200] Following passage of the 19th amendment to the constitution in 2015, the President has two terms, which previously stood at no term limit.
- Legislative: The Parliament of Sri Lanka is a unicameral 225-member legislature with 196 members elected in multi-seat constituencies and 29 elected by proportional representation.[201] Members are elected by universal suffrage for a five-year term. The president may summon, suspend, or end a legislative session and dissolve Parliament any time after four and a half years. The parliament reserves the power to make all laws.[202] The president's deputy, the Prime Minister, leads the ruling party in parliament and shares many executive responsibilities, mainly in domestic affairs.
- Judicial: Sri Lanka's judiciary consists of a Supreme Court – the highest and final superior court of record,[202] a Court of Appeal, High Courts and a number of subordinate courts. The highly complex legal system reflects diverse cultural influences.[203] Criminal law is based almost entirely on British law. Basic Civil law derives from Roman law and Dutch law. Laws pertaining to marriage, divorce, and inheritance are communal.[204] Due to ancient customary practices and/or religion, the Sinhala customary law (Kandyan law), the Thesavalamai, and Sharia law are followed in special cases.[205] The President appoints judges to the Supreme Court, the Court of Appeal, and the High Courts. A judicial service commission, composed of the Chief Justice and two Supreme Court judges, appoints, transfers, and dismisses lower court judges.
Administrative divisions
For administrative purposes, Sri Lanka is divided into nine provinces[206] and twenty-five districts.[207]
Provinces There have been provinces in Sri Lanka since the 19th century, but they had no legal status until 1987 when the 13th Amendment to the 1978 constitution established provincial councils after several decades of increasing demand for a decentralisation of the Government of Sri Lanka.[208] Each provincial council is an autonomous body not under the authority of any Ministry. Some of its functions had been undertaken by central government ministries, departments, corporations, and statutory authorities,[208] but authority over land and police is not as a rule given to provincial councils.[209][210] Between 1989 and 2006, the Northern and Eastern provinces were temporarily merged to form the North-East Province.[211][212] Prior to 1987, all administrative tasks for the provinces were handled by a district-based civil service which had been in place since colonial times. Now each province is administered by a directly elected provincial council:
| Administrative Divisions of Sri Lanka | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Province | Capital | Area (km2) | Area (mi2) | Population | |||
| Central | Kandy | 5,674 | 2,191 | 2,556,774 | |||
| Eastern | Trincomalee | 9,996 | 3,859 | 1,547,377 | |||
| North Central | Anuradhapura | 10,714 | 4,137 | 1,259,421 | |||
| Northern | Jaffna | 8,884 | 3,430 | 1,060,023 | |||
| North Western | Kurunegala | 7,812 | 3,016 | 2,372,185 | |||
| Sabaragamuwa | Ratnapura | 4,902 | 1,893 | 1,919,478 | |||
| Southern | Galle | 5,559 | 2,146 | 2,465,626 | |||
| Uva | Badulla | 8,488 | 3,277 | 1,259,419 | |||
| Western | Colombo | 3,709 | 1,432 | 5,837,294 | |||
Districts and local authorities Sri Lanka is also divided into 25 districts.[213] Each district is administered under a District Secretariat. The districts are further subdivided into 256 divisional secretariats, and these, in turn, to approximately 14,008 Grama Niladhari divisions.[214] The Districts are known in Sinhala as Disa and in Tamil as Māwaddam. Originally, a Disa (usually rendered into English as Dissavony) was a duchy, notably Matale and Uva. A government agent, who is known as District Secretary, administers a district.

There are three other types of local authorities: Municipal Councils (18), Urban councils (13) and Pradeshiya Sabha, also called Pradesha Sabhai (256).[215] Local authorities were originally based on feudal counties named korale and rata, and were formerly known as 'D.R.O. divisions' after the 'Divisional Revenue Officer'.[216] Later the D.R.O.s became 'Assistant Government Agents' and the divisions were known as 'A.G.A. divisions'. These Divisional Secretariats are currently administered by a 'Divisional Secretary'.
Foreign relations

Sri Lanka is a founding member of the Non-Aligned Movement (NAM). While ensuring that it maintains its independence, Sri Lanka has cultivated relations with India.[217] Sri Lanka became a member of the United Nations in 1955. Today, it is also a member of the Commonwealth, the SAARC, the World Bank, the International Monetary Fund, the Asian Development Bank, and the Colombo Plan.
One of the two parties that have governed Sri Lanka since its independence, the United National Party, has traditionally favoured links with the West, while its left-leaning counterpart, the Sri Lanka Freedom Party, has favoured links with the East.[217] Sri Lankan Finance Minister J. R. Jayewardene, together with then Australian Foreign Minister Sir Percy Spencer, proposed the Colombo Plan at the Commonwealth Foreign Minister's Conference held in Colombo in 1950.[218] At the San Francisco Peace Conference in 1951, while many countries were reluctant, Sri Lanka argued for a free Japan and refused to accept payment of reparations for World War II damage because it believed it would harm Japan's economy.[219] Sri Lanka-China relations started as soon as the PRC was formed in 1949. The two countries signed an important Rice-Rubber Pact in 1952.[220] Sri Lanka played a vital role at the Asian–African Conference in 1955, which was an important step in the crystallisation of the NAM.[221]
The Bandaranaike government of 1956 significantly changed the pro-western policies set by the previous UNP government. It recognised Cuba under Fidel Castro in 1959. Shortly afterward, Cuba's revolutionary Ernesto Che Guevara paid a visit to Sri Lanka.[222] The Sirima-Shastri Pact of 1964[223] and Sirima-Gandhi Pact of 1974[224] were signed between Sri Lankan and Indian leaders in an attempt to solve the long-standing dispute over the status of plantation workers of Indian origin. In 1974, Kachchatheevu, a small island in Palk Strait, was formally ceded to Sri Lanka.[225] By this time, Sri Lanka was strongly involved in the NAM and Colombo held the fifth NAM summit in 1976.[226] The relationship between Sri Lanka and India became tense under the government of J. R. Jayawardene.[132][227] As a result, India intervened in the Sri Lankan Civil War and subsequently deployed an Indian Peace Keeping Force in 1987.[228] In the present, Sri Lanka enjoys extensive relations with China,[229] Russia,[230] and Pakistan.[231]
Military
 Sri Lanka Army T-55AM2 main battle tank |
.jpg) Sri Lanka Navy Flag Ship SLNS Sayurala |
Sri Lanka Air Force Mil Mi-24 Attack Helicopter |
The Sri Lanka Armed Forces, comprising the Sri Lanka Army, the Sri Lanka Navy, and the Sri Lanka Air Force, come under the purview of the Ministry of Defence (MoD).[232] The total strength of the three services is around 346,000 personnel, with nearly 36,000 reserves.[233] Sri Lanka has not enforced military conscription.[234] Paramilitary units include the Special Task Force, the Civil Security Force, and the Sri Lanka Coast Guard.[235][236]
Since independence in 1948, the primary focus of the armed forces has been internal security, crushing three major insurgencies, two by Marxist militants of the JVP and a 26-year-long conflict with the LTTE. The armed forces have been in a continuous mobilised state for the last 30 years.[237][238]
The Sri Lankan Armed Forces have engaged in United Nations peacekeeping operations since the early 1960s, contributing forces to permanent contingents deployed in several UN peacekeeping missions in Chad, Lebanon, and Haiti.[239]
Economy
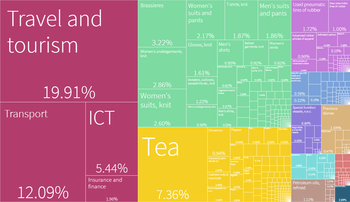
According to the International Monetary Fund, Sri Lanka's GDP in terms of purchasing power parity is the second most highest in the South Asian region in terms of per capita income.
In the 19th and 20th centuries, Sri Lanka became a plantation economy famous for its production and export of cinnamon, rubber, and Ceylon tea, which remains a trademark national export.[240] The development of modern ports under British rule raised the strategic importance of the island as a centre of trade.[241] From 1948 to 1977, socialism strongly influenced the government's economic policies. Colonial plantations were dismantled, industries were nationalised, and a welfare state established. In 1977, the free market economy was introduced to the country incorporating privatisation, deregulation, and the promotion of private enterprise.[124]
While the production and export of tea, rubber, coffee, sugar, and other commodities remain important, industrialisation has increased the importance of food processing, textiles, telecommunications, and finance. The country's main economic sectors are tourism, tea export, clothing, rice production, and other agricultural products. In addition to these economic sectors, overseas employment, especially in the Middle East, contributes substantially in foreign exchange.[242]
As of 2010, the service sector makes up 60% of GDP, the industrial sector 28%, and the agriculture sector 12%.[242] The private sector accounts for 85% of the economy.[243] China, India and the United States are Sri Lanka's largest trading partners.[244] Economic disparities exist between the provinces with the Western Province contributing 45.1% of the GDP and the Southern Province and the Central Province contributing 10.7% and 10%, respectively.[245] With the end of the war, the Northern Province reported a record 22.9% GDP growth in 2010.[246]
The per capita income of Sri Lanka has doubled since 2005.[248] During the same period, poverty has dropped from 15.2% to 7.6%, unemployment rate has dropped from 7.2% to 4.9%, market capitalisation of the Colombo Stock Exchange has quadrupled and the budget deficit has doubled.[242] Over 90% of the households in Sri Lanka are electrified. 87.3% of the population have access to safe drinking water and 39% have access to pipe-borne water.[242] Income inequality has also dropped in recent years, indicated by a Gini coefficient of 0.36 in 2010.[249] Sri Lanka's cellular subscriber base has shown a staggering 550% growth from 2005 to 2010.[242] Sri Lanka was the first country in the South Asian region to introduce 3G, 3.5G (HSDPA), 3.75G (HSUPA) and 4G (LTE) mobile telecommunication technologies.[250]
The Global Competitiveness Report, published by the World Economic Forum, has described Sri Lanka's economy as transitioning from the factor-driven stage to the efficiency-driven stage and that it ranks 52nd in global competitiveness.[251] Also, out of the 142 countries surveyed, Sri Lanka ranked 45th in health and primary education, 32nd in business sophistication, 42nd in innovation, and 41st in goods market efficiency. Sri Lanka ranks 5th in the World Giving Index, registering high levels of contentment and charitable behaviour in its society.[252] In 2010, The New York Times placed Sri Lanka at the top of its list of 31 places to visit.[253] S&P Dow Jones Indices classifies Sri Lanka as a frontier market as of 2018,[254] and Citigroup classified it as a 3G country in February 2011.[255] Sri Lanka ranks well above other South Asian countries in the Human Development Index (HDI) with an index of 0.750.
Sri Lanka's road network consists of 35 A-Grade highways and two controlled-access highways (E01 and E03).[256][257] The railway network, operated by the state-run national railway operator Sri Lanka Railways, spans 1,447 kilometres (900 mi).[258] Sri Lanka also has three deep-water ports at Colombo, Galle, and Trincomalee, in addition to the newest port being built at Hambantota. The port at Trincomalee is the fifth largest natural harbour in the world; during World War II, the British stated that they could place their entire navy in the harbour with room to spare. Sri Lanka's flag carrier airline is SriLankan Airlines. Fitch Ratings has affirmed Sri Lanka's Foreign- and Local-Currency Issuer Default Ratings (IDRs) at 'BB-' with a "stable" outlook. With a grant of 20 million dollars from the US and help from China, a space academy has been set up for the purpose of developing an indigenous space sector to launch satellites of other nations as well as of Sri Lanka. This dual use of launching technology will also serve to develop missile technology. On 26 September 2012 China launched Sri Lanka's first satellite, with plans for more launches in the coming years.[259][260][261]
During the past few years, the country's debt has soared as it was developing its infrastructure to the point of near bankruptcy which required a bailout from the International Monetary Fund (IMF)[262] The IMF had agreed to provide a US$1.5 billion bailout loan in April 2016 after Sri Lanka provided a set of criteria intended to improve its economy. By the fourth quarter of 2016, the debt was estimated to be $64.9 billion. Additional debt had been incurred in the past by state-owned organisations and this was said to be at least $9.5 billion. Since early 2015, domestic debt increased by 12 percent and external debt by 25 percent.[263]
In November 2016, the International Monetary Fund reported that the initial disbursement was larger than US$150 million originally planned, a full US$162.6 million (SDR 119.894 million), to Sri Lanka. The agency's evaluation for the first tranche was cautiously optimistic about the future. Under the program Sri Lankan government implemented a new Inland Revenue Act and an automatic fuel pricing formula which were noted by the IMF in its fourth review. In 2018 China agreed to bail out Sri Lanka with a loan of $1.25 billion to deal with foreign debt repayment spikes in 2019 to 2021.[264][265][266]
Demographics
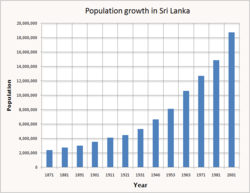
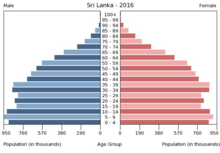
Sri Lanka is the 57th most populated nation in the world,[5] with roughly 21,670,000 people, and an annual population growth rate of 1.14%. Sri Lanka has a birth rate of 17.6 births per 1,000 people and a death rate of 6.2 deaths per 1,000 people.[242] Population density is highest in western Sri Lanka, especially in and around the capital. Sinhalese constitute the largest ethnic group in the country, with 74.8% of the total population.[267]
Sri Lankan Tamils are the second major ethnic group in the island, with a percentage of 11.2%. Sri Lankan Moors comprise 9.2%. Tamils of Indian origin were brought into the country as indentured labourers by British colonists to work on estate plantations. Nearly 50% of them were repatriated following independence in 1948.[268] They are distinguished from the native Tamil population that has resided in Sri Lanka since ancient times. There are also small ethnic groups such as the Burghers (of mixed European descent) and Malays from Southeast Asia. Moreover, there is a small population of Vedda people who are believed to be the original indigenous group to inhabit the island.[269]
Languages
Sinhala and Tamil are the two official languages of Sri Lanka.[270] The Constitution defines English as the link language. English is widely used for education, scientific and commercial purposes. Members of the Burgher community speak variant forms of Portuguese Creole and Dutch with varying proficiency, while members of the Malay community speak a form of Creole Malay that is unique to the island.[271]
Religion
Sri Lanka is a multi-religious country. Buddhists comprise 70% of the population,[274] with the Theravada school being predominant.[275] Most Buddhists are of the Sinhalese ethnic group. Buddhism was introduced to Sri Lanka in the 2nd century BCE by Venerable Mahinda.[275] A sapling of the Bodhi Tree under which the Buddha attained enlightenment was brought to Sri Lanka during the same time. The Pāli Canon (Thripitakaya), having previously been preserved as an oral tradition, was first committed to writing in Sri Lanka around 30 BCE.[276]
Sri Lanka has the longest continuous history of Buddhism of any predominantly Buddhist nation,[275] with the Sangha having existed in a largely unbroken lineage since its introduction in the 2nd century BCE. During periods of decline, the Sri Lankan monastic lineage was revived through contact with Thailand and Burma.[276] Buddhism is given special recognition in the Constitution which requires Sri Lankans to "protect and foster the Buddha Sasana".[277]
Hinduism is the second most prevalent religion in Sri Lanka and predates Buddhism. Today, Hinduism is dominant in Northern, Eastern and Central Sri Lanka.[278]
Islam is the third most prevalent religion in the country, having first been brought to the island by Arab traders over the course of many centuries, starting around the 7th century CE. Most Muslims are Sunni who follow the Shafi'i school.[279] Most followers of Islam in Sri Lanka today are believed to be descendants of those Arab traders and the local women they married.[280]
Christianity reached the country through Western colonists in the early 16th century.[281] Around 7.4% of the Sri Lankan population are Christians, of whom 82% are Roman Catholics who trace their religious heritage directly to the Portuguese. Sri Lankan Tamil Catholics attribute their religious heritage to St. Francis Xavier as well as Portuguese missionaries. The remaining Christians are evenly split between the Anglican Church of Ceylon and other Protestant denominations.[282]
There is also a small population of Zoroastrian immigrants from India (Parsis) who settled in Ceylon during the period of British rule,[283] but this community has steadily dwindled in recent years.[284] Religion plays a prominent role in the life and culture of Sri Lankans. The Buddhist majority observe Poya Days each month according to the Lunar calendar, and Hindus and Muslims also observe their own holidays. In a 2008 Gallup poll, Sri Lanka was ranked the third most religious country in the world, with 99% of Sri Lankans saying religion was an important part of their daily life.[285]
Urban centres
Health
Sri Lankans have a life expectancy of 77.9 years at birth, which is 10% higher than the world average.[242] The infant mortality rate stands at 8.5 per 1,000 births and the maternal mortality rate at 0.39 per 1,000 births, which is on par with figures from the developed countries. The universal "pro-poor"[287] health care system adopted by the country has contributed much towards these figures.[288]
Sri Lanka ranks first among southeast Asian countries with respect to commitment of suicide, with 33 deaths per 100,000 persons. According to the Department of Census and Statistics, poverty, destructive pastimes and inability to cope with stressful situations, are the main causes behind the high suicide rates.[289]
Education

With a literacy rate of 92.5%,[242] Sri Lanka has one of the most literate populations amongst developing nations.[290] Its youth literacy rate stands at 98%,[291] computer literacy rate at 35%,[292] and primary school enrolment rate at over 99%.[293] An education system which dictates 9 years of compulsory schooling for every child is in place. The free education system established in 1945,[294] is a result of the initiative of C. W. W. Kannangara and A. Ratnayake.[295][296] It is one of the few countries in the world that provide universal free education from primary to tertiary stage.[297]
Kannangara led the establishment of the Madhya Maha Vidyalayas (Central Schools) in different parts of the country in order to provide education to Sri Lanka's rural children.[292] In 1942 a special education committee proposed extensive reforms to establish an efficient and quality education system for the people. However, in the 1980s changes to this system saw the separation of the administration of schools between the central government and the provincial government. Thus the elite National Schools are controlled directly by the Ministry of Education and the provincial schools by the provincial government. Sri Lanka has approximately 9675 government schools, 817 private schools and Pirivenas.[242]
Sri Lanka has 15 public universities.[298] A lack of responsiveness of the education system to labour market requirements, disparities in access to quality education, lack of an effective linkage between secondary and tertiary education remain major challenges for the education sector.[299] A number of private, degree awarding institutions have emerged in recent times to fill in these gaps, yet the participation at tertiary level education remains at 5.1%.[300] The proposed private university bill has been withdrawn by the Higher Education Ministry after university students' heavy demonstrations and resistance.[301]
The late British science fiction author Arthur C. Clarke served as Chancellor of Moratuwa University in Sri Lanka from 1979 to 2002.[302]
Transport
Sri Lanka has an extensive road network for inland transportation. With more than 100,000 km (62,000 mi) of paved roads,[303] it has one of the highest road densities in the world (1.5 km or 0.93 mi of paved roads per every 1 km2 or 0.39 sq mi of land). E-grade highways are the latest addition to Sri Lanka's road network. These are access-controlled, high-mobility roads with permitted speeds up to 100 km/h (62 mph).[304] These highways connect local communities together, by-passing busy and congested town centres.
A and B grade roads are national (arterial) highways administered by Road Development Authority.[305] C and D grade roads are provincial roads coming under the purview of the Provincial Road Development Authority of the respective province. The other roads are local roads falling under local government authorities.
The rail network of Sri Lanka consists of main lines, coastal lines, and up-country lines.[306] In addition, air- and water-based transportation modalities augment the inland transport of the country.
Human rights and media
The Sri Lanka Broadcasting Corporation (formerly Radio Ceylon) is the oldest-running radio station in Asia,[307] established in 1923 by Edward Harper just three years after broadcasting began in Europe.[307] The station broadcasts services in Sinhala, Tamil, English and Hindi. Since the 1980s, many private radio stations have also been introduced. Broadcast television was introduced to the country in 1979 when the Independent Television Network was launched. Initially, all Television stations were state-controlled, but private television networks began broadcasts in 1992.[308]
As of 2010, 51 newspapers (30 Sinhala, 10 Tamil, 11 English) are published and 34 TV stations and 52 radio stations are in operation.[242] In recent years, freedom of the press in Sri Lanka has been alleged by media freedom groups to be amongst the poorest in democratic countries.[309] Alleged abuse of a newspaper editor by a senior government minister[310] achieved international notoriety because of the unsolved murder of the editor's predecessor, Lasantha Wickrematunge,[311] who had also been a critic of the government and had presaged his own death in a posthumously published article.[312]
Officially, the constitution of Sri Lanka guarantees human rights as ratified by the United Nations. However, human rights in Sri Lanka have come under criticism by Amnesty International, Freedom from Torture, Human Rights Watch,[313] and the United States Department of State.[314] British colonial rulers,[315] the separatist Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam (LTTE), and the government of Sri Lanka are accused of violating human rights. A report by an advisory panel to the UN secretary-general has accused both the LTTE and the Sri Lankan government of alleged war crimes during final stages of the civil war.[316][317] Corruption remains a problem in Sri Lanka, and there is currently very little protection for those who stand up against corruption.[318] The 135-year-old Article 365 of the Sri Lankan Penal Code criminalises gay sex and provides for a penalty of up to ten years in prison.[319]
The UN Human Rights Council has documented over 12,000 named individuals who have undergone disappearance after detention by security forces in Sri Lanka, the second highest figure in the world since the Working Group came into being in 1980.[320] The Sri Lankan government has confirmed that 6,445 of these are dead. Allegations of human rights abuses have not ended with the close of the ethnic conflict.[321]
UN Human Rights Commissioner Navanethem Pillay visited Sri Lanka in May 2013. After her visit, she said: "The war may have ended [in Sri Lanka], but in the meantime democracy has been undermined and the rule of law eroded." Pillay spoke about the military's increasing involvement in civilian life and reports of military land grabbing. She also said that, while in Sri Lanka, she had been allowed to go wherever she wanted, but that Sri Lankans who came to meet her were harassed and intimidated by security forces.[322][323]
In 2012, the UK charity Freedom from Torture reported that it had received 233 referrals of torture survivors from Sri Lanka for clinical treatment or other services provided by the charity. In the same year, Freedom from Torture published Out of the Silence, which documents evidence of torture in Sri Lanka and demonstrates that the practice has continued long after the end of the civil war in May 2009.[324]
On 29 July 2020, Human Rights Watch said that the Sri Lanka government has targeted lawyers, human rights defenders, and journalists to suppress criticism against government.[325]
Culture
The culture of Sri Lanka dates back over 2500 years.[326] It is influenced primarily by Buddhism and Hinduism.[327] Sri Lanka is the home to two main traditional cultures: the Sinhalese (centred in the ancient cities of Kandy and Anuradhapura) and the Tamil (centred in the city of Jaffna). In more recent times, the British colonial culture has also influenced the locals. Sri Lanka claims a democratic tradition matched by few other developing countries.[328]
The first Tamil immigration was probably around the 3rd century BC.[327] Tamils co-existed with the Sinhalese people since then, and the early mixing rendered the two ethnic groups almost physically indistinct.[329] Ancient Sri Lanka is marked for its genius in hydraulic engineering and architecture. The rich cultural traditions shared by all Sri Lankan cultures is the basis of the country's long life expectancy, advanced health standards and high literacy rate.[328]
Food and festivals

Dishes include rice and curry, pittu, kiribath, wholemeal roti, string hoppers, wattalapam (a rich pudding of Malay origin made of coconut milk, jaggery, cashew nuts, eggs, and spices including cinnamon and nutmeg), kottu, and hoppers.[330] Jackfruit may sometimes replace rice. Traditionally food is served on a plantain leaf or lotus leaf.
Middle Eastern influences and practices are found in traditional Moor dishes, while Dutch and Portuguese influences are found with the island's Burgher community preserving their culture through traditional dishes such as Lamprais (rice cooked in stock and baked in a banana leaf), Breudher (Dutch Holiday Biscuit), and Bolo Fiado (Portuguese-style layer cake).
In April, Sri Lankans celebrate the Buddhist and Hindu new year festival.[331] Esala Perahera is a symbolic Buddhist festival consisting of dances and decorated elephants held in Kandy in July and August.[332] Fire-dances, whip-dances, Kandian dances and various other cultural dances are integral parts of the festival. Christians celebrate Christmas on 25 December to celebrate the birth of Jesus Christ and Easter to celebrate the resurrection of Jesus. Tamils celebrate Thai Pongal and Maha Shivaratri, and Muslims celebrate Hajj and Ramadan.
Visual, literary and performing arts
.jpg)
The movie Kadawunu Poronduwa (The broken promise), produced by S. M. Nayagam of Chitra Kala Movietone, heralded the coming of Sri Lankan cinema in 1947. Ranmuthu Duwa (Island of treasures, 1962) marked the transition cinema from black-and-white to colour. It in the recent years has featured subjects such as family melodrama, social transformation and the years of conflict between the military and the LTTE.[333] The Sri Lankan cinematic style is similar to Bollywood movies. In 1979, movie attendance rose to an all-time high, but has been in steady decline since then.[334]
An influential filmmaker is Lester James Peiris, who has directed a number of movies which led to global acclaim, including Rekava (Line of destiny, 1956), Gamperaliya (The changing village, 1964), Nidhanaya (The treasure, 1970) and Golu Hadawatha (Cold heart, 1968).[335] Sri Lankan-Canadian poet Rienzi Crusz, is the subject of a documentary on his life in Sri Lanka. His work is published in Sinhala and English. Similarly, naturalised-Canadian Michael Ondaatje, is well known for his English-language novels and three films.
The earliest music in Sri Lanka came from theatrical performances such as Kolam, Sokari and Nadagam.[336] Traditional music instruments such as Béra, Thammátama, Daŭla and Răbān were performed at these dramas. The first music album, Nurthi, recorded in 1903, was released through Radio Ceylon (founded in 1925). Songwriters like Mahagama Sekara and Ananda Samarakoon and musicians such as W. D. Amaradeva, Victor Ratnayake, Nanda Malini and Clarence Wijewardene have contributed much towards the upliftment of Sri Lankan music.[337] Baila is another popular music genre in the country, originated among Kaffirs or the Afro-Sinhalese community.[338]

There are three main styles of Sri Lankan classical dance. They are, the Kandyan dances, low country dances and Sabaragamuwa dances. Of these, the Kandyan style, which flourished under kings of the Kingdom of Kandy, is more prominent. It is a sophisticated form of dance,[339] that consists of five sub-categories: Ves dance, Naiyandi dance, Udekki dance, Pantheru dance and 18 Vannam.[340] An elaborate headdress is worn by the male dancers and a drum called Geta Béraya is used to assist the dancer to keep on rhythm.[341] In addition, four folk drama variants named Sokri, Kolam Nadagam, Pasu, and several devil dance variants such as Sanni Yakuma and Kohomba Kankariya can be also observed.[340]
The history of Sri Lankan painting and sculpture can be traced as far back as to the 2nd or 3rd century BC.[342] The earliest mention about the art of painting on Mahavamsa, is to the drawing of a palace on cloth using cinnabar in the 2nd century BC. The chronicles have description of various paintings in relic-chambers of Buddhist stupas, and in monastic residence.
Theatre moved into the country when a Parsi theatre company from Mumbai introduced Nurti, a blend of European and Indian theatrical conventions to the Colombo audience in the 19th century.[340] The golden age of Sri Lankan drama and theatre began with the staging of Maname, a play written by Ediriweera Sarachchandra in 1956.[343] It was followed by a series of popular dramas like Sinhabāhu, Pabāvatī, Mahāsāra, Muudu Puththu and Subha saha Yasa.
Sri Lankan literature spans at least two millennia, and is heir to the Aryan literary tradition as embodied in the hymns of the Rigveda.[344] The Pāli Canon, the standard collection of scriptures in the Theravada Buddhist tradition, was written down in Sri Lanka during the Fourth Buddhist council, at the Alulena cave temple, Kegalle, as early as 29 BC.[345] Ancient chronicles such as the Mahāvamsa, written in the 6th century, provide vivid descriptions of Sri Lankan dynasties. According to the German philosopher Wilhelm Geiger, the chronicles are based on Sinhala Atthakatha (commentary), that dates few more centuries back.[344] The oldest surviving prose work is the Dhampiya-Atuva-Getapadaya, compiled in the 9th century.[344]
The greatest literary feats of medieval Sri Lanka include Sandesha Kāvya (poetic messages) such as Girā Sandeshaya (Parrot message), Hansa Sandeshaya (Swan message) and Salalihini Sandeshaya (Myna message). Poetry including Kavsilumina, Kavya-Sekharaya (diadem of poetry) and proses such as Saddharma-Ratnāvaliya, Amāvatura (Flood of nectar) and Pujāvaliya are also notable works of this period, which is considered to be the golden age of Sri Lankan literature.[344] The first modern-day novel, Meena, a work of Simon de Silva appeared in 1905,[340] and was followed by a number of revolutionary literary works. Martin Wickramasinghe, the author of Madol Doova is considered the iconic figure of Sri Lankan literature.[346]
Sports
While the national sport in Sri Lanka is volleyball, by far the most popular sport in the country is cricket.[347] Rugby union also enjoys extensive popularity,[348] as do athletics, football (soccer), netball and tennis. Sri Lanka's schools and colleges regularly organise sports and athletics teams, competing on provincial and national levels.
The Sri Lanka national cricket team achieved considerable success beginning in the 1990s, rising from underdog status to winning the 1996 Cricket World Cup.[349] They also won the 2014 ICC World Twenty20 played in Bangladesh, beating India in the final. In addition, Sri Lanka became the runners-up of the Cricket World Cup in 2007[350] and 2011,[351] and of the ICC World Twenty20 in 2009 and 2012.[352]
Former Sri Lankan off-spinner Muttiah Muralitharan has been rated as the greatest Test match bowler ever by Wisden Cricketers' Almanack,[353] and four Sri Lankan cricketers ranked 2nd (Sangakkara), 4th (Jayasuriya), 5th (Jayawardene) and 11th (Dilshan) highest ODI run scorers of all time, which is the second best by a team. Sri Lanka has won the Asia Cup in 1986,[354] 1997,[355] 2004,[356] 2008[357] and 2014.[358] Sri Lanka once held highest team score in all three formats of cricket, where currently holds Test team total.[359] The country co-hosted the Cricket World Cup in 1996 and 2011, and hosted the 2012 ICC World Twenty20.
Sri Lankans have won two medals at Olympic Games, one silver, by Duncan White at 1948 London Olympics for men's 400 metres hurdles[360] and one silver by Susanthika Jayasinghe at 2000 Sydney Olympics for women's 200 metres.[361] In 1973, Muhammad Lafir won the World Billiards Championship, the highest feat by a Sri Lankan in a Cue sport.[362] Sri Lanka has also won the Carrom World Championship titles twice in 2012, 2016[363] and 2018, men's team becoming champions and women's team won second place. Aquatic sports such as boating, surfing, swimming, kitesurfing[364] and scuba diving on the coast, the beaches and backwaters attract many Sri Lankans and foreign tourists. There are two styles of martial arts native to Sri Lanka, Cheena di and Angampora.[365]
The Sri Lanka national netball team has won the Asian Netball Championship five times and are the current Asian Champions as well.
See also
- Index of Sri Lanka-related articles
- Outline of Sri Lanka
References
Citations
- "Sri Jayewardenepura Kotte". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 12 May 2020.
- "Colombo". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 12 May 2020.
- "Department of Official Languages".
- "South Asia: Sri Lanka". CIA The World Factbook.
- "Mid-year population projection" (PDF). Retrieved 30 October 2018.
- "Census of Population and Housing 2011 Enumeration Stage February–March 2012" (PDF). Department of Census and Statistics – Sri Lanka. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 December 2013. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "World Economic Outlook Database, October 2019". IMF.org. International Monetary Fund. Retrieved 8 December 2019.
- "Gini Index". World Bank.
- "Human Development Report 2019" (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. 10 December 2019. Retrieved 10 December 2019.
- ""Sri Lanka" in several reference works". Dictionary.com. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "Carnegie Mellon University Pronouncing Dictionary". Carnegie Mellon University. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- Roberts, Brian (2006). "Sri Lanka: Introduction". Urbanization and sustainability in Asia: case studies of good practice. ISBN 978-971-561-607-2.
- Jack Maguire (2001). Essential Buddhism: A Complete Guide to Beliefs and Practices. Simon and Schuster. p. 69. ISBN 978-0-671-04188-5.
... the Pali Canon of Theravada is the first known collection of Buddhist writings ...
- "Religions – Buddhism: Theravada Buddhism". BBC. 2 October 2002.
- Bandaranayake, Senake (1990). "Sri Lankan Role in the Maritime Silk Route". Sri Lanka and the silk road of the sea. p. 21. ISBN 978-955-9043-02-7.
- British Prime Minister Winston Churchill described the moment a Japanese fleet prepared to invade Sri Lanka as "the most dangerous and distressing moment of the entire conflict". – Commonwealth Air Training Program Museum, The Saviour of Ceylon
- "A Brief History of Sri Lanka". www.localhistories.org. Retrieved 14 August 2017.
- Reuters Sri Lanka wins civil war, says kills rebel leaderreuters (18 May 2009). Retrieved on 18 November 2012.
- "2018 Human Development Report". United Nations Development Programme. 2018. Archived from the original on 14 September 2018. Retrieved 14 September 2018.
- "Sri Lanka's Constitution of 1978 with Amendments through 2015" (PDF). constituteproject.org. Retrieved 29 October 2017.
- "Vedda". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- Nanda Pethiyagoda Wanasundera (2002). Sri Lanka. Marshall Cavendish. p. 26. ISBN 978-0-7614-1477-3.
- John M. Senaveratna (1997). The story of the Sinhalese from the most ancient times up to the end of "the Mahavansa" or Great dynasty. Asian Educational Services. p. 11. ISBN 978-81-206-1271-6.
- Skutsch, Carl (2005). Encyclopedia of the world's minorities. Routledge. ISBN 978-1579584702.
- Ganguly, Rajat (20 May 2013). Autonomy and Ethnic Conflict in South and South-East Asia. Routledge. ISBN 978-1136311888.
- Dehejia, Vidya (18 October 1990). Art of the Imperial Cholas. Columbia University Press. p. 51. ISBN 978-0231515245.
- Abeydeera, Ananda. "In Search of Taprobane: the Western discovery and mapping of Ceylon".
- "Hobson-Jobson". Dsalsrv02.uchicago.edu. 1 September 2001. Retrieved 15 August 2018.
- "Serendipity – definition of serendipity by The Free Dictionary". Thefreedictionary.com. 10 November 2017. Retrieved 15 August 2018.
- Rajasingham, K. T. "Sri Lanka: The untold story". Asia Times.
- Zubair, Lareef. "Etymologies of Lanka, Serendib, Taprobane and Ceylon". Archived from the original on 22 April 2007.
- "Chapter I – The People, The State And Sovereignty". The Constitution of the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka. Archived from the original on 31 May 2014. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- Haviland, Charles (1 January 2011). "Sri Lanka erases colonial name, Ceylon". BBC.
- Deraniyagala, Siran U. "Pre and Protohistoric settlement in Sri Lanka". International Union of Prehistoric and Protohistoric Sciences. XIII U. I. S. P. P. Congress Proceedings – Forli, 8–14 September 1996. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "Pahiyangala (Fa-Hiengala) Caves". angelfire.com. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- Kennedy, Kenneth A.R., Disotell, T.W., Roertgen, J., Chiment, J., Sherry, J. Ancient Ceylon 6: Biological anthropology of upper Pleistocene hominids from Sri Lanka: Batadomba Lena and Beli Lena caves. pp. 165–265.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- De Silva 1981, pp. 6–7
- Deraniyagal, Siran (1992). The Prehistory of Sri Lanka. Colombo: Department of Archaeological Survey. p. 454. ISBN 978-955-9159-00-1.
- Keshavadas, Sant (1988). Ramayana at a Glance. Motilal Banarsidass. ISBN 978-81-208-0545-3.
- Parker, H. (1992). Ancient Ceylon. Asian Educational Services. p. 7. ISBN 978-81-206-0208-3.
- Padma Edirisinghe (2009). "Ravana – historical or mythical figure?". The Sunday Observer. Archived from the original on 3 November 2014. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- Deraniyagala, S.U. "Early Man and the Rise of Civilisation in Sri Lanka: the Archaeological Evidence". lankalibrary.com. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "Ancient graves during pre-Wijeya era found". www.dailymirror.lk. Retrieved 20 October 2015.
- "The Coming of Vijaya". The Mahavamsa.
- "Vijaya (Singha) and the Lankan Monarchs – Family #3000". Ancestry.com. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "World Heritage site: Anuradhapura". worldheritagesite.org. Archived from the original on 7 January 2004. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "Waterworld: Ancient Sinhalese Irrigation". mysrilankaholidays.com. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- Perera H. R. "Buddhism in Sri Lanka: A Short History". accesstoinsight.org. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- Holt, John Clifford (2004). "Sri Lanka". In Buswell, Robert E. Jr. (ed.). Macmillan Encyclopedia of Buddhism. Macmillan Reference. pp. 795–799. ISBN 978-0-8160-5459-6.
- "King Devanampiya Tissa (306 BC – 266 BC)". Mahavamsa. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "Buddhism in Sri Lanka". buddhanet.net. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- Maung Paw, p. 6
- Gunawardana, Jagath. "Historical trees: Overlooked aspect of heritage that needs a revival of interest". Daily Mirror. Archived from the original on 15 July 2012. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- De Silva, Harris. "Distortion of history for political purposes". Ancestry.com. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- Lopez 2013, p. 200.
- "The History of Ceylon". sltda.gov.lk. Archived from the original on 8 August 2014. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- Ponnamperuma, Senani (2013). Story of Sigiriya. Melboune: Panique Pty Ltd. ISBN 978-0-9873451-1-0.
- Bandaranayake, Senake (1999). Sigiriya: City, Palace, and Royal Gardens. Colombo: Central Cultural Fund, Ministry of Cultural Affairs. ISBN 978-955-613-111-6.
- Siriweera, W. I. (1994). A Study of the Economic History of Pre Modern Sri Lanka. Vikas Publishing House. pp. 44–45. ISBN 978-0-7069-7621-2.
- Codrington, Ch. 4
- Lambert, Tim. "A Brief History of Sri Lanka". localhistories.org. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- Bokay, Mon (1966). Relations between Ceylon and Burma in the 11th Century AD. Artibus Asiae Publishers. 23. Artibus Asiae Publishers. pp. 93–95. JSTOR 1522637.
- "Ancient Irrigation Works". lakdiva.org. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- Herath, R. B. (2002). Sri Lankan Ethnic Crisis: Towards a Resolution. Trafford Publishing. p. 19. ISBN 978-1-55369-793-0.
Parakramabahu 1 further extended the system to the highest resplendent peak of hydraulic civilization of the country's history.
- Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society of Great Britain and Ireland: Volume 7. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press for the Royal Asiatic Society. 1875. p. 152.
... and when at the height of its prosperity, during the long and glorious reign of Parakramabahu the Great ...
- Beveridge, H. (1894). "The Site of Karna Suvarna". Journal of the Asiatic Society of Bengal. 62: 324 – via Google Books.
His [Parakramabahu's] reign is described by Tumour as having been the most martial, enterprising, and glorious in Singhalese history.
- Herath, R.B. (2002). Sri Lankan Ethnic Crisis: Towards a Resolution. Trafford Publishing. pp. 18–21. ISBN 978-1-55369-793-0.
- "Parakrama Samudra". International Lake Environment Committee. Archived from the original on 5 June 2011.
- "ParakramaBahu I: 1153–1186". lakdiva.org. Archived from the original on 4 February 2014.
- Jayasekera, P.V.J. (1992). Security dilemma of a small state, Part 1. Peradeniya: Institute for International Studies University of Peradeniya, Sri Lanka. p. 25. ISBN 978-81-7003-148-2.
..His invasion in 1215 was more or less a looting expedition..
- Nadarajan, V History of Ceylon Tamils, p. 72
- Indrapala, K Early Tamil Settlements in Ceylon, p. 16
- Gnanaprakasar, Swamy (2003). A Critical History of Jaffna. New Delhi: Asian Educational Services. p. 122. ISBN 978-81-206-1686-8.
- Holt, John Clifford (1991). Buddha in the Crown: Avalokitesvara in the Buddhist Traditions of Sri Lanka. Oxford University Press. p. 304. ISBN 978-0-19-506418-6.
- Codrington, Ch. 6
- "South East Aisa in Ming Shi-lu". Geoff Wade, 2005. Retrieved 13 April 2015.
- "Voyages of Zheng He 1405–1433". National Geographic. Retrieved 13 April 2015.
- "Ming Voyages". Columbia University. Retrieved 13 April 2015.
- "Admiral Zheng He". aramco world. Archived from the original on 31 October 2014. Retrieved 13 April 2015.
- "The trilingual inscription of Admiral Zheng He". lankalibrary forum. Archived from the original on 20 June 2015. Retrieved 13 April 2015.
- "Zheng He". world heritage site. Archived from the original on 12 April 2010. Retrieved 13 April 2015.
- "Sri Lanka History". Thondaman Foundation.
- "King Wimaladharmasuriya". S.B. Karalliyadde – The Island. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- Knox, Robert (1681). An Historical Relation of the Island Ceylon. London: Reprint. Asian Educational Services. pp. 19–47.
- Anthonisz, Richard Gerald (2003). The Dutch in Ceylon: an account of their early visits to the island, their conquests, and their rule over the maritime regions during a century and a half. Asian Educational Services. pp. 37–43. ISBN 978-81-206-1845-9.
- Bosma, U. (2008). "1". Being "Dutch" in the Indies: a history of creolisation and empire, 1500–1920. University of Michigan. ISBN 978-0-89680-261-2.
- "A kingdom is born, a kingdom is lost". The Sunday Times. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- Dharmadasa, K.N.O. (1992). Language, Religion, and Ethnic Assertiveness: The Growth of Sinhalese Nationalism in Sri Lanka0. University of Michigan Press. pp. 8–12. ISBN 978-0-472-10288-4.
- Codrington, Ch. 9
- "The first British occupation and the definitive Dutch surrender". colonialvoyage.com. 18 February 2014.
- "History of Sri Lanka and significant World events from 1796 AD to 1948". scenicsrilanka.com. Archived from the original on 2 November 2013. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- Codrington, Ch. 11
- "Keppetipola and the Uva Rebellion". lankalibrary.com. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- Corea, Gamani & Kelegama, Saman (2004). Economic policy in Sri Lanka: Issues and debates. SAGE. pp. 405–406. ISBN 978-0-7619-3278-9.
- Nubin 2002, p. 115
- "Gongale Goda Banda (1809–1849) : The leader of the 1848 rebellion". Wimalaratne, K.D.G. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- Lennox A. Mills (1964). Ceylon Under British Rule, 1795–1932. Psychology Press. p. 246. ISBN 978-0714620190.
- Nubin 2002, pp. 116–117
- Bond, George D. (1992). The Buddhist revival in Sri Lanka: Religious tradition, reinterpretation and response. Motilal Banarsidass Publications. pp. 11–22. ISBN 978-81-208-1047-1.
- "Cutting edge of Hindu revivalism in Jaffna". Balachandran, P.K. 25 June 2006.
- De Silva 1981, p. 387
- De Silva 1981, p. 386
- De Silva 1981, pp. 389–395
- "Chronology of events related to Tamils in Sri Lanka (1500–1948)". Hellmann-Rajanayagam, Dagmar. National University of Malaysia. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- De Silva 1981, p. 423
- "Sinhalese Parties". Library of Congress Country Studies. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "Sinhalese Parties". Library of Congress Country Studies. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- Nubin 2002, pp. 121–122
- Weerakoon, Batty. "Bandaranaike and Hartal of 1953". The Island. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- Nubin 2002, p. 123
- Ganguly, Šumit (2003). Brown, Michael E. (ed.). Fighting Words: language policy and ethnic relations in Asia. The MIT Press. pp. 136–138. ISBN 978-0-262-52333-2. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- Schmid, Bettina; Schroeder, Ingo, eds. (2001). Anthropology of Violence and Conflict. Routledge. p. 185. ISBN 978-0-415-22905-0. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "Sri Lanka Profile". BBC News. 5 November 2013.
- Peebles, Patrick (2006). The History of Sri Lanka. Greenwood Press. pp. 109–111. ISBN 978-0-313-33205-0.
- University of Edinburgh. "Staff profile: Jonathan Spencer". Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "Sri Lanka: The untold story – Assassination of Bandaranaike". Rajasingham, K. T. Asia Times. 2002. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- Nubin 2002, pp. 128–129
- De Silva; K. M. (July 1997). "Affirmative Action Policies: The Sri Lankan Experience" (PDF). International Centre for Ethnic Studies. pp. 248–254. Archived from the original (PDF) on 30 September 2011.
- Jayasuriya, J.E. (1981). Education in the Third World. Pune: Indian Institute of Education. OCLC 7925123.
- Taraki Sivaram (May 1994). "The Exclusive Right to Write Eelam History". Tamil Nation.
- Hoffman, Bruce (2006). Inside Terrorism. New York: Columbia University Press. p. 139. ISBN 978-0-231-12699-1.
- Rohan Gunaratna (December 1998). "International and Regional Implications of the Sri Lankan Tamil Insurgency" (PDF).
- Rajasingham, K.T. (2002). "Tamil militancy – a manifestation". Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "Sri Lanka – an Overview". Fulbright commission.
- "Remembering Sri Lanka's Black July – BBC News". BBC News. 23 July 2013. Retrieved 20 October 2015.
- "The Black July 1983 that Created a Collective Trauma". Jayatunge, Ruwan M. LankaWeb. 2010. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "LTTE: the Indian connection". Sunday Times. 1997. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "Uppermost in our minds was to save the Gandhis' name". Express India. 1997. Archived from the original on 11 August 2007.
- "For firmer and finer International Relations". Wijesinghe, Sarath. Sri Lanka Guardian. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- Stokke, K.; Ryntveit, A.K. (2000). "The Struggle for Tamil Eelam in Sri Lanka". A Journal of Urban and Regional Policy. 31 (2): 285–304. doi:10.1111/0017-4815.00129.
- Gunaratna, Rohan (1998). Sri Lanka's Ethnic Crisis and National Security. Colombo: South Asian Network on Conflict Research. p. 353. ISBN 978-955-8093-00-9.
- "Chapter 30: Whirlpool of violence, Sri Lanka: The Untold Story". Asia Times. 2002. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "1990, The War Year if Ethnic Cleansing Of The Muslims From North and the East of Sri Lanka". lankanewspapers.com. 2008. Archived from the original on 5 March 2016. Retrieved 21 May 2015.
- "WSWS.org". WSWS.org. 29 December 2005.
- Weaver, Matthew; Chamberlain, Gethin (19 May 2009). "Sri Lanka declares end to war with Tamil Tigers". The Guardian. London.
- "Up to 100,000 killed in Sri Lanka's civil war: UN". ABC Australia. 20 May 2009.
- Olsen, Erik. "Sri Lanka". New York Time. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "40,000 Tamil civilians killed in final phase of Lanka war, says UN report". Hindustan Times. 25 April 2011.
- Haviland, Charles (13 March 2010). "Sri Lanka Tamil party drops statehood demand". BBC.
- Burke, Jason (14 March 2010). "Sri Lankan Tamils drop demand for separate independent homeland". The Guardian. London.
- "Sri Lanka ready for the challenge". The Sunday Observer. 20 March 2011. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016.
- "Sri Lanka's displaced face uncertain future as government begins to unlock the camps". Amnesty International. 11 September 2009.
- "Bloodbath in Sri Lanka". www.amnesty.org.uk.
- "UN mourns Sri Lanka 'bloodbath'". BBC News. 11 May 2009.
- "Situation Report as of 15-12-2011" (PDF). Ministry of Resettlement in Sri Lanka. 15 December 2011. p. 2. Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 January 2012.
- "Sri Lanka: President appoints Lessons Learnt and Reconciliation Commission". ReliefWeb. 17 May 2010.
- Mallawarachi, Bharatha (16 December 2011). "Sri Lankan commission: Civilians weren't targeted". Associated Press/CBS News.
- "The 15 Fastest-Growing Economies in the World". Business Insider. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "Lanka among fastest growing millionaire populations – report". 24 June 2011.
- Seth Stein. "The January 26, 2001 Bhuj Earthquake and the Diffuse Western Boundary of the Indian Plate" (PDF). www.earth.northwestern.edu.
- "Geographic Coordinates for Sri Lanka Towns and Villages". jyotisha.00it.com. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "Gods row minister offers to quit". BBC. 15 September 2007.
- Garg, Ganga Ram (1992). "Adam's Bridge". Encyclopaedia of the Hindu World. A–Aj. New Delhi: South Asia Books. p. 142. ISBN 978-81-261-3489-2.
- "Ramar Sethu, a world heritage centre?". Rediff.com. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "Adam's Bridge". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 21 December 2015.
- Aves, Edward (2003). Sri Lanka. London: Footprint Travel Guides. p. 372. ISBN 978-1-903471-78-4.
- "Introducing Sri Lanka". Lonely Planet. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "Depletion of coastal resources" (PDF). United Nations Environment Programme. p. 86. Archived from the original (PDF) on 31 March 2012.
- "5 Coral Reefs of Sri Lanka: Current Status And Resource Management". Food and Agriculture Organization. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "Information Brief on Mangroves in Sri Lanka". International Union for Conservation of Nature. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "Sri Lanka Graphite Production by Year". indexmundi.com. 2009. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "Availability of sizeable deposits of thorium in Sri Lanka". Tissa Vitharana. Asian Tribune. 2008. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "Three Dimensional Seismic Survey for Oil Exploration in Block SL-2007-01-001 in Gulf of Mannar–Sri Lanka" (PDF). Cairn Lanka. 2009. pp. iv–vii. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "Climate & Seasons: Sri Lanka". mysrilanka.com. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "Sri Lanka Rainfall". mysrilanka.com. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "Sri Lanka Climate Guide". climatetemp.info. Archived from the original on 25 June 2012.
- Integrating urban agriculture and forestry into climate change action plans: Lessons from Sri Lanka, Marielle Dubbeling, the RUAF Foundation, 2014
- "Sri Lanka Survey Finds More Elephants Than Expected". Voice of America. 2 September 2011. Archived from the original on 29 January 2012. Retrieved 15 September 2011.
- Russell Mittermeier, Norman Myers and Cristina Mittermeier (2000). Hotspots: Earth's Biologically Richest and Most Endangered Terrestrial Ecoregions. Arlington, Virginia: Conservation International. ISBN 978-968-6397-58-1.
- "Environment Sri Lanka". www.environmentlanka.com. Archived from the original on 25 July 2014. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "An interview with Dr. Ranil Senanayake, chairman of Rainforest Rescue International". news.mongabay.com. Archived from the original on 8 December 2012. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "Ecotourism Sri Lanka". www.environmentlanka.com. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "Forests, Grasslands, and Drylands – Sri Lanka" (PDF). p. 4. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 October 2007.
- "Sri Lanka". UNESCO. 1 September 2006.
- "Minneriya National Park". www.trabanatours.com. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "Kumana National Wildlife Park". www.srilankaecotourism.com. Archived from the original on 29 July 2014. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "Forests of Sri Lanka". srilankanwaterfalls.net. Archived from the original on 11 April 2009.
- Sri Lanka. MSN Encarta Encyclopedia. Archived from the original on 21 October 2009.
- Norton, James H.K. (2001). India and South Asia. United States: McGraw-Hill. ISBN 978-0-07-243298-5.
- Russell, Jane (1982). Communal Politics Under the Donoughmore Constitution. Colombo: Tisara Publishers.
- "The Constitution of Sri Lanka – Contents". Parliament of Sri Lanka. Archived from the original on 16 June 2010.
- Kanapathipillai, Valli (2009). Citizenship and Statelessness in Sri Lanka: The Case of the Tamil Estate Workers. India: Anthem Press. p. 187. ISBN 978-1-84331-791-3.
DS Senanayake, as the leader of the UNP and the first prime minister of Sri Lanka, wore the robes of a "constitutionalist" who peacefully pressured the British for constitutional rights
- Nubin 2002, p. 95
- "Political Parties in Sri Lanka". Department of Election, Sri Lanka. July 2011. Archived from the original on 5 August 2012.
- "Sri Lanka's oldest political party". Daily News. 18 December 2010.
- "UNP: The Story of the Major Tradition". unplanka.com. Archived from the original on 18 May 2014. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "Charting a new course for Sri Lanka's success". Daily News. 16 November 2009.
- "Ceylon chooses world's first woman PM". BBC. 20 July 1960.
- Society of Jesus in India (1946). New review, Volume 23. India: Macmillan and co. ltd. p. 78.
- Lakshman, W. D. and Tisdell, Clem (2000). Sri Lanka's development since independence: socio-economic perspectives and analyses. New York: Nova Publishers. p. 80. ISBN 978-1-56072-784-2.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- "Sri Lanka: Post Colonial History". Lanka Library. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "Sri Lanka Tamil National Alliance denies having talks with Buddhist prelates". Asian Tribune. 24 February 2011.
- "Revolutionary Idealism and Parliamentary Politics" (PDF). Asia-Pacific Journal of Social Sciences. December 2010. p. 139. Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 September 2011.
- "Sri Lankan Muslims: Between ethno-nationalism and the global ummah". Dennis B. McGilvray. Association for the Study of Ethnicity and Nationalism. January 2011.
- "National Symbols of Sri Lanka". My Sri Lanka. Retrieved 25 August 2011.
- "Sri Lanka names its national butterfly". The Sunday Times. Retrieved 25 August 2011.
- "Chapter 1 – The People, The State and Sovereignty". The Official Website of the Government of Sri Lanka. Archived from the original on 31 May 2014. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "The Executive Presidency". The Official Website of the Government of Sri Lanka. Archived from the original on 21 September 2014. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "The Constitution of Sri Lanka – Contents". The Official Website of the Government of Sri Lanka. 20 November 2003. Archived from the original on 18 November 2014.
- "Presidential Immunity". constitution.lk.
- "Evolution of the Parliamentary System". Parliament of Sri Lanka. Archived from the original on 16 June 2010.
- "The Legislative Power of Parliament". Parliament of Sri Lanka. Archived from the original on 16 June 2010.
- "Sri Lanka public administration" (PDF). United Nations Public Administration Network. p. 2. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "Background Note: Sri Lanka". United States Department of State. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "Sri Lanka Society & Culture: Customs, Rituals & Traditions". lankalibrary.com. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "The Constitution of Sri Lanka – Eighth Schedule". Priu.gov.lk. Archived from the original on 16 October 2014. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "The Constitution of Sri Lanka – First Schedule". Priu.gov.lk. Archived from the original on 16 October 2014. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "Provincial Councils". The Official Website of the Government of Sri Lanka. 3 September 2010. Archived from the original on 7 July 2009.
- "Lanka heads for collision course with India: Report". Indian Express. 12 June 2011.
- "Accepting reality and building trust". Jehan Perera. peace-srilanka.org. 14 September 2010. Archived from the original on 6 October 2010.
- "North-East merger illegal: SC". LankaNewspapers.com. 17 October 2006. Archived from the original on 24 May 2009.
- "North East De-merger-At What Cost? Update No. 107". Hariharan, R. southasiaanalysis.org. 19 October 2010. Archived from the original on 13 June 2010.
- "District Secretariats Portal". District an Divisional Secretariats. Archived from the original on 9 March 2011.
- "List of Codes for the Administrative Divisions of Sri Lanka 2001" (PDF). Department of Census and Statistics. p. 3. Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 May 2011.
- Commonwealth Secretariat (2004). Commonwealth Local Government Handbook. London. p. 146. ISBN 978-0-9542917-9-2.
- Dilesh Jayanntha (2006). Electoral Allegiance in Sri Lanka. London: Cambridge University Press. pp. 82–85. ISBN 978-0-521-02975-9.
- "Foreign Relations". Library of Congress Country Studies. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- Jayasekera, Upali S. "Colombo Plan at 57". Colombo Plan. Archived from the original on 13 January 2012.
- "Sri Lanka excels at the San Francisco Peace Conference" (PDF). The Island. 7 September 2009.
- "Lanka-China bilateral ties at its zenith". The Sunday Observer. 3 October 2010. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016.
- "Bandung Conference of 1955 and the resurgence of Asia and Africa". The Daily News. 21 April 2005.
- "Lanka-Cuba relations should be strengthened". The Daily News. 14 January 2004.
- "29 October 1964". Pact.lk. Archived from the original on 28 January 2015. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "Statelessness abolished?". cope.nu. Archived from the original on 13 August 2014. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- Suryanarayan, V. (22 August 2011). "India-Sri Lanka: 1921 Conference On Fisheries And Ceding Of Kachchatheevu – Analysis". Albany Tribune. Archived from the original on 2 April 2012.
- "NAM Golden Jubilee this year". The Sunday Observer. 10 July 2011. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016.
- Murthy, P. (2000). "Indo‐Sri Lankan security perceptions: Divergences and convergences". Strategic Analysis. 24 (2): 343. doi:10.1080/09700160008455216.
- Weisman, Steven R. (5 June 1987). "India airlifts aid to Tamil rebels". New York Times.
- "Sri Lanka: Background and U.S. Relations" (PDF). Federation of American Scientists. p. 6. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "Russia and Sri Lanka to strengthen bilateral relations". Asian Tribune. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "World leaders send warm greeting to Sri Lanka on Independence Day". Asian Tribune. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "CIA World Factbook: Sr Lanka". Central Intelligence Agency. 16 August 2011.
- International Institute for Strategic Studies (3 February 2010). Hackett, James (ed.). The Military Balance 2010. London: Routledge. pp. 370–371. ISBN 978-1-85743-557-3.
- "Conscription (most recent) by country". NationMaster.
- "Sri Lanka coast guard sets up bases". Lanka Business Online. 10 August 2009. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016.
- "Coast Guard bill passed in Parliament". Sri Lanka Ministry of Defence. 7 October 2009. Archived from the original on 3 March 2016.
- "How Sri Lanka's military won". BBC. 22 May 2009.
- Doucet, Lyse (13 November 2012). "BBC News – UN 'failed Sri Lanka civilians', says internal probe". Bbc.co.uk. Retrieved 10 September 2013.
- "UN Mission's Summary detailed by Country – March 2012" (PDF). United Nations. April 2012. p. 33.
- Fernando, Maxwell. "Echoes of a Plantation Economy". historyofceylontea.com. Archived from the original on 17 January 2012.
- "The Strategic Importance of Sri Lanka to Australia". asiapacificdefencereporter.com. Archived from the original on 7 August 2014. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "Annual Report 2010" (PDF). Ministry of Finance – Sri Lanka. 2011. Archived from the original (PDF) on 1 December 2011. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "Country Partnership Strategy" (PDF). Asian Development Bank. 2008. p. 1. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 November 2013. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "Sri Lanka's Top Trading Partners". Lakshman Kadiragamar Institute. 2018. Retrieved 14 October 2018.
- "Western Province share of national GDP falling: CB". Sunday Times. 17 July 2011.
- "Sri Lanka's Northern province has recorded the highest GDP growth rate of 22.9 per cent last year". Asian Tribune. 18 July 2011.
- "Sri Lanka Tea Board". worldteanews.com.
- "Per capita income has doubled". tops.lk. 2011.
- "Inequality drops with poverty" (PDF). Department of Census and Statistics. p. 3. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "Saarc: Sri Lanka Takes a Lead". voicendata.ciol.com. 31 August 2011. Archived from the original on 8 June 2012.
- Schwab, Klaus (2011). The Global Competitiveness Report 2011–2012 (PDF) (Report). World Economic Forum. pp. 326–327. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "CAF world giving index 2016" (PDF). cafonline.org. Charities aid foundation. Retrieved 18 August 2019.
- "The 31 Places to Go in 2010". The New York Times. 24 January 2010.
- "A Closer Look at Indices Country Classifications".
- Joe Weisenthal (22 February 2011). "3G Countries". Businessinsider.com.
- "Southern Expressway". Road Development Authority. Archived from the original on 15 April 2009. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "Colombo_Katunayaka Expressway". Road Development Authority. Archived from the original on 17 April 2009. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "Statistics – Sri Lanka Railways". Ministry of Transport Sri Lanka. Archived from the original on 28 December 2012.
- F_493 (28 November 2012). "Sri Lanka's first satellite launched from China – People's Daily Online". English.peopledaily.com.cn. Retrieved 8 January 2014.
- "China to launch Sri Lanka's first satellite". Tamilguardian.com. 18 November 2012. Retrieved 8 January 2014.
- Sirilal, Ranga (27 November 2012). "China launches Sri Lanka's first satellite as India watches ties grow". Reuters. Retrieved 8 January 2014.
- Shaffer, Leslie (2 May 2016). "Why Sri Lanka's economic outlook is looking less rosy". CNBC. CNBC LLC. Retrieved 14 January 2017.
While the government is aiming to raise its low revenue collection, partly through an increase in the value-added tax rate ... the country has a spotty record on tax collection.
- Shepard, Wade (30 September 2016). "Sri Lanka's Debt Crisis Is So Bad The Government Doesn't Even Know How Much Money It Owes". Forbes. Forbes. Retrieved 14 January 2017.
"We still don't know the exact total debt number," Sri Lanka's prime minister admitted to parliament earlier this month.
- "IMF Completes First Review of the Extended Arrangement Under the EFF with Sri Lanka and Approves US$162.6 Million Disbursement". IMF. IMF. 18 November 2016. Retrieved 14 January 2017.
[IMF] completed the first review of Sri Lanka's economic performance under the program supported by a three-year extended arrangement under the Extended Fund Facility (EFF) arrangement.
- "Sri Lanka : 2018 Article IV Consultation and the Fourth Review Under the Extended Arrangement Under the Extended Fund Facility-Press Release; Staff Report; and Statement by the Executive Director for Sri Lanka". IMF. Retrieved 5 August 2018.
- "China on track to bail out Sri Lanka with US$1.25bn in 2018". economynext.com. Archived from the original on 5 August 2018. Retrieved 5 August 2018.
- "Sri Lanka Census of Population and Housing, 2011 – Population by Ethnicity" (PDF). Department of Census and Statistics, Sri Lanka. 20 April 2012.
- Hoole, Rajan (2001). Sri Lanka: The Arrogance of Power. University Teachers for Human Rights (Jaffna). p. 15. ISBN 978-955-9447-04-7.
- "Early Man and the Rise of Civilisation in Sri Lanka: the Archaeological Evidence". lankalibrary.com. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "Official Languages Commission". Archived from the original on 14 February 2012.
- "How unique is Sri Lanka Malay?" (PDF). Peter Bakker. Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology.
- "A3 : Population by religion according to districts, 2012". Census of Population & Housing, 2011. Department of Census & Statistics, Sri Lanka.
- "Census of Population and Housing 2011". Department of Census and Statistic. Retrieved 13 October 2019.
- "Sri Lanka". International Religious Freedom Report 2007. Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights, and Labor. 14 September 2007.
- "Theravada: Buddhism in Sri Lankan". Buddhanet.net. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "Theravada Buddhism and Shan/Thai/Dai/Laos Regions Boxun News". Peacehall.com. 28 March 2005.
- "The Constitution of Sri Lanka: Chapter II – Buddhism". Archived from the original on 3 March 2016.
The Republic of Sri Lanka shall give to Buddhism the foremost place and accordingly it shall be the duty of the State to protect and foster the Buddha Sasana, while assuring to all religions the rights granted by Articles 10 and 14(1)(e)
- "Hinduism in Sri Lanka". Lakpura LLC. 14 January 2016. Archived from the original on 1 May 2009.
- "Lankan Muslims' historical links with India". Indianmuslims.info. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016.
- "Origins and Affinities of the Sri Lankan Moors" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 29 July 2014.
- Young, R. F. & Sēnānāyaka, J. E. B. (1998). The carpenter-heretic: a collection of Buddhist stories about Christianity from the 18th century Sri Lanka. Colombo: Karunaratne & Sons. ISBN 978-955-9098-42-3.
- "Sri Lanka – Christianity". Mongabay.
- "The Parsi Community of Sri Lanka". Ancestry.com.
- "Sri Lankan Parsis facing extinction?". The Sunday Times.
- "What Alabamians and Iranians Have in Common". The Gallup Organization. 9 February 2009.
- "Population of Municipal Councils and Urban Councils by sex Census 2012" (PDF). statistics.gov.lk. Department of Census and Statistics. 2012. Retrieved 6 July 2017.
- "Our Pro-poor health care policy rewarded". The Island.
- "Universal Health Care". quickoverview.com. Archived from the original on 12 April 2014. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "Social Conditions of Sri Lanka" (PDF). statistics.gov.lk. pp. 15–17. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 November 2017. Retrieved 10 March 2018.
- Gunawardena, Chandra (1997). "Problems of Illiteracy in a Literate Developing Society: Sri Lanka". International Review of Education. 43 (5/6): 595–609. Bibcode:1997IREdu..43..595G. doi:10.1023/A:1003010726149. JSTOR 3445068.
- "Sri Lanka – literacy rate". indexmundi.com.
- "Govt targets 75% computer literacy rate by 2016". The Daily News.
- "Sri Lanka – Statistics". UNICEF.
- De Silva, K.M. (1981). A Short History of Sri Lanka. Los Angeles: University of California Press. p. 472. ISBN 978-0-520-04320-6.
- "Honouring the Father of Free Education". The Daily News.
- "Who was "Father" of free education in Sri Lanka?: C.W.W. Kannangara or A. Ratnayake?". Trans Currents. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 21 November 2012.
- "Education: Traditional and Colonial Systems". Library of Congress Country Studies.
- "Sri Lanka University Statistics 2010" (PDF). University Grants Commission. p. 3.
- "Facing Global and Local Challenges: The New Dynamics for Higher Education – Sri Lanka Country Report" (PDF). UNESCO. pp. 3–4. Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 June 2013.
- "Educational Indicators 1980–2009". University Grants Commission (Sri Lanka). Archived from the original on 22 February 2011.
- "Private University Bill". Sri Lanka University News.
- "Sir Arthur Charles Clarke". University of Moratuwa. Archived from the original on 21 June 2014.
- Sri Lanka: Transport At a Glance – Core Road Performance Indicators worldbank.org
- "Safe use of the Expressway". www.exway.rda.gov.lk.
- "Class A, B & E Roads". Archived from the original on 28 April 2016.
- "Sri Lanka / Ceylon Railway". lanka.com. 29 September 2015. Retrieved 8 March 2018.
- "Radio Ceylon/Sri Lanka Broadcasting Corporation: The history of broadcasting in Sri Lanka" (PDF). Sri Lanka Broadcasting Corporation. p. 1. Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 March 2016. Retrieved 15 September 2011.
- "Sri Lanka Press, Media, TV, Radio, Newspapers". Pressreference.com.
- "Media under fire: Press freedom lockdown in Sri Lanka" (PDF). International Press Freedom and Freedom of Expression Mission to Sri Lanka. pp. 5–6.
- Jansz, Frederica (8 July 2012). "Gota goes berserk". Sunday Leader. Archived from the original on 20 October 2012. Retrieved 24 November 2012.
- "Chronicle of a death foretold". The Economist. 15 January 2009. Retrieved 24 November 2012.
- Wickramasinghe, Lasantha (11 January 2009). "And then they came for me". Sunday Leader. Archived from the original on 16 October 2012. Retrieved 25 November 2012.
- "Amnesty International – Sri Lanka Human Rights Reports". Amnesty International.
- "Sri Lanka: Country Report on Human Rights Practices". United States Department of State. 23 February 2001. Archived from the original on 7 June 2001.
- Keerthisinghe, Lakshman I. (2013). "The British duplicity in protecting human rights in Sri Lanka". Daily Mirror. Archived from the original on 21 October 2013. Retrieved 21 October 2013.
- "Report of the Secretary – General's Panel of Experts on Accountability in Sri Lanka" (PDF). United Nations. 31 March 2011. p. 71.
- "L'ONU a caché l'ampleur des massacres au Sri Lanka". Le Monde.fr. Lemonde.fr. 28 May 2009. Retrieved 26 February 2013.
- "Business Corruption in Sri Lanka". Business Anti-Corruption Portal. Archived from the original on 8 April 2014. Retrieved 8 April 2014.
- "Department for Justice" (PDF).
- United Nations, Human Rights Council Nineteenth session. "Report of the Working Group on Enforced or Involuntary Disappearances" (PDF). UN. pp. 3, 113. Retrieved 24 November 2012.
'The original mandate derives from Commission on Human Rights resolution 20 (XXXVI) of 29 February 1980','Since its establishment, the Working Group has transmitted 12,460 cases to the Government; of those, 40 cases have been clarified on the basis of information provided by the source, 6,535 cases have been clarified on the basis of information provided by the Government, 214 cases were found to be duplications and were therefore deleted, and 5,671 remain outstanding.'
- Disappearances in Sri Lanka (14 January 2012). "Murky business: People are disappearing – and the government has been accused". The Economist. Retrieved 24 November 2012.
- "UN Human Rights Commissioner: 'democracy has been undermined' in Sri Lanka". GlobalPost. 31 August 2013. Retrieved 10 September 2013.
- "BBC News – UN's Navi Pillay attacks Sri Lanka human rights record". Bbc.co.uk. 31 August 2013. Retrieved 10 September 2013.
- Sri Lanka: Out of the Silence. freedomfromtorture.org
- "Sri Lanka: Human Rights Under Attack". Human Rights Watch. Retrieved 29 July 2020.
- "Sri Lankan culture and history". reddottours.com.
- "Pre-Colonial Sri Lankan History". panix.com.
- Nubin 2002, p. 94
- Nubin 2002, p. 97
- Jayakody, Padmini (2008). Simply Sri Lankan. Australia: Lulu.com. p. 3. ISBN 978-1-4092-1942-2.
- Wickremeratne, Swarna (2006). Buddha in Sri Lanka: remembered yesterdays. SUNY Press. p. 31. ISBN 978-0-7914-6881-4.
- Dassanayake, M. B. (1970). The Kandy Esala perahera: Asia's most spectacular pageant. Colombo: Lake House Bookshop. p. 7.
- Dissanayake, Wimal (2006). Contemporary Asian cinema: popular culture in a global frame, Chapter 8. Berg. pp. 108–119. ISBN 978-1-84520-237-8.
- Lakshman, W. D. (2000). Sri Lanka's development since independence. New York: Nova Publishers. p. 253. ISBN 978-1-56072-784-2.
- "Dr. Lester James Peiris, Father of Sri Lankan Cinema, celebrates 90th Birthday". Asian Tribune.
- Brandon, James R. (1997). The Cambridge guide to Asian theatre. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 226–229. ISBN 978-0-521-58822-5.
- McConnachie, James (2000). World music: the rough guide, Volume 2. Rough Guides. p. 230. ISBN 978-1-85828-636-5.
- Atkinson, Brett (2009). Lonely Planet Sri Lanka. Lonely Planet. p. 50. ISBN 978-1-74104-835-3.
- "Kandyan dance". Encyclopædia Britannica.
- Cummings, Joe (2006). Sri Lanka. Lonely Planet. pp. 50–52. ISBN 978-1-74059-975-7.
- "Dance of Sri Lanka". lanka.com. 28 July 2014. Archived from the original on 14 July 2014.
- "History of painting and sculpture in Sri Lanka". lankalibrary.com. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 20 September 2011.
- "The Sinhala Theatre of Sri Lanka: A Form of Political Discourse". artsrilanka.org.
- "A survey of Sinhalese poetry from ancient times to the modern period". lankalibrary.com.
- "Challenge to Buddha Jayanthi Stamp Selection Board". The Island.
- "Martin Wickramasinghe: An icon of world intellectual heritage". The Daily News.
- Gurusinghe, Nimal (2 October 2008). "Can Sri Lanka form an invincible cricket team?". The Daily News.
- "Rugby: Sri Lanka, Asia's little-known rugby haven". Dawn. 25 May 2011. Archived from the original on 8 April 2012.
- Selvey, Mike (18 March 1996). "Sri Lanka light up the world". The Guardian. London.
- ESPNcricinfo. "Final: Australia v Sri Lanka at Bridgetown, Apr 28, 2007".
- Sheringham, Sam (2 April 2011). "India power past Sri Lanka to Cricket World Cup triumph". BBC.
- McGlashan, Andrew (21 June 2009). "Afridi fifty seals title for Pakistan". ESPNcricinfo.
- "Murali 'best bowler ever'". BBC Sport. London. 13 December 2002.
- "John Player Gold Leaf Trophy (Asia Cup) 1985/86 (Final)". cricketarchive.co.uk. 6 April 1986.
- Thawfeeq, Sa'adi. "Pepsi Asia Cup, 1997–98". ESPNcricinfo.
- Vasu, Anand (1 August 2004). "Sri Lanka win the Asia Cup". ESPNcricinfo.
- "Asia Cup 2008". ESPNcricinfo. 6 July 2008.
- "Asia Cup 2014". ESPNcricinfo. 8 March 2014.
- "Sri Lanka National Cricket Team". exzoon.com. Archived from the original on 1 November 2013. Retrieved 15 September 2011.
- "Duncan White – the greatest Sri Lankan athlete". The Daily News. 12 June 2008.
- "Athlete Susanthika Jayasinghe". olympic.org. 20 June 2016.
- "LKY's prejudice". Daily Mirror. 7 June 2010. Archived from the original on 18 December 2013.
- "Sri Lanka emerged as world champions". Prepare. 10 November 2016.
- "Kitesurf Sri Lanka". kitesurfingsrilanka.com.
- "Sri Lankan martial arts". sinhalaya.com. Archived from the original on 25 January 2016. Retrieved 15 September 2011.
Cited references
- Codrington, H.W. (1926). A Short History of Ceylon. London: Macmillan & Co. ISBN 978-0-8369-5596-5. OCLC 2154168.
- Nubin, Walter (2002). Sri Lanka: Current issues and historical background. Nova Publishers. ISBN 978-1-59033-573-4.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- "Theri Sanghamitta and the Bodhi Tree" (PDF). Paw, Maung. usamyanmar.net.
- De Silva, K. M. (1981). A history of Sri Lanka. University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-04320-6.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
External links
| Wikisource has the text of the 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica article Ceylon. |
Government
- Official Sri Lankan Government Web Portal, a gateway to government sites.
- Official website of the Parliament of Sri Lanka.
- Official Government News Portal
- Official website of the President of Sri Lanka.
- Official website of the Prime Minister of Sri Lanka / Prime Minister's Office.
- Official website of the Office of the Cabinet of Ministers of Sri Lanka.
- Official website of the Supreme Court of Sri Lanka.
Overviews and data
- "Sri Lanka". The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency.
- Official site of the Department of Census and Statistics.
- Annual Report 2010 from the Ministry of Finance and Planning.
- Sri Lanka from UCB Libraries GovPubs.
- Sri Lanka at Curlie
- Sri Lanka profile from the BBC News.
- Sri Lanka in the Encyclopædia Britannica.
- Introducing Sri Lanka Overview of the country from Lonely Planet.
- Key Development Forecasts for Sri Lanka from International Futures.
History
- Mahavamsa an ancient Sri Lankan chronicle written in the 6th century.
- Sketches of the Natural History of Ceylon by Sir James Emerson Tennent, 1861.
Maps

- Sri Lanka Map in Google Maps.
Trade




.svg.png)