Greater Poland uprising (1918–19)
The Greater Poland uprising of 1918–1919, or Wielkopolska uprising of 1918–1919 (Polish: powstanie wielkopolskie 1918–19 roku; German: Großpolnischer Aufstand) or Posnanian War was a military insurrection of Poles in the Greater Poland region (German: Grand Duchy of Posen or Provinz Posen) against German rule. The uprising had a significant effect on the Treaty of Versailles, which granted a reconstituted Second Polish Republic the area won by the Polish insurrectionists. The region had been part of the Kingdom of Poland and then Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth before the 1793 Second Partition of Poland when it was annexed by the German Kingdom of Prussia. It had also, following the 1806 Greater Poland Uprising, been part of the Duchy of Warsaw (1807–1815), a French puppet state during the Napoleonic Wars.
| Greater Poland Uprising | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the aftermath of World War I | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||||
|
|
| ||||||||
| Territorial evolution of Poland in the 20th century |
|---|
|
Post World War I
|
|
|
Post World War II
|
|
Areas
|
|
Demarcation lines
|
|
Adjacent countries |
Background
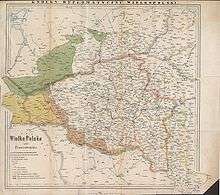
After the Third Partition of Poland in 1795, the Polish nation had ceased to exist as an independent state. From 1795 through the beginning of World War I, several unsuccessful uprisings to regain independence took place. The Great Poland Uprising of 1806 was followed by the creation of the Duchy of Warsaw, which lasted for eight years before it was partitioned again between Prussia and Russia. Under German rule, Poles faced systematic discrimination and oppression.[1][2][3] The Poles living in the region of Greater Poland were subjected to Germanisation and land confiscations to make way for German colonization.
At the end of World War I, US President Woodrow Wilson's Fourteen Points and the idea of national self-determination were met with opposition from European powers standing to lose influence or territory, such as Germany, which dominated Greater Poland. German politicians had signed an armistice leading to a ceasefire on 11 November 1918. Also, Germany had signed the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk with the Bolshevik Russia to settle the territorial boundaries of the eastern frontiers. That treaty took into consideration of a future Polish state and so from then until the Treaty of Versailles was fully ratified in January 1920, many territorial and sovereignty issues remained unresolved.
Wilson's proposal for an independent Poland initially did not set borders that could be universally accepted. Most of Poland that was partitioned and annexed to Prussia in the late 18th-century was still part of Greater Germany at the close of World War I, the rest of the Kingdom of Poland being in Austria-Hungary. The portion in Germany included the region of Greater Poland, of which Poznań (Posen) was a major industrial city and its capital. The majority of the population was Polish (more than 60%)[4] and hoped to be within the borders of the new Polish state.
Uprising


In late 1918, Poles hoping for a sovereign Poland started serious preparations for an uprising after Wilhelm II's abdication on 9 November 1918, which marked the end of the German Empire. The monarchy was replaced by the Weimar Republic.
The uprising broke out on 27 December 1918 in Poznań, after a patriotic speech by Ignacy Paderewski, the famous pianist, who would become the Polish prime minister in 1919.
The insurrectionist forces consisted of members of the Polish Military Organization, who formed the Straż Obywatelska (Citizen's Guard), later renamed as Straż Ludowa (People's Guard), which included many volunteers, who were mainly veterans of World War I. The first contingent to reach the Bazar Hotel, from where the uprising was initiated, was a 100-strong force from wildecka kompania Straży Ludowej (Wilda's People's Guard) led by Antoni Wysocki. The ruling body was the Naczelna Rada Ludowa (Supreme People's Council). Initially, the members of the Council, including Captain Stanisław Taczak and General Józef Dowbor-Muśnicki were against the uprising, but they changed their minds in support of the insurrection on 9 January 1919.
The timing was advantageous for the insurrectionists since between late 1918 and early 1919, internal conflict had weakened Germany, and many of its soldiers and sailors engaged in mutinous actions against the state. Demoralized by the signing of the armistice on 11 November 1918, the new German government was further embroiled in subduing the German Revolution.
By 15 January 1919, Poles had taken control of most of the province, and they engaged in heavy fighting with the regular German army and irregular units such as the Grenzschutz. Fighting continued until the renewal of the truce between the Entente and Germany on 16 February. The truce also affected the front line in Greater Poland, but despite the ceasefire, skirmishes continued until the final signing of the Treaty of Versailles on 28 June 1919.
The uprising is one of the two most successful Polish uprisings, the other being the Great Poland Uprising of 1806, which ended with the entry of Napoleon's army on the side of the Poles fighting against Prussia.
Many of the Greater Poland insurrectionists later took part in the Silesian Uprisings against German rule, which started in late 1919 and ended in 1921.
Reaction

The uprising had a significant effect on the decisions in Versailles that granted Poland not only the area won by the insurrectionists but also the lands of the Polish Corridor, which were also part of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth before the First Partition of Poland in 1772 and connected Poland to the Baltic Sea. Some of the major cities included Bydgoszcz (Bromberg), Leszno (Lissa) and Rawicz (Rawitsch). The riots initiated by the minority Germans later influenced the decision to have popular votes in Silesia, where the public was allowed to vote whether it wanted to be part of Poland or Germany.
Germany's territorial losses following the Treaty of Versailles incited German revanchism,[5] and created unresolved problems such as the status of the independent Free City of Danzig and of the Polish Corridor between East Prussia and the rest of Germany. Attending to these issues was part of Adolf Hitler's political platform. Throughout the 1920s and 1930s, Poland refused several German proposals for popular referendums, population transfers, highway projects and customs union reforms for fear of an eventual land grab from Germany.
Timeline
Earlier events
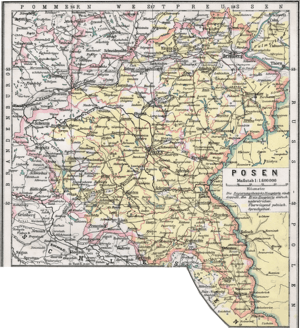
- January 1916: creation of Secret Inter-Party Citizen's Committee (pl. Tajny Międzypartyjny Komitet Obywatelski) formed by members of the German Reichstag of Polish nationality.
- July 1918: a network of local Citizens' Committees is created on area of Prussian Partition.
- 11 October 1918: Polish organizations in the German Empire publicise common documents in which they declare the will to create independent Polish state and, in effect, revolution.
- 9 November 1918: beginning of the German Revolution, which also occurred in Greater Poland. Poles organized secret military structures in the Poznań garrison, Jarocin and Inowrocław.
- 10 November 1918: events of the so-called Republika Ostrowska.
- 11 November 1918
- Armistice signed, ending the hostilities of World War I.
- The Citizens' Guard (Straż Obywatelska), renamed a few days later to the People's Guard (Straż Ludowa), comes out from the underground. The mayor of Poznań (Posen), Ernst Wilms, is removed from office. German military authorities give permission for functioning of the People's Guard to keep peace in the Province of Posen.
- 12 November 1918
- The Central Citizen's Committee, later renamed to the Supreme People's Council (Naczelna Rada Ludowa, NRL), creates temporary "government-in-waiting" Commission (Komisariat): Stanisław Adamski, Wojciech Korfanty, and Adam Poszwiński.
- Jarogniew Drwęski becomes the Mayor of Poznań.
- 13 November 1918
- Commission of the High People's Council calls citizens of German portion of Poland to keep calm in spite of the revolution.
- "Assassination on City Hall": dominated by Germans, the Execution Department of Worker's and Soldier's Council proceeded to Poznań's City Hall, an armed group of Poles forces it to change four of the German delegates with Polish ones: Bohdan Hulewicz, Mieczysław Paluch, Henryk Śniegocki and Zygmunt Wiza. Poles thus gain control over the headquarters of Poznań Garrison and 5th Corps.
- 17 November 1918: the Commission of the NRL calls for a one-time collection of money called a "national tax".
- 18 November 1918: elections to Poviat's People's Councils and members of the partition's Sejm (1399 MPs).
- 20 November 1918: the Polish government in Warsaw publishes przyłączenie Wielkopolski będzie jednym z pierwszych naszych zadań (the joining of Greater Poland will be one of our first tasks).
- 3 December 1918: The Partition Sejm of Poznań begins its official proceedings in the "Apollo" Cinema. MPs represent all lands of the Prussian Partition and Polish economic emigration, mainly from Westfalen.
- 5 December 1918: the end of the Partition Sejm, which declared its desire for unification with the other partitions in a renewed Poland, and the NRL officially elected its members.
- 6 December 1918: the first meeting of the NRL has Bolesław Krysiewicz become the speaker. Election of executive body, Commission of the NRL, formed by representatives of Greater Poland - Stanisław Adamski and Władysław Seyda; Upper Silesia: Wojciech Korfanty and Józef Rymer; Eastern Pomerania: Stefan Łaszewski; Kuyavia: Adam Poszwiński.
- 11 December 1918: the Polish language and the teaching of religion in Polish return to schools.
- 15 December 1918: the Polish government in Warsaw breaks diplomatic relations with Germany.
Uprising

- 27 December 1918: The uprising starts in the evening with shooting in front of Poznań's police headquarters. Fighting also start in other towns: Szamotuły, Środa Wielkopolska, Pniewy, Opalenica, Buk, Trzemeszno, Września and Gniezno are captured. Poles in Poznań capture the main train station, the main post office and part of city fortifications.
- 28 December 1918:
- The Poles in Poznań capture Cytadela (a main stronghold), Fort Grolmann and an armory on ul. Wielkie Garbary
- The commission of the NRL promotes Captain Stanisław Taczak to temporary commander-in-chief of the uprising (he is also promoted to rank of major).
- 29 December 1918: The Poles capture Grodzisk Wielkopolski, Kłecko, Kórnik, Wielichowo, Gostyń, Witkowo and other towns.
- 30 December 1918
- Failure of peace talks between the insurgents and the German authorities, the latter refusing to take the responsibility for the hostilities of 27 December.
- In Poznań, the Poles force the German 6th Regiment of Grenadiers from their barracks. After talks, the regiment leaves the city with their weapons.
- The Poles capture Wronki, Wągrowiec, Gołańcz. Polish soldiers stop a German offensive against Gniezno near Zdziechowa.
- 31 December 1918
- The Poles capture Kościan, Oborniki Wielkopolskie, Ostrów Wielkopolski.
- A unit of Poles under command of Paweł Cymes begins offensive on Cuiavia.
- 1 January 1919
- 3 January 1919: to avoid anarchy in Greater Poland, the Commission of the NRL decides to take over control of the spontaneous uprising but also decides that the decision should be kept secret.
- 4 January 1919: The Commission of the NRL decrees a new president of the Province of Poznań, Wojciech Trąmpczyński. German authorities call for boycotting him.
- 5 January 1919: Czarnków, Jutrosin, Kruszwica, Nakło, Nowy Tomyśl, Miejska Górka, Rawicz, Strzelno and Wolsztyn are captured by the Poles.
- 6 January 1919
- The Poles capture Ławica Airport, Poznań, with all aircraft undamaged.
- Fighting near Czersk and Kościerzyna in Pomerania.
- Inowrocław captured.
- 7 January 1919
- 8 January 1919
- The Commission of the NRL takes all civil and military authority without declaring territorial range of that power. It also promotes General Józef Dowbor-Muśnicki to commander-in-chief of the uprising forces.
- The Poles recapture Chodzież Battle of Chodzież and Czarnków. They also win the Battle of Ślesin and capture Sieraków.
- 9 January 1919
- The NRL officially announces that it takes control over Greater Poland. Beginning of polonisation of administration, most former anti-Polish officials being fired. In powiats, German landrats are subordinated to Polish starostas, which latw take all their power.
- Poles lose Nakło.
- Polish airmen bomb military airfield in Frankfurt (Oder)
- 10 January 1919: fights on southern front near Kąkolewo, Leszno and Rydzyna. Poles capture Sarnowa.
- 11 January 1919: The Germans recapture Sarnowa and win in Battle of Zbąszyń; Polish victory in Battle of Szubin and capture Łabiszyn, Złotniki and Żnin.
- 12 January 1919: fighting near Leszno and Lipno.
- 13 January 1919: The Germans recapture Szamocin.
- 14 January 1919: The Commission of tge NRL appeals to Roman Dmowski for help negotiate a ceasefire.
- 15 January 1919: failed attempt to recapture Szamocin by Poles.
- 16 January 1919
- The first number of Tygodnik Urzędowy Naczelnej Rady Ludowej, with the laws of the NRL, is published.
- The Polish government of Ignacy Paderewski has two politicians of Greater Poland: Józef Englich, the minister of treasury, and Kazimierz Hącia, the minister of industry and trade.
- 17 January 1919: Men born in 1897, 1898, and 1899 are called up and drafted into Great Polish Army.
- 20 January 1919: the transfer of money to banks of Germany on the other side of the front line is forbidden.
- 21 January 1919
- NRL creates oath of soldiers of Great Polish Army.
- Evidence of false information about Polish attacks on German civilians published by authorities in Berlin, suggesting behaviour like that the Germans, is sent to Paris. Meanw, the NRL appeals to Allies asking for a military mission, suggesting the possibility of the Great Polish Army fighting against Bolsheviks. Many articles about the situation in Greater Poland appear in Western newspapers.
- 22 January 1919
- Northern front: Poles are forced to leave Potulice.
- Southern front: Poles win the Battle of Robaczysko.
- Joseph Noules is nominated by Supreme Council of Allied Countries as chief of Allied mission in Poland.
- 23 January 1919: Poles defend Miejska Górka after heavy fighting.
- 25 January 1919
- 26 January 1919: Great Polish Army soldiers, commanded by Dowbór-Muśnicki, give an oath on Wilhelm Platz, renamed on Plac Wolności (Freedom Square), in Poznań.
- 28 January 1919: German offensive ("Butteroffensive") in area of Bydgoszcz and Nakło. In the Battle of Rynarzewo, the Germans capture Szubin.
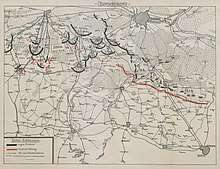
- 29 January 1919: Roman Dmowski gives a speech in front of Supreme Council of Allied Countries in which he asserts Polish rights to the Prussian Partition and accuses the Germans of two-faced policies.
- 2 February 1919: Polish-German talks start in Berlin.
- 3 February 1919: The Poles stop a German offensive on the northern front. Their counterattack forces a German withdrawal to northern bank of the Noteć River. The Poles recapture Rynarzewo and win the Battle of Kcynia.
- 4 February 1919
- 5 February 1919: Failure of talks in Berlin, with Germans denanding the demobilisation of the Great Polish Army, Polish recognition of German claims to Greater Poland and the payment by the Poles for all damage made during the uprising. However, the Triple Entente remarks that both sides are ready for peace talks.
- 6 February 1919: end of talks about representation of the Prussian Partition in Sejm Ustawodawczy. Since Cuiavia, Silesia and Pomerania are still officially part of Germany, to avoid international repercussions, the Polish government and the NRL decide to cancel the planned election of 126 MPs, giving temporary right of representation of the Prussian Partition to 16 MPs of Reichstag.
- 7 February 1919
- Heavy fighting in Kolno, which is captured many times by both sides.
- The Commission of the NRL promotes 122 former NCOs of the German Army to second lieutenant.
- Józef Piłsudski signs a decree officially allowing 16 MPs from the Prussian Partition to participate in Sejm Ustawodawczy.
- 9 February 1919: The Poles stop a German offensive near Trzciel.
- 10 February 1919: The Poles stop a German attack near Rawicz.
- 11 February 1919: The Commission of the NRL dissolves all town councils, giving 25 March as date of new elections.
- 12 February 1919: Germans use an armoured train to capture Kargowa and Babimost, but their offensive is stopped near Kopanica.
- 14 February 1919
- Talks start on extending the ceasefire that ended World War I. The German delegation is against extending it for Greater Poland, but France forces it through.
- The German headquarters is moved to Kolberg, as a part of preparations to use all forces against Greater Poland.
- 16 February 1919: The extension of the Allied-German ceasefire in Trier is signed, which also refers to Greater Poland. The Polish army is referred to as Allied forces.
Between ceasefire and reunification

- 18 February 1919: In spite of the ceasefire, there is fighting near Rynarzewo. The Poles capture the armoured train.
- 9 February 1919: A volunteer company of Great Polish soldiers moves to Lesser Poland to fight against the Ukrainians.
- 20 March 1919: The Ostmarkenzulage, a special allowance for German officials working in the eastern provinces to stimulate the German colonization of the Prussian Partition, is canceled.
- 23 March 1919: The Poles win a landslide in elections to the city council of Poznań.
- 24 March 1919: The Commission of the NRL asks the Polish government in Warsaw to create separate administration of the former Prussian Partition, as it is far more developed than the rest of the country. Ignacy Paderewski forces the government to leave all power in hands of the NRL until the final recognition of Polish-German border, with later autonomy there (only Upper Silesia would obtain it). The NRL mobilises men born in 1891, 1892, 1893, 1894 and 1901.
- 5 April 1919: The Sejm Ustawodawczy announces byelections in the former Province of Posen for next 42 MPs.
- 9 April 1919: The Commission of the NRL decrees an eight-hour workday in industry and trade.
- 10 April 1919: The Commission of the NRL decrees the removal of signs in German language from offices and train stations the changing of all streets names into Polish. The punishment for breaking the law is two years of prison and 10,000 Polish marks.
- 16 April 1919: The NRL decides that 3 May is the national holiday.
- 7 May 1919: The Wszechnica Piastowska is opened.
- 15 May 1919: Polish becomes the only official language. German is auxiliary, but a lack of Polish-speaking officials means German is still used in the judiciary until 1920.
- 25 May 1919: The Army of Great Poland is subjugated to the headquarters of the Polish Army but keeps its separate organisation.
- 30 May 1919: The People's Guard is transformed to the Home Defence (Obrona Krajowa).
- 1 June 1919: By-elections of MPs to Sejm Ustawodawczy.
- 6 June 1919
- Skirmishes near Bydgoszcz (Bromberg).
- The rising threat of a German offensive induces the Commission of the NRL to introduce a state of emergency in all lands under its jurisdiction. In a belt of 20 km from the front line, it introduces martial law. A few days later, the NRL announces capital punishment for acting against the Great Polish Army or for the German army.
- 18 June 1919: Skirmishes near Rynarzewo.
- 28 June 1919: The Treaty of Versailles gives almost all of Greater Poland to Poland.
- 1 July 1919
- The Commission of the NRL removes customs border with ex-Kingdom of Poland.
- Artillery fire at front.
- 9 July 1919: Farther than 20 km from the front, end of state of emergency.
- 10 July 1919: proceedings of the Polish government with Commission of the NRL on further policy in the former Prussian Partition (Były Zabór Pruski). Creation of the Ministry of the Former Prussian Partition (Ministerstwo Byłej Dzielnicy Pruskiej).
- 1 August 1919: Sejm Ustawodawczy votes on a resolution on the "Temporary Organisation of Government in the former Prussian Partition" (O tymczasowej organizacji zarządu byłej dzielnicy pruskiej), creating the Ministry of the Former Prussian Partition and a plan of gradual unification of Greater Poland with the rest of the country.
- 12 August 1919: Władysław Seyda becomes the first Minister of the Former Prussian Partition.
- 19 August 1919: The NRL is dissolved.
- 28 August 1919: The headquarters of the Polish Army decides that the Greater Polish Army will join the Polish Army and that its headquarters will be transferred to the headquarters of the Seventh Corps.
- 6 November 1919: The Commission of the NRL is dissolved.
- 10 January 1920: Ratification of Treaty of Versailles, which has Polish forces in Greater Poland take control over small amounts of Greater Poland's territories given to Poland that are resisting German control and Eastern Pomerania.
- 13 January 1920: The hadquarters of the Greater Poland front orders preparations for implementating the treaty
- 17 January 1920: beginning of the occupation of the remaining German-held territories assigned to Poland by the treaty.
- 8 March 1920: The Greater Poland front is dissolved.
Epilogue
- 24 March 2005: the last surviving Polish fighter in the uprising, Lieutenant Jan Rzepa, dies at the age of 106.
References
- Racisms Made in Germany, edited by Wulf D. Hund, Wulf Dietmar Hund, Christian Koller, Moshe Zimmermann LIT Verlag Münster 2011 page 20, 21
- The Ideology of Kokugo: Nationalizing Language in Modern Japan, Lee Yeounsuk page 161 University of Hawaii Press 2009
- The Immigrant Threat: The Integration of Old and New Migrants in Western Europe since 1850 (Studies of World Migrations) Leo Lucassen, p.61, University of Illinois Press, 2005
- "Historia 1871–1939" Anna Radziwiłł, Wojciech Roszkowski Warsaw 1998
- Boemeke, Manfred F.; Feldman, Gerald D.; Gläser, Elisabeth, eds. (1998). The Treaty of Versailles: A Reassessment After 75 Years. Publications of the German Historical Institute. Cambridge University Press. p. 220. ISBN 0521621321.
Bibliography
- Antoni Czubiński, Powstanie Wielkopolskie 1918–1919. Geneza-charakter-znaczenie, Poznań 1978
- Antoni Czubiński, Rola Powstania Wielkopolskiego w walce narodu polskiego o powstrzymanie niemieckiego >parcia na wschód<, Przegląd Zachodni 1968, nr 5-6
- A.Czubiński, Z.Grot, B.Miśkiiewcz, Powstanie Wielkopolskie 1918–1919. Zarys dziejów, Warszawa 1978
- K.Dembski, Wielkopolska w początkach II Rzeczypospolitej. Zagadnienia prawno-ustrojowe, Poznań 1972
- Roman Dmowski, Polityka polska i odbudowanie państwa 1925
- Z. Grot (ed.), Powstanie wielkopolskie 1918–1919, Poznań 1968
- Z.Grot, I.Pawłowski, M.Pirko, Wielkopolska w walce o niepodległość 1918–1919. Wojskowe i polityczne aspekty Powstania Wielkopolskiego, Warszawa 1968
- P.Hauser, Niemcy wobec sprawy polskiej X 1918–VI 1919, Poznań 1984
- K.Kandziora, Działalność POW w Poznaniu. Przyczynek do historii Polskiej Organizacji Wojskowej zaboru pruskiego w latach 1918–1919, Warszawa 1939
- S.Kubiak, Niemcy a Wielkopolska 1918–1919, Poznań 1969
- Joseph Lamia: Der Aufstand in Posen (The Uprising in Poznan). Berlin 1919 (in German).
- Materiały Sesji Naukowej z okazji 50-lecia Powstania Wielkopolskiego 1918/1919, Zaszyty Naukowe UAM 1970, Historia t.10
- Witold Mazurczak, Anglicy i wybuch powstania wielkopolskiego. Z dziejów genezy brytyjskiej misji płka H.H.Wade'a w Polsce, [in:] Antoni Czubiński (ed.), Polacy i Niemcy. Dziesięć wieków sąsiedztwa, PWN, Warszawa 1987
- Janusz Pajewski, Rodział XXII. Powstanie Wielkopolskie, [in:] J.Pajewski, Odbudowa państwa polskiego 1914–1918, Warszawa 1985,
- Janusz Pajewski, Znaczenia Powstania Wielkopolskiego dla odbudowy Państwa Polskiego w 1918 r., Zeszyty Naukowe UAM, Historia 1970, t.10
- S.Rybka, Zerwane pęta. Wspomnienia z dni rewolucji niemieckiej i powstania polskiego 1918-1919, Poznań 1919
- A.Rzepecki, Powstanie grudniowe w Wielkopolsce. 27 XII 1918, Poznań 1919
- Z.Wieliczka, Wielkopolska w Prusy w dobie powstania 1918/1919, Poznań 1932
- Z.Wroniak, Paderewski w Poznaniu, Kronika Miasta Poznania 1959, nr 4
- H.Zieliński, Rola powstania wielkopolskiego oraz powstań śląskich w walce o zjednoczenie ziem zachodnich z Polską; (1918–1921), [in:] Droga przez Półwiecze.
- Dietrich Vogt: Der großpolnische Aufstand 1918/1919: Bericht, Erinnerungen, Dokumente. Marburg 1980 (J.-G.-Herder-Institut) ISBN 3-87969-147-9
- Richard Blanke, Orphans of Versailles. The Germans in Western Poland 1918-1939, Lexington, KY.,1993 (presents somehow pro-German vision of the events)
External links

- Greater Poland Uprising (website of the Institute of National Remembrance)




