Yuan dynasty
The Yuan dynasty (Chinese: 元朝; pinyin: Yuán Cháo), officially the Great Yuan[6] (Chinese: 大元; pinyin: Dà Yuán; Middle Mongolian: ᠳᠠᠢ
ᠥᠨ
ᠤᠯᠤᠰ, Dai Ön Ulus, literally "Great Yuan State"[note 3]), was the empire or ruling dynasty of China established by Kublai Khan, leader of the Mongol Borjigin clan. It lasted from 1271 to 1368, following the Song dynasty and preceding the Ming dynasty.
Great Yuan 大元 ᠳᠠᠢ ᠥᠨ ᠤᠯᠤᠰ (Dai Ön Ulus, "Great Yuan State" in Middle Mongolian) | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1271–1368 | |||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||
 Provinces of Yuan in 1330 | |||||||||||||||
| Status | Khagan-ruled division of the Mongol Empire Conquest dynasty of Imperial China | ||||||||||||||
| Capital | Khanbaliq (Beijing) Shangdu (summer capital) | ||||||||||||||
| Common languages | Mongolian (Middle Mongol) Chinese (Old Mandarin) | ||||||||||||||
| Religion | Buddhism (Tibetan Buddhism as de facto state religion), Mongolian Tengrism/Chinese Heaven worship, Shamanism, Taoism, Confucianism, Chinese folk religion, Chinese Nestorian Christianity, Roman Catholic Christianity, Judaism, Chinese Manichaeism, Islam, Legalism | ||||||||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||||||||
| Emperor | |||||||||||||||
• 1259–1294 | Kublai Khan | ||||||||||||||
• 1332–1368 | Toghon Temür | ||||||||||||||
| Chancellor | |||||||||||||||
• 1264–1282 | Ahmad Fanakati | ||||||||||||||
• 1340–1355 | Toqto'a | ||||||||||||||
| Historical era | Postclassical Era | ||||||||||||||
| Spring, 1206 | |||||||||||||||
• Formal proclamation of the Yuan dynasty[3] | 5 November 1271 | ||||||||||||||
| 1268–1273 | |||||||||||||||
• Conquest of Southern Song | 4 February 1276 | ||||||||||||||
| 19 March 1279 | |||||||||||||||
• Red Turban Rebellion | 1351–1368 | ||||||||||||||
• Fall of Khanbaliq | 14 September 1368 | ||||||||||||||
• Formation of Northern Yuan dynasty | 1368–1388 | ||||||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||||||
| 1310[4] | 11,000,000 km2 (4,200,000 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||
| 1330[5] | 13,720,000 km2 (5,300,000 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||
| Population | |||||||||||||||
• 1290 | 77,000,000 | ||||||||||||||
• 1293 | 79,816,000 | ||||||||||||||
• 1330[5] | 83,873,000 | ||||||||||||||
• 1350 | 87,147,000 | ||||||||||||||
| Currency | Predominantly Paper Currency (Jiaochao), with a small amount of Chinese cash in use | ||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
| History of the Mongols |
|---|
|
Timeline · History · Rulers · Nobility Culture · Language · Proto-Mongols |
|
 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANCIENT | ||||||||
| Neolithic c. 8500 – c. 2070 BCE | ||||||||
| Xia c. 2070 – c. 1600 BCE | ||||||||
| Shang c. 1600 – c. 1046 BCE | ||||||||
| Zhou c. 1046 – 256 BCE | ||||||||
| Western Zhou | ||||||||
| Eastern Zhou | ||||||||
| Spring and Autumn | ||||||||
| Warring States | ||||||||
| IMPERIAL | ||||||||
| Qin 221–207 BCE | ||||||||
| Han 202 BCE – 220 CE | ||||||||
| Western Han | ||||||||
| Xin | ||||||||
| Eastern Han | ||||||||
| Three Kingdoms 220–280 | ||||||||
| Wei, Shu and Wu | ||||||||
| Jin 266–420 | ||||||||
| Western Jin | ||||||||
| Eastern Jin | Sixteen Kingdoms | |||||||
| Northern and Southern dynasties 420–589 | ||||||||
| Sui 581–618 | ||||||||
| Tang 618–907 | ||||||||
| (Wu Zhou 690–705) | ||||||||
| Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms 907–979 |
Liao 916–1125 | |||||||
| Song 960–1279 | ||||||||
| Northern Song | Western Xia | |||||||
| Southern Song | Jin | Western Liao | ||||||
| Yuan 1271–1368 | ||||||||
| Ming 1368–1644 | ||||||||
| Qing 1636–1912 | ||||||||
| MODERN | ||||||||
| Republic of China on mainland 1912–1949 | ||||||||
| People's Republic of China 1949–present | ||||||||
| Republic of China on Taiwan 1949–present | ||||||||
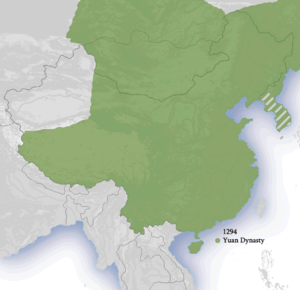
Although the Mongols had ruled territories including modern-day North China for decades, it was not until 1271 that Kublai Khan officially proclaimed the dynasty in the traditional Chinese style,[7] and the conquest was not complete until 1279 when the Southern Song dynasty was defeated in the Battle of Yamen. His realm was, by this point, isolated from the other Mongol khanates and controlled most of modern-day China and its surrounding areas, including modern Mongolia.[8] It was the first non-Han Chinese dynasty to rule all of China and lasted until 1368 when the Ming dynasty defeated the Yuan forces. Following that, the rebuked Genghisid rulers retreated to their Mongolian homeland and continued to rule as the Northern Yuan dynasty.[9]
Some of the Mongol emperors of the Yuan mastered the Chinese language, while others only used their native language (i.e. Mongolian) and the 'Phags-pa script.[10]
After the division of the Mongol Empire, the Yuan dynasty was the khanate ruled by the successors of Möngke Khan. In official Chinese histories, the Yuan dynasty bore the Mandate of Heaven. The dynasty was established by Kublai Khan, yet he placed his grandfather Genghis Khan on the imperial records as the official founder of the dynasty and accorded him the temple name Taizu.[note 4] In the edict titled Proclamation of the Dynastic Name,[3] Kublai announced the name of the new dynasty as Great Yuan and claimed the succession of former Chinese dynasties from the Three Sovereigns and Five Emperors to the Tang dynasty.[3]
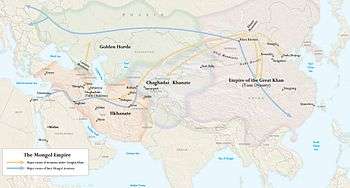
In addition to Emperor of China, Kublai Khan also claimed the title of Great Khan, supreme over the other successor khanates: the Chagatai, the Golden Horde, and the Ilkhanate. As such, the Yuan was also sometimes referred to as the Empire of the Great Khan. However, while the claim of supremacy by the Yuan emperors was at times recognized by the western khans, their subservience was nominal and each continued its own separate development.[11][12]
Name
| Yuan dynasty | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
.svg.png) "Yuan dynasty" in Chinese characters (top) and "Great Yuan State" (Yehe Yüan Ulus, a modern form) in Mongolian script (bottom) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chinese | 元朝 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Literal meaning | "Yuan dynasty" | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dynastic name | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chinese | 大元 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Literal meaning | Great Yuan | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative official full name: ᠳᠠᠢ ᠥᠨ ᠶᠡᠬᠡ ᠮᠣᠩᠭᠣᠯ ᠤᠯᠤᠰ Dai Ön Yeqe Mongɣul Ulus | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 大元大蒙古國 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 大元大蒙古国 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Literal meaning | "Great Yuan" (Middle Mongol transliteration of Chinese "Dà Yuán") Great Mongol State | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
In 1271, Kublai Khan imposed the name Great Yuan (Chinese: 大元; pinyin: Dà Yuán; Wade–Giles: Ta-Yüan), establishing the Yuan dynasty.[6] "Dà Yuán" (大元) is from the clause "大哉乾元" (pinyin: dà zāi Qián Yuán; lit.: 'Great is Qián, the Primal') in the Commentaries on the Classic of Changes section[13] regarding the first hexagram Qián (乾).[3] The counterpart in the Mongolian language was Dai Ön Ulus, also rendered as Ikh Yuan Üls or Yekhe Yuan Ulus. In Mongolian, Dai Ön (Middle Mongol transliteration of Chinese "Dà Yuán") was often used in conjunction with the "Yeke Mongghul Ulus" (lit. "Great Mongol State"), resulting in ᠳᠠᠢ
ᠥᠨ
ᠶᠡᠬᠡ
ᠮᠣᠩᠭᠣᠯ
ᠤᠯᠤᠰ (Dai Ön Yeqe Mongɣul Ulus),[14][15] meaning "Great Yuan Great Mongol State". The Yuan dynasty is also known by westerners as the "Mongol dynasty"[16] or "Mongol Dynasty of China",[17] similar to the names "Manchu dynasty"[18] or "Manchu Dynasty of China"[19] which were used by westerners for the Qing dynasty. Furthermore, the Yuan is sometimes known as the "Empire of the Great Khan" or "Khanate of the Great Khan",[20] which particularly appeared on some Yuan maps, since Yuan emperors held the nominal title of Great Khan. Nevertheless, both terms can also refer to the khanate within the Mongol Empire directly ruled by Great Khans before the actual establishment of the Yuan dynasty by Kublai Khan in 1271.
History
Background
Genghis Khan united the Mongol tribes of the steppes and became Great Khan in 1206.[21] He and his successors expanded the Mongol empire across Asia. Under the reign of Genghis' third son, Ögedei Khan, the Mongols destroyed the weakened Jin dynasty in 1234, conquering most of northern China.[22] Ögedei offered his nephew Kublai a position in Xingzhou, Hebei. Kublai was unable to read Chinese but had several Han teachers attached to him since his early years by his mother Sorghaghtani. He sought the counsel of Chinese Buddhist and Confucian advisers.[23] Möngke Khan succeeded Ögedei's son, Güyük, as Great Khan in 1251.[24] He granted his brother Kublai control over Mongol held territories in China.[25] Kublai built schools for Confucian scholars, issued paper money, revived Chinese rituals, and endorsed policies that stimulated agricultural and commercial growth.[26] He adopted as his capital city Kaiping in Inner Mongolia, later renamed Shangdu.[27]
Many Han Chinese and Khitan defected to the Mongols to fight against the Jin. Two Han Chinese leaders, Shi Tianze, Liu Heima (劉黑馬, aka Liu Ni),[28][29][30][31] and the Khitan Xiao Zhala (蕭札剌) defected and commanded the 3 Tumens in the Mongol army.[32][33][34][35] Liu Heima and Shi Tianze served Ogödei Khan.[36] Liu Heima and Shi Tianxiang led armies against Western Xia for the Mongols.[37] There were 4 Han Tumens and 3 Khitan Tumens, with each Tumen consisting of 10,000 troops. The three Khitan Generals Shimobeidier (石抹孛迭兒), Tabuyir (塔不已兒), and Zhongxi, the son of Xiaozhaci (蕭札刺之子重喜) commanded the three Khitan Tumens and the four Han Generals Zhang Rou, Yan Shi, Shi Tianze, and Liu Heima commanded the four Han tumens under Ogödei Khan.[38][39]
Möngke Khan commenced a military campaign against the Chinese Song dynasty in southern China.[40] The Mongol force that invaded southern China was far greater than the force they sent to invade the Middle East in 1256.[41] He died in 1259 without a successor.[42] Kublai returned from fighting the Song in 1260 when he learned that his brother, Ariq Böke, was challenging his claim to the throne.[43] Kublai convened a kurultai in Kaiping that elected him Great Khan.[44] A rival kurultai in Mongolia proclaimed Ariq Böke Great Khan, beginning a civil war.[45] Kublai depended on the cooperation of his Chinese subjects to ensure that his army received ample resources. He bolstered his popularity among his subjects by modeling his government on the bureaucracy of traditional Chinese dynasties and adopting the Chinese era name of Zhongtong.[46] Ariq Böke was hampered by inadequate supplies and surrendered in 1264.[47] All of the three western khanates (Golden Horde, Chagatai Khanate and Ilkhanate) became functionally autonomous, although only the Ilkhans truly recognized Kublai as Great Khan.[48][49] Civil strife had permanently divided the Mongol Empire.[50]
Rule of Kublai Khan
Early years
Instability troubled the early years of Kublai Khan's reign. Ögedei's grandson Kaidu refused to submit to Kublai and threatened the western frontier of Kublai's domain.[51][52] The hostile but weakened Song dynasty remained an obstacle in the south.[51] Kublai secured the northeast border in 1259 by installing the hostage prince Wonjong as the ruler of the Kingdom of Goryeo (Korea), making it a Mongol tributary state.[53][51] Kublai was also threatened by domestic unrest. Li Tan, the son-in-law of a powerful official, instigated a revolt against Mongol rule in 1262. After successfully suppressing the revolt, Kublai curbed the influence of the Han advisers in his court.[54] He feared that his dependence on Chinese officials left him vulnerable to future revolts and defections to the Song.[55]
Kublai's government after 1262 was a compromise between preserving Mongol interests in China and satisfying the demands of his Chinese subjects.[56] He instituted the reforms proposed by his Chinese advisers by centralizing the bureaucracy, expanding the circulation of paper money, and maintaining the traditional monopolies on salt and iron.[57] He restored the Imperial Secretariat and left the local administrative structure of past Chinese dynasties unchanged.[58] However, Kublai rejected plans to revive the Confucian imperial examinations and divided Yuan society into three, later four, classes with the Han occupying the lowest rank. Kublai's Chinese advisers still wielded significant power in the government, but their official rank was nebulous.[57]
Founding the dynasty

Kublai readied the move of the Mongol capital from Karakorum in Mongolia to Khanbaliq in 1264,[59] constructing a new city near the former Jurchen capital Zhongdu, now modern Beijing, in 1266.[60] In 1271, Kublai formally claimed the Mandate of Heaven and declared that 1272 was the first year of the Great Yuan (大元) in the style of a traditional Chinese dynasty.[61] The name of the dynasty originated from the I Ching and describes the "origin of the universe" or a "primal force".[62] Kublai proclaimed Khanbaliq the Daidu (大都; Dàdū; 'Great Capital') of the dynasty.[63] The era name was changed to Zhiyuan to herald a new era of Chinese history.[64] The adoption of a dynastic name legitimized Mongol rule by integrating the government into the narrative of traditional Chinese political succession.[65] Khublai evoked his public image as a sage emperor by following the rituals of Confucian propriety and ancestor veneration,[66] while simultaneously retaining his roots as a leader from the steppes.[65]
Kublai Khan promoted commercial, scientific, and cultural growth. He supported the merchants of the Silk Road trade network by protecting the Mongol postal system, constructing infrastructure, providing loans that financed trade caravans, and encouraging the circulation of paper banknotes (鈔; Jiaochao). During the beginning of the Yuan dynasty, the Mongols continued issuing coins; however, under Külüg Khan coins were completely replaced by paper money. It wasn't until the reign of Toghon Temür that the government of the Yuan dynasty would attempt to reintroduce copper coinage for circulation.[67][68][69] The Pax Mongolica, Mongol peace, enabled the spread of technologies, commodities, and culture between China and the West.[70] Kublai expanded the Grand Canal from southern China to Daidu in the north.[71] Mongol rule was cosmopolitan under Kublai Khan.[72] He welcomed foreign visitors to his court, such as the Venetian merchant Marco Polo, who wrote the most influential European account of Yuan China.[73] Marco Polo's travels would later inspire many others like Christopher Columbus to chart a passage to the Far East in search of its legendary wealth.[74]
Military conquests and campaigns
After strengthening his government in northern China, Kublai pursued an expansionist policy in line with the tradition of Mongol and Chinese imperialism. He renewed a massive drive against the Song dynasty to the south.[75] Kublai besieged Xiangyang between 1268 and 1273,[76] the last obstacle in his way to capture the rich Yangzi River basin.[59] An unsuccessful naval expedition was undertaken against Japan in 1274.[77] The Duan family ruling the Kingdom of Dali in Yunnan submitted to the Yuan dynasty as vassals and were allowed to keep their throne, militarily assisting the Yuan dynasty against the Song dynasty in southern China. The Duan family still ruled Dali relatively independently during the Yuan dynasty.[78] The Tusi chieftains and local tribe leaders and kingdoms in Yunnan, Guizhou and Sichuan submitted to Yuan rule and were allowed to keep their titles. The Han Chinese Yang family ruling the Chiefdom of Bozhou which was recognized by the Song dynasty and Tang dynasty also received recognition by the Mongols in the Yuan dynasty and later by the Ming dynasty. The Luo clan in Shuixi led by Ahua were recognized by the Yuan emperors, as they were by the Song emperors when led by Pugui and Tang emperors when led by Apei. They descended from the Shu Han era king Huoji who helped Zhuge Liang against Meng Huo. They were also recognized by the Ming dynasty.[79][80]
Kublai captured the Song capital of Hangzhou in 1276,[81] the wealthiest city of China,[82] after the surrender of the Southern Song Han Chinese Emperor Gong of Song. Emperor Gong of Song (personal name Zhao Xian) was married off to a Mongol princess of the royal Borjigin family of the Yuan dynasty.[83] Song loyalists escaped from the capital and enthroned a young child as Emperor Bing of Song, who was Emperor Gong's younger brother. The Yuan forces commanded by Han Chinese General Zhang Hongfan led a predominantly Han navy to defeat the Song loyalists at the battle of Yamen in 1279. The last Song emperor drowned, bringing an end to the Song dynasty.[84] The conquest of the Song reunited northern and southern China for the first time in three hundred years.[85]
The Yuan dynasty created a "Han Army" (漢軍) out of defected Jin troops and an army of defected Song troops called the "Newly Submitted Army" (新附軍).[86]
Kublai's government faced financial difficulties after 1279. Wars and construction projects had drained the Mongol treasury.[87] Efforts to raise and collect tax revenues were plagued by corruption and political scandals.[88] Mishandled military expeditions followed the financial problems.[87] Kublai's second invasion of Japan in 1281 failed because of an inauspicious typhoon.[77] Kublai botched his campaigns against Annam, Champa, and Java,[89] but won a Pyrrhic victory against Burma.[90] The expeditions were hampered by disease, an inhospitable climate, and a tropical terrain unsuitable for the mounted warfare of the Mongols.[89][77] The Trần dynasty which ruled Annam (Đại Việt) defeated the Mongols at the Battle of Bạch Đằng (1288). Annam, Burma, and Champa recognized Mongol hegemony and established tributary relations with the Yuan dynasty.[91]
Internal strife threatened Kublai within his empire. Kublai Khan suppressed rebellions challenging his rule in Tibet and the northeast.[92] His favorite wife died in 1281 and so did his chosen heir in 1285. Kublai grew despondent and retreated from his duties as emperor. He fell ill in 1293, and died on 18 February 1294.[93]
Successors after Kublai
Temür Khan
Following the conquest of Dali in 1253, the former ruling Duan dynasty were appointed as Maharajah.[94] Local chieftains were appointed as Tusi, recognized as imperial officials by the Yuan, Ming, and Qing-era governments, principally in the province of Yunnan. Succession for the Yuan dynasty, however, was an intractable problem, later causing much strife and internal struggle. This emerged as early as the end of Kublai's reign. Kublai originally named his eldest son, Zhenjin, as the Crown Prince, but he died before Kublai in 1285.[95] Thus, Zhenjin's third son, with the support of his mother Kökejin and the minister Bayan, succeeded the throne and ruled as Temür Khan, or Emperor Chengzong, from 1294 to 1307. Temür Khan decided to maintain and continue much of the work begun by his grandfather. He also made peace with the western Mongol khanates as well as neighboring countries such as Vietnam,[96] which recognized his nominal suzerainty and paid tributes for a few decades. However, the corruption in the Yuan dynasty began during the reign of Temür Khan.
Külüg Khan
.jpg)
Külüg Khan (Emperor Wuzong) came to the throne after the death of Temür Khan. Unlike his predecessor, he did not continue Kublai's work, largely rejecting his objectives. Most significantly he introduced a policy called "New Deals", focused on monetary reforms. During his short reign (1307–11), the government fell into financial difficulties, partly due to bad decisions made by Külüg. By the time he died, China was in severe debt and the Yuan court faced popular discontent.[97]
Ayurbarwada Buyantu Khan
The fourth Yuan emperor, Buyantu Khan (born Ayurbarwada), was a competent emperor. He was the first Yuan emperor to actively support and adopt mainstream Chinese culture after the reign of Kublai, to the discontent of some Mongol elite.[98] He had been mentored by Li Meng, a Confucian academic. He made many reforms, including the liquidation of the Department of State Affairs (尚書省), which resulted in the execution of five of the highest-ranking officials.[98] Starting in 1313 the traditional imperial examinations were reintroduced for prospective officials, testing their knowledge on significant historical works. Also, he codified much of the law, as well as publishing or translating a number of Chinese books and works.
Gegeen Khan and Yesün Temür

Emperor Gegeen Khan, Ayurbarwada's son and successor, ruled for only two years, from 1321 to 1323. He continued his father's policies to reform the government based on the Confucian principles, with the help of his newly appointed grand chancellor Baiju. During his reign, the Da Yuan Tong Zhi (《大元通制》; Comprehensive Institutions of the Great Yuan), a huge collection of codes and regulations of the Yuan dynasty begun by his father, was formally promulgated. Gegeen was assassinated in a coup involving five princes from a rival faction, perhaps steppe elite opposed to Confucian reforms. They placed Yesün Temür (or Taidingdi) on the throne, and, after an unsuccessful attempt to calm the princes, he also succumbed to regicide.
Before Yesün Temür's reign, China had been relatively free from popular rebellions after the reign of Kublai. Yuan control, however, began to break down in those regions inhabited by ethnic minorities. The occurrence of these revolts and the subsequent suppression aggravated the financial difficulties of the Yuan government. The government had to adopt some measure to increase revenue, such as selling offices, as well as curtailing its spending on some items.[99]
Jayaatu Khan Tugh Temür

When Yesün Temür died in Shangdu in 1328, Tugh Temür was recalled to Khanbaliq by the Qipchaq commander El Temür. He was installed as the emperor (Emperor Wenzong) in Khanbaliq, while Yesün Temür's son Ragibagh succeeded to the throne in Shangdu with the support of Yesün Temür's favorite retainer Dawlat Shah. Gaining support from princes and officers in Northern China and some other parts of the dynasty, Khanbaliq-based Tugh Temür eventually won the civil war against Ragibagh known as the War of the Two Capitals. Afterwards, Tugh Temür abdicated in favour of his brother Kusala, who was backed by Chagatai Khan Eljigidey, and announced Khanbaliq's intent to welcome him. However, Kusala suddenly died only four days after a banquet with Tugh Temür. He was supposedly killed with poison by El Temür, and Tugh Temür then remounted the throne. Tugh Temür also managed to send delegates to the western Mongol khanates such as Golden Horde and Ilkhanate to be accepted as the suzerain of Mongol world.[100] However, he was mainly a puppet of the powerful official El Temür during his latter three-year reign. El Temür purged pro-Kusala officials and brought power to warlords, whose despotic rule clearly marked the decline of the dynasty.
Due to the fact that the bureaucracy was dominated by El Temür, Tugh Temür is known for his cultural contribution instead. He adopted many measures honoring Confucianism and promoting Chinese cultural values. His most concrete effort to patronize Chinese learning was founding the Academy of the Pavilion of the Star of Literature (奎章閣學士院), first established in the spring of 1329 and designed to undertake "a number of tasks relating to the transmission of Confucian high culture to the Mongolian imperial establishment". The academy was responsible for compiling and publishing a number of books, but its most important achievement was its compilation of a vast institutional compendium named Jingshi Dadian (《經世大典》). Tugh Temür supported Zhu Xi's Neo-Confucianism and also devoted himself in Buddhism.
Toghon Temür
After the death of Tugh Temür in 1332 and subsequent death of Rinchinbal (Emperor Ningzong) the same year, the 13-year-old Toghon Temür (Emperor Huizong), the last of the nine successors of Kublai Khan, was summoned back from Guangxi and succeeded to the throne. After El Temür's death, Bayan became as powerful an official as El Temür had been in the beginning of his long reign. As Toghon Temür grew, he came to disapprove of Bayan's autocratic rule. In 1340 he allied himself with Bayan's nephew Toqto'a, who was in discord with Bayan, and banished Bayan by coup. With the dismissal of Bayan, Toqto'a seized the power of the court. His first administration clearly exhibited fresh new spirit. He also gave a few early signs of a new and positive direction in central government. One of his successful projects was to finish the long-stalled official histories of the Liao, Jin, and Song dynasties, which were eventually completed in 1345. Yet, Toqto'a resigned his office with the approval of Toghon Temür, marking the end of his first administration, and he was not called back until 1349.
Decline of the empire

The final years of the Yuan dynasty were marked by struggle, famine, and bitterness among the populace. In time, Kublai Khan's successors lost all influence on other Mongol lands across Asia, while the Mongols beyond the Middle Kingdom saw them as too Chinese. Gradually, they lost influence in China as well. The reigns of the later Yuan emperors were short and marked by intrigues and rivalries. Uninterested in administration, they were separated from both the army and the populace, and China was torn by dissension and unrest. Outlaws ravaged the country without interference from the weakening Yuan armies.
From the late 1340s onwards, people in the countryside suffered from frequent natural disasters such as droughts, floods and the resulting famines, and the government's lack of effective policy led to a loss of popular support. In 1351, the Red Turban Rebellion led by Song loyalists started and grew into a nationwide uprising and the Song loyalists established a renewed Song dynasty in 1351 with its capital at Kaifeng. In 1354, when Toghtogha led a large army to crush the Red Turban rebels, Toghon Temür suddenly dismissed him for fear of betrayal. This resulted in Toghon Temür's restoration of power on the one hand and a rapid weakening of the central government on the other. He had no choice but to rely on local warlords' military power, and gradually lost his interest in politics and ceased to intervene in political struggles. He fled north to Shangdu from Khanbaliq (present-day Beijing) in 1368 after the approach of the forces of the Míng dynasty (1368–1644), founded by Zhu Yuanzhang in the south. Zhu Yuanzhang was a former Duke and commander in the army of the Red Turban Song dynasty and assumed power as Emperor after the death of the Red Turban Song Emperor Han Lin'er, who had tried to regain Khanbaliq, which eventually failed, and who died in Yingchang (located in present-day Inner Mongolia) two years later (1370). Yingchang was seized by the Ming shortly after his death. Some royal family members still live in Henan today.[101]
The Prince of Liang, Basalawarmi established a separate pocket of resistance to the Ming in Yunnan and Guizhou, but his forces were decisively defeated by the Ming in 1381. By 1387 the remaining Yuan forces in Manchuria under Naghachu had also surrendered to the Ming dynasty. The Yuan remnants retreated to Mongolia after the fall of Yingchang to the Ming in 1370, where the name Great Yuan (大元) was formally carried on, and is known as the Northern Yuan dynasty.[9]
Impact
A rich cultural diversity developed during the Yuan dynasty. The major cultural achievements were the development of drama and the novel and the increased use of the written vernacular. The political unity of China and much of central Asia promoted trade between East and West. The Mongols' extensive West Asian and European contacts produced a fair amount of cultural exchange. The other cultures and peoples in the Mongol World Empire also very much influenced China. It had significantly eased trade and commerce across Asia until its decline; the communications between Yuan dynasty and its ally and subordinate in Persia, the Ilkhanate, encouraged this development.[102][103] Buddhism had a great influence in the Yuan government, and the Tibetan-rite Tantric Buddhism had significantly influenced China during this period. The Muslims of the Yuan dynasty introduced Middle Eastern cartography, astronomy, medicine, clothing, and diet in East Asia. Eastern crops such as carrots, turnips, new varieties of lemons, eggplants, and melons, high-quality granulated sugar, and cotton were all either introduced or successfully popularized during the Yuan dynasty.[104]
Western musical instruments were introduced to enrich Chinese performing arts. From this period dates the conversion to Islam, by Muslims of Central Asia, of growing numbers of Chinese in the northwest and southwest. Nestorianism and Roman Catholicism also enjoyed a period of toleration. Buddhism (especially Tibetan Buddhism) flourished, although Taoism endured certain persecutions in favor of Buddhism from the Yuan government. Confucian governmental practices and examinations based on the Classics, which had fallen into disuse in north China during the period of disunity, were reinstated by the Yuan court, probably in the hope of maintaining order over Han society. Advances were realized in the fields of travel literature, cartography, geography, and scientific education.

Certain Chinese innovations and products, such as purified saltpetre, printing techniques, porcelain, playing cards, and medical literature, were exported to Europe and Western Asia, while the production of thin glass and cloisonné became popular in China. The Yuan exercised a profound influence on the Chinese Ming dynasty. The Ming Emperor Zhu Yuanzhang (1368–97) admired the Mongols' unification of China and adopted its garrison system.[104]
Aside from the ancient Roman embassies, the first recorded travels by Europeans to China and back date from this time. The most famous traveler of the period was the Venetian Marco Polo, whose account of his trip to "Cambaluc," the capital of the Great Khan, and of life there astounded the people of Europe. The account of his travels, Il milione (or, The Million, known in English as the Travels of Marco Polo), appeared about the year 1299. Some doubted the accuracy of Marco Polo's accounts due to the lack of mentioning the Great Wall of China, tea houses, which would have been a prominent sight since Europeans had yet to adopt a tea culture, as well the practice of foot binding by the women in capital of the Great Khan. Recent studies however show that Polo's account is largely accurate and unique.[106][107]
The Yuan undertook extensive public works. Among Kublai Khan's top engineers and scientists was the astronomer Guo Shoujing, who was tasked with many public works projects and helped the Yuan reform the lunisolar calendar to provide an accuracy of 365.2425 days of the year,[108] which was only 26 seconds off the modern Gregorian calendar's measurement. Road and water communications were reorganized and improved. To provide against possible famines, granaries were ordered built throughout the empire. The city of Beijing was rebuilt with new palace grounds that included artificial lakes, hills and mountains, and parks. During the Yuan period, Beijing became the terminus of the Grand Canal of China, which was completely renovated. These commercially oriented improvements encouraged overland and maritime commerce throughout Asia and facilitated direct Chinese contacts with Europe. Chinese travelers to the West were able to provide assistance in such areas as hydraulic engineering. Contacts with the West also brought the introduction to China of a major food crop, sorghum, along with other foreign food products and methods of preparation.
The Yuan dynasty was the first time that non-native Chinese people ruled all of China. In the historiography of Mongolia, it is generally considered to be the continuation of the Mongol Empire. Mongols are widely known to worship the Eternal Heaven, and according to the traditional Mongolian ideology Yuan is considered to be "the beginning of an infinite number of beings, the foundation of peace and happiness, state power, the dream of many peoples, besides it there is nothing great or precious."[109] In traditional historiography of China, on the other hand, the Yuan dynasty is usually considered to be the legitimate dynasty between the Song dynasty and the Ming dynasty. Note, however, Yuan dynasty is traditionally often extended to cover the Mongol Empire before Kublai Khan's formal establishment of the Yuan in 1271, partly because Kublai had his grandfather Genghis Khan placed on the official record as the founder of the dynasty or Taizu (Chinese: 太祖). Despite the traditional historiography as well as the official views (including the government of the Ming dynasty which overthrew the Yuan dynasty), there also exist Chinese people who did not consider the Yuan dynasty as a legitimate dynasty of China, but rather as a period of foreign domination. The latter believe that Hans were treated as second-class citizens, and that China stagnated economically and scientifically.
The dynasty chose white as its imperial color, which corresponds to the Metal element according to the theory of the Five Elements (wuxing). Note that the Metal element does not follow from the Song's dynastic element Five in the creation sequence of the five elements. Instead, it follows from the Jin Dynast's dynastic element Earth. Although the Yuan did not openly announce it, its choice of white as its imperial color suggests that it considered Jin, another conquest dynasty, rather than the Han-Chinese Song dynasty, as its rightful predecessor.[110]
The dragon clothing of Imperial China was used by the Ilkhanids, the Chinese Huangdi (Emperor) title was used by the Ilkhanids due to heavy clout upon the Mongols of the Chinese system of politics. Seals with Chinese characters were created by the Ilkhanids themselves besides the seals they received from the Yuan dynasty which contain references to a Chinese government organization.[111]
Government

The structure of the Yuan government took shape during the reign of Kublai Khan (1260–1294). While some changes took place such as the functions of certain institutions, the essential components of the government bureaucracy remained intact from the beginning to the end of the dynasty in 1368.
The system of bureaucracy created by Kublai Khan reflected various cultures in the empire, including that of the Hans, Khitans, Jurchens, Mongols, and Tibetan Buddhists. While the official terminology of the institutions may indicate the government structure was almost purely that of native Chinese dynasties, the Yuan bureaucracy actually consisted of a mix of elements from different cultures. The Chinese-style elements of the bureaucracy mainly came from the native Tang, Song, as well as Khitan Liao and Jurchen Jin dynasties. Chinese advisers such as Liu Bingzhong and Yao Shu gave strong influence to Kublai's early court, and the central government administration was established within the first decade of Kublai's reign. This government adopted the traditional Chinese tripartite division of authority among civil, military, and censorial offices, including the Central Secretariat (Zhongshu Sheng) to manage civil affairs, the Privy Council (樞密院; Shūmì Yuàn) to manage military affairs, and the Censorate to conduct internal surveillance and inspection. The actual functions of both central and local government institutions, however, showed a major overlap between the civil and military jurisdictions, due to the Mongol traditional reliance on military institutions and offices as the core of governance. Nevertheless, such a civilian bureaucracy, with the Central Secretariat as the top institution that was (directly or indirectly) responsible for most other governmental agencies (such as the traditional Chinese-style Six Ministries), was created in China. At various times another central government institution called the Department of State Affairs (Shangshu Sheng) that mainly dealt with finance was established (such as during the reign of Külüg Khan or Emperor Wuzong), but was usually abandoned shortly afterwards.
While the existence of these central government departments and the Six Ministries (which had been introduced since the Sui and Tang dynasties) gave a Sinicized image in the Yuan administration, the actual functions of these ministries also reflected how Mongolian priorities and policies reshaped and redirected those institutions. For example, the authority of the Yuan legal system, the Ministry of Justice, did not extend to legal cases involving Mongols and Semuren, who had separate courts of justice. Cases involving members of more than one ethnic group were decided by a mixed board consisting of Chinese and Mongols. Another example was the insignificance of the Ministry of War compared with native Chinese dynasties, as the real military authority in Yuan times resided in the Privy Council.
The Kingdom of Qocho, Kingdom of Dali, Chiefdom of Bozhou, other Tusi kingdoms and Goryeo were ruled by kings inside the Yuan empire.
Science and technology
Mathematics
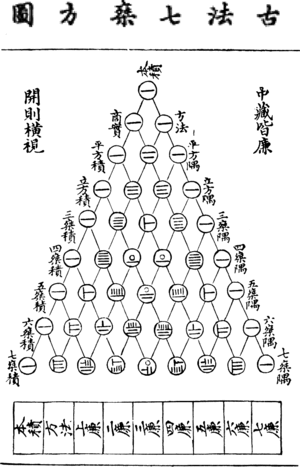
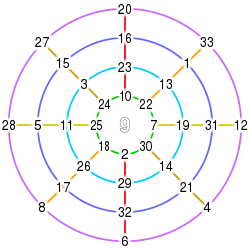
Advances in polynomial algebra were made by mathematicians during the Yuan era. The mathematician Zhu Shijie (1249–1314) solved simultaneous equations with up to four unknowns using a rectangular array of coefficients, equivalent to modern matrices.[112][113] Zhu used a method of elimination to reduce the simultaneous equations to a single equation with only one unknown.[114] His method is described in the Jade Mirror of the Four Unknowns, written in 1303. The opening pages contain a diagram of Pascal's triangle. The summation of a finite arithmetic series is also covered in the book.[115]
Guo Shoujing applied mathematics to the construction of calendars. He was one of the first mathematicians in China to work on spherical trigonometry.[116] Gou derived a cubic interpolation formula for his astronomical calculations.[117] His calendar, the Shoushi Li (《授時暦》; Time Granting Calendar), was disseminated in 1281 as the official calendar of the Yuan dynasty.[118] The calendar may have been influenced solely by the work of Song dynasty astronomer Shen Kuo or possibly by the work of Arab astronomers.[116] There are no explicit signs of Muslim influences in the Shoushi calendar, but Mongol rulers were known to be interested in Muslim calendars.[118] Mathematical knowledge from the Middle East was introduced to China under the Mongols, and Muslim astronomers brought Arabic numerals to China in the 13th century.[116]
Medicine
The physicians of the Yuan court came from diverse cultures.[119] Healers were divided into non-Mongol physicians called otachi and traditional Mongol shamans. The Mongols characterized otachi doctors by their use of herbal remedies, which was distinguished from the spiritual cures of Mongol shamanism.[119] Physicians received official support from the Yuan government and were given special legal privileges. Kublai created the Imperial Academy of Medicine to manage medical treatises and the education of new doctors.[120] Confucian scholars were attracted to the medical profession because it ensured a high income and medical ethics were compatible with Confucian virtues.[121][120]
The Chinese medical tradition of the Yuan had "Four Great Schools" that the Yuan inherited from the Jin dynasty. All four schools were based on the same intellectual foundation, but advocated different theoretical approaches toward medicine.[121] Under the Mongols, the practice of Chinese medicine spread to other parts of the empire. Chinese physicians were brought along military campaigns by the Mongols as they expanded towards the west. Chinese medical techniques such as acupuncture, moxibustion, pulse diagnosis, and various herbal drugs and elixirs were transmitted westward to the Middle East and the rest of the empire.[122] Several medical advances were made in the Yuan period. The physician Wei Yilin (1277–1347) invented a suspension method for reducing dislocated joints, which he performed using anesthetics.[123] The Mongol physician Hu Sihui described the importance of a healthy diet in a 1330 medical treatise.[123]
Western medicine was also practiced in China by the Nestorian Christians of the Yuan court, where it was sometimes labeled as huihui or Muslim medicine.[124] The Nestorian physician Jesus the Interpreter founded the Office of Western Medicine in 1263 during the reign of Kublai.[125] Huihui doctors staffed at two imperial hospitals were responsible for treating the imperial family and members of the court.[120] Chinese physicians opposed Western medicine because its humoral system contradicted the yin-yang and wuxing philosophy underlying traditional Chinese medicine.[121] No Chinese translation of Western medical works is known, but it is possible that the Chinese had access to Avicenna's The Canon of Medicine.[124]
Printing and publishing

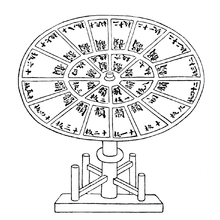
The Mongol rulers patronized the Yuan printing industry.[126][127] Chinese printing technology was transferred to the Mongols through Kingdom of Qocho and Tibetan intermediaries.[126] Some Yuan documents such as Wang Zhen's Nong Shu were printed with earthenware movable type, a technology invented in the 12th century. However, most published works were still produced through traditional block printing techniques.[128] The publication of a Taoist text inscribed with the name of Töregene Khatun, Ögedei's wife, is one of the first printed works sponsored by the Mongols. In 1273, the Mongols created the Imperial Library Directorate, a government-sponsored printing office.[126] The Yuan government established centers for printing throughout China.[126] Local schools and government agencies were funded to support the publishing of books.[129]
Private printing businesses also flourished under the Yuan. They published a diverse range of works, and printed educational, literary, medical, religious, and historical texts. The volume of printed materials was vast.[130] In 1312, 1,000 copies of a Buddhist text commented by Cosgi Odsir were printed just within Beijing.[131] By 1328, annual sales of printed calendars and almanacs reached over three million in the Yuan dynasty.[132]
One of the more notable applications of printing technology was the Jiaochao, the paper money of the Yuan. Jiaochao were made from the bark of mulberry trees.[131] The Yuan government used woodblocks to print paper money, but switched to bronze plates in 1275.[133] The Mongols experimented with establishing the Chinese-style paper monetary system in Mongol-controlled territories outside of China. The Yuan minister Bolad was sent to Iran, where he explained Yuan paper money to the Il-khanate court of Gaykhatu.[134] The Il-khanate government issued paper money in 1294, but public distrust of the exotic new currency doomed the experiment.[135]
Foreign observers took note of Yuan printing technology. Marco Polo documented the Yuan printing of paper money and almanac pamphlets called tacuini.[131] The vizier Rashid-al-Din recognized that printing was a valuable technological breakthrough, and expressed regret that the Mongol experiment with printing paper money had failed in the Muslim world. Rashid-al-Din's view was not shared by other chroniclers in the Middle East, who were critical of the experiment's disruptive impact on the Il-khanate.[132]
Ceramics

In Chinese ceramics the period was one of expansion, with the great innovation the development in Jingdezhen ware of underglaze painted blue and white pottery. This seems to have begun in the early decades of the 14th century, and by the end of the dynasty was mature and well-established. Other major types of wares continued without a sharp break in their development, but there was a general trend to some larger size pieces, and more decoration. This is often seen as a decline from Song refinement. Exports expanded considerably, especially to the Islamic world.
Society
Imperial lifestyle
Since its invention in 1269, the 'Phags-pa script, a unified script for spelling Mongolian, Tibetan, and Chinese languages, was preserved in the court until the end of the dynasty. Most of the Emperors could not master written Chinese, but they could generally converse well in the language. The Mongol custom of long standing quda/marriage alliance with Mongol clans, the Onggirat, and the Ikeres, kept the imperial blood purely Mongol until the reign of Tugh Temur (Emperor Wenzong), whose mother was a Tangut concubine. The Mongol Emperors had built large palaces and pavilions, but some still continued to live as nomads at times. Tugh Temür was an example of a Yuan emperor who actively sponsored cultural activities; including in his imperial capacity and in his personal activities such as writing poetry, painting, reading Chinese classical texts, and ordering the compilation of books.[136]
The average Mongol garrison family of the Yuan dynasty seems to have lived a life of decaying rural leisure, with income from the harvests of their Chinese tenants eaten up by costs of equipping and dispatching men for their tours of duty. The Mongols practiced debt slavery, and by 1290 in all parts of the Mongol Empire commoners were selling their children into slavery. Seeing this as damaging to the Mongol nation, Kublai in 1291 forbade the sale abroad of Mongols. Kublai wished to persuade the Chinese that he was becoming increasingly sinicized while maintaining his Mongolian credentials with his own people. He set up a civilian administration to rule, built a capital within China, supported Chinese religions and culture, and devised suitable economic and political institutions for the court. But at the same time he never abandoned his Mongolian heritage.[137]
Culture

In the China of the Yuan, or Mongol era, various important developments in the arts occurred or continued in their development, including the areas of painting, mathematics, calligraphy, poetry, and theater, with many great artists and writers being famous today. Due to the coming together of painting, poetry, and calligraphy at this time many of the artists practicing these different pursuits were the same individuals, though perhaps more famed for one area of their achievements than others. Often in terms of the further development of landscape painting as well as the classical joining together of the arts of painting, poetry, and calligraphy, the Song dynasty and the Yuan dynasty are linked together.
In Chinese painting during the Yuan dynasty there were many famous painters. In the area of calligraphy many of the great calligraphers were from the Yuan dynasty era. In Yuan poetry, the main development was the qu, which was used among other poetic forms by most of the famous Yuan poets. Many of the poets were also involved in the major developments in the theater during this time, and the other way around, with people important in the theater becoming famous through the development of the sanqu type of qu. One of the key factors in the mix of the zaju variety show was the incorporation of poetry both classical and of the newer qu form. One of the important cultural developments during the Yuan era was the consolidation of poetry, painting, and calligraphy into a unified piece of the type that tends to come to mind when people think of classical Chinese art. Another important aspect of Yuan times is the increasing incorporation of the then current, vernacular Chinese into both the qu form of poetry and the zaju variety show. Another important consideration regarding Yuan dynasty arts and culture is that so much of it has survived in China, relatively to works from the Tang dynasty and Song dynasty, which have often been better preserved in places such as the Shōsōin, in Japan.
Religion

There were many religions practiced during the Yuan dynasty, such as Buddhism, Islam, Christianity and Manichaeism. The establishment of the Yuan dynasty had dramatically increased the number of Muslims in China. However, unlike the western khanates, the Yuan dynasty never converted to Islam. Instead, Kublai Khan, the founder of the Yuan dynasty, favored Buddhism, especially the Tibetan variants. As a result, Tibetan Buddhism was established as the de facto state religion. The top-level department and government agency known as the Bureau of Buddhist and Tibetan Affairs (Xuanzheng Yuan) was set up in Khanbaliq (modern Beijing) to supervise Buddhist monks throughout the empire. Since Kublai Khan only esteemed the Sakya sect of Tibetan Buddhism, other religions became less important. He and his successors kept a Sakya Imperial Preceptor (Dishi) at court. Before the end of the Yuan dynasty, 14 leaders of the Sakya sect had held the post of Imperial Preceptor, thereby enjoying special power.[138] Furthermore, Mongol patronage of Buddhism resulted in a number of monuments of Buddhist art. Mongolian Buddhist translations, almost all from Tibetan originals, began on a large scale after 1300. Many Mongols of the upper class such as the Jalayir and the Oronar nobles as well as the emperors also patronized Confucian scholars and institutions. A considerable number of Confucian and Chinese historical works were translated into the Mongolian language.
At the same time the Mongols imported Central Asian Muslims to serve as administrators in China, the Mongols also sent Hans and Khitans from China to serve as administrators over the Muslim population in Bukhara in Central Asia, using foreigners to curtail the power of the local peoples of both lands.[139]
Genghis Khan and the following Yuan emperors forbade Islamic practices like Halal butchering, forcing Mongol methods of butchering animals on Muslims, and other restrictive degrees continued. Muslims had to slaughter sheep in secret.[140] Genghis Khan directly called Muslims and Jews "slaves" and demanded that they follow the Mongol method of eating rather than the halal method. Circumcision was also forbidden. Jews were also affected and forbidden by the Mongols to eat Kosher.[141]
Among all the [subject] alien peoples only the Hui-hui say “we do not eat Mongol food”. [Cinggis Qa’an replied:] “By the aid of heaven we have pacified you; you are our slaves. Yet you do not eat our food or drink. How can this be right?” He thereupon made them eat. “If you slaughter sheep, you will be considered guilty of a crime.” He issued a regulation to that effect ... [In 1279/1280 under Qubilai] all the Muslims say: “if someone else slaughters [the animal] we do not eat”. Because the poor people are upset by this, from now on, Musuluman [Muslim] Huihui and Zhuhu [Jewish] Huihui, no matter who kills [the animal] will eat [it] and must cease slaughtering sheep themselves, and cease the rite of circumcision.[142]
The Muslims in the semu class revolted against the Yuan dynasty in the Ispah Rebellion, but the rebellion was crushed and the Muslims were massacred by the Yuan loyalist commander Chen Youding. Some Muslim communities had the name in Chinese meaning "barracks" and also meaning "thanks"; many Hui Muslims claim it is because that they played an important role in overthrowing the Mongols and it was named in thanks by the Hans for assisting them.[143]
During the Ming conquest of Yunnan, Muslim generals Mu Ying and Lan Yu led Muslim troops loyal to the Ming dynasty against Mongol and Muslim troops loyal to the Yuan dynasty.[144][145]
Hindu statues were found in Quanzhou dating to the Yuan period.[146]
Social classes
Politically, the system of government created by Kublai Khan was the product of a compromise between Mongolian patrimonial feudalism and the traditional Chinese autocratic-bureaucratic system. Nevertheless, socially the educated Chinese elite were in general not given the degree of esteem that they had been accorded previously under native Chinese dynasties. Although the traditional Chinese elite were not given their share of power, the Mongols and the Semu people (various allied groups from Central Asia and the western end of the empire) largely remained strangers to the mainstream Chinese culture, and this dichotomy gave the Yuan regime a somewhat strong "colonial" coloration.[147] The unequal treatment is possibly due to the fear of transferring power to the ethnic Chinese under their rule. The Mongols and Semuren were given certain advantages in the dynasty, and this would last even after the restoration of the imperial examination in the early 14th century. In general there were very few North Chinese or Southerners reaching the highest-post in the government compared with the possibility that Persians did so in the Ilkhanate.[148] Later the Yongle Emperor of the Ming dynasty also mentioned the discrimination that existed during the Yuan dynasty. In response to an objection against the use of "barbarians" in his government, the Yongle Emperor answered: "... Discrimination was used by the Mongols during the Yuan dynasty, who employed only "Mongols and Tartars" and discarded northern and southern Chinese and this was precisely the cause that brought disaster upon them".[149]

The Mongols had employed foreigners long before the reign of Kublai Khan, the founder of the Yuan dynasty. But during Kublai's reign a hierarchy of reliability was introduced in China. The population was divided into the following classes:
- Mongols. The Mongols were called "Gao-chen" (the citizens of the ruling empire) by the conquered Southern Song population[150]
- Semu, consisting of non-Mongol foreigners from the west and Central Asia, like Buddhist Uyghurs from Turfan, Tanguts, Tibetans, Jews, Nestorian Christians, and Muslims from Central Asia
- "Han", or all subjects of the former Jin dynasty, including Hans, Khitans, Jurchens in northern China, and other peoples like Koreans[151][152][153][154][155][156][157][158]
- Southerners, or all subjects of the former Southern Song dynasty, including Hans and minority native ethnic groups in southern China, sometimes called "Manzi" during the Yuan
Partner merchants and non-Mongol overseers were usually either immigrants or local ethnic groups. Thus, in China they were Uighur Buddhists, Turkestani and Persian Muslims, and Christians. Foreigners from outside the Mongol Empire entirely, such as the Polo family, were everywhere welcomed.
At the same time the Mongols imported Central Asian Muslims to serve as administrators in China, the Mongols also sent Hans and Khitans from China to serve as administrators over the Muslim population in Bukhara in Central Asia, using foreigners to curtail the power of the local peoples of both lands.[139] Hans were moved to Central Asian areas like Besh Baliq, Almaliq, and Samarqand by the Mongols where they worked as artisans and farmers.[159] Alans were recruited into the Mongol forces with one unit called "Right Alan Guard" which was combined with "recently surrendered" soldiers, Mongols, and Chinese soldiers stationed in the area of the former Kingdom of Qocho and in Besh Balikh the Mongols established a Chinese military colony led by Chinese general Qi Kongzhi (Ch'i Kung-chih).[160] After the Mongol conquest of Central Asia by Genghis Khan, foreigners were chosen as administrators and co-management with Chinese and Qara-Khitays (Khitans) of gardens and fields in Samarqand was put upon the Muslims as a requirement since Muslims were not allowed to manage without them.[161][162] The Yuan-appointed Governor of Samarqand was a Khitan from the Qara Khitai, held the title Taishi, familiar with Chinese culture his name was Ahai.[163]
Han officials and colonists were sent by the Yuan dynasty to areas of Lingbei province including Henning Circuit, Yilan Prefecture, and Qian Prefecture.[164]
Despite the high position given to Muslims, some policies of the Yuan emperors severely discriminated against them, restricting Halal slaughter and other Islamic practices like circumcision, as well as Kosher butchering for Jews, forcing them to eat food the Mongol way.[165] Toward the end, corruption and the persecution became so severe that Muslim generals joined Hans in rebelling against the Mongols. The Ming founder Zhu Yuanzhang had Muslim generals like Lan Yu who rebelled against the Mongols and defeated them in combat. Some Muslim communities had a Chinese surname which meant "barracks" and could also mean "thanks". Many Hui Muslims claim this is because that they played an important role in overthrowing the Mongols and it was given in thanks by the Hans for assisting them.[166] During the war fighting the Mongols, among the Ming Emperor Zhu Yuanzhang's armies was the Hui Muslim Feng Sheng.[167] The Muslims in the semu class also revolted against the Yuan dynasty in the Ispah Rebellion but the rebellion was crushed and the Muslims were massacred by the Yuan loyalist commander Chen Youding.
The historian Frederick W. Mote wrote that the usage of the term "social classes" for this system was misleading and that the position of people within the four-class system was not an indication of their actual social power and wealth, but just entailed "degrees of privilege" to which they were entitled institutionally and legally, so a person's standing within the classes was not a guarantee of their standing, since there were rich and well socially standing Chinese while there were less rich Mongol and Semu than there were Mongol and Semu who lived in poverty and were ill-treated.[168]
The reason for the order of the classes and the reason why people were placed in a certain class was the date they surrendered to the Mongols, and had nothing to do with their ethnicity. The earlier they surrendered to the Mongols, the higher they were placed, the more they held out, the lower they were ranked. The Northern Chinese were ranked higher and Southern Chinese were ranked lower because southern China withstood and fought to the last before caving in.[169][170] Major commerce during this era gave rise to favorable conditions for private southern Chinese manufacturers and merchants.[171]
When the Mongols placed the Uighurs of the Kingdom of Qocho over the Koreans at the court the Korean King objected, then the Mongol Emperor Kublai Khan rebuked the Korean King, saying that the Uighur King of Qocho was ranked higher than the Karluk Kara-Khanid ruler, who in turn was ranked higher than the Korean King, who was ranked last, because the Uighurs surrendered to the Mongols first, the Karluks surrendered after the Uighurs, and the Koreans surrendered last, and that the Uighurs surrendered peacefully without violently resisting.[172][173]
Japanese historians like Uematsu, Sugiyama and Morita criticized the perception that a four-class system existed under Mongol rule and Funada Yoshiyuki questioned the very existence of the Semu as a class.[174]
Nobility
Many Tusi chiefdoms and kingdoms in southwestern China which existed before the Mongol invasions were allowed to retain their integrity as vassals of the Yuan dynasty after surrendering, including the Kingdom of Dali, the Han Chinese Yang family ruling the Chiefdom of Bozhou with its seat at the castle Hailongtun, Chiefdom of Lijiang, Chiefdom of Shuidong, Chiefdom of Sizhou, Chiefdom of Yao'an, Chiefdom of Yongning and Mu'ege. As were Korea under Mongol rule and the Kingdom of Qocho.
The Han Chinese nobles Duke Yansheng and Celestial Masters continued possessing their titles in the Yuan dynasty since the previous dynasties.
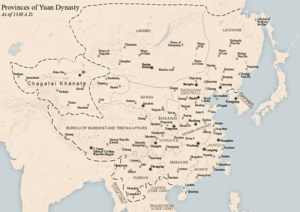
Administrative divisions
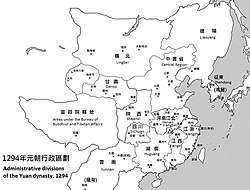
The territory of the Yuan dynasty was divided into the Central Region (腹裏) governed by the Central Secretariat and places under control of various provinces (行省) or Branch Secretariats (行中書省), as well as the region under the Bureau of Buddhist and Tibetan Affairs.
The Central Region, consisting of present-day Hebei, Shandong, Shanxi, the south-eastern part of present-day Inner Mongolia and the Henan areas to the north of the Yellow River, was considered the most important region of the dynasty and directly governed by the Central Secretariat (or Zhongshu Sheng) at Khanbaliq (modern Beijing); similarly, another top-level administrative department called the Bureau of Buddhist and Tibetan Affairs (or Xuanzheng Yuan) held administrative rule over the whole of modern-day Tibet and a part of Sichuan, Qinghai and Kashmir.
Branch Secretariats or simply provinces, were provincial-level administrative organizations or institutions, though they were not exactly provinces in modern sense. There were 11 "regular" provinces in Yuan dynasty,[175] and their administrations were subordinated to the Central Secretariat.
Below the level of provinces, the largest political division was the circuit (道), followed by lù (路), fǔ (府) and zhōu (州). These are three kinds of prefecture-like divisions. The lowest political division was the county (縣).
Basically, lù is higher than fǔ, and fǔ is higher than zhōu. However, the actual relationship between them could be very complicated. Both lù, fǔ and zhōu could administer counties. Some fǔ and zhōu are directly administered by the province, while some exist inside a lù. A lù usually administers several counties, along with several fǔ and zhōu, and the fǔ or zhōu themselves could also administer their own counties. As a result, it is impossible to exactly define how many tiers of divisions there are under a province.
This government structure at the provincial level was later inherited and modified by the Ming and Qing dynasties.
Gallery
 Magic square in Arabic numerals (Yuan dynasty)
Magic square in Arabic numerals (Yuan dynasty) smelting machines (Yuan dynasty)
smelting machines (Yuan dynasty) Water wheel (Yuan dynasty)
Water wheel (Yuan dynasty) Water hammer (Yuan dynasty)
Water hammer (Yuan dynasty) Weaving machine (Yuan dynasty)
Weaving machine (Yuan dynasty) water mill gear (Yuan dynasty)
water mill gear (Yuan dynasty) loom (Yuan dynasty)
loom (Yuan dynasty) Yuan painting (Zhao Mengfu)
Yuan painting (Zhao Mengfu) Chuangzi Nu (Yuan dynasty)[176]
Chuangzi Nu (Yuan dynasty)[176] Military costume.
Military costume. Yuan painting of a legendary figure riding on a dragon.
Yuan painting of a legendary figure riding on a dragon. Yuan cavalry
Yuan cavalry- Yuan Mongol soldier
- Genghis Khan's grandson, Kublai Khan during his youth
 Mongol warrior on horseback, preparing a mounted archery shot.
Mongol warrior on horseback, preparing a mounted archery shot.- Chinese stone inscription of a Nestorian Christian Cross from a monastery of Fangshan District in Beijing (then called Dadu, or Khanbaliq), dated to the Yuan Dynasty
See also
- List of emperors of the Yuan dynasty
- Emperor's family tree
- Mongol Empire
- Mughal Empire
- History of Mongolia
- History of China
- Administrative divisions of the Yuan dynasty
- Yuan dynasty in Inner Asia
- Tibet under Yuan rule
- Mongolia under Yuan rule
- Manchuria under Yuan rule
- Korea under Yuan rule
- Yuan dynasty coinage
- Islam during the Yuan dynasty
- Europeans in Medieval China
- Hua-Yi distinction
- Jun ware
- List of largest empires
Notes
- The situation of Goryeo during Yuan dynasty was disputed. Some scholars (such as Tan Qixiang) regarded it as a country;[1] others regarded it as a part of Yuan.
- The situation of Goryeo during Yuan dynasty was disputed. Some scholars (such as Tan Qixiang) regarded it as a country;[2] others regarded it as a part of Yuan.
- Modern Mongolian form commonly used by modern Mongolian and Chinese academics: ᠶᠡᠬᠡ
ᠶᠤᠸᠠᠨ
ᠤᠯᠤᠰ, Yehe Yuan Ulus or Ikh Yuan Üls/Yekhe Yuan Ulus; Их Юань улс in Mongolian Cyrillic. - Before Kublai Khan announced the dynastic name "Great Yuan" in 1271, Khagans (Great Khans) of the Mongol Empire (Ikh Mongol Uls) already started to use the Chinese title of Emperor (Chinese: 皇帝; pinyin: Huángdì) practically in the Chinese language since Genghis Khan.
References
Citations
- Tan, Qixiang; et al. (1987). 《中国历史地图集》 [The Historical Atlas of China] (in Chinese). 7. SinoMaps Press. ISBN 9787503118449.
- Tan, Qixiang; et al. (1987). 《中国历史地图集》 [The Historical Atlas of China] (in Chinese). 7. SinoMaps Press. ISBN 9787503118449.
- Kublai Khan (18 December 1271), 《建國號詔》 [Edict to Establish the Name of the State], 《元典章》[Statutes of the Yuan] (in Chinese)
- Taagepera, Rein (September 1997). "Expansion and Contraction Patterns of Large Polities: Context for Russia". International Studies Quarterly. 41 (3): 499. doi:10.1111/0020-8833.00053. JSTOR 2600793.
- Song (宋), Yan (岩) (1994). 《中国历史上几个朝代的疆域面积估算》 [Estimation of Territory Areas of Several Dynasties in Chinese History] (in Chinese). Beijing: Chinese Academy of Social Sciences. p. 150.
- Simon, Karla W. Civil Society in China: The Legal Framework from Ancient Times to the 'New Reform Era'. Oxford University Press. p. 39 (note 69).
- Mote 1994, p. 624.
- Atwood, Christopher Pratt (2004). Encyclopedia of Mongolia and the Mongol Empire. Facts On File. ISBN 978-0-8160-4671-3.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- The History of China. Retrieved 4 March 2015.
- Franke, Herbert, Could the Mongol emperors read and write Chinese?
- Saunders, J. J. The History of Mongol Conquests.
- Grousset, René (1939). L'empire des steppes: Attila, Gengis-Khan, Tamerlan [The Empire of Steppes] (in French).
- . 《易傳》 [Commentaries on the Classic of Changes] (in Chinese).
《彖》曰:大哉乾元,萬物資始,乃統天。
- The Early Mongols: Language, Culture and History by Volker Rybatzki & Igor de Rachewiltz, p. 116.
- "Bolor Dictionary". www.bolor-toli.com. Retrieved 12 July 2020.
- Asian Nationalism, by Michael Leifer, Professor of International Relations Michael Leifer, p. 23.
- A Military History of Japan: From the Age of the Samurai to the 21st Century: From the Age of the Samurai to the 21st Century, John T. Kuehn Ph.D., p. 61.
- Voyages in World History, by Valerie Hansen, Ken Curtis, p. 53.
- The Military Engineer, Volume 40, p. 580.
- Focus On World History: The Era Of Expanding Global Connections - 1000-1500 C.E.: Grades 7-9, by Kathy Sammis, p. 46.
- Ebrey 2010, p. 169.
- Ebrey 2010, pp. 169–170.
- Rossabi 1994, p. 415.
- Allsen 1994, p. 392.
- Allsen 1994, p. 394.
- Rossabi 1994, p. 418.
- Rossabi 2012, p. 65.
- Collectif (1 January 2002). "Revue bibliographique de sinologie, n° 19/2001 - Collectif". Books.google.com. Retrieved 27 May 2016.
- ""萬戶路"、"千戶州" ——蒙古千戶百戶制度與華北路府州郡體制 - 新疆哲學社會科學". Big5.xjass.com. 27 February 2013. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 27 May 2016.
- "白话元史-刘伯林传(附刘黑马传)". Wenxue100.com. Retrieved 27 May 2016.
- ""万户路"、"千户州"——蒙古千户百户制度与华北路府州郡体制 - 中国人民大学清史研究所". Iqh.net.cn. 30 April 2013. Retrieved 27 May 2016.
- Timothy Michael May (14 January 2009). "The Mechanics of Conquest and Governance: The Rise and Expansion of the ..." Books.google.com. Retrieved 27 May 2016.
- "您的访问出错了。". 123.125.114.20. Retrieved 27 May 2016.
- "¹ú¼ÊÈåѧÈËÎïÐÅϢƽ̨". 121.199.12.114:99. 14 March 2012. Retrieved 27 May 2016.
- 【doc】-兼论金元之际的汉地七万户 - 豆丁网 (in Chinese). Docin.org. 26 October 2013. Retrieved 27 May 2016.
- Schram, Stuart Reynolds (1 January 1987). Foundations and Limits of State Power in China. ISBN 9780728601390. Retrieved 27 May 2016.
- Seaman, Gary; Marks, Daniel (2 September 2008). Rulers from the steppe: state formation on the Eurasian periphery. ISBN 9781878986016. Retrieved 27 May 2016.
- Hu (胡), Xiaopeng (小鹏). 窝阔台汗己丑年汉军万户萧札剌考辨——兼论金元之际的汉地七万户 [A Study of XIAO Zha-la the Han Army Commander of 10,000 Families in the Year of 1229 during the Period of Khan (O)gedei]. D.wanfangdata.com.cn (in Chinese). Retrieved 27 May 2016."国家哲学社会科学学术期刊数据库". Nssd.org. Retrieved 27 May 2016.
-

Wikisource has original text related to this article: - Allsen 1994, p. 410.
- John Masson Smith, Jr. (1998). "Review: Nomads on Ponies vs. Slaves on Horses Reviewed Work: Mongols and Mamluks: The Mamluk-Īlkhānid War, 1260-1281 by Reuven Amitai-Preiss". Journal of the American Oriental Society. 118 (1): 54–62. JSTOR 606298.
- Allsen 1994, p. 411.
- Rossabi 1994, p. 422.
- Rossabi 1988, p. 51.
- Rossabi 1988, p. 53.
- Rossabi 1994, p. 423–424.
- Morgan 2007, p. 104.
- Rossabi 1988, p. 62.
- Allsen 1994, p. 413.
- Allsen 2001, p. 24.
- Rossabi 1988, p. 77.
- Morgan 2007, p. 105.
- Rossabi 1994, pp. 436–437.
- Rossabi 1994, p. 426.
- Rossabi 1988, p. 66.
- Rossabi 1994, p. 427.
- Rossabi 1988, pp. 70–71.
- Rossabi 2012, p. 70.
- Ebrey 2010, p. 172.
- Rossabi 1988, p. 132.
- Mote 1994, p. 616.
- Rossabi 1988, p. 136.
- Mote 1999, p. 460.
- Mote 1999, p. 458.
- Mote 1999, p. 616.
- Rossabi 1994, p. 458.
- David Miles; Andrew Scott (14 January 2005). Macroeconomics: Understanding the Wealth of Nations. John Wiley & Sons. p. 273. ISBN 978-0-470-01243-7.
- "CoinWeek Ancient Coin Series: Coinage of the Mongols". Mike Markowitz (CoinWeek). 22 May 2016. Retrieved 14 June 2017.
- Hartill, David (22 September 2005). Cast Chinese Coins. Trafford, United Kingdom. ISBN 1412054664
- Rossabi 2012, p. 72.
- Rossabi 2012, p. 74.
- Rossabi 2012, p. 62.
- Rossabi 1994, p. 463.
- Allsen 2001, p. 61.
- Rossabi 1994, p. 429.
- Rossabi 2012, p. 77.
- Morgan 2007, p. 107.
- Anderson, James A.; Whitmore, John K. (2014). China's Encounters on the South and Southwest: Reforging the Fiery Frontier Over Two Millennia (reprint, revised ed.). BRILL. p. 146. ISBN 978-9004282483.
- Herman, John. E. (2005). Di Cosmo, Nicola; Wyatt, Don J (eds.). Political Frontiers, Ethnic Boundaries and Human Geographies in Chinese History (illustrated ed.). Routledge. p. 260. ISBN 978-1135790950.
- Crossley, Pamela Kyle; Siu, Helen F.; Sutton, Donald S., eds. (2006). Empire at the Margins: Culture, Ethnicity, and Frontier in Early Modern China. 28 of Studies on China (illustrated ed.). University of California Press. p. 143. ISBN 978-0520230156.
- Morgan 2007, p. 106.
- Rossabi 1994, p. 430.
- Hua, Kaiqi (2018). "Chapter 6 The Journey of Zhao Xian and the Exile of Royal Descendants in the Yuan Dynasty (1271 1358)". In Heirman, Ann; Meinert, Carmen; Anderl, Christoph (eds.). Buddhist Encounters and Identities Across East Asia. Leiden, Netherlands: BRILL. p. 213. doi:10.1163/9789004366152_008. ISBN 978-9004366152.
- Rossabi 2012, pp. 77–78.
- Morgan 2007, p. 113.
- Charles O. Hucker (1985). ä¸ĺ ˝ĺ ¤äťŁĺŽ ĺ čž ĺ ¸. p. 66. ISBN 9780804711937. Retrieved 27 May 2016.
- Rossabi 1994, p. 473.
- Rossabi 2012, p. 111.
- Rossabi 2012, p. 113.
- Rossabi 1988, p. 218.
- Rossabi 1988, pp. 218–219.
- Rossabi 1988, pp. 487–488.
- Rossabi 1994, p. 488.
- Stone, Zofia (2017). Genghis Khan : a Biography. New Delhi: Vij Books India Private Limited. ISBN 9789386367112. OCLC 975222159.
- Craughwell, Thomas J. (2010). The rise and fall of the second largest empire in history : how Genghis Khan's Mongols almost conquered the world. Beverly, MA: Fair Winds Press. p. 251. ISBN 9781616738518. OCLC 777020257.
- Howard, Michael C. (2012). Transnationalism in ancient and medieval societies : the role of cross-border trade and travel. Jefferson, NC: McFarland. p. 84. ISBN 9780786490332. OCLC 779849477.
- San, Tan Koon (2014). Dynastic China : an elementary history. Kuala Lumpur: The Other Press. p. 323. ISBN 9789839541885. OCLC 898313910.
- Powers, John; Templeman, David (2012). Historical dictionary of Tibet. Lanham, MD: Scarecrow Press. p. 742. ISBN 978-0810879843. OCLC 801440529.
- Hsiao 1994, p. 551.
- Hsiao 1994, p. 550.
- "成吉思汗直系后裔现身河南 巨幅家谱为证(组图)_新民网". News.xinmin.cn. 6 February 2007. Retrieved 27 May 2016.
- Guzman 1988, pp. 568-570.
- Allsen 2001, p. 211.
- C.P. Atwood - Encyclopedia of Mongolia and the Mongol Empire, p.611
- Birmingham Museum of Art (2010). Birmingham Museum of Art: A Guide to the Collection. London: Giles. p. 28. ISBN 978-1-904832-77-5. Archived from the original on 10 September 2011. Retrieved 1 July 2011.
- Hans Ulrich Vogel (21 November 2012). Marco Polo Was in China: New Evidence from Currencies, Salts and Revenues. BRILL. ISBN 978-9004231931.
- Haw, Stephen G. (2006), Marco Polo's China: a Venetian in the realm of Khubilai Khan, Volume 3 of Routledge studies in the early history of Asia, Psychology Press, pp. 52–57, ISBN 978-0-415-34850-8
- Marilyn Shea. "Guo Shoujing - 郭守敬 - Chinese Astronomy - 中国天文学". Hua.umf.maine.edu. Retrieved 27 May 2016.
- Ganbold et al., op. cit., 2006, p.20–21.
- Chen, Yuan Julian. ""Legitimation Discourse and the Theory of the Five Elements in Imperial China." Journal of Song-Yuan Studies 44 (2014): 325-364". Journal of Song-Yuan Studies.
- Ho, Kai-Lung (2008). "Central Asiatic Journal". Central Asiatic Journal. 52: 46.
- Joseph 2011, p. 196.
- Dauben 2007, p. 344.
- Dauben 2007, p. 346.
- Ho 1985, p. 101.
- Ho 1985, p. 105.
- Joseph 2011, p. 247.
- Allsen 2001, p. 172.
- Allsen 2001, p. 142.
- Rossabi 1988, p. 125.
- Allsen 2001, p. 157.
- Lane 2006, pp. 138–139.
- Lane 2006, p. 140.
- Allsen 2001, p. 151.
- Allsen 2001, p. 155.
- Allsen 2001, p. 182.
- Wu 1950, p. 460.
- Allsen 2001, pp. 176–177.
- Wu 1950, p. 463.
- Allsen 2001, p. 181.
- Allsen 2001, p. 183.
- Allsen 2001, p. 184.
- Allsen 2001, p. 179.
- Allsen 2001, p. 177.
- Allsen 2001, p. 178.
- Mote 1999, p. 471.
- The Cambridge History of China (Volume 6), by Denis C. Twitchett, Herbert Franke, John King Fairbank, p. 488-489
- History of civilizations of Central Asia: A.D. 750 to the end of the fifteenth century. Part two: The achievements, p. 59
- Buell, Paul D. (1979). "Sino-Khitan Administration in Mongol Bukhara". Journal of Asian History. 13 (2): 137–8. JSTOR 41930343.
- Michael Dillon (1999). China's Muslim Hui community: migration, settlement and sects. Richmond: Curzon Press. p. 24. ISBN 978-0-7007-1026-3. Retrieved 28 June 2010.
- Johan Elverskog (2010). Buddhism and Islam on the Silk Road (illustrated ed.). University of Pennsylvania Press. p. 228. ISBN 978-0-8122-4237-9. Retrieved 28 June 2010.
- Donald Daniel Leslie (1998). "The Integration of Religious Minorities in China: The Case of Chinese Muslims" (PDF). The Fifty-ninth George Ernest Morrison Lecture in Ethnology. p. 12. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 December 2010. Retrieved 30 November 2010.
- Dru C. Gladney (1991). Muslim Chinese: ethnic nationalism in the People's Republic (2, illustrated, reprint ed.). Council on East Asian Studies, Harvard University. p. 234. ISBN 978-0-674-59495-1. Retrieved 28 June 2010.
- Tan Ta Sen, Dasheng Chen (2009). Cheng Ho and Islam in Southeast Asia. Institute of Southeast Asian Studies. p. 170. ISBN 978-981-230-837-5. Retrieved 28 June 2010.
- Michael Dillon (1999). China's Muslim Hui community: migration, settlement and sects. Richmond: Curzon Press. p. 34. ISBN 978-0-7007-1026-3. Retrieved 28 June 2010.
- Chow, Chung-wah (7 September 2012). "What to do in Quanzhou: China's forgotten historic port | CNN Travel". Travel.cnn.com. Retrieved 27 May 2016.
- Hsiao 1994, pp. 491-492.
- Morgan 1982, p. 135.
- Morgan 1982, pp. 124-136.
- Natsagdorj, S., and C. Dalai. 2003. “Yuan gürnii üyeiin Mongol oron.” In Mongol Ulsiin Tuukh, vol. 2: XII-XIV Zuunii Dund üy, edited by C. Dalai and T. Ishdorj. Ulaanbaatar: Admon, p. 225
- Mote, Frederick W. (2003). Imperial China 900-1800. Harvard University Press. pp. 490–. ISBN 978-0-674-01212-7.
- Tanner, Harold Miles (12 March 2010). China: A History: Volume 1: From Neolithic cultures through the Great Qing Empire 10,000 BCE–1799 CE. Hackett Publishing Company. pp. 257–. ISBN 978-1-60384-564-9.
- Tanner, Harold Miles (13 March 2009). China: A History. Hackett Publishing. pp. 257–. ISBN 978-0-87220-915-2.
- Kupfer, Peter (2008). Youtai - Presence and Perception of Jews and Judaism in China. Peter Lang. pp. 189–. ISBN 978-3-631-57533-8.
- Oh, Young Kyun (24 May 2013). Engraving Virtue: The Printing History of a Premodern Korean Moral Primer. Brill. pp. 50–. ISBN 978-90-04-25196-0.
- Zhao, George Qingzhi (2008). Marriage as Political Strategy and Cultural Expression: Mongolian Royal Marriages from World Empire to Yuan Dynasty. Peter Lang. pp. 24–. ISBN 978-1-4331-0275-2.
- Rossabi, Morris (1983). China Among Equals: The Middle Kingdom and Its Neighbors, 10th-14th Centuries. University of California Press. pp. 247–. ISBN 978-0-520-04562-0.
- Haw, Stephen G. (1 January 1970). "The Semu ren in the Yuan Empire - who were they? | Stephen G. Haw". Academia.edu. Retrieved 27 May 2016.
- Biran, Michal (15 September 2005). The Empire of the Qara Khitai in Eurasian History: Between China and the ... p. 96. ISBN 9780521842266. Retrieved 27 May 2016.
- Morris Rossabi (1983). China Among Equals: The Middle Kingdom and Its Neighbors, 10th-14th Centuries. University of California Press. pp. 255–. ISBN 978-0-520-04562-0.
- E.J.W. Gibb memorial series. 1928. p. 451.
- Bretschneider, Emil (1888). "The Travels of Ch'ang Ch'un to the West, 1220-1223 recorded by his disciple Li Chi Ch'ang". Mediæval Researches from Eastern Asiatic Sources. Barnes & Noble. pp. 37–108.
- E.J.W. Gibb memorial series. 1928. p. 451.
- 《元史》 [History of Yuan] (in Chinese).
- Leslie, Donald Daniel (1998). "The Integration of Religious Minorities in China: The Case of Chinese Muslims" (PDF). The Fifty-ninth George Ernest Morrison Lecture in Ethnology. p. 12. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 December 2010. Retrieved 30 November 2010.
- Gladney, Dru C. (1991). Muslim Chinese: ethnic nationalism in the People's Republic (2nd, illustrated, reprint ed.). Council on East Asian Studies, Harvard University. p. 234. ISBN 978-0-674-59495-1. Retrieved 28 June 2010.
- "China's Islamic Communities Generate Local Histories". China Heritage Quarterly. 19 October 2015. Retrieved 27 May 2016.
- Mote 2003, p. 492.
- ed. Zhao 2007, p. 265.
- Bakhit 2000, p. 426.
- Ford 1991, p. 29.
- ed. Rossabi 1983, p. 247.
- Haw, Stephen G. (1 January 1970). "The Semu ren in the Yuan Empire - who were they? | Stephen G. Haw". Academia.edu. Retrieved 27 May 2016. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - Yoshiyuki, Funada (1 January 1970). "The Image of the Semu People: Mongols, Chinese, and Various Other Peoples under the Mongol Empire | Funada Yoshiyuki". Paper Presented at the International Roundtable Entitled "The Nature of the Mongol Empire and Its Legacy", Centre for Studies in Asian Cultures and Social Anthropology, Austrian Academy of Sciences, Vienna. Retrieved 27 May 2016.
- Duosang Mongol History, Vol. 1; Zhong-gou Tong-shi; History of Zhong-gou Border Nationalities; The New Yuan-shih
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2 December 2009. Retrieved 11 November 2009.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
Sources
- Allsen, Thomas (1994). "The rise of the Mongolian empire and Mongolian rule in north China". In Denis C. Twitchett; Herbert Franke (sinologist); John King Fairbank (eds.). The Cambridge History of China: Volume 6, Alien Regimes and Border States, 710–1368. Cambridge University Press. pp. 321–413. ISBN 978-0-521-24331-5.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- 陳學霖, Hok-Lam Chan (1991). ""Ta Chin" (Great Golden): The Origin and Changing Interpretations of the Jurchen State Name". T'oung Pao. Second Series. 77 (4/5): 253–299. doi:10.1163/156853291X00046. JSTOR 4528536.
- Dauben, Joseph (2007). "Chinese Mathematics". In Victor Katz (ed.). The Mathematics of Egypt, Mesopotamia, China, India, and Islam: A Sourcebook. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-11485-9.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Ebrey, Patricia Buckley (2010) [1996]. The Cambridge Illustrated History of China (2nd ed.). Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-12433-1.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Guzman, Gregory G. (1988). "Were the Barbarians a Negative or Positive Factor in Ancient and Medieval History?". The Historian. 50 (4): 558–571. doi:10.1111/j.1540-6563.1988.tb00759.x.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Ho, Peng Yoke (1985). Li, Qi and Shu: An Introduction to Science and Civilization in China. Hong Kong University Press. ISBN 978-0-486-41445-4.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Hsiao, Ch'i-Ch'ing (1994). "Mid-Yuan Politics". In Denis C. Twitchett; Herbert Franke (sinologist); John King Fairbank (eds.). The Cambridge History of China: Volume 6, Alien Regimes and Border States, 710–1368. Cambridge University Press. pp. 490–560. ISBN 978-0-521-24331-5.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Joseph, George Gheverghese (2011). The Crest of the Peacock: Non-European Roots of Mathematics. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-13526-7.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Lane, George (2006). Daily Life in the Mongol Empire. Greenwood Publishing. ISBN 978-0-313-33226-5.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Morgan, David (1982). "Who Ran the Mongol Empire?". The Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society of Great Britain and Ireland. 114 (1): 124–136. doi:10.1017/S0035869X00159179.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Morgan, David (2007). The Mongols. Wiley-Blackwell. ISBN 978-1-4051-3539-9.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Rossabi, Morris (1988). Khubilai Khan: His Life and Times. Los Angeles: University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-06740-0.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Rossabi, Morris (1994). "The reign of Khubilai Khan". In Denis C. Twitchett; Herbert Franke (sinologist); John King Fairbank (eds.). The Cambridge History of China: Volume 6, Alien Regimes and Border States, 710–1368. Cambridge University Press. pp. 414–489. ISBN 978-0-521-24331-5.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Rossabi, Morris (2012). The Mongols: A Very Short Introduction. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-984089-2.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Mote, Frederick W. (1999). Imperial China: 900–1800. Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-674-01212-7.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Mote, Frederick W. (1994). "Chinese society under Mongol rule, 1215-1368". In Denis C. Twitchett; Herbert Franke (sinologist); John King Fairbank (eds.). The Cambridge History of China: Volume 6, Alien Regimes and Border States, 710–1368. Cambridge University Press. pp. 616–664. ISBN 978-0-521-24331-5.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Smith, Jr., John Masson (January–March 1998). "Review: Nomads on Ponies vs. Slaves on Horses". Journal of the American Oriental Society. 118 (1): 54–62. doi:10.2307/606298. JSTOR 606298.
- Wu, K. T. (1950). "Chinese Printing under Four Alien Dynasties: (916-1368 A. D.)". Harvard Journal of Asiatic Studies. 13 (3/4): 447–523. doi:10.2307/2718064. ISSN 0073-0548. JSTOR 2718064.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Zhao, Gang (January 2006). "Reinventing China: Imperial Qing Ideology and the Rise of Modern Chinese National Identity in the Early Twentieth Century". Modern China. 32 (1): 3–30. doi:10.1177/0097700405282349. JSTOR 20062627.
Further reading
| Library resources about Yuan dynasty |
- Birge, Bettine (1995). "Levirate marriage and the revival of widow chastity in Yüan China". Asia Major. 3rd series. 8 (2): 107–146. JSTOR 41645519.
- Brook, Timothy. The Troubled Empire: China in the Yuan and Ming Dynasties (History of Imperial China) (Harvard UP, 2010). excerpt
- Chan, Hok-lam; de Bary, W.T., eds. (1982). Yuan Thought: Chinese Thought and Religion Under the Mongols. New York, NY: Columbia University Press. ISBN 978-0-231-05324-2.
- Cotterell, Arthur (2007). The Imperial Capitals of China - An Inside View of the Celestial Empire. London, England: Pimlico. ISBN 9781845950095.
- Dardess, John (1994). "Shun-ti and the end of Yuan rule in China". In Denis C. Twitchett; Herbert Franke (sinologist); John King Fairbank (eds.). The Cambridge History of China: Volume 6, Alien Regimes and Border States, 710–1368. Cambridge University Press. pp. 561–586. ISBN 978-0-521-24331-5.
- Ebrey, Patricia Buckley (24 November 2009). Chinese Civilization: A Sourcebook (2nd ed.). Simon and Schuster. ISBN 978-1-4391-8839-2.
- Endicott-West, Elizabeth (1986). "Imperial governance in Yüan times". Harvard Journal of Asiatic Studies. 46 (2): 523–549. doi:10.2307/2719142. JSTOR 2719142.
- Endicott-West, Elizabeth (1994). "The Yuan government and society". In Denis C. Twitchett; Herbert Franke (sinologist); John King Fairbank (eds.). The Cambridge History of China: Volume 6, Alien Regimes and Border States, 710–1368. Cambridge University Press. pp. 587–615. ISBN 978-0-521-24331-5.
- Langlois, John D. (1981). China Under Mongol Rule. Princeton: Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-10110-1.
- Langlois, John D. (1977). "Report on the research conference: The Impact of Mongol Domination on Chinese Civilization". Sung Studies Newsletter. 13 (13): 82–90. JSTOR 23497251.
- Paludan, Ann (1998). Chronicle of the China Emperors. London, England: Thames & Hudson. ISBN 978-0-500-05090-3.
- Saunders, John Joseph (2001) [1971]. The History of the Mongol Conquests. University of Pennsylvania Press. ISBN 978-0-812-21766-7.
- Owen, Stephen, "The Yuan and Ming Dynasties," in Stephen Owen, ed. An Anthology of Chinese Literature: Beginnings to 1911. New York: W. W. Norton, 1997. pp. 723 743. (Archive).
- “Directory of Scholars Working in Sung, Liao, Chin and Yüan”. 1987. “Directory of Scholars Working in Sung, Liao, Chin and Yüan”. Bulletin of Sung and Yüan Studies, no. 19. Society for Song, Yuan, and Conquest Dynasty Studies: 224–54. JSTOR 23497542.
External links

| Preceded by Song dynasty Jin dynasty Western Liao Western Xia Dali Kingdom Mongol Empire Remnants of Tibet Goryeo |
Dynasties in Chinese history History of Mongolia / Tibet / Korea 1271–1368 |
Succeeded by Ming dynasty Northern Yuan dynasty Phagmodrupa dynasty Goryeo dynasty |


