Crown of the Kingdom of Poland
The Crown of the Kingdom of Poland (Polish: Korona Królestwa Polskiego; Latin: Corona Regni Poloniae), known as the Polish Crown, or the Crown, is the common name for the historic Late Middle Ages territorial possessions of the King of Poland, including the Kingdom of Poland proper. The Polish Crown was at the helm of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth from 1569 to 1795.
Crown of the Kingdom of Poland Corona Regni Poloniae (in Latin) Korona Królestwa Polskiego (in Polish) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1569–1795 | |||||||||||||
 Royal Banner (c. 1621)
| |||||||||||||
| Status | Part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth (1569–1795) | ||||||||||||
| Capital | Kraków (before 1569) Warsaw (after 1569) | ||||||||||||
| Official languages | Polish, Latin | ||||||||||||
| Religion | Roman Catholicism | ||||||||||||
| Government | Constitutional, eventually elective monarchy | ||||||||||||
| King | |||||||||||||
• 1569–1572 | Sigismund II Augustus (first) | ||||||||||||
• 1764–1795 | Stanisław II August (last) | ||||||||||||
| Historical era | Middle Ages Early modern Europe | ||||||||||||
| August 14, 1569 | |||||||||||||
| July 1, 1569 | |||||||||||||
• Constitution of 1791 | May 3, 1791 | ||||||||||||
| January 7, 1795 | |||||||||||||
| Currency | Grosz | ||||||||||||
| ISO 3166 code | PL | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
Major political events

The Kingdom of Poland has been traditionally dated back to c. 966, when Mieszko I and his pagan Slavic realm joined Christian Europe (Baptism of Poland), establishing the state of Poland, a process started by his Polan Piast dynasty ancestors. His oldest son and successor, Prince Bolesław I Chrobry, Duke of Poland, became the first crowned King of Poland in 1025.
Union of Krewo
The Union of Krewo (Polish: unia w Krewie; Lithuanian: Krėvos sutartis) was a set of prenuptial agreements made in the Kreva Castle on August 13, 1385. Once Jogaila confirmed the prenuptial agreements on August 14, 1385, Poland and Lithuania formed a personal union. The agreements included the adoption of Christianity, repatriation of lands "stolen" from Poland by its neighbours, and terras suas Lithuaniae et Russiae Coronae Regni Poloniae perpetuo applicare, the clause which formed the personal union. After being baptized at the Wawel Cathedral in Kraków on February 15, 1386, Jogaila began to formally use the name Władysław. Three days after his baptism, the marriage between Jadwiga and Władysław II Jagiełło took place.
Union of Lublin
The Union of Lublin (Polish: unia lubelska; Lithuanian: Liublino unija) created the single state of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth on July 1, 1569 with a real union between the Crown and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. Before then, the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania only had a personal union. The Union of Lublin also made the Crown an elective monarchy; this ended the Jagiellonian dynasty once Henry de Valois was elected on May 16, 1573 as monarch.
On May 30, 1574, two months after Henry de Valois was crowned King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania on February 22, 1574, he was made King of France, and was crowned King of France on February 13, 1575. He left the throne of the Crown on May 12, 1575, two months after he was crowned King of France. Anna Jagiellon was elected after him.
Constitution of 1791
The Constitution of May 3, 1791 is the second-oldest, codified national constitution in history, and the oldest codified national constitution in Europe; the oldest being the United States Constitution. It was called the Government Act (Ustawa Rządowa) Drafting for it began on October 6, 1788 and lasted 32 months. Stanisław II Augustus was the principal author of the Constitution, and he wanted the Crown to be a constitutional monarchy, similar to the one in Great Britain. On May 3, 1791, the Great Sejm convened, and they read and adopted the new constitution. It enfranchised the bourgeoisie, separated the government into three branches, abolished liberum veto, and stopped the abuses of the Repnin Sejm.
It made Poland a constitutional monarchy with the King as the head of the executive branch with his cabinet of ministers, called the Guardians of the Laws. The legislative branch was bicameral with an elected Sejm and an appointed Senate; the King was given the power to break ties in the Senate, and the head of the Sejm was the Sejm Marshal. The Crown Tribunal, the highest appellate court in the Crown, was reformed. The Sejm would elect their judges for the Sejm Court (the Crown's parliamentary court) from their deputies (posłowie).
The Government Act angered Catherine II who believed that Poland needed permission from the Russian Empire for any political reform; she argued that Poland had fallen pray to radical Jacobinism that was prominent in France at the time. Russia invaded the Commonwealth in 1792.[2][3] The Constitution was in place for less than 19 months; it was annulled by the Grodno Sejm.[4][5][6][7][8][9][10][11][12]
Politics
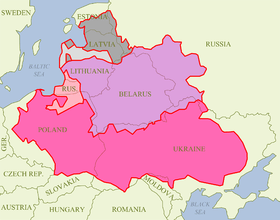
The creation of the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland was a milestone in the evolution of Polish statehood and the European identity. It represented the concept of the Polish kingdom (nation) as distinctly separate from the person of the monarch.[13] The introduction of the concept marked the transformation of the Polish government from a patrimonial monarchy (a hereditary monarchy) to a "quasi-constitutional monarchy" (monarchia stanowa)[13] in which power resided in the nobility, the clergy and (to some extent) the working class, also referred to as an "elective monarchy".
A related concept that evolved soon afterward was that of Rzeczpospolita ("Commonwealth"), which was an alternate to the Crown as a name for the Polish state after the Treaty of Lublin in 1569.[13] The Crown of the Kingdom of Poland was also related to other symbols of Poland, such as the capital (Kraków), the Polish coat of arms and the flag of Poland.[13]
Geography
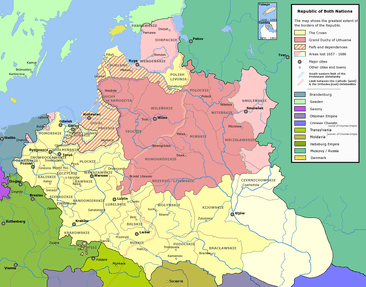
The concept of the Crown also had geographical aspects, particularly related to the indivisibility of the Polish Crown's territory.[13] It can be also seen as a unit of administrative division, the territories under direct administration of the Polish state from the Middle Ages to the late 18th century (currently part of Poland, Ukraine and some border counties of Russia, Belarus, Moldova, Slovakia, and Romania, among others). Parts formed part at the early Kingdom of Poland, then, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth until its final collapse in 1795.
At the same time, the Crown also referred to all lands that the Polish state (not the monarch) could claim to have the right to rule over, including those that were not within Polish borders.[13]
The term distinguishes those territories federated with the Grand Duchy of Lithuania ( ) from various fiefdom territories (which enjoyed varying degrees of autonomy or semi-independence from the King), such as the Duchy of Prussia ( ) and the Duchy of Courland ( ).
Prior to the 1569 Union of Lublin, Crown territories may be understood as those of the Kingdom of Poland proper, inhabited by Poles, or other areas under the sovereignty of the Polish king (such as Royal Prussia) or the szlachta. With the Union of Lublin, however, most of present-day Ukraine (which had a negligible Polish population and had until then been governed by the Lithuania), passed onto Polish administration, thus becoming Crown territory.
During that period, a term for a Pole from the Crown territory was koroniarz (plural: koroniarze) - or Crownlander(s) in English - derived from Korona - the Crown.
Depending on context, the Polish "Crown" may also refer to "The Crown", a term used to distinguish the personal influence and private assets of the Commonwealth's current monarch from government authority and property. It often meant a distinction between persons loyal to the elected king (royalists) and persons loyal to Polish magnates (confederates).
Provinces
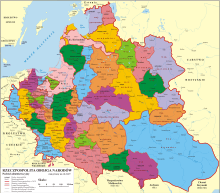
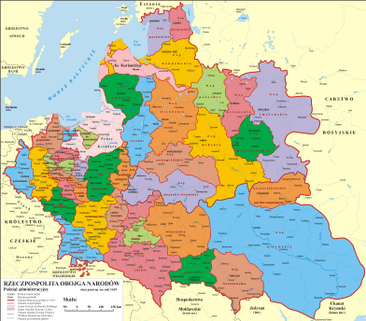
After the Union of Lublin (1569) Crown lands were divided into two provinces: Lesser Poland (Polish: Małopolska) and Greater Poland (Polish: Wielkopolska). These were further divided into administrative units known as voivodeships (the Polish names of the voivodships and towns are shown below in brackets).
Greater Poland Province
- Brześć Kujawski Voivodeship (województwo brzesko-kujawskie, Brześć Kujawski)
- Gniezno Voivodeship (województwo gnieźnieńskie, Gniezno) from 1768
- Inowrocław Voivodeship (województwo inowrocławskie, Inowrocław)
- Kalisz Voivodeship (województwo kaliskie, Kalisz)
- Łęczyca Voivodeship (województwo łęczyckie, Łęczyca)
- Mazovian Voivodeship (województwo mazowieckie, of Mazowsze, Warsaw)
- Poznań Voivodeship (województwo poznańskie, Poznań)
- Płock Voivodeship (województwo płockie, Płock)
- Podlaskie Voivodeship (województwo podlaskie, Drohiczyn)
- Rawa Voivodeship (województwo rawskie, Rawa)
- Sieradz Voivodeship (województwo sieradzkie, Sieradz)
- Prince-Bishopric of Warmia
Lesser Poland Province
- Bełz Voivodeship (województwo bełzkie, Bełz)
- Bracław Voivodeship (województwo bracławskie, Bracław)
- Czernihów Voivodeship (województwo czernihowskie, Czernihów)
- Kijów Voivodeship (województwo kijowskie, Kijów)
- Kraków Voivodeship (województwo krakowskie, Kraków)
- Lublin Voivodeship (województwo lubelskie, Lublin)
- Podole Voivodeship (województwo podolskie, Kamieniec Podolski)
- Ruś Voivodeship (województwo ruskie, Lwów)
- Sandomierz Voivodeship (województwo sandomierskie, Sandomierz)
- Wołyń Voivodeship (województwo wołyńskie, Łuck)
- Duchy of Siewierz (Siewierz)
Royal Prussia Province (1569–1772)
Royal Prussia (Polish: Prusy Królewskie) was a semi-autonomous province of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth from 1569 to 1772. Royal Prussia included Pomerelia, Chełmno Land (Kulmerland), Malbork Voivodeship (Marienburg), Gdańsk (Danzig), Toruń (Thorn), and Elbląg (Elbing). Polish historian Henryk Wisner writes that Royal Prussia belonged to the Province of Greater Poland.[14]
Other holdings or fiefs
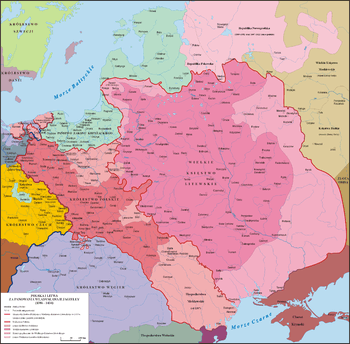
Principality of Moldavia (1387-1497)
The history of Moldavia has long been intertwined with that of Poland. The Polish chronicler Jan Długosz mentioned Moldavians (under the name Wallachians) as having joined a military expedition in 1342, under King Władysław I, against the Margraviate of Brandenburg.[15] The Polish state was powerful enough to counter the Hungarian Kingdom which was consistently interested in bringing the area that would become Moldavia into its political orbit.
Ties between Poland and Moldavia expanded after the Polish annexation of Galicia in the aftermath of the Galicia–Volhynia Wars and the founding of the Moldavian state by Bogdan of Cuhea. Bogdan, a Vlach voivode from Maramureș who had fallen out with the Hungarian king, crossed the Carpathian mountains in 1359, took control of Moldavia, and succeeded in transforming it into an independent political entity. Despite being disfavored by the brief union of Angevin Poland and Hungary (the latter was still the country's overlord), Bogdan's successor Lațcu, the Moldavian ruler also likely allied himself with the Poles. Lațcu also accepted conversion to Roman Catholicism around 1370, but his gesture was to remain without lasting consequences.
Petru I profited from the end of the Hungarian-Polish union and moved the country closer to the Jagiellon realm, becoming a vassal of Władysław II on September 26, 1387. This gesture was to have unexpected consequences: Petru supplied the Polish ruler with funds needed in the war against the Teutonic Knights, and was granted control over Pokuttya until the debt was to be repaid; as this is not recorded to have been carried out, the region became disputed by the two states, until it was lost by Moldavia in the Battle of Obertyn (1531). Prince Petru also expanded his rule southwards to the Danube Delta. His brother Roman I conquered the Hungarian-ruled Cetatea Albă in 1392, giving Moldavia an outlet to the Black Sea, before being toppled from the throne for supporting Fyodor Koriatovych in his conflict with Vytautas the Great of Lithuania. Under Stephen I, growing Polish influence was challenged by Sigismund of Hungary, whose expedition was defeated at Ghindăoani in 1385; however, Stephen disappeared in mysterious circumstances.
Although Alexander I was brought to the throne in 1400 by the Hungarians (with assistance from Mircea I of Wallachia), this ruler shifted his allegiances towards Poland (notably engaging Moldavian forces on the Polish side in the Battle of Grunwald and the Siege of Marienburg), and placed his own choice of rulers in Wallachia. His reign was one of the most successful in Moldavia's history, but also saw the very first confrontation with the Ottoman Turks at Cetatea Albă in 1420, and later even a conflict with the Poles. A deep crisis was to follow Alexandru's long reign, with his successors battling each other in a succession of wars that divided the country until the murder of Bogdan II and the ascension of Peter III Aaron in 1451. Nevertheless, Moldavia was subject to further Hungarian interventions after that moment, as Matthias Corvinus deposed Aron and backed Alexăndrel to the throne in Suceava. Petru Aron's rule also signified the beginning of Moldavia's Ottoman Empire allegiance, as the ruler agreed to pay tribute to Sultan Mehmed II.
The principality of Moldavia covered the entire geographic region of Moldavia. In various periods, various other territories were politically connected with the Moldavian principality. This is the case of the province of Pokuttya, the fiefdoms of Cetatea de Baltă and Ciceu (both in Transylvania) or, at a later date, the territories between the Dniester and the Bug rivers.
Towns in Spisz (Szepes) County (1412–1795)
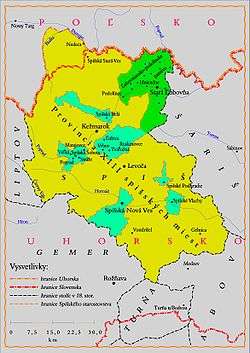
As one of the terms of the Treaty of Lubowla, the Hungarian crown exchanged, for a loan of sixty times the amount of 37,000 Prague groschen (approximately seven tonnes of pure silver), 16 rich salt-producing towns in the area of Spisz (Zips), as well as a right to incorporate them into Poland until the debt was repaid. The towns affected were: Biała, Lubica, Wierzbów, Spiska Sobota, Poprad, Straże, Spiskie Włochy, Nowa Wieś, Spiska Nowa Wieś, Ruszkinowce, Wielka, Spiskie Podgrodzie, Maciejowce, Twarożne.
Duchy of Siewierz (1443–1795)
Wenceslaus I sold the Duchy of Siewierz to the Archbishop of Kraków, Zbigniew Cardinal Oleśnicki, for 6,000 silver groats in 1443.[16] After that point it was considered to be associated with the Lesser Poland Province[17] and was the only ecclesiastical duchy in Lesser Poland. The junction of the duchy with the Lesser Poland Province was concluded in 1790 when the Great Sejm formally incorporated the Duchy, as part of the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, into the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth.
Prince-Bishopric of Warmia (1466–1772)
The Prince-Bishopric of Warmia[18] (Polish: Biskupie Księstwo Warmińskie,[19]) was a semi independent ecclesiastical state, ruled by the incumbent ordinary of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Warmia, and a protectorate of Kingdom of Poland, later part of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth after the Peace of Thorn (1466-1772)[20]
Lauenburg and Bütow Land
After the childless death of the last of the House of Pomerania, Bogislaw XIV in 1637, Lauenburg and Bütow Land again became a terra (land, ziemia) of the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland. In 1641 it became part of the Pomeranian Voivodeship of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. After the 1657 Treaty of Bydgoszcz, which amended the Treaty of Wehlau, it was granted to the Hohenzollern dynasty of Brandenburg-Prussia in return for her help against Sweden in the Swedish-Polish War under the same favorable conditions the House of Pomerania had enjoyed before. Lauenburg and Bütow Land was officially a Polish fiefdom until the First Partition of Poland in 1772 when King Frederick II of Prussia incorporated the territory into Prussia and the subsequent Treaty of Warsaw in 1773[21] made the former conditions obsolete.
Duchy of Courland and Semigallia (Courland) (1562–1791)
The Duchy of Courland and Semigallia is a duchy in the Baltic region that existed from 1562 to 1791 as a vassal state of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and later the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. In 1791 it gained full independence, but on 28 March 1795, it was annexed by the Russian Empire in the Third Partition of Poland. The duchy also had colonies in Tobago and Gambia
Duchy of Prussia (1569–1657)
The Duchy of Prussia was a duchy in the eastern part of Prussia from 1525–1701. In 1525 during the Protestant Reformation, the Grand Master of the Teutonic Knights, Albert of Hohenzollern, secularized the Prussian State of the Teutonic Order, becoming Albert, Duke in Prussia. His duchy, which had its capital in Königsberg (Kaliningrad), was established as a fief of the Crown of Poland, as had been Teutonic Prussia since the Second Peace of Thorn in October 1466. This treaty had ended the War of the Cities or Thirteen Years' War and provided for the Order's cession of its rights over the western half of its territories to the Polish crown, which became the province of Royal Prussia, while the remaining part of the Order's land became a fief of the Kingdom of Poland (1385–1569). In the 17th century King John II Casimir of Poland submitted Frederick William to regain Prussian suzerainty in return for supporting Poland against Sweden. On July 29, 1657, they signed the Treaty of Wehlau in Wehlau (Polish: Welawa; now Znamensk), whereby Frederick William renounced a previous Swedish-Prussian alliance and John Casimir recognised Frederick William's full sovereignty over the Duchy of Prussia.[22] Full sovereignty was a necessary prerequisite for upgrading the Duchy to Kingdom of Prussia in 1701.
Duchy of Livonia (Inflanty) (1569–1772)
The Duchy of Livonia[23] was a territory of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania – and later a joint domain (Condominium) of the Polish Crown and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania.
Protectorates
Caffa
In 1462, during the expansion of the Ottoman Empire and the Crimean Tatars, Caffa placed itself under the protection of King Casimir IV of Poland. The proposition of protection was accepted by the Polish king but when the real danger came, help for Caffa never arrived.[24]
See also
- Administrative division of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth
- Lands of the Crown of Saint Stephen
- Lands of the Crown of Saint Wenceslaus
Notes
- "Gaude Mater Polonia Creation and History". Retrieved 14 November 2017.
- Henry Smith Williams (1904). The Historians' History of the World: Poland, The Balkans, Turkey, Minor eastern states, China, Japan. Outlook Company. pp. 88–91. Retrieved 19 November 2017.
- Jerzy Lukowski; W. H. Zawadzki (2001). A Concise History of Poland: Jerzy Lukowski and Hubert Zawadzki. Cambridge University Press. pp. 101–103. ISBN 978-0-521-55917-1. Retrieved 19 November 2017.
- Bill Moyers (5 May 2009). Moyers on Democracy. Random House Digital, Inc. p. 68. ISBN 978-0-307-38773-8. Retrieved 19 November 2017.
- Sandra Lapointe; Jan Wolenski; Mathieu Marion (2009). The Golden Age of Polish Philosophy: Kazimierz Twardowski's Philosophical Legacy. Springer. p. 4. ISBN 978-90-481-2400-8. Retrieved 19 November 2017.
- Norman Davies (1996). Europe: A History. Oxford University Press. p. 699. ISBN 0-19-820171-0.
- Dorothy Carrington (July 1973). "The Corsican constitution of Pasquale Paoli (1755–1769)". The English Historical Review. 88 (348): 481. doi:10.1093/ehr/lxxxviii.cccxlviii.481. JSTOR 564654.
- Jacek Jędruch (1998). Constitutions, elections, and legislatures of Poland, 1493–1977: a guide to their history. EJJ Books. p. 175. ISBN 978-0-7818-0637-4. Retrieved 19 November 2017.
- Jerzy Lukowski (3 August 2010). Disorderly liberty: the political culture of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth in the eighteenth century. Continuum International Publishing Group. pp. 227–228. ISBN 978-1-4411-4812-4. Retrieved 19 November 2017.
- Jacek Jędruch (1998). Constitutions, elections, and legislatures of Poland, 1493–1977: a guide to their history. EJJ Books. pp. 181–182. ISBN 978-0-7818-0637-4. Retrieved 19 November 2017.
- Joseph Kasparek-Obst (1 June 1980). The constitutions of Poland and of the United States: kinships and genealogy. American Institute of Polish Culture. p. 51. ISBN 978-1-881284-09-3.
- Jacek Jędruch (1998). Constitutions, elections, and legislatures of Poland, 1493–1977: a guide to their history. EJJ Books. pp. 181–182. ISBN 978-0-7818-0637-4. Retrieved 19 November 2017.
- Juliusz Bardach, Boguslaw Lesnodorski, and Michal Pietrzak, Historia panstwa i prawa polskiego (Warsaw: Paristwowe Wydawnictwo Naukowe, 1987, p.85-86
- Henryk Wisner, Rzeczpospolita Wazów. Czasy Zygmunta III i Władysława IV. Wydawnictwo Neriton, Instytut Historii PAN, Warszawa 2002, page 26
- The Annals of Jan Długosz, p. 273
- Davies, Norman (2005). God's Playground: A History of Poland. Columbia University Press. pp. 174. ISBN 978-0-231-12817-9.
- Zygmunt Gloger Geografia historyczna ziem dawnej Polski "Właściwą Małopolskę stanowiły województwa: Krakowskie, Sandomierskie i Lubelskie, oraz kupione (w wieku XV) przez Zbigniewa Oleśnickiego, biskupa krakowskiego, u książąt śląskich księstwo Siewierskie"
- Lubieniecki, Stanisław; George Huntston Williams (1995). History of the Polish Reformation. Fortress Press. ISBN 978-0-8006-7085-6.
- Biskupie Księstwo Warmińskie @ Google books
- Lukowski, Jerzy; Hubert Zawadzki (2006). A Concise History of Poland. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-85332-3.
- Translation of a treaty between the King of Prussia and the King and Republic of Poland. In: The Scots Magazine, vol. XXXV, Edinburgh 1773, pp. 687–691.
- Henryk Rutkowski, 'Rivalität der Magnaten und Bedrohung der Souveränität', in: Polen. Ein geschichtliches Panorama, Warszawa: Wydawnictwo Interpress, 1983, pp. 81-91, here p. 83. ISBN 83-223-1984-3
- Trade, Diplomacy and Cultural Exchange: Continuity and Change in the North ISBN 90-6550-881-3, p 17
- Historia Polski Średniowiecze, Stanisław Szczur, Kraków 2002, s. 537.
References
- Henryk Litwin, Central European Superpower, BUM Magazine, October 2016.
- Jan Herburt, Statuta Regni Poloniae: in ordinem alphabeti digesta, Cracoviae (Kraków) 1563.
- Jan Dąbrowski(author), Korona Królestwa Polskiego w XIV wieku:studium z dziejów rozwoju polskiej monarchii stanowej, Zakład im. Ossolińskich, 1956.
- Stanisław Szczur, Historia Polski Średniowiecze (History of Poland - Middle Ages), Wydawnictwo Literackie 2002, ISBN 83-08-03272-9
.svg.png)